Understanding the CO2 lag in past climate change
Posted on 5 January 2011 by Anne-Marie Blackburn
Earth’s climate has varied widely over its history, from ice ages characterised by large ice sheets covering many land areas, to warm periods with no ice at the poles. Several factors have affected past climate change, including solar variability, volcanic activity and changes in the composition of the atmosphere. Data from Antarctic ice cores reveals an interesting story for the past 400,000 years. During this period, CO2 and temperatures are closely correlated, which means they rise and fall together. However, changes in CO2 follow changes in temperatures by about 600 to 1000 years, as illustrated in figure 1 below. This has led some to conclude that CO2 simply cannot be responsible for current global warming.
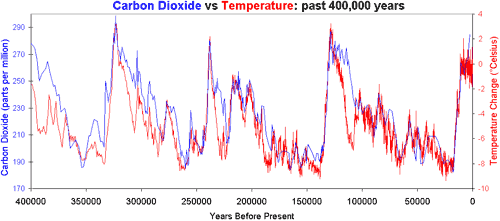
Figure 1: Vostok ice core records for carbon dioxide concentration and temperature change.
This statement does not tell the whole story. The initial changes in temperature during this period are explained by changes in the Earth’s orbit around the sun, which affects the amount of seasonal sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface. In the case of warming, the lag between temperature and CO2 is explained as follows: as ocean temperatures rise, oceans release CO2 into the atmosphere. In turn, this release amplifies the warming trend, leading to yet more CO2 being released. In other words, increasing CO2 levels become both the cause and effect of further warming. This positive feedback is necessary to trigger the shifts between glacials and interglacials as the effect of orbital changes is too weak to cause such variation. Additional positive feedbacks which play an important role in this process include other greenhouse gases, and changes in ice sheet cover and vegetation patterns.
The only conclusion that can be reached from the observed lag between CO2 and temperatures in the past 400,000 years is that CO2 did not initiate the shifts towards interglacials. To understand current climate change, scientists have looked at many factors, such as volcanic activity and solar variability, and concluded that CO2 and other greenhouse gases are the most likely factor driving current climate change. This conclusion is not based on the analysis of past climate change, though this provides key insights into the way climate responds to different forcings and adds weight to the several lines of evidence that strongly support the role of greenhouse gases in recent warming.
This post is the Basic version (written by Anne-Marie Blackburn) of the skeptic argument "CO2 lags temperature". This argument actually peeped its way into the top ten during December but then "We're heading into an ice age" shouldered its way back to the #10 spot (so there's a real dog fight between those two to climb over each other in the rankings).































 Arguments
Arguments






























[John Cook] I've added CO2 History to our list of Climate Graphics. It's under a Creative Commons licence so you're free to use it elsewhere:
- Multiple orbital changes (orbital shape and inclination, axial tilt and precession, apsidal precession) occur in just the right combinations.
- These alter the length/strength of the northern hemisphere summer past a tipping point.
- Winter snow/ice cover on the northern continents does not melt back far enough during the summer.
- The northern hemisphere albedo changes, reflecting more sunlight back into space, cooling the planet.
- Atmospheric CO2 is absorbed by the cooling ocean, reducing the GHG effect, and cooling the planet.
- The snow/ice melts even less.
- The albedo increases further, and the planet cools more.
- Even more CO2 is absorbed by the ocean (and, I've always presumed, more vegetation is covered with snow/ice without a chance to decay and return to the atmosphere), cooling the planet even more.
- With the drop in global temperatures, atmospheric H2O also drops, further reducing the GHG effect.
- The planet cools even more.
- The cycle continues -- cooling -- more ice, higher albedo, less CO2, less H2O -- more cooling.
- Eventually, the expanding snow/ice extent reaches a latitude where summers are simply too long/warm for it to remain, and the process halts -- in a new glacial period that will last until the orbital forcings alter again, to run the entire "program" in reverse.
How very simple! :)