Recent Comments
Prev 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 Next
Comments 4751 to 4800:
-
Bob Loblaw at 12:44 PM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
Hal Kantrud @ 8:
As Eclectic points out, you need to define your time scales fully.
Several Skeptical Science posts cover CO2 changes over different time scales:
The last 100 million years (or so)
Hundreds of millions of years ago
-
Eclectic at 10:50 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
Hal Kantrud @8 ~ your meaning does not come through very clearly, at all. Do you mean long term periods as decades, or mega-years? What are these spikes (plural) that you are referring to? Clarity of explanation would be most welcome! Indeed, essential.
(b) Thanks once again, Bob Loblaw. I have been tinkering with trials of back-and-forth with tabs etcetera - but the website has a strong inclination towards deleting whatever has been typed in the comments box. (Previously I had naively assumed that the entries inside the comments box were the criterion for "activity". But your advices make me come to the realization that it would of course be difficult for "offsite" text work within the box to register at SkS site.)
Simplest overall: I hope that the Administrator could add 60 minutes or so to the qualifying time recognized by the server. Would there be some security concern in using a longer time? Or is it a congestion problem, or something else?
Moderator Response:[BL] Pretty much the only thing I know about the code development is that it is a volunteer process. We'll look at it, but no promises.
You need to stick to one comment box, in one tab. But that session is linked to timing of other sessions (as far as I can tell), so as long as you are clicking on links or refreshing a different page, your login is active.
A web site is not an interactive ongoing dialog between server and browser. It's "you ask, I send, I don't know you any more, so next time you ask I have no idea you were here before". Cookies were invented to get around that limitation: "Oh, I gave you a cookie. Now I remember who you are". Much else in terms of modern web page design works around some of that, but in the case of the comments box here, it is still just "you are typing on your computer, and I (the server) know nothing until you click 'submit'".
-
Hal Kantrud at 08:46 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
So did burning fuels create most of the greenhouse gas blanket? I would guess there are significant lag times but are there long-term temperature data that generally follow the long-term increase in atmospheric CO2? If they increase together, the recent spikes look small compared to the long term trends.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 08:07 AM on 13 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
What Bob Loblaw presents in his comment @19 is consistent with the evidence. It is independently verifiable understanding.
Building on Bob's points, admittedly triggered by him correctly pointing out the annoying claims some people make that the required changes to limit the harm done to the future of humanity (the rapid ending of fossil fuel use and other changes of developed activity) “will hurt the poor today”, there are many other harmful unsustainable developed human activities and unjust claimed excuses for them, not only the ones that can be connected to the harm done by human activity that increases CO2 levels.
That leads to an understanding based on the evidence (still open to improvement):
Actions, like attempts to end poverty, that depend on harmful unsustainable activity are not helpful, but will be developed by people who believe they will benefit from their development. And their helpfulness, especially their limiting of harm done, will be limited to what they believe they need to do to avoid personally suffering a lose of perceptions of status. They will continue to benefit from being harmful if they can get away with it. Their 'helpful' actions are harmfully unsustainable regardless of perceptions of helpfulness. Also, developed perceptions of enjoyment or superiority, or the opportunity for continued or increased perceptions of enjoyment and superiority, from understandably harmful developed systems and actions makes it harder to get people to unlearn, and resist liking, beliefs and claims that are developed to excuse harmful unsustainable developments they developed a liking for potentially benefiting from.
-
Eclectic at 07:28 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
(A) Yes, thanks BL ~ those are useful tips.
I hadn't gotten round to using a copy/paste using Word or similar: nor was I aware of the potential of the "html junk" problem.
My assumption had been that the "time out" was relating to activity within the comment box itself. But if it's just a matter of refreshing the whole page, then that is easier to deal with.
Nevertheless, the Alexandrian solution is to extend the qualifying period.
(B) As Scaddenp points out, increasing the soil carbon is excellent in many ways. Like AGW, the soil quality degradation seems a gradual "non-urgent" problem that we really should be tackling seriously.
Moderator Response:[BL] The catch is that typing in the comments box is just filling out a box provided by your browser. It isn't until you click "submit" that your browser posts the text you have typed to the server, and the server has a chance to think "oh, an active session".
If you refresh the page with the comment box you are working in, the browser tells the server "send me that page again", and the server (which knows nothing about what you typed in the box) will send you an updated page - with another empty comments box again.
I have been told that if you click "submit" and your comment disappears, you can use the "back" button on your browser to get back to the version of the page with your text in the box. At that point, you could copy the contents, paste elsewhere, log back in, and continue.
To keep your session active, and keep the contents of your comments box intact, you need to interact with skepticalscience.com using another tab or window. The activity in the other tab will extend the timeout for all tabs/windows connected to skepticalscience.com.
-
scaddenp at 06:55 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
Hal, the IPCC report estimate the contribution from land use change but they have wide error bars. However, carbon from soils has a different isotopic composition from carbon from fossil fuels. The build up of CO2 in the atmosphere is consistant with largely FF source. Some more details here.
However, increasing soil carbon reserves is a useful (in many ways) mitigation strategy.
-
Eclectic at 04:52 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
Swampfox & Hal Kantrud ~ yes, I've had a comment, on various occasions, simply disappear when I press the Enter button.
Almost always, it has happened when I've taken my time to type up a comment. If say, I'm interrupted during the typing-up . . . or if I've taken my time to arrange and consider/review my wording . . . plus proofreading, etc.
My impression is (for my case) that it is a "timing-out" problem. If that's all it is ~ then I hope the Administrator will consider lengthening the available window.
Moderator Response:[BL]. Yes there is a time limit on logins. If no activity is detected, you are automatically logged out. Typing in the comments box does not seem to be considered "activity".
If this is what is happening, you will find that your typed comment has disappeared and you are no longer logged in after you click "submit".
I do not know what the time limit is, but I can try to find out.
As a workaround to prevent the problem, there are a few choices:
- Open a second tab with a Skeptical Science page in it. You will see that you are already logged in. Periodically refresh that page (or click to another Skeptical Science page) and your session will stay active.
- Prepare long comments in a text editor, and then paste them into the comment box when you are ready for final editing. Avoid a word processor, as they tend to include a lot of html junk that is hidden from you in the copy/paste process.
- Before clicking submit, select all the text in the comment box, and copy/paste it into a word processoor text editor. If the "submit" fails, at least you don't have to start over.
-
Hal Kantrud at 03:41 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
Did we not create the greenhouse gas blanket by mining the soil for carbon during the last ten millennia, mostly from the perennial grasslands, the old "land of milk and honey"? I think a strong case can be made that the post-Industrial Revolution spike in atmospheric carbon dioxide resulted as much or more from the conversion of the New World grasslands to cropland and pasture than to the energy sources used for that effort. After all, in many areas, the plows were pulled by humans, then animals, then wood and coal for the steam engines, and only recently by petroleum.
We transferred most of the carbon to the oceans, rivers, and wetlands, so perhaps we should begin a retrieval effort to begin rebuilding soil carbon. Since we still rely on carbon remaining in the former perennial grasslands to feed ourselves, perhaps we should consider planting perennial grasses in areas where carbon has been most severely depleted such as former forests, shrublands, and deserts. Planting trees and injecting carbon deep underground makes little sense to me
-
swampfoxh at 03:11 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
Hal Kantrud....happens to me, occasionally...don't know why.
-
swampfoxh at 03:07 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
The authors point to "...existing energy producing systems and capital stock", which are only half the problem. The other half of the TWO LEADING PROBLEMS of GHG emissions is Industrial Animal Agriculture. These authors are silent on this topic (?) Further, GGEs should occupy only a small space alloted to the topic of environmental/ecological damage. Deforestation, desertification, excess fresh water useage, wildlife habitat destruction/extinction, widespread land use conversions for the support of animal agriculture, eutrophication of fresh and saltwaters, human diseases connected to domestic livestock, herbicides, pesticides, chemical fertilizers...overfishing...an exceedingly long list of eco-distructive activities and behaviors that may not materially affect the quantity of GGEs in the atmosphere, but even at 270 or 350ppm, (now long gone) would dangerously affect the future welfare of living things...especially humans.
-
Hal Kantrud at 02:40 AM on 13 January 2022The 1.5 degrees goal: Beware of unintended consequences
dammit had a comment typed in and it disappeared. Don't know what I did wrong.
-
Bob Loblaw at 00:03 AM on 13 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
The problem I have with the "it's not climate change, it's greenhouse gases" narrative is that the chain of causality never ends. And at each step of the chain, the contrarians will come up with an excuse to ignore it.
After "it's greenhouse gases", the contrarians wll come up with one of the following bogus arguments:
- It's not CO2, it's water vapour.
- Methane is a more powerful greenhouse gas.
- Climate sensitivty is low.
- CO2 lags temperature
- etc.
Once you successfully argue that it is CO2, then you get
- Human CO2 emissions are minor
- Volcanoes emit more CO2 than humans
- CO2 is coming from the ocean
- The rise in CO2 is natural
- etc.
and then if you manage to establish that the rise in CO2 is due to burning fossil fuels, you get all the "it's not bad", "technology will save us", "you'll hurt the poor", etc arguments.
There are many such arguments on the Skeptical Science "Arguments" page. I have only linked to a few.
-
Eclectic at 16:20 PM on 12 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
Wilddouglascounty, thanks for your comment. No, I wasn't wishing in any way to imply that the current rapid global warming has a component of raised TSI ~ the evidence is quite clear that it doesn't.
I was interested in how you would choose to discuss the "attribution" of weather events, when talking with a layman ( 99% of the population - including politicians). You seem keen to use the phrasing which specifies the underlying cause ( CO2/greenhouse). Fair enough, mentioned once in a conversation. Yet I suspect your audience would soon tire of the repetition of a six-word phrase, when the two-word phrase ("global warming" or even vaguer: "climate change") conveys essentially the same message.
"Global warming" and "climate change" are terms now bandied about, throughout the media, and very frequently. People are used to hearing it, as a concept. Apart from Denialists, and people who are simply not interested in the topic ~ most people will know what you are talking about (and know the cause, as specified by scientists & science reporters). And that is why I am unclear why you wish to make use of "a distinction without a difference". Or perhaps better described as ~ a distinction which is unimportant to the man in the street.
That is where I am missing the subtlety of your message here.
-
wilddouglascounty at 15:05 PM on 12 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
15 Eclectic:
Global warming is a measurement that tracks one effect of an increased amount of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere. The reason it is always important to take causality back to greenhouse gases is for the same reason we take the cause of an enhanced performance back to the ingested steroids instead of attributing that enhanced performance to the improved statistics that that performer has now.
If it were increased solar activity that was warming the planet say 1.5 degrees Celsius, you would have to look at the physics of the increased radiative output of the sun, just we look at the physics of increased heat retention provided by greenhouse gases, and calculate how the sun, not greenhouse gases or other components of the energy balance created the net increase.
We know quite a bit about the physics of solar irradiation and its warming component in the energy balance equation, just as we know quite a bit about the physics of greenhouse gas heat retention in that same equation, right? Both could cause the exact same amount of global warming, but the physics of both, being different and testable, are distinguishable, which is why we have concluded that the GW should have an "A" in front of it, not an "S" right?
-
Bob Loblaw at 12:08 PM on 12 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
The original emailer has sent in a follow-up to the Skeptical Science contact page, asking about black-body radiation and differences between emissions at 255K and 288K. A temperature of 255K is the commonly-cited radiative temperature at which the earth-atmosphere system emits IR radiation to space, while 288K is the commonly-cited global mean temperature for the earth's surface. The difference is a measure of the role of the atmosphere - the greenhouse effect - and this difference is predicted to continue to rise as atmospheric greenhouse gases continue to increase.
The blog post focuses on atmospheric absorption, not emission, but atmospheric absorption by CO2 is a key factor in the greenhouse effect. So, how might that temperature difference - 288K at the surface, 255K at high altitude - affect this process?
A few of the comments to the post touch on aspects of IR emission, and in figure 2 and comment #10 I mentioned Planck's Law, which governs radiation emission. Figure 2 was intended to show the difference between solar (5800K) and terrestrial (255K) sources of radiation, but does not touch on differences for the range of temperatures within the earth-atmosphere system. The recent follow-up email asked to see Planck curves for 255K and 288K (and to see them on a linear scale), so here is that graph:
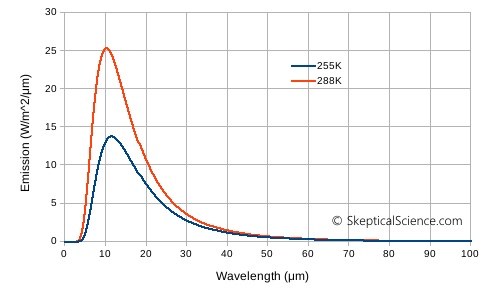
The horizontal axis is wavelength in μm, and the vertical axis is energy in W/m2/μm.
There are three obvious features:
- At the hotter temperature, the area under the curve is much larger. This area represents the total energy emitted. Hotter sources emit more energy overall.
- At the hotter temperature, the peak happens at a slightly shorter wavelength. Hotter sources shift a larger proportion of their emissions to shorter wavelengths.
- The 288K curve always lies above the 255K curve, so even at a specific wavelength, the hotter source emits more radiation than the cooler source.
The "hotter source" explains why I used a logarithm scale in figure 2. The sun emits a lot more energy than the earth. There is also one more "feature" to figure 2: I scaled the solar output so that instead of giving the intensity at the surface of the sun, where it is emitted, I scaled it down to the value appropriate at the earth's orbit around the sun. That was the only way to get the two lines to graph anywhere close to each other.
So, if we look back at our discussion of the Beer-Lambert Law, what difference does the source temperature have on the absorption of IR radiation? (The original email had mentioned 15 μm, which we see is a little to the right of the peak in the above graph.)
Well, it turns out that the temperature of the source has absolutely no effect whatsoever on the absorption according to the Beer-Lambert Law.
- In the blog post, note that the equations for the Beer-Lambert Law do not have temperature in them.
- You can add a subscript to the Beer-Lambert Law to indicate wavelength, as the absorption coefficent is highly-dependent on wavelength, but it does not matter what temperature the source was at that emitted the radiation.
- It also does not matter what the temperature is at the location the absorbing is happening.
Why is this? Well, there are several factors:
- The Beer-Lambert Law just tells us the probability that a single photon will be absorbed.
- Each individual photon is either absorbed, or not. Do, or do not. There is no try.
- If the photon is absorbed, all the energy goes into the molecule that does the absorbing (and is then transferred to heat all gases through molecular collision).
- If the photon is not absorbed, then the photon will continue along its way, and be transmitted through the atmosphere.
- An absorption coefficient of 0.01 means that there is a 1% chance that a single photon will be absorbed. It does not mean that each photon loses 1% of its energy - it means that 1% of all the photons lose 100% of their energy and the oher 99% lose none.
And all 15 μm photons are the same.
- They travel at the same speed, and they contain the same amount of energy.
- They do not contain more energy if they were emitted from a source at 288K than if they were emitted from a source at 255K.
- The source at 288K that is emitting more total energy at 15 μm is not emitting higher-energy 15 μm photons, it is just emitting more of them.
- The difference between the two curves in the graph above is just that a 288K source emits more photons at all wavelengths, compared to the 255K source. The 288K source can do this because it has more energy (it's hotter!) that can be transformed into radiation.
When CO2 absorbs a 15 μm photon in the atmosphere, it has no way of knowing if that photon was emtited from the surface at 288K, a kilometre away at 270K, or a metre away at 255K. It is just another 15 μm photon carrying the same amount of energy that every other 15 μm photon carries. And that amount of energy just happens to fit nicely into the different energy states that CO2 likes, so it is easy for CO2 to absorb it.
So, the CO2 will absorb the photon, and that heat is added to the local atmosphere, and it does not matter if the location where it is absorbed is warmer or colder than where the photon was emitted.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 02:33 AM on 12 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
Because of the perspective I presented @12 I appreciate that the ways that the changes of climate will affect developed food production are more significant concerns regarding the attribution of human causes to climate change.
Every regional developed food production system is at risk, and needs to attempt to adapt to the changes if the regional climate changes (with no guarantees that the climate changes will support continued food production). And the more significant, and more rapidly, the regional climate changes occur the more harm is done to the global developed food production system. Sustainable total global food production, and systems developed to ensure that every human gets at least basic decent nutrition, is the measure that matters. The studies I have seen indicate that, globally, any regional positives of global warming are outweighed by regional negatives. And until the human impacts causing rapid climate change are actually ended, or are clearly on track to being ended, it is hard to know what future climate conditions food producers and distributors will need to try to adapt to.
Not knowing if the peak climate impact will be 1.5C, 2.0C, 2.5C, 3.0C, 3.5C means there is no way to plan new developments or revise existing developments for the demands of the future. But what is known is that the future of humanity is more damaged by more warming.
Attribution of climate change impacts to actual events that are seen to be harmful is essential to help convince the fence-sitting pragmatic moderates that it is harmful to compromise or ‘balance’ the understanding of the need to end harm done by human pursuits of benefit with the desires of people who want to benefit from continuing or expanding understandably harmful unsustainable actions.
-
Eclectic at 14:47 PM on 11 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
Wilddouglascounty ~ so far in this discussion, my mind has not been subtle enough to discern the effect of the distinction, or difference, that you draw between the concept of global warming vs increased greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.
To clarify your position: how would you describe the distinction (regarding increase in extreme weather events) in the - strictly hypothetical - case that the current rapid global warming were instead being caused by an ongoing rise in total solar irradiation?
Admittedly there is the crucial difference that such global warming would be beyond direct human intervention in its causation ~ but otherwise the nett effects would mimic AGW. But how would one (i.e. you) draw distinctions in the wording of attribution? And why so?
-
wilddouglascounty at 02:23 AM on 11 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
#11 David Kirtley,
Thank you for referring me to the Grist post, which I had not read before. Yes, Mr. Roberts accurately captures the inherent difficulties in trying to create causal distinctions between different parts of one atmosphere. The point I was making can best be outlined in his article by quoting his steroid example:
"When the public asks, “Did climate change cause this?” they are asking a confused question. It’s like asking, “Did steroids cause the home run Barry Bonds hit on May 12, 2006?” There’s no way to know whether Bonds would have hit the home run without steroids. But who cares? Steroids mean more home runs. That’s what matters."
I just wish Mr. Roberts had gone on to say that while "climate change" is a compilation or measure of the severity and frequency of weather episodes, it is greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that are causing it to change. It is best to say that increased greenhouse gases mean more extreme weather events. That's what matters.
-
nigelj at 06:26 AM on 10 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
There are some people that suggest that saying "climate change is causing changes in the severity of the weather" is a misnomer, because climate change is in fact changes in the severity of the weather (eg: more intense or frequent droughts or storms).
They say we should really say that global warming or increasing greenhouse gas concentrations are causing changes in the weather. I think its all a bit pedantic. I don't think anyone is really confused as to what is causing changes in the weather. OPOF's comment seems more pertinent.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 09:56 AM on 9 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
As a civil/structural engineer I have a different perspective regarding the debate about the merits of attribution analysis of extreme weather.
Civil designs, especially water run-off collection systems, and structures need to be designed to withstand 'weather extremes'. The rapid changes of weather extremes due to human action causing global warming and resulting climate change is critically important work.
It is inevitable that more frequent and more severe extreme events will be attributed to the human impacts. We have to hope that our designed systems are designed to perform successfully under the more extreme conditions, and fix already built stuff that isn't up to the challenge because it wasn't anticipated to need to be.
The science that anticipates the attribution of more extreme weather impacts is critical to the success/survival of what we build.
-
David Kirtley at 01:37 AM on 9 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
If I can butt in, hopefully without adding more confusion, I think what wilddouglascounty is saying is something that Dave Roberts said 10 years ago in a Grist post about the "semantic debate" involved whenever the issue of climate change attribution comes up. He even uses the example of steroids in baseball causing more home runs. I think this paragraph probably sums up wilddouglascounty's viewpoint:
There is no division, in the physical world, between “climate change storms” and “non-climate change storms.” Climate change is not an exogenous force acting on the atmosphere. There is only the atmosphere, changing. Everything that happens in a changed atmosphere is “caused” by the atmosphere, even if it’s within the range of historical variability. Climate change is just the term we use to describe those changes.
Wilddouglascounty, please correct me if I am putting words in your mouth.
-
wilddouglascounty at 05:46 AM on 8 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
I posted earlier, but it did not show up, so am briefly posting one more time: In a nutshell, I have no objections whatsoever with any of the terms: climate, climate change and Anthropogenic Global Warming. I fully support them as valid concepts and useful measures of the impacts that have resulted from increasing the amount of greenhouse gases residing in our atmosphere.
My one and only point is that those composite measures are statistical abstractions that measure the impact of greenhouse gases, and there is a tendency to reify them by saying that the measures are causing the observed changes, when it in actuality is the greenhouse gas composition of the atmosphere that is the causal force. So for clarity's sake it is much better to refer to greenhouse gases as the reason that a storm event is more severe and occurring more frequently, not the tool of measurement, i.e. "climate change." If you want to attribute the increased frequency and increased amount of energy, I think it is worth pointing to the fact that there has been an increase of 47% in the composite greenhouse gas index since 1990 (AGGI index increasing to 1.47 since 1990) as the cause for the observed phenonenon. I hope this clarifies this once and for all, but feel free to agree/disagree/clarify as you see fit.
-
MA Rodger at 06:11 AM on 7 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
wilddouglascounty @8,
This interchange becomes perplexing.
I expressed the situation as I saw it @7 saying "I feel you are still attempting to paper over the idea that extreme weather will be worse under AGW and that will bring with it serious problems for humanity," believing you were happy that AGW resulted from increased GHGs in the atmosphere but that you had objection to the "statistical abstration" involved with the assessment of AGWs influence on extreme weather events.
But @8 you say I am wrong in this interpretation of your position.
It appears now that you are attempting to paper over the concept of "climate change" or AGW as you want the term "climate change" replaced by the rather lengthy phrase "a 40% increase in CO2 in the atmosphere or whatever mix of all greenhouse gases you want to choose." You even @8 describe "climate change" as being a"statistical construct we've created to monitor the impact of greenhouse gases" while @4 it is "climate" you describe as being "a statistical abstraction."
So is it simply use of the terms "climate change" and "AGW" or even use of the term "climate" you are objecting to? And I would find an affirmative response "perplexing" given your opening line @1 and your final line @8.
-
BaerbelW at 19:18 PM on 6 January 2022The Conspiracy Theory Handbook: Downloads and translations
The Conspiracy Theory Handbook is now also available in Swedish as the 14th translation!
-
wilddouglascounty at 08:19 AM on 6 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
MA Rodger,
Thanks so much for voicing your concerns, which I can assure you are completely unfounded. You say you feel that I am attempting to paper over the idea that extreme weather will be worse with AGW and cause increasing problems for humanity, but your concerns are completely unfounded. Nowhere do I imply this and I'm sorry you draw this conclusion from my stating and restating that my concern is that people are being inaccurate by saying that the statistical construct we've created to monitor the impact of greenhouse gases, i.e. "climate change" is CAUSING the observed changes (more severe, frequent extreme weather events, sea level rise, acidification, etc.). It is the greenhouse gases that are CAUSING the climate to change, the rising sea levels, the acidification, etc. Climate change is merely a constructed indicator that we use to communicate the impact of increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (and oceans, for acidification's sake). The only way to reduce and reverse AGW is to reduce the greenhouse gases being emitted to a level that the carbon sinks on our planet can absorb in order to return to an equilibrium that results in a climate we have become accustomed to.
In other words, when talking about attribution, instead of saying that a drought's severity is increased X percent due to climate change, I would like to see folks say that the drought's severity is increased X percent due to a 40% increase in CO2 in the atmosphere or whatever mix of all greenhouse gases you want to choose.
-
MA Rodger at 23:51 PM on 5 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
wilddouglascounty @4,
Thank you for the added clarity but I feel you are still attempting to paper over the idea that extreme weather will be worse under AGW and that will bring with it serious problems for humanity. (Of course, the sporting analogy breaks down here.)You appear to be saying that the science should restrict itself to study of the physics of "the roll of greenhouse gases in changing the atmospheric chemistry and its heat retention properties." You say "science should be focusing more on the physical impact of greenhouse gases than on what fraction of an event can be attributed to climate change."
So AGW should be understood soley as, what, causing an increase in average global surface temperature of a degree or so, or more? Or perhaps even global averages are too statistical to have any meaning in the real world where AGW can even result in regional cooling. And sea level rise too. That may seen a solid physics thing but outside a few amphidromic points it is still dwarfed by the tidal range and requires weather to drive tidal surges.
Weather is a series of events and climate is a measure of what weather events can be expected. The science of climatology attempts to unravel the whats and the whys of weather stuff that together comprise climate. If climate changes so will the weather we can expect.
Yet you appear to be wanting to ignore the impacts of AGW, of say, 100-year events happening every year (on average) and even unprecidented 10,000-year events potentially now happening because it is not CO2 that directly causes these events as they are caused more correctly due to the effect of the atmospheric warming resulting from higher CO2 concentrations which in turn cause, say, on average deeper cyclones at higher latitudes which in turn occasionally drives far greater volumes of atmospheric H2O to suddenly rain-out over places where it will cause flash flooding that destroys buildings and forests and communities that have been happily standing for centuries and which would be a complete disaster if there happens to be an 'r' in the month; all of which is a "statistical abstration" which we shouldn't be bothering ourselves with. -
Bob Loblaw at 07:24 AM on 5 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
The way I think of it is that a "weather event" is not really a single item. A heat wave is a higher-than-something temperature, and it carries with it an area of coverage and a length of time. It can be unusual or unexpected if it exceeds previous high temperatures, or if it covers a larger area than normal, or lasts longer than normal.
And "normal" itself has a geographical characteristic - temperatures that are normal in one place (and one time of year) may not be "normal" in another location or time of year.
All components of that "heat wave" may be subject to the effects of a globally warmer climate. "Attribution" needs to look at all aspects of that "event", and assess the probability that it would have happened in a climate that has not warmed.
For a simpler example, what about flooding? Let's say that a region has planned and built for river flooding up to 10 m above normal water levels. This has protected the region for decades, but then under a warmer climate there is heavier rainfall, and an 11 m flood overtops the protection and the region is flooded.
We can ask, "which metre of flood water caused the protection to fail? There are several possible answers, all of which could be argued with at least some success:
- The obvious answer is "all of them". Take away any single metre of flood water, and we're back to only 10m and the protection works.
- The next obvious answer is "the last one". The first 10m did not cause a problem, it was only the last one.
- The first problem with this answer is that you then have to ask "which factor caused that last metre of flood water?". Which means needing to determine the source of all of the metres of flood, from the first to the last. Which gets you back to "what caused 11 m of flooding?"
- The second problem with that answer is that the last metre would not have overtopped the protection if any the previous 10 metres of flood had not already happened. Why should it get the blame?
- So, finally, we get to another possible answer: the flood was caused by the 1 metre of flood water that was never there before. It does not matter if it was the first metre during that event, somewhere in the middle of the event, or the last metre added to the flood water during that event. In the past, there was one factor that was not present, and all the other factors that have been around for ages never managed to exceed 10 m. The problem was caused when the new kid on the block added another metre of flood water to the mix.
So, in this case, I think we can safely say that the 11 m flood was the result of climate change (precipitation in the thought experiment). But we still need to accept that something unusual might have happened without climate change, so the attribution is done on the basis of probabilities. We're 99% sure that the flood would not have happened if it were not for climate change.
...and I think that an essential part of the climate change message is pointing out that we are already seeing the effects. It is not a feature of the imagined future - it is now.
-
nigelj at 05:10 AM on 5 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
I think I see the point wilddouglas country is making about attribution studies. Its something I have also wondered about. The term attribition is defined in online dictionaries as "the action of regarding something as being caused by a person or thing." However climate attribution studies do not really say that specific weather events are caused by a warming climate. They typically find that the event is exceedingly unlikely to have happened but for climate change. Not questioning this finding, but the term attribution just doesn't seem accurate. Climate influence studies would be more accurate.
-
BaerbelW at 03:37 AM on 5 January 20222021 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #53
CelesteRosemary @ 1 & Jonas @2
Thanks for your feedback! Putting together the weekly summary doesn't take long so my question was just to satisfy my curiosity and not to find reasons to discontinue posting it.
As our SkS page on Facebook is public and as our posts there are shared publicly, they can be read without an acount (or being logged in).
-
wilddouglascounty at 02:54 AM on 5 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
Phillipe, MA Roger,
Sorry for not being more clear: what I am saying is that just as the conversation in athletics is about how steroid use impacts the batting average/number of sixes, instead of focusing on the nonsensical statement that that last hit can be attributed to an increased batting average, science should be focusing more on the physical impact of greenhouse gases than on what fraction of an event can be attributed to "climate change."
Climate is a statistical abstraction that can be summarized in all kinds of ways, whereas the roll of greenhouse gases in changing the atmospheric chemistry and its heat retention properties is a physical process that can be addressed by science. In other words "climate change" does not CAUSE more extreme weather events: a changed atmospheric chemistry does, and climate indicators are proof of those impacts CAUSED by greenhouse gases. Hope this helps.
-
MA Rodger at 19:33 PM on 4 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
wilddouglascounty @1,
I'm not familiar enough with the game of baseball to discuss a "last individual baseball hit" but if this were the game of cricket, the analogy of an increased incidence of extreme weather would perhaps be analogous to a batsman hitting more sixes which would be a contribution to an overall increase in the steroid-taking batsman's batting average, the overall increase being analogous to the changing climate.
So in the analogy we can see the batting average increasing with the steroid-taking and we can see within that performance, the rise in the number of almost-sixes, the rise in actual sixes and the times now in which the ball sails clean out of the stadium. A statisitcal assessment can thus be made.
Note that your posed question "Did the increased batting average cause the (baseball) player to hit that ball further, or was it the steroids?" was answered by you within your analogy as you say "Now it is the steroids which caused the change, just as a jump in the amount of greenhouses in the atmosphere has caused an increase in extreme weather events that cumulatively changes the climate, right?"
-
Jonas at 10:30 AM on 4 January 20222021 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #53
Happy new year Baerbel and whole SkS Team.
I usually (partially) read 7-10 of the linked articles but I also profit from the headlines (I would read more if I were not already reading too much stuff; for the research list, the fraction I read is much smaller and the overview thing more important: I am a lay person and research articles often are hard or completely undigestable ..).
I don't have an FB account, but I just checked that I can read there (was that different in the past?). I now hate FB even more since a member of my familiy became victim of corona misinformation on FB, but I will go there and check SkS there if posting the links here is too much effort.
Thanks for all you do. I remember how glad I was, when I found this website, way back in .. 2008? (don't remember ..): I can't count how often I passed and still pass the link to SkS, just recently to two colleagues.
Utopian greetings,
Jonas -
Philippe Chantreau at 08:00 AM on 4 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
WDC, you're splitting hair.
It is a little ironic, since another, even more intense, winter heatwave has just hit Western Europe again.
A warming climate is predicted to lead to an increased frequency of extreme weather events. The climate is warming, and an increased frequency of extreme weather events is observed.
Going into the subtleties of: "this event was x times more likely to reach the extent that it did in a warming climate, but can not definitely be said to have done so because of it," may have merit, but is beyond the comprehension of the vast majority of the general public, who have no concept about differential probabilities. They can hardly even wrap their mind around probabilities at all, and are stunted in their quantitative thinking in general, as has been showed by the recent waves of denial and incomprehension associated with the pandemic.
Meanwhile, there is this: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/billions/time-series
-
supak at 05:15 AM on 4 January 2022Patrick Michaels: Cato's Climate Expert Has History Of Getting It Wrong
Pat has officially lost this bet. He is ignoring me. He owes the Climate Scientist Legal Defense Fund $250.
-
CelesteRosemary at 03:59 AM on 4 January 20222021 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #53
I appreciate the weekly summary blog posts because I don't go on FB often, and this post gives me a chance to see the articles of interest I may have missed during the week. I checked out 5 articles on this recent post.
-
wilddouglascounty at 01:01 AM on 4 January 2022How weather forecasts can spark a new kind of extreme-event attribution
Isn't attribution of individual extreme weather events more of a psychological pursuit than actual science? I mean, climate is an aggregated construct that is not unlike a baseball batting average, i.e. a statistical cumulative creation designed not to predict weather, but to evaluate what past activities show us and to tease out trends, correct? For a baseball player, if he starts injecting steroids into his body, all things being equal, his batting average or the number of homeruns may jump.
Now it is the steroids which caused the change, just as a jump in the amount of greenhouses in the atmosphere has caused an increase in extreme weather events that cumulatively changes the climate, right? But it seems to me that just as it is questionable science to try to tease out how much those steroids added to that last individual baseball hit compared to that player hitting that ball before he started taking steroids, the same pursuit with individual extreme weather events seems to be confusing the cumulative indicator with the observed data point. In other words, did the increased batting average cause the baseball player to hit that ball further, or was it the steroids? To conflate the two is a psychological pursuit, not a scientific one in my mind.
-
Eclectic at 10:12 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
My apologies, BL ~ I should have allowed more response time than 24 hours (and perhaps moreso in a holiday period).
My concern was that the readers (other than myself) might be unaware of the relevant context of CD's thinking. Yes, we should focus on the precise point of argument put forward by any protagonist at all, however unphysical their background ideas.
-
Eclectic at 08:55 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
Thank you, Bob Loblaw @11
CD = Climate Detective . . . well now, who da thunk ;-)
But it is now more than 24 hours since the presumed bloggy author has posted here at SkS. Likely he has sailed away . . . or quite possibly sunk (considering how you delivered some heavy hits below his waterline).
To save SkS readers from wasting their time on the Climate Detective's blogsite, I will give a quick thumbnail sketch of the blog's contents. The author's blog contents range from: some technically correct stuff . . . to some definitely incorrect stuff . . . through to some quite bizarre stuff.
Much of the author's content has a mildly Wattsupian flavor . . . such as the cherrypicking of temperature charts for times and regions which are intended to demonstrate the wrongness of mainstream climate science & of all the national scientific bodies. That sort of thing ~ rather Wattsupian, but with a soft-pedal on the International Conspiracy Theories.
Then there was a slightly political take on the recent International Climate Conference in the UK ~ and the disastrous immorality of cutting out the consumption of petroleum oil. # "we [the rich West] will devastate the economies of many [Third World] oil producers." (Such callous disregard . . . cataclysmic impact . . . etcetera.) But # "alternative strategy . . . getting the producers to cut supply by 5% per year . . . result . . . global economic collapse."
~ An interesting demonstration of Motivated Reasoning. Binary thinking - only two future possibilities in that direction: Catastrophe A or Catastrophe B . Third or fourth possibilities are not conceivable. (Such is the effect of emotional bias on the intelligent mind - and there is no doubt that the author has an above-average I.Q. )
Elsewhere, the author raises the flag of Chaos, and becomes almost mystical: "[the AGW] that climate scientists think they are measuring is probably all just low frequency noise resulting from the random fluctuations of a chaotic non-linear system." And more: "this is because the fluctuations are actually the result of dynamic effects that played out long ago but which are only now becoming visible." (Not even the good Dr J. Curry rises to such elevation of the Butterfly Effect.)
And more (after plotting certain noisy graphs) ~ With a grand sweep of a mathematical wand, the author abolishes the multi-millennial swing from glaciation to deglaciation; abolishes Milanovitch cycles; abolishes solar variability . . . CO2 variations . . . volcanic aerosols . . . etcetera.
Apparently it is all a result of chaos mathematics and fractal geometry and self-similarity in nature. By this time, the author has disappeared down a fractal rabbit hole, into his own microcosmic concepts. He has failed to recognize that his ideas are unphysical.
Moderator Response:[BL] Although I usually hesitate to step in as moderator when I am participating in a discussion, in this case I am also the author of the blog post and all this discussion of what someone may have on their own web site is really getting off topic.
Please restrict your comments on CD's views of climate expressed on his own web site to the items that CD links to in support of his statements here.
As for CD's response time - it's the holidays. Lighten up.
-
Bob Loblaw at 07:54 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
I encountered the Manabe and Strickler/Wetherald papers as a grad student in the 1980s, when they were still fairly new.
The Manabe and Wetherald paper is also part of The Warming Papers.
I often find that older papers cover more of the basics than you find in newer papers. Newer papers do not repeat the well-established science, and often tend to assume certain knowledge on the part of the informed reader. This is also true of the IPCC reports - for the basics, I often suggest reading the first one from 1990.
-
Charlie_Brown at 06:39 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
Bob @ 10, 14, 15
Good posts. Thanks for the references to Manabe. Both of these articles and also Modtran are referenced in the justification and scientific background for the Nobel Prize in Physics 2021.
Sorry for the re-post to CD. I am new to this site and fumbled the submit button.
Moderator Response:[BL] I deleted the duplicate copy...
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:23 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
As a further comment on upper atmosphere IR transfer, two of the early key papers in this field were:
A key finding of this work is stratospheric cooling in response to increased CO2, shown clearly in figure 16 from the second paper.
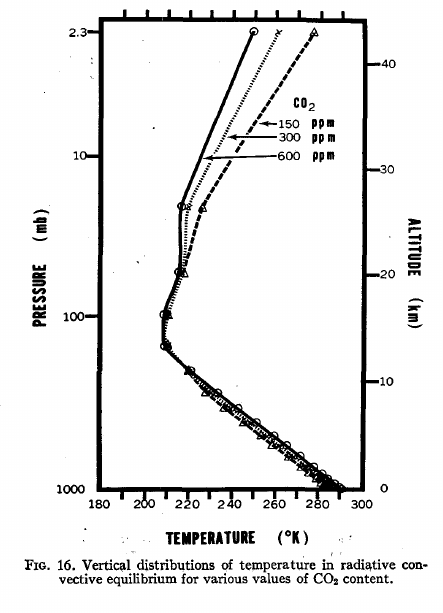
You will find many detailed explanations of this effect across the 'net, but one aspect of it is that adding CO2 also increases the emissivity, which means you get greater IR emission at the same temperature. In the stratosphere, where IR is easily lost to space, this increase in emissivity means that the earth-atmosphere system can emit the same IR to space at a cooler temperature. In the stratosphere, the Plancks' Law emission response to increased CO2 is stronger than the Beer-Lambert Law absorption response.
Moderator Response:[BL] 2022-08-06 image link fixed
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:10 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
charlie_brown @ 12:
Your use of the phrase "saturation" (even though you put it in scare quotes) with respect to the broadening of the absorption wings, etc., is one of the few contexts where "saturation" makes sense.
Most of the "arguments" made that claim the CO2 effect is "saturated" (as I linked to in the original post) seem to look at the overall transmission after a long path length, and "saturated" does not make sense in that context.
The question of the degree of resolution of spectral radiation calculations is a valid one. To run a GCM at many points and many time steps, you can't do a full high-resolution radiative transfer model. (Well, you couldn't 40 years ago. Computer horsepower is greater now - I'm not sure what is included in current GCMs.) You can, however, use a lower resolution model and test it against the high-resolution models to make sure it is getting the important bits right. Of course, the high-resolution models are ultimately validated against measurements.
-
Charlie_Brown at 03:10 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
CD,
While Beer’s Law is valid, using it to track the fate of radiant energy by wavelength leaving the surface is problematic. In the lower atmosphere, the 14-16 micron band reaches 100% absorptance within only about 100 meters. With re-emission, half up and half down, it doesn’t take many kilometers before the absorption band is depleted. However, radiant energy emitted from CO2 depends only its presence and its temperature. It does not depend on the path or number of absorption/re-emission exchanges. The temperature profile for radiant emission in the troposphere is determined by the lapse rate. Conduction between molecules keeps CO2 at the same temperature as the atmosphere.
IR that makes its way back to the surface is not the way to determine the effect of a change in CO2 on surface temperature. The surface temperature results from the overall global energy balance. It is much easier to consider the radiant heat loss to space as it is the only output energy stream for the balance. In the range for CO2, the principles of Beer’s Law determine that the uppermost emitting layer for that range is in the tropopause and lower stratosphere, which is cold at 217 K. For the US Standard atmosphere, the tropopause lies between 10-20 km. The available path length is very long. At an altitude of 20 km, the pressure is about 5% of 1 atmosphere, so 100% absorptance can be reached in about 2000 . Despite the low pressure, there are sufficient molecules in the path for CO2 to have a significant effect on radiant heat loss.As CO2 in the cold tropopause increases, the absorption lines extend and the absorption band widens, reducing the heat loss to space. To return the energy balance to steady state, the reduced heat loss must be compensated by increased energy radiating through transparent wavelengths. This can only be accomplished by increasing the temperature of the source, which is the Earth’s surface. The effect on the IR spectrum of the Earth-atmosphere system as viewed from space will be a decrease of energy flux in the wavelength bands that are absorbed by GHG and an increase of flux through wavelengths that are transparent to IR. This effect is described in detail Brindley, H. E., and R. J. Bantges, “The Spectral Signature of Recent Climate Change,” Current Climate Change Reports, 2 (3), pp. 112–126 (Sept. 2016).
-
Charlie_Brown at 03:09 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
Bob @ #7
Thank you for providing the graph for HITRAN data. The point that I wanted to make is that increasing CO2 increases the individual high resolution absorption lines in the wings. That is why the effect of CO2 is not “saturated,” but is diminishing with increasing CO2. Moderate transmission programs use algorithms to simplify the detailed line-by-line calculations into an absorption band. Essentially, it is an approach to average the lines within an absorption band, which makes the calculations easier. With this approach, increasing CO2 increases the width of the band, effectively by increasing the inclusion of small lines at the end of the wings.
I have used the version of MODTRAN hosted by the University of Chicago quite a bit, and I find it to be an excellent tool for understanding atmospheric radiation. It is similar to the free demo version from Spectral Sciences, Inc Fortunately, it makes all of the calculations, including Beer’s Law, molar density, temperature, pressure, etc., for you. There is no need to do a lot of math on your own. It is easy to run several cases and plot the Upward IR Heat Flux as a function of increasing CO2. The upward IR heat flux is the energy lost to space. It becomes apparent that the diminishing effect is logarithmic. Because it is an atmospheric radiation model and not an energy balance model, it is a little bit trickier to resolve the overall heat balance to determine the effect on surface temperature, but it can be done. The surface temperature is an input with a default value of 299.7 K for a tropical atmospheric profile and 288.2K for the 1976 U.S Std atmosphere. One can adjust the surface temperature manually, then use trial-and-error to find a surface temperature that causes the overall global energy balance to be closed. This means the upward IR heat flux needs to be constant, since the only other factor in the balance is solar energy in. The logarithmic diminishing effect of increasing CO2 is the same.
-
Bob Loblaw at 02:26 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
Eclectic:
I think that CD = Climate Detective, so you may have a tough ride ahead trying to convince CD that something on his web site is not worth linking to.
-
Bob Loblaw at 02:25 AM on 2 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
CD @ 8:
Well, on your own web site, equation 88.1 is stated to describe the situation when the atmosphere is in "thermal equilibrium". (I assume you mean that temperature is not changing with time, rather than the atmosphere is isothermal.) You also claim that this implies an equality between absorbed radiation and emitted radiation. You are wrong, in more ways than one.
- Conservation of energy applies to all forms of energy. Much of the energy in the atmosphere comes from thermal transfer between the surface (hot) and the air (cooler), and this energy flux extends throughout the troposphere. Additional energy is moved from the surface to the atmosphere as latent heat (evaporation at the surface, condensation in the atmosphere). This is not a "secondary issue".
- The atmosphere is also absorbing some solar radiation, but it is not emitting any radiation at all at those wavelengths. That energy needs to be dissipated by other means - either moved away from where it was absorbed by convection, or emitted as IR radiation at completely different wavelengths. There is no equality between absorbed solar and emitted solar - at any height.
- All radiation energy absorbed in the atmosphere will be shared with all gases at that height (both GH and non-GH gases) by molecular collision. The emission at that height is not dictated by the absorption, but by Planck's Law, which includes temperature and emissivity. Since temperature is affected by all energy fluxes, not just radiation, you cannot assume that other energy fluxes are "secondary" or that radiation absorbed = radiation emitted.
- "Conservation of energy" applies to the total of all gases. Since all gases share thermal energy through collisions, the emission of IR radiation by any single GH gas requires that the temperature of that gas be determined in combination with all other gases. The emitted IR at any height will be the sum of the Planck's Law emissions for all individual gases, and this process does not at all resemble "scattering" or "transmission".
- The absorption of IR radiation at any height is a combination of the absorption of upwelling IR and the absorption of downwelling IR. In an atmosphere with a temperature gradient these will not be equal - in the tropsphere, where temperature decreases with height, upwelling IR is larger than downwelling. The emission will be equal up and down, though, so we immediately see that treating the change in IR radiation as a "transmission/scattering" issue leads to the absurd result that your "scattering" process leads to a case where "scattering" causes more downward IR than is received.
Look at the graphs provided by the MODTRAN web site I mentioned previously. It defaults to "looking down" - i.e., upwelling IR. Choose altitudes of 2, 5, 10 km etc and see how the IR flux decreases as height increases.
Now, repeat with the "looking up" option (downwelling IR). See how the fluxes increase as altitude decreases - i.e., as the IR radiation continues in the downward direction, more and more IR radiation is added to the stream. You cannot interpret this as "scattering with transmission <1". If your theory of the mathematics is correct, this increasing IR radiation requires a transmission coefficient that exceeds 1.
Your mathematics are not correct. They assume things that are not true (absorption = emission, non-radiative energy fluxes are not important).
If you follow the link to Schwarzschild’s equation, you will see that it has independent terms for absoprtion and emission - terms that cover the Beer-Lambert absorption and the Planck emission. This is the correct way to do it.
You started your comments here with the statement that the Beer-Lambert Law does not apply. The argument that you have presented appears to implicitly suggest that Planck's Law also does not apply. You have invented your own theory of radiation transfer, and it has some serious problems.
-
Eclectic at 12:51 PM on 1 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
CD @ #8 and prior :
Best if you avoid the blogsite you have linked to [ClimateScienceInvestigations blogspot by "Climate Detective"].
It is one of those sad blogsites where much is correct, but much is wrong.
Rather like the famous "Curate's Egg" ~ where parts of it are quite good, but parts of the egg are rotten.
The "good" parts can never compensate for the bad parts.
-
From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
@6 Bob Loblaw
Ok, perhaps saying the Beer-Lambert Law was not applicable was a bit strong. But my point is that relying on it, and it alone, gives the wrong answer for the amount of radiation that is transmitted through the gas. More importantly it underestimates the transmission for large thicknesses of gas as my original comment (@5) states, and so underestimates the impact of any large increases in the CO2 concentration.
As for the idea that my "concept of transmission" leads to a transmissivity > 1, the equations 88.8 and 88.14 set out here clear demonstrate otherwise. It is also true from the equations set out in the link that the reflected radiation flux Id is always less than that upward IR flux Iu at all altitudes x.
Finally, before claiming that energy transfers from CO2 to non-GHG molecules (and back again) invalidate my analysis, I suggest you look again at the principle of detailed balance. In thermal equilibrium, what goes in must come out, otherwise you start to violate the 1st & 2nd laws of thermodynamics. Yes there are complicating factors such as convection and direct heating of the atmosphere from the Sun, but these are secondary issues.
I am aware that the atmosphere is a complicated body, but that does not mean it cannot be largely understood by considering idealized models in the first instance. That is how modellers approach the problem. The Beer-Lambert Law is one such idealized model.
-
Bob Loblaw at 06:55 AM on 1 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
charlie_brown:
The image from figure 1 of the SpectralCalc document you link to would be this one:
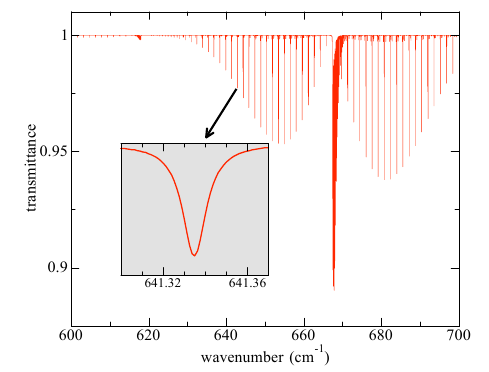
This diagram clearly shows the high level of variation with wavelength. Radiation transfer codes vary in their spectral resolution. You mention HITRAN. There is also a web site here that lets you work with an older lower-resolution model: MODTRAN. You can select different temperature profiles, change gas concentrations, cloud cover, etc., and choose looking up or down at selected altitudes.
All of the equations discussed - Beer-Lambert Law, Schwarzschild equation, etc. - are most properly applied to spectral radiation where properties such as absorption coefficients are highly variable with wavelength. For solids and liquids, some ranges of wavelengths can be treated as having proprties that are fairly constant. That is a Bad Idea (tm) for gases though.
The "cylinders" in the blog post diagrams and discussion are theoretical ones: the walls are perfectly transparent and do nothing to impede any sort of energy transfer. In the real world, the equations are differential ones. Keeping things simple usualy means not doing Calculus, though.
Introductory meteorology courses love talking about "parcels of air" (e.g. for explaining atmospheric instability), but of course the atmosphere is made up of continuous flows of air, not small balloons of air. Likewise, radiation does not work with distinct cylinders of air, but with air as a continuous medium. Your "shells" are an infinite number of identical stacks of columns, side by side.
-
Bob Loblaw at 06:14 AM on 1 January 2022From the eMail Bag: the Beer-Lambert Law and CO2 Concentrations
CD:
You are making some pretty strong assertions for someone that has clearly not read the entire post and comments in detail.
As is stated at the end of the original post, "For IR radiation, the earth and atmosphere are also doing the reverse of absorption – thermal energy is being transformed into photons, resulting in the emission of IR radiation in all directions." This is also discussed in more detail in the comments by charlie_brown and myself. You are not introducing any concept that has not already been mentioned. The post acknowledges that there are additional concepts that are needed for the full picture.
It may be a matter of semantics, but you are wrong in saying that the Beer-Lambert Law "is not applicable here". It is only part of the story, but is is clearly applicable to the absorption part of the story.
Where you go wrong is in claiming that the process of re-emission "looks like scattering". It most certainly does not. Scattering results in changing the direction of travel of radiation - but the radiation is still the same wavelength as the incident radiation, and each photon carries the same energy it had before it was scattered. You cannot create new radiation travelling in a new direction at a new wavelength through scattering, and scattering will not create new radiative energy. Emission does create new radiation.
For absorption/re-emission, the emitted IR radiation will not necessarily be at the same wavelength as any radiation what was absorbed. The absorbed radiation energy is not immediately emitted as new IR radiation - it virtually always gets lost by the GHG molecule to other molecules (including non-GHG ones). There is a good description of this over at Eli's. The energy that appears as emitted IR radiation does not need to come from the absorption of radiation - it almost always comes from collisions with other molecules that can get their energy from anywhere.
As a result, any emitted IR radiation is dependent on two factors:
- The number of all GHG molecules present that can pick up thermal energy through collisions with other molecules. The emitted IR radiation may not be coming from CO2, and its wavelength will depend on the emission spectra of that other GHG molecule.
- The temperature of the surrounding air. This controls the overall availability of thermal energy to drive IR emission. If the atmosphere is very cold, IR emissions will be less than if the air is very warm.
As mentioned in comment #2, Schwarzschild’s equation covers the case where an atmosphere is both absorbing and re-emitting, and the net change in IR radiation with height is dependent on the temperature gradient.
One thing you have correct: IR radiation is equal in all directions, and in this sense it resembles scattered light (which occurs in all directions, but is not exacly equal in all directions), but that is the only similarity.
A key aspect of the dependence of net IR radiation on the temperature gradient is that upward IR fluxes normally decrease with increasing height, while downward IR fluxes normally increase as you go lower in the atmosphere. If we applied your concept of "transmission" to the downward flux, we would have transmissivity >1, This makes no sense.
"Transmission" is not a useful concept when the air can create new IR radiation and add it to the stream. It is a concept that only applies to IR radiation that originates elsewhere and is passing through the air. And that is exacly what the Beer-Lambert Law describes.
I have briefly looked at the URL you provided. It suffers from the same basic errors: confusing re-emission with scattering, and treating the addition of emitted IR to the upward stream as if it is a "transmission" question. It is not.
Proper radiation transfer theory and the effects in the atmosphere take into account all energy fluxes, and properly account for the process of absorbing IR radiation, transforming it into thermal energy contained in all gases, possibly moving it through convection, and then re-emitting that energy as IR radiation (by all GH gases).
Prev 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























