Recent Comments
Prev 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 Next
Comments 3301 to 3350:
-
Eric (skeptic) at 21:27 PM on 6 September 2022How climate change spurs megadroughts
The connection between drought intensity and global warming is clear. However droughts start and end naturally and they should mention that there has been persistent La Nina since 1999. There have been four major La Nina and one major (super) El Nino. From 1980 to 1998 the numbers were reversed: four major El Nino and one major La Nina.
While persistent La Nina creating the present drought in the western US, it may be also be true that persistent El Nino and it's excess moisture masked the drying effects of global warming in 80's and 90's. Possibly separate from ENSO (not sure), there was a lack of monsoon rains starting in 2000. There was substantial monsoon this year which tempers evaporation in some locations.
Lawns will dry up; lush golf courses will disappear. The very character of the West - and of many arid parts of the globe - will be transformed
I would say "revert" and mostly for the better.
-
David-acct at 12:02 PM on 5 September 2022Skeptical Science New Research for Week #33 2022
www.washingtonpost.com/weather/2022/02/20/texas-energy-winter-renewable-jacobson-dessler-rogan/
The above article is praising Jacobsons work and analysis of 100% renewables.
I have posted the money quote describing jacobsons 30 sec test of the supply and demand of electricity. See if you can spot the logic flaw in jacobsons analysis.
"In the recent study, Jacobson and colleagues showed how to meet energy demands every 30 seconds across the United States with no blackouts in a greener, more populated nation in 2050 and 2051.
They modeled grid stability throughout the contiguous United States, including data from a weather-climate-air pollution model, which includes climate factors and statistically typical weather patterns that occur in a given region. Using energy consumption data from the Energy Information Administration, the team simulated energy demands for 2050 to 2051. Energy supply had to equal energy demand every 30 seconds, otherwise the model shut down.
"The team found that the actual energy demand decreased significantly by simply shifting to renewable resources, which are more efficient. For the entire United States, total end-use energy demand decreased by about 57 percent. Per capita household annual energy costs were about 63 percent less than a “business as usual” scenario."
-
Eclectic at 05:26 AM on 5 September 2022Models are unreliable
Lomborg today sounds more like Fox News & Tucker Carlson.
That's a slight exaggeration, JohnCalvinNYU ~ but Lomborg's ideas seem to be wandering further away from common sense . . . almost like he's getting all his information from the Murdoch media empire.
John, please widen your education. Avoid Fox and suchlike propagandists.
-
Bob Loblaw at 05:09 AM on 5 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
John Oneill:
...and if we had an expectation that the conditions that led to early development of nuclear in places such as France could occur again, and provide us with large quantities of nuclear energy in the very near future at reasonable/competitive cost, then nuclear would be a useful path in the future.
But like they say in any investment advice, "past performance is not indicative of future results". You really need to make sure that the conditions that led to past performance will actually exist and continue in the future.
-
Bob Loblaw at 05:02 AM on 5 September 2022Models are unreliable
JohnCalvinNYU:
I"m really not sure just what definition of "accurate" you are using. If you are expecting it to be "perfect", then prepare to be disappointed. Science (and life in general) does not produce perfect results. Any scientific prediction, projection, estimate, etc. comes with some sort of range for the expected results - either implicitly, or explicitly.
You will often see this expressed as an indication of the "level of confidence" in a result. (This applies to any analysis, not just models.) In the most recent IPCC Summary for Policymakers, the state that they use the following terms (footnote 4, page 4):
Each finding is grounded in an evaluation of underlying evidence and agreement. A level of confidence is expressed using five qualifiers: very low, low, medium, high and very high, and typeset in italics, for example, medium confidence. The following terms have been used to indicate the assessed likelihood of an outcome or result: virtually certain 99–100% probability; very likely 90–100%; likely 66–100%; about as likely as not 33–66%; unlikely 0–33%; very unlikely 0–10%; and exceptionally unlikely 0–1%. Additional terms (extremely likely 95–100%; more likely than not >50–100%; and extremely unlikely 0–5%) are also used when appropriate. Assessed likelihood is typeset in italics, for example, very likely. This is consistent with AR5. In this Report, unless stated otherwise, square brackets [x to y] are used to provide the assessed very likely range, or 90% interval.
So, the logical answer to your question of why models are constantly being updated or improved is so that we can increase the accuracy of the models and increase our confidence in the results. Since nothing is perfect, there is always room for improvement - even if the current accuracy is good enough for a specific practical purpose.
Models also have a huge number of different outputs - temperature, precipitation, winds, pressure - basically if it is measured as "weather" then you can analysis the model output in the same way that you can analyze weather. A model can be very accurate for some outputs, and less accurate for others. It can be very accurate for some regions, and less accurate for others. It can be very accurate for some periods of geological time, and less accurate for others. The things it is accurate for can be used to guide policy, while the things we have less confidence in we may want to hedge our bets on.
Saying "none of the climate catastrophes predicted in the last 50 years" is such a vague claim. If you want to be at all convincing in your claim, you are going to have to actually provide specific examples of what predictions you are talking about, and provide links to accurate analyses that show these predictions to be in error. Climate models have long track records of accurate predictions.
Here at SkS, you can use the search box (upper left" to search for "lessons from past climate predictions" and find quite a few posts here that look at a variety of specific predictions. (Spoiler alert: you'll find a few posts in there that show some pretty inaccurate predictions from some of the key "contrarians" you might be a fan of.)
As for Lomborg: very little he says is accurate. Or if it is accurate, it omits other important variables to such an extent that his conclusions are inaccurate. I have no idea where I would find the article of his that you mention, and no desire to spend time trying to find it. If that is your source of your "none of the climate catastrophes" claim, then I repeat: you need to provide specific examples and something better than a link to a Lomborg opinion piece.
There have been reviews, etc. posted here of previous efforts by Lomborg, such as:
https://skepticalscience.com/open-letter-to-wsj-scientist-response-to-misleading-lomborg.html
https://skepticalscience.com/lomborg-WSJ-debunk-CSRRT.html
https://skepticalscience.com/lomborg-detailed-citation-analysis.html
...and Lomborg has a page over at DesmogBlog.
In short, you're going to have to do a lot better if you expect to make a convincing argument.
-
JohnCalvinNYU at 01:45 AM on 5 September 2022Models are unreliable
If climate models are accurate then why are they constantly being updated or improved? Assuming there's even a logical answer to that question, how are scientiests certain that the "improved" versions of the models are actually improved? None of the climate catastrophes predicted during the past 50 years ago have come to pass (see "False Alarm: How Climate Change Panic Costs Us Trillions, Hurts the Poor, and Fails to Fix the Planet" by Bjorn Lomborg) so why is the scientific community convinced it is correct now given it's history of failing to make accutrate climate predictions?
-
John ONeill at 22:32 PM on 4 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
The graph with the concave blue line and the convex red line is actually a good cartoon of what actually happened to the electricity emissions of France and Germany, the exemplars of the 'Mesmer plan' accelerated reactor buildout, and the 'Energiewende' attempt to decarbonise with mainly wind and solar. French electricity emissions, and fossil fuel use, plummeted, and are still among the lowest in Europe, even though at the moment, the nuclear industry is only running at 34% of its capacity. Germany started later, its emissions have gone down much more slowly, it's still producing on average 3 to 4 times as much CO2 as France, and there's no guarantee that the reduction curve will get steeper - at the moment, it's not looking good, with mothballed coal plants being started up to replace the Russian gas that's supposed to be 'firming' solar and wind. Peak power production over the last 24 hrs was 69 GW, close to the full capacity of either solar, 65 GW, or wind, 64 GW. But solar averaged only about 11 GW, and wind only 14 GW. German nuclear, unlike French, has been running at 98% capacity all day. The batteries that will supposedly back variable renewables are nowhere to be seen. Pumped hydro makes an appearance for just four hours, at from 2 to 11% of demand. Meanwhile, the 'brown coal', of which Gemany is the world's largest user, continues to be the largest single source of electricity, as it has been for the last thirty years.app.electricitymaps.com/zone/DE
-
wayne19608 at 08:55 AM on 4 September 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
thanks Rodger
there is this older article
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40641-015-0014-6
I guess from a political perspective there is not much point in thinking past 2100
-
Bob Loblaw at 02:09 AM on 4 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
The difference between getting to net zero first versus minimizing the total emissions between now and reaching net zero is not a trivial distinction.
Look at the following figure. The red line reaches zero after 40 years. The blue line has not quite reached zero after 60 years. The total emissions under the red line are about 3x the total under the blue line. Waiting 30 years for "better technology" is not a good choice.

-
sekwisniewski at 01:06 AM on 4 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
Replying to 315:
Bob Loblaw:
"Getting faster to net zero" is not necessarily the issue. Minimizing total emissions between now and "getting to net zero" is what matters.
I did not intend to suggest otherwise and used "faster/cheaper" quantifiers as possible scenario constraints.
-
MA Rodger at 23:09 PM on 3 September 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
Wayne @4,
I was in two minds on continuing our interchange, but I decided I would continue when I came across coverage of the paper underlying this SkS OP which surprisingly appeared today on the pages of my local rag with the title "Zombie ice to raise global sea level". On-line I see the same story getting into newspapers elsewhere (eg The Washigton Post).In terms of an SLR-CO2 correlations, I don't recall seeing Hansen provide it. I believe the closest he got was in Hansen et al (2013) 'Climate sensitivity, sea level and atmospheric carbon dioxide' (with its well-used Fig 1) which looked at temperature & SLR but only inferred CO2 levels with very cursory checks to actual CO2 reconstructions.

And for me, Hansen's 5m SLR by 2100 was always a bit of theorising that I struggled with. Even after it appeared properly written up in Hansen et al (2016), which at least answered the energy equations that were my initial objection to such a large SLR projections, for me it still remains more 'discussion document' than a full-blooded argued case. In my view, worrying as it is, the future SLR from Greenland & Antarctica depends on the Precipitation minus Ice-Loss balances and that puts us in the hands of climatologists for the precipitaion and glaciologists for the ice-loss. The application of paleoclimatology and whether Greenland melted out in the Eemian isn't so relevant for our future SLR.Just to throw in my other SLR bug bear which also becomes relevant here, I've always reckoned SLR ain't gonna stop at 2100. So why do we go on so long about the 2100 SLR when by 2150, 2200, 2300 etc it's going to be seriously bigger? (A total of 2.3m SLR/ºC AGW according to IPCC AR5 fig13.14.)
The SLR-ΔCO2 relationship is of course a paleoclimate thing, so may not be immediately relevant outside the Eemian or now we have a Panama Isthmus connecting N&S America. That said, the SLR-ΔCO2 relationship is usually a step beyond what most graphics provide, but fig 6 of Rea et al (2021) 'Atmospheric CO2 over the Past 66 Million Years from Marine Archives' does provide us a ΔT-SLR-ΔCO2 graphic. Note that they do not attempt to be definitive with this CO2 reconstruction, saying "While each method has uncertainties, these are largely independent, so their broad convergence on similar CO2 histories is encouraging."
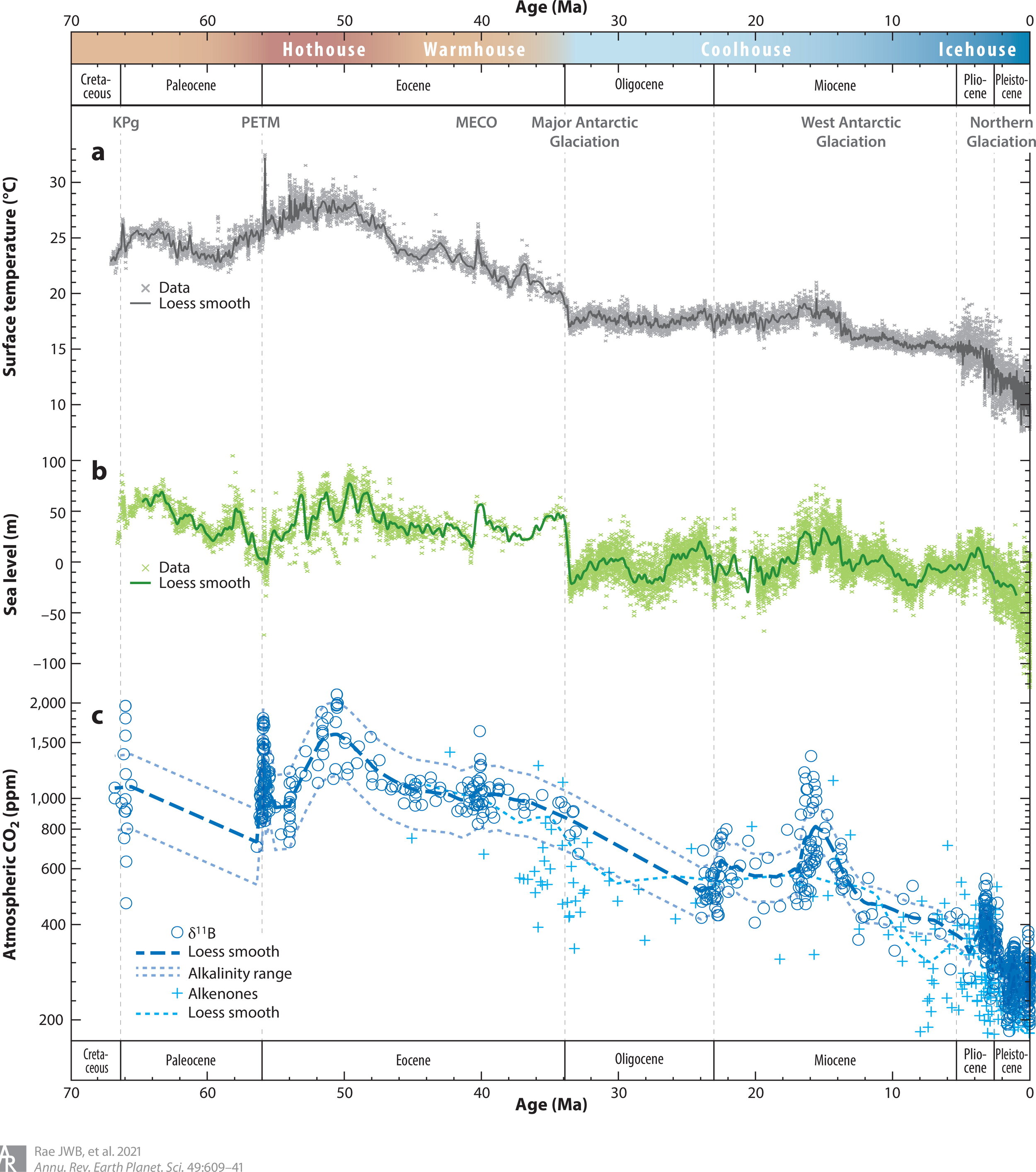
But I stress the idea that paleoclimate stuff should concede precedence to glaciology when it comes to the melting ice caps today and glaciology is where the paper underlying the SkS OP above comes from, Box et al (2022) 'Greenland ice sheet climate disequilibrium and committed sea-level rise'. I read that paper as saying that, as of now (2000-19), Greenland is not tipped over into melt-out mode (which I think was always seen as requiring a little more AGW to do that tipping, but nonetheless is good news to hear said) and that the Greenland melt which we are committed-to will happen in the next several decades, not several centuries, and will be mainly over by 2100.
So at least for Greenland under the AGW so-far, my bug bear (that we are in denial ignoring massive SLR awaiting us post-2100) is assuaged.
Mind, the SLR thus awaiting from Greenland isn't trivial. And there is still Antarctica. And not forgetting we still have the tiny task of halting future AGW.
-
Bob Loblaw at 09:40 AM on 3 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
sekwisniewski:
I already said:
It doesn't matter whether you label them as "nuclear' or "fossil". The emissions end up in the atmosphere.
What matters is complete accounting. Item 4, which I think we agree on.
"Getting faster to net zero" is not necessarily the issue. Minimizing total emissions between now and "getting to net zero" is what matters.
-
sekwisniewski at 06:54 AM on 3 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
Replying to 313:
Of course, by definition the lifecycle emissions should account only for a given source (wind, solar, nuclear, hydro, etc) LIFECYCLE. Once we've established those, we could construct various scenarios of building those sources in time in an interacting system. Only then could we optimize and assess if there are "opportunity emissions" for different scenarios, i.e. does including nuclear bring us faster/cheaper to net zero or not? Still, these wouldn't be lifecycle emissions. Does this make sense?
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:23 AM on 3 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
Seriously, sekwisniewski? "Conservation of mass" arguments?
Taking life-cycle emissions, using only what happens during construction and operation of the plant violates the "conservation of a consistent argument" requirement when looking at item 4. Either we are taking the entire system and results into account, or we are selecting only the part that supports a particular argument (AKA cherry picking).
-
sekwisniewski at 01:55 AM on 3 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
Replying to 311:
1. You can't add opportunity emissions to lifecycle emissions, because it violates the conservation of mass, if those lifecycle emissions are then used to calculate physical emissions.
2. Another counterfactual to maintaining nuclear is replacing it with a mix of fossil and renewable sources. Fossil backup of renewables is suggested in Abbott (2012). Renewables replacing nuclear wouldn't reduce emissions either according to your logic, which does not seem to be a good framing.
3. Yes, but when nuclear covers new demand opportunity emissions of = 0.
4. Absolutely, we've got to take the overall picture into account, which is studied in the field of energy systems modeling.
-
Bob Loblaw at 00:05 AM on 3 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
A few problems with that list, sekwisniewski.
- It doesn't matter whether you label them as "nuclear' or "fossil". The emissions end up in the atmosphere.
- If nuclear is being built to replace existing nuclear, then it doesn't replace fossil-fuel-based capacity and does nothing to reduce fossil fuel emissions.
- Other sources coming on line now can also cover future demand.
- Yes. The calculations need to cover all sources of electricity, and all the CO2 emissions that are produced if a particular path is chosen. Cherry picking a compartmentalized view - where you only count emissions when a plant is operating (e.g., wind vs. nuclear) and you ignore how this fits into the overall picture - is a bad approach.
-
sekwisniewski at 23:50 PM on 2 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
A few problems with the opportunity emissions of nuclear:
- if they are added to lifecycle emissions, they'd need to be subtracted from fossil emisions,
- nuclear may be built to replace aging nuclear (repowering),
- nuclear coming online in the future may cover new demand arising from clean electrification,
- any other source should have opportunity emissions added too.
-
rip71749 at 11:09 AM on 2 September 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
It's hard to be optimistic. Record temperatures, record fires (Siberia burns year round and Russia started flaring and burning their natural gas that they don't want to send to Europe because they can't shut down their wells), record floods, shrinking albedo and record amounts of fossil fuels used. Countries are trying to find new sources of fossil fuels. I live in southern Calif and the temp yesterday was 112oF and probably warmer today and all next week, really hot! China is turning more to coal, probably India too. Clearly the world has to work together to solve these problems, and then you look at the top 4 fossil fuel emitters - China, US, India and Russia. It's hard to imagine those 4 ever working together. 6' by 2100 sounds conservative to me.
-
Bob Loblaw at 10:22 AM on 2 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Thanks, Baerbel, for that information on arXiv. It indeed seems to be simply a place for people to upload papers with little regard to quality. They may or may not be papers that are submitted elsewhere. Calling something a "publication" because one puts a copy on arXiv is hubris at the extreme.
On their "About" page, arXiv states the following (emphasis mine):
Material is not peer-reviewed by arXiv - the contents of arXiv submissions are wholly the responsibility of the submitter and are presented “as is” without any warranty or guarantee. By hosting works and other materials on this site, arXiv, Cornell University, and their agents do not in any way convey implied approval of the assumptions, methods, results, or conclusions of the work.
The main arXiv page actually has a warning related to Covid-19 submissions (again, emphasis mine):
Important: e-prints posted on arXiv are not peer-reviewed by arXiv; they should not be relied upon without context to guide clinical practice or health-related behavior and should not be reported in news media as established information without consulting multiple experts in the field.
I agree with MA Rodger's initial evaluation of the merit of these "publications" - not worth the time to look at.
-
Bob Loblaw at 10:05 AM on 2 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
The mention of "opportunity costs" ties into what I suspected may be leading to the differences in estimates/opinions here.
"Opportunity cost" is a common term in economics, and may need a little explaining. Let's say that I have $1000 sitting in a bank account, making 3% interest. One point of view is "hey, that's great! In a year, I'll have $1030! What a good investment!" But if a different investment vehicle will turn that $1000 into $1050 in a year, then I am actually losing out on $20 of lost income - $20 of money that could have been mine next year if I had switched investments. Although I think I am making $30 in the year, I have lost the opportunity to make another $20 - the "opportunity cost" of my current choice of investment.
What Michael Sweet is saying is that the "cost" of nuclear needs to include the lost opportunity of reducing carbon emissions while we wait for nuclear to be built. The carbon emissions in the next 30 years will be either 30 years of wind built today, or 10 years of fossil fuels plus 20 years of nuclear if we say "but direct emissions from nuclear are as good or better than wind".
Going back to the $1000 investment, are we further ahead if we invest at 3% for 30 years, or nothing for 10 years and 5% for 20 years? You need to include the opportunity cost of "nothing for 10 years" to make an accurate comparison.
It's kind of like Popeye's friend Wimpy: "I'll gladly pay you next Tuesday for a hamburger today".
-
wayne19608 at 09:05 AM on 2 September 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
MA Rodger, I think ive read that in numerous postings by Hansen and others over time. You seem to confirm at least partially with respect to 13mya
-
MA Rodger at 08:40 AM on 2 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
There was mention @10 of previous SkS words on van Wijngaarden and Happer. This 'mention' may refer to the treatment one of their un-published papers got in this thread from a year ago.
The top 3 listed 'publications' are the only ones that have these two authors van Wijngaarden and Happer, their first cooperation writing since they were doing physics back thirty years ago.
These 3 listed 'publications' seem rather odd to me. It is as though some other un-attributed authors have contributed to the work but who then had no input into the final version. I say that as many of the numbers presented are not entirely wrong) but the way the papers are written sets them out to give the wrong conclusion. And there are rather too many inconsistencies suggesting too many cooks.
Thus, for example, the third in the list tells us it is a "a summary of a more detailed paper on radiative forcing by greenhouse gases that the authors plan to publish in the near future." And while there are two different titles given for this "more detailed paper" of which there is no sign, they are presumably referring to the top two in the list, all three being pretty similar in their coverage but strangely different in how they say it (and none of which get published). And strangely this 'third' paper 'summary' gives an odd message in its abstract that doesn't really match that given the full account. I call the message in the abstract 'odd' as it tells us not to be scared by methane because it is adding a forcing only one-tenth the CO2 forcing (which agrees with the NOAA AGGI numbers of the last decade) and that together they are adding a climate forcing of +0.05Wm^-2/y (which is 50% higher than the NOAA AGGI numbers of the last decade) but this will apparently only increase global temperatures by +0.012ºC/y (this about half the warming rate of the last decade).
Within the full text, this message is lost with the message being that CO2 is far more powerful a GHG than methane but that the biggest power of a GHG is when it is at low concentration which is why small increases of methane have such a big effect molecule-for-molecule that the higher concentrations of CO2, this being entirely true. But so what?
Untangling the totality of all this strangeness would be quite a task but given the papers are evident garbage, such a debunking task isn't really merited.
-
michael sweet at 07:26 AM on 2 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
John Oneil:
In your post at 392 you claimed:
"'Over the last 50 years, countries that adopted nuclear power consistently reduced emissions intensity, by more than three times as much as those that went without nuclear."'
Your link was apparently not peer reviewed. Your most recent links suggest similar reductions between nuclear and renewables. My cite found renewables resulted in less emissions. As I said at 296, I doubt we will agree on his topic since different papers reach different conclusions.
Your citations only address emissions during the running of nuclear plants, the opportunity cost emissions of nuclear are about 10 times the total emissions of wind and solar due to the very long build times of nuclear. They are calculated in Jacobson 2009, linked above at 304, and are the main reason Jacobson rejects nuclear as a future power source. In addition, since it takes 10-14 years on average to build a single nuclear plant we would see no nuclear power from proposed plants before 2035. That is after all electricity should be converted to low catbon. 2035 is too late.
Nuclear is too expensive, takes too long to build and there is not enough uranium.
-
BaerbelW at 06:43 AM on 2 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Just to clarify what ArXiv is and isn't, here is the beginning of the Wikipedia entry for it:
arXiv (pronounced "archive"—the X represents the Greek letter chi ⟨χ⟩)[1] is an open-access repository of electronic preprints and postprints (known as e-prints) approved for posting after moderation, but not peer review. It consists of scientific papers in the fields of mathematics, physics, astronomy, electrical engineering, computer science, quantitative biology, statistics, mathematical finance and economics, which can be accessed online. [...]
So, it's a somewhat moderated archive but nothing close to a peer reviewed journal and having papers listed there, doesn't really tell you anything about their quality.
As it was mentioned upthread, there is a successor to or at least archive of Beall's list of potentially predatory publishers available at https://beallslist.net/
Hope this helps!
-
Bob Loblaw at 06:05 AM on 2 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
A followup to my own comment @14:
Looking a bit further into arxiv.org, I was able to find the two papers that van Wijngaarden lists on his publication record. There are also two more there, also co-authored with Happer.
None of the four give an indication - on the main page for each providing the abstract, or in the linked PDF files - that they have been submitted to or accepted in any actual journals. I don't know if this is normal for arxiv.org or not.
-
Bob Loblaw at 00:08 AM on 2 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Cowpuncher:
Both Happer and van Wijingaarden are physicists with no real background in climate science.
From van Wijingaarden's profile page at York University, his research area is:
Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics
High-precision laser spectroscopy; Laser cooling and atom trapping; Ultracold atoms, Bose-Einstein condensation, and quantum information; Optical lattices; Environmental pollutant monitoring and climate change.
I highlighted the "climate change" part. It is not really his area of expertise. His publication list shows several recent climate-related titles. Looking at the titles, some are simple data analysis papers. Looking at some of the "journals", I notice that two of the papers with Happer are listed as "Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics arXiv". As far as I can tell, this is not an actual journal - just a place for people to post "papers". The PDFs are hosted on van Wijingaarden's York U web site, and give no indication that they have actually been published anywhere. They did not show up when I searched on arxiv.org.
Another paper is listed as "accepted Open Atmospheric Journal (2016)". Also links to a PDF on his own web page. I can find a journal called "Open Atmospheric Science Journal", but that paper does not appear in a search for "Wijingaarden" on their web page. Downloading the PDF from the YorkU site shows that the full title of the journal really is "Open Atmospheric Science Journal", and it lists Bentham Open as the publisher. Bentham Science Publishers has a page on Wikipedia, which notes:
Bentham Open, its open access division, has received criticism for questionable peer-review practices as well as invitation spam; it was listed as a "potential, possible, or probable predatory scholarly open access publisher" in Jeffrey Beall's list of predatory publishers, before the list went defunct.
Some of the "publications" give no journal name at all.
To put it bluntly - that list of "publications" is padded to the extreme. You may wish to believe that these "papers" represent some radically-innovative evidence that the field of climate science is keep the truth hidden. It is much more likely that they are crap, and the only way that the authors can "publish" them is to place them in locations where literally any old crap is accepted.
-
Bob Loblaw at 23:12 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Rosross @ 4:
Do not confuse "science" and "stuff that people pretend is science". Yes, a lot of crap that people do and push as part of their agenda is crap, and not deserving of being call science proper. But that is the trick - just because someone wraps up their crap in sciencey terms does not make it science. I can call my Ford Pinto a Lamborghini Countach, but that does not make it one.
The fact is that using the terms that come from science helps the shysters sell their swamp land in Florida. People are fooled, because of their lack of knowledge and background in science. It looks sciencey, and without the critical thinking skills that are discussed in this blog post, people get fooled.
And even "scientists" that have successful careers are sometimes fooled. A successful academic career can result from publishing a lot of poor quality work. Publish or perish. Quantity, not quality. Sometimes they just want to fool others to move their career along. Other times, they fool themselves into thinking their long list of publications in poor quality journals actually represents "good science".
Hopefully, the information in the blog post helps people recognize what really is good science from the boatloads of crap that are sold under the "science" sign.
-
MA Rodger at 21:06 PM on 1 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
John ONeill @306,
You do your reputation no favours when you say of Wagner (2021) 'CO2 emissions of nuclear power and renewable energies: a statistical analysis of European and global data' that you "don't believe the authors have any connection to the nuclear industry." You appear not to even have noted that there was but one author. And had you checked you would find Frederick Wagner was an emeritus professor of Plasma Physics, so deeply connected to the technology, and that his commentary (eg here) shows his connections also to the industry. But that doesn't make his paper unreliable although it is good to read such work before nailing its colours to your own masthead, even if as in this case the battle is against a pretty easy target, which Sovacool et al (2020) certainly is. Maybe you have not noted that presented @303 is another swip at Sovacool et al., namely Fell et al (2020) 'Nuclear power and renewable energy are both associated with national decarbonization'.
-
TVC15 at 18:42 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
@8 Cowpuncher
"By breathing out, we are simply returning to the air the same CO2 that was there to begin with".
Source: Does breathing contribute to CO2 buildup in the atmosphere? -
TVC15 at 18:40 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
@8 Cowpuncher
Happer has a long list of touted climate myths.
Climate Misinformation by Source: William Happer -
John ONeill at 18:17 PM on 1 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
This 2021 paper refutes the conclusions of Sovacool et al. I don't believe the authors have any connection to the nuclear industry.
link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01508-7.pdf
CO2 emissions of nuclear power and renewable energies:
a statistical analysis of European and global data'Our results are in complete contradiction to a recent publication (Sovacool et al. in Nat Energy 5:928–935,2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-020-00696-3). The authors of this paper conclude that nuclear power does not reduce the CO2 emissions, but renewable power efficiently does. In addition, they argue that these two technologies crowd out each other. The possible reason for their claims may result from a specific conditioning of the data. In contrast, our analysis clearly confirms the adequacy of both nuclear and renewable power generation.'
-
Eclectic at 17:39 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Rosross @4 :
You are certainly correct - to some extent. ( I agree with "OPOF" on that. )
OPOF makes good points on the unhappy level of corruption/marketization of modern science. It is something which a cynic would regard as difficult to avoid in this modern commercial world.
# Nevertheless, Rosross, the modern science system is like modern democracy ~ far from perfect, yet better than any alternative so far tried. If you have a more perfect (and practical !) system in mind, then it would be most interesting to read your description of it. (Doubtless you know the old joke about the overly-critical voyeur.)
Cowpuncher @8 ~ sorry, but your vanWijngaarden publications link shows as "highly insecure" and my computer won't proceed. If you have some excellently salient points (from Wijngaarden & colleagues) then please summarize those points.
Happer and vanW have received some earlier attention here at SkS ~ and as far as I recall, they were not making any notable advance in climate science. Basically, theirs was a re-hash of already-understood material . . . plus a large dob of bizarre motivated reasoning (but not as extreme as Lindzen's stuff). ~Motivated reasoning strongly influenced by political extremism, I mean. In other words, very poor science.
-
TVC15 at 17:11 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Thank you Guest Author for this well written piece! I wish everyone on this planet had a copy to read!
-
Cowpuncher at 16:16 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Thanks scaddenp. I checked both your references and I didnt see "junk" in Happer's comment about CO2 being breathed out. Also the list of "myths" are points of view shared by many scientists. Some appear wrong, others sensible. I suggest checking out https://wvanwijngaarden.info.yorku.ca/publications/ It seems to me to include studies that deserves to be published and not shunned from a political perspective. As I commented on the original paper it seems only some "new discoveries" can get published.
Moderator Response:[BL] Link activated.
The web software here does not automatically create links. You can do this when posting a comment by selecting the "insert" tab, selecting the text you want to use for the link, and clicking on the icon that looks like a chain link. Add the URL in the dialog box.Note: the link does not seem problematic to my browser (later comment by eclectic notwithstanding).
-
scaddenp at 13:52 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Cowpuncher - dont know van Wijingaarden, but in Happer case, yep, it is really hard to get your politically-motivated junk published. Getting basic errors through peer-review is a tough process. If you have somehow missed Happer's problems - then try here skepticalscience.com/Evidence-Squared-10-Debunking-William-Happer-carbon-cycle-myth.html and here skepticalscience.com/William_Happer_arg.htm
-
Cowpuncher at 13:03 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
I am interested in the quote: "Scientists are incentivized to find new discoveries, errors in each other’s work, or disconfirm existing knowledge, not to go with the flow. Individual scientists may dissent from the consensus... ". In light of this why have scientists like van Wijngaarden and Happer found it difficult to have their work published? Should this section of the paper not elaborated on the role that politics plays in science?
-
One Planet Only Forever at 12:37 PM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Rosross @4,
In a limited evidence based way I agree with you. A clear case is the ways that the 'science' of marketing is abused.
There are many harmful misleading marketers. Regarding climate science they have misled people to delay the rate of increased awareness and understanding of climate science. They want to delay learning among the general (voting) population because that learning would lead to more rapid corrections of what has become popular and profitable. Those corrections, and making amends for harm done, would be disadvantageous to the misleading marketers and their misled fans.
-
DK_ID at 12:27 PM on 1 September 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
I had read of this study. I wish the expected minimum of GL melt were added to the expected SLR from land glaciers and thermal expansion plus an expected contribution from Antarctica. I believe SLR is tracking at or above IPCC maximum expectatons which would give 3-ft by 2100 without much contribution from the big ice sheets. The ARs have started icluded a footnote re the unlikely but feasible collapse of portions of the big ice sheets. But isn't collapsing how the Laurentide sheet left so quickly?
Hansen, et al 2015 showed that melt water from the GIS could slow the overtuning current resulting in more warmth staying in the Southern Ocean at the same depth as the grounding line for Antarctic draining glaciers. DeConto Pollard 2015 modeled collapse mechanisms (structural instabilities) of tall ice cliffs produced by melting and calving of those glaciers.
So I'd think the bad news from GL means bad news for the west and east Antarctic Ice Sheets and expected SLR by 2100 could be closer to 6' in a moderate emissions scenario. The question is, how much of that is already locked in? I understand the compulsion to not be too unconservative, but maybe it's time for a realistic look at what we are really expecting.
-
rosross at 10:47 AM on 1 September 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
This is an excellent article on what science should be, what science claims to be, what science at its very best must be, but the reality is that in this day and age and for much too long, this is not what the scientific system of enquiry is. That is the problem.
This essay is like the Church in centuries past claiming what it is, while ignoring the corruption and distortions inherent in its system.
Much of modern science is not science by any stretch of imagination and the vested agendas who use it as tool and weapon, make it impossible for it to be real science, good science. If only the scientific system of enquiry were as the writers so breathlessly describes. But it is not. -
sekwisniewski at 03:59 AM on 1 September 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
"Who do you believe?" - wow, so much science! What is going here, folks? Is this some kind of bait for trolls? This thread does not look like a serious effort to summarize knowledge on nuclear, so I don't think anyone will respond.
Moderator Response:[PS] As stated in the article, the primary purpose of this thread is to keep nuclear discussions away from other threads for people who want to talk about it. No one on the SksSc team has any particular expertise in the science of nuclear power though some frequent commentators here are well versed.
SksSc would welcome guest contributions that are willing to focus on peer-reviewed papers. We would especially welcome any peer-reviewed rebuttals of Abbott. We are not particularly interested in the opinions of self-proclaimed experts that are not willing to back their assertions with reviewed references.Other sites are definitely a better place to discuss the economics, safety and politics of nuclear power.
-
MA Rodger at 23:10 PM on 31 August 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
wayne @1,
I'm not sure of which 'geological record' you are looking at, but I would reckon the tectonocally-changing 'geology' itself had some impact on the relative global temperature & thus sea level back when CO2 was last up at 425ppm.
The last time we saw 425ppm would be back 13 million years ago when the Arctic had no ice caps. The Arctic began getting seriously icy about 3 million years ago, apparently due to the Panama Isthmus forming to connect N & S America. There was also a widening of Drakes Passage at this time. The climate went through some interesting periods at this time 3my ago, with a period of warming with rising CO2 (but not quite back up to 425ppm) leading on to cooling & the icy Arctic.
-
michael sweet at 22:36 PM on 31 August 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
Sekwisniewski:
Analysis of lifecycle emissions of nuclear power compared to renewables by scientists generally indicate that nuclear plants emit 5-10 times as much carbon dioxide as renewables. Nuclear industry sources find emissions are comparable. Who do you believe?.
Jacobson 2009 reviews the data at that time. Since 2009 renewables have reduced their emissions while nuclear has not changed. In addition, Jacobson calculates emissions due to opportunity cost.
It takes about 2-4 years to plan and build wind and solar plants. It takes about 10-14 years to plan and build a nuclear plant. For the entire time you are building the nuclear plant you have to use fossil fuels. You save much more carbon by building the rapidly completed renewable energy plants.
Since 2009 the cost of renewables has plummeted. Nuclear costs have risen. Nuclear reduces carbon much slower and at much greater cost. For me that is not "on par" with wind and solar. Some people do not care about time and cost and feel nuclear is comparable.
-
wayne19608 at 22:05 PM on 31 August 2022What’s going on with the Greenland ice sheet?
I thought I read that at 425ppm global sea rise would be 25m just based on the geological record?
-
sekwisniewski at 21:09 PM on 31 August 2022Is Nuclear Energy the Answer?
Both renewables and nuclear decarbonize.
Fell, H., Gilbert, A., Jenkins, J. D., & Mildenberger, M. (2022). Nuclear power and renewable energy are both associated with national decarbonization. Nature Energy, 7(1), 25-29. [Link]
...which is a response to flawed analysis found here:
Sovacool, B. K., Schmid, P., Stirling, A., Walter, G., & MacKerron, G. (2020). Differences in carbon emissions reduction between countries pursuing renewable electricity versus nuclear power. Nature Energy, 5(11), 928-935. [Link]
Nuclear is low carbon, on par with wind and solar, right?
-
scvblwxq1 at 13:13 PM on 31 August 2022How not to solve the climate change problem
Your welcome. The US wants to bring factories back from China. They could put some in Brazil in exchange for keeping the rainforest and the factories could provide employment for those that were converting the rainforest into farms and probably many others. Plus the US companies would get cheap labor.
-
Bob Loblaw at 07:47 AM on 31 August 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
I really like this post, too.
One of the things that might raise eyebrows is the claim that with science "bad ideas are weeded out and good ideas are built upon". In this sentence, the words "bad" and "good" have a fairly specific context. As described later in the article, this is not about moral good or moral bad, or good/bad as personal preferences. It is about ideas that enable us to make good evaluations of the world around us - evaluations that help us understand and predict how the world works (whether we like it or not).
Good ideas also gives us clues to the uncertainty in our understanding. People who are dogmatically certain about their viewpoints are not being very scientific. (And, yes, the IPCC looks at uncertainties.)
One of the ways that science works is by looking at competing explanations from the point of view of "what is the difference in the predictions they make?" If two ideas result in no differences, then they are functionally identical. Only by their differences can you tell them apart - and then going out and observing what actually happens will tell you which idea is more likely to be correct. A track record of accurate predictions gives confidence.
And we prefer explanations that can make a lot of accurate predictions with fewer assumptions. If every prediction fails and requires adding new assumptions to fit the observations, then the explanation is not very good.
With good scientific ideas, we can get reliable predictions about things we have not yet seen or measured - what will happen if we add more CO2 to the atmosphere, where to dig to find gold, how to make a faster airplane, what will be most the likely outcome of a particular medical treatment, etc. We know that falling off a tall building is dangerous because we truly do understand that gravity still works.
-
nigelj at 07:37 AM on 31 August 2022Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
Excellent commentary. I dont recall learning anything in school about the scientific method or the purpose of science or logical thinking skills. The cynic in me thinks this is because the education system didn't want young people learning analytical skills, and thinking too much for themselves, and therefore maybe challenging the teachers!
-
One Planet Only Forever at 05:14 AM on 31 August 2022A next-level water crisis: Colorado River Basin faces Tier 2 restrictions
Jimspy,
Agreed that self interest governed by the pursuit of increased awareness and understanding of what is harmful is essential to sustainably improve things (truly make things better).
The best 'certain to be viable' futures for humanity appear to require all humans to be governed by the pursuit of learning and accepting the diversity of ways to be human that fit into, are sustainable parts of, the robust diversity of life on this amazing planet.
Everyone self governing that way would be great ... But that is unlikely (a fantasy). Some people will likely need to be governed by others to limit the harm they cause in pursuit of personal benefit.
-
BaerbelW at 04:51 AM on 31 August 2022Reposted articles from Thinking is Power
Updated the overview page for our Thinking is Power reposts with a mention of Melanie Trecek-King's highly recommended article Science: What it is, how it works, and why it matters
-
jimspy at 04:50 AM on 31 August 2022A next-level water crisis: Colorado River Basin faces Tier 2 restrictions
"Self interested pursuit of benefit" is OK as long as it is informed by the human capacity for abstraction and the realization that altruism, or even pseudo-altruism, can inure to one's benefit. It's called "enlightened self-interest." I fear we as a species have been losing that quality of late.































 Arguments
Arguments



























