Recent Comments
Prev 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 Next
Comments 26751 to 26800:
-
Rob Honeycutt at 12:36 PM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC @37... He was offering up an example of a position statement from a scientific organization, of the sort that John Cook was talking about.
-
NecktopPC at 12:06 PM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Glenn Tamblyn@33 - "So NASA, as an organisation, did not make an official endorsement of any cooling prediction."
But would they want to make an official endorsement of atmospheric cooling at this stage of the game?
Is the following statement getting any colser to such an official endorsement; do you think?
In a NASA first, researchers at GISS accomplished such a feat as they calculated the temperature impact of each of these variables — greenhouse gases, natural and manmade aerosols, ozone concentrations, and land use changes — based on historical observations from 1850 to 2005 using a massive ensemble of computer simulations. Analysis of the results showed that these climate drivers do not necessarily behave like carbon dioxide, which is uniformly spread throughout the globe and produces a consistent temperature response; rather, each climate driver has a particular set of conditions that affects the temperature response of Earth.
The new calculations reveal their complexity, said Kate Marvel, a climatologist at GISS and the paper's lead author. “Take sulfate aerosols, which are created from burning fossil fuels and contribute to atmospheric cooling,” she said. LINK
Moderator Response:[PS] This is an example of official endorsement on climate change. Similar statements can found by most of the world's academy.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 12:03 PM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC @34... No, that is just a paper (one of a great many) listed on the NASA website. That is not a position statement made by NASA.
Moderator Response:[PS] I think some definitions would help keep this discussion focused. "Endorsement" by an organization means a position statement from that organizations governing body. (Such as a great many science organization have made about global warming). Scientific consensus is the collective judgment, position, and opinion of the community of scientists in a particular field of study. No one paper is evidence for a consensus.
-
NecktopPC at 11:21 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Glenn Tamblyn@33
Yes; NASA did youse those exact words. LINK
There is evidence that the Sun has had similar periods of inactivity in the more distant past. The connection between solar activity and terrestrial climate is an area of on-going research. LINK
The extra snowfall that began 10,000 years ago has been slowly accumulating on the ice sheet and compacting into solid ice over millennia, thickening the ice in East Antarctica and the interior of West Antarctica by an average of 0.7 inches (1.7 centimeters) per year. This small thickening, sustained over thousands of years and spread over the vast expanse of these sectors of Antarctica, corresponds to a very large gain of ice - enough to outweigh the losses from fast-flowing glaciers in other parts of the continent and reduce global sea level rise.
"The good news is that Antarctica is not currently contributing to sea level rise, but is taking 0.23 millimeters per year away," Zwally said. "But this is also bad news. If the 0.27 millimeters per year of sea level rise attributed to Antarctica in the IPCC report is not really coming from Antarctica, there must be some other contribution to sea level rise that is not accounted for." Read more
Can we irrefutibly say that the jury is out on this issue?
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 11:14 AM on 3 February 2016Joseph E. Postma and the Greenhouse Effect
Joe, Regarding figure 1 from your pdf.
Here is the accompanying text related to that diagram from the original source.
"A simple approachWe can get the above results directly by recognizing that the top
layer of the atmosphere must emit 239.7 W/m2 of infrared radiation
to space (same amount of solar radiation that enters the atmosphere:
what goes in must go out). The bottom layer of the atmosphere
will emit an equal amount downward to the surface of the planet.
Hence, for thermal equilibrium, the surface of the planet must emit
enough radiation to balance not only the amount it receives from the
sun (239.7 W/m2), but also what it receives in the form of downward
infrared radiation from the atmosphere 239.7 W/m2). Hence, its emission
must match 239.7+239.7 = 479.4 W/m2. Applying the Stefan-Boltzmann
law: constant x T 4 = 479.4 W/m2. We thus calculate T = 303 K.
The figure below illustrates this calculation. Contrast it to the figure
above where we assumed no atmosphere, and you will see where
the greenhouse effect comes in."
Your diagram goes here
"The effective temperature we calculate in this manner is much warmer than the actual temperature of the Earth (288 K), because we made a number of simplifying assumptions.Limitations of this calculation
1) It's assumed that the atmosphere is isothermal. The layer of the
real atmosphere that's most important in terms of the greenhouse
effect is the troposphere, where temperature decreases with height.
Because of this height dependence, the real atmosphere emits more
radiation in the downward direction than in the upward direction (88
units vs. 70 units in Fig. 3-19).2) It's assumed that the atmosphere absorbs all the outgoing
radiation at all wavelengths in the infrared part of the
electromagnetic spectrum. In reality, the absorption of radiation by
the atmosphere is highly wavelength dependent. At some wavelengths
there's very little absorption and the radiation emitted by the
earth's surface escapes to space, while at other wavelengths it gets
absorbed, reemitted, absorbed and reemitted many times before it
finally escapes. To carry out this calculation accurately it has to
be done wavelength-by wavelength... to capture the fine scale detail
in the spectrum requires literally thousands of calculations
analogous to the one we did in class.3) Radiative transfer isn't the only process by which energy escapes
from the earth's surface. Conduction of heat and evaporation of water
transfer about twice as much energy from the earth's surface to the
atmosphere as the net upward flux of infrared radiation from the
radiation does. If the temperature distribution on earth were
determined only by radiative transfer (as in this example) the Earth
would be so hot as to be uninhabitable. In this sense the true
'greenhouse effect' on Earth is much larger than the 33 K difference
between the observed surface temperature (288 K) and the effective
radiating temperature (255 K) ascribed to it in your text." (my emphasis)
This diagram is an intermediate stage as part of a teaching exercise in developing an understanding of the GH effect. It most certainly is not a definitive description of the GH effect.You have built a house of cards from extrapolating a simplification too far.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 11:06 AM on 3 February 2016Joseph E. Postma and the Greenhouse Effect
Joe
"The temperatures where they used reflectors to increase the internal flux are not relevant to a test of the greenhouse effect."
What has anything you are talking about got to do with testing the greenhouse effect?
The box you describe is so different from the actual processes in the atmosphere that you can draw no conclusion from it. Without the ability to include convective heat transport and the vertical Lapse Rate anything you might do in such a test is rather meaningless wrt the GH Effect. -
Glenn Tamblyn at 10:57 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC
From the abstract for the Rassol and Schneider paper from 1971:
"An increase by only a factor of 4 in global aerosol background concentration may be sufficient to reduce the surface temperature by as much as 3.5 ° K. If sustained over a period of several years, such a temperature decrease over the whole globe is believed to be sufficient to trigger an ice age." (my emphasis).They certainly did not predict that an ice age would happen. Rather, to paraphrase them, 'if air pollution gets a lot worse and is sustained for some years then we think that might trigger an ice age'.
And within a few years they subsequently reversed that conclusion. Stephen Sccheider, then a young researcher, described this paper as one of the biggest mistakes of his life.
And they both worked at the Goddard Institute of Space Studies at the time. Yes a research division of NASA. But hardly NASA as a whole.
Large organisations such as NASA tend not to 'endorse' every single published paper that their scientists produce - not all of them will be correct. All science is tentative until corroborated by further research.Such organisations, when they do 'endorse' something, usually do it when a body of science has built up sufficiently on a subject. In this case the cooling paper was actually overturned several years later.
So NASA, as an organisation, did not make an official endorsement of any cooling prediction. And they did not 'endorse' the idea of warming officially till many years later. -
Daniel Bailey at 10:56 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
"The world could be as little as 50 or 60 years away from a disastrous new ice age"
Evidence says otherwise. No, the Sun isn't going to save us from Global Warming:

RC on 'Not even a solar minimum'."Those hoping that the sun could save us from climate change look set for disappointment. The recent lapse in solar activity is not the beginning of a decades-long absence of sunspots – a dip that might have cooled the climate. Instead, it represents a shorter, less pronounced downturn that happens every century or so."
"According to the Gleissberg cycle, the next solar maximum – in about 2024 – will probably be a dud too, but then cycles will become more energetic once again, and any cooling effect the brief downturn has had on Earth's climate will also vanish."
"Thus if the sun remains “out”, i.e., stuck for a long period in the current solar minimum, it can offset only about 7 years of CO2 increase. The human-made greenhouse gas climate forcing is now relentlessly, monotonically, increasing at a rate that overwhelms variability of natural climate forcings. Unforced variability of global temperature is great, as shown in Figure 4, but the global temperature trend on decadal and longer time scales is now determined by the larger human-made climate forcing. Speculation that we may have entered a solar-driven long-term cooling trend must be dismissed as a pipe-dream."
Basically, even a Grand Solar Minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming.
Even on the regional level, the effects are very limited (per Nature):
"This offsets or delays the global warming trend by ~2 years and is small compared with the modelled global warming"
Gavin Schmidt at RC (Unforced Variations thread):
"It’s a 60% reduction in the magnitude of the solar cycle (not solar activity), and it’s not obviously terrible. It’s a statistical projection with no physics, so the extent to which it’s believable is unclear. The connection to a new ‘mini ice age’ is completely made up. That level of change in solar forcing is about -0.1W/m2, which would be made up in just 3 years of current CO2 concentration growth."
-
Rob Honeycutt at 10:53 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
This is an article referencing a research paper that was published by Rasool and Schneider. There's an accurate accounting of this paper on wiki here.
The paper was later retracted.
But again, this was not a stated position of NASA. It was merely one paper that was quickly retracted.
-
ubrew12 at 10:41 AM on 3 February 2016Climate scientists' open letter to the Wall Street Journal on its snow job
jmath@19 said: "between 0.3 and 0.6C temperature change... is the result of... 30% of... a doubling" That suggests the sensitivity to a doubling = average(0.3,0.6)/0.3 = 1.5C per doubling, which is half the generally expected sensitivity. Perhaps Earth's thermal system is not just a resistor but also a capacitor? That would explain the shortfall: you're suggesting equilibrium in a nonequilibrium system.
-
NecktopPC at 10:22 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
U.S. Scientist Sees New Ice Age Coming
The world could be as little as 50 or 60 years away from a disastrous new ice age, a leading atmospheric scientist predicts. Dr. S. I. Rasool of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and Columbia University. LINK
RE: "None of these bodies (at least the ones that existed back then) endorsed ice age predictions in the 70's."
Did they (NASA) not endorse Dr. Rasool?
What is NASA without its scientists, which it, hires?
-
Tom Curtis at 10:07 AM on 3 February 2016Joseph E. Postma and the Greenhouse Effect
JPostma @153,
1) The temperature I quoted for the Sudanese Cooker was that achieved with the external mirror removed and the internal mirrors covered by black papers. Ergo neither contributed to the elevated temperature achieved.
2) The shape of the box is irrelevant given that, with the mirrors covered, their is not method of concentrating the heat in a particular part within the solar cooker.
3) That temperature was achieved in late April or early May. Ergo the TOA insolation at the time was not 1410 W/m^2 but 1362 W/m^2 or less. The actual surface radiation would have been significantly less than that, and probably not more than 1200 W/m^2. The TOA radiation gives a theoretical maximum temperature of 120.5 C if there is no radiative greenhouse effect as per your claims. The actual temperature achieved was 5 C above that, comfortably falsifying your claims.
@154, the temperature should have skyrocketed, as you put it, only if:
a) There was no heat loss through conduction through the sides;
b) There was no heat loss through air escaping;
c) There was no reflectance of Short Wave Radiation from the interior of the box;
d) The glass panes had zero reflectance of Long Wave Radiation; and
e) The glass panes had zero absorptivity of Long Wave Radiation.
All of these conditions are known to be false. Further, the temperature should only have skyrocketed if the actual insolation approached the theoretical maximum, which as the box was near sea level, is also known to be false.
All of this is irrelevant as to whether the Sudanese Cooker experiment (with external mirror removed and internal mirrors covered) refutes your theory, which places a clear upper limit on temperature achieved. That upper limit is exceeded despite the inefficiencies listed above.
-
Andy Skuce at 09:50 AM on 3 February 2016The Quest for CCS
Sharon: It's a common argument that the upstream emissions of the oil sands amount to only 0.2% of the world's emissions, with the implication being that it is an amount that is too small to worry about.
As a rejoinder, one could argue that the proportion of the world's population that lives in Alberta is only 0.06%, so why should the rest of worry about what happens to them?
Having worked in the Alberta oil patch myself through many brutal rounds of downsizing, particularly in the 1980s, I know what a devastating effect these oil busts can have on individuals and their families. I still have many friends in the province who are watching their investments of time and expertise circle the drain, through no fault of their own. In particular, I feel bad for the many younger people who have kids, mortgages and student loans who suddenly see their futures change from one of prosperity to one of uncertainty and the fear of personal bankruptcy. It's really tough.
So, I would not be inclined to make that kind of a counter-argument since it appears indifferent to individual suffering. It's in the nature of the climate crisis that negative effects of the climate impacts and the effects of the economic disruption that mitigation will bring are not distributed fairly or evenly.
As you point out, all change brings with it winners and losers, much of it unintended. A nasty feature of the climate crisis is that those who will suffer most had the least to do with causing the problem. Also, the changes to to the climate will endure for millennia. In contrast, the damage from the worst catastophes of the past would heal in the space of a generation or two.
I would agree though that the oil sands are often demonized disproportionately. The coal industry, for example, is far worse. And the critics of oil producers are often themselves big consumers.
PS, somebody once told me that "Csikszentmihalyi" is pronounced "cheeks sent me high".
-
Rob Honeycutt at 08:43 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Yes, the sun could perhaps go into a low irradiance state similar to that of the Maunder Minimum. But what you have to understand is the relative radiative forcing compared to changes in CO2 and other human caused factors.
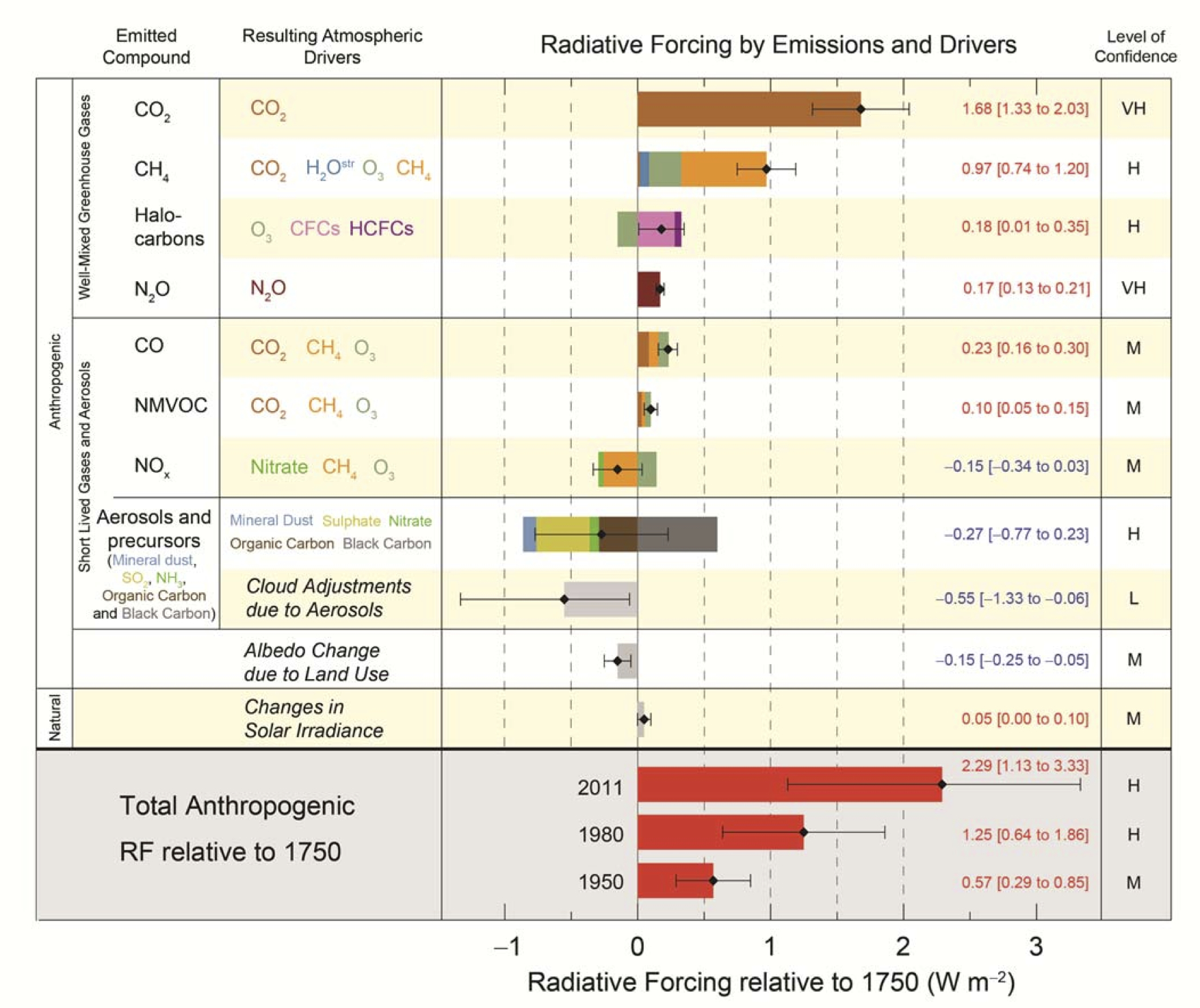
We are very fortunate to live on a planet that goes around a very stable star whose radiative output varies only a fraction of a percent. So, that change in radiative forcing of maybe -0.3W/m2 for a new Maunder Minimum is small compared to the 2.3W/m2 we see for human factors.
Moderator Response:[PS] Straying off topic again. Any further discussion should perhaps be here.
-
NecktopPC at 08:23 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
One might assume that other scientist have been, and are continuing to follow in the footsteps of Dr. Roberts...NCAR:
There will be another Little Ice Age in 2030, according to solar scientists – the last one was 300 years ago- http://www.independent.co.uk/environment/climate-change/mini-ice-age-coming-in-next-fifteen-years-new-model-of-the-suns-cycle-shows-10382400.html
Moderator Response:[PS] Dont assume - produce evidence.
-
POJO at 08:04 AM on 3 February 201610 Indicators of a Human Fingerprint on Climate Change
MA Rodger
The IPCC stance as noted on pge 9 of AR% for policy makers.
"A decrease in diurnal temperature range (DTR) was reported in the TAR, but the data available then extended only from 1950 to 1993. Updated observations reveal that DTR has not changed from 1979 to 2004 as both day- and night-time temperature have risen at about the same rate. The trends are highly variable from one region to another. {3.2}"
Backed away and OPt back in. They may not be scientific terms MA. But they very obvious to everyday meaning. I am sure you know what they mean.
In regards to Vose etal paper.
Again the obvious stands out. Back then old data was used. Since then the global data has had several changes to it via its rigourous homeginisation process.
Crutem 4 is the LATEST dataset. Analysis now is at a fingertip. Tmax - Tmin.
Voss anomalie chart is the same as the IPCC in TAR.
And here is Vose's response to the chart is below
Both maximum and minimum temperature increases from 1979-2004 whereas the DTR is basically trendless. The maximum and minimum temperature trends are nearly identical (0.287 versus 0.295°C dec-1),............
And lastly the data has moved on since way back then. Know one needs a paper to look at a chart. It is what it is.
If you have a problem with my source for the Charting best you take that up with the home of Data. It is fresh from The CLIMATE RESEARCH UNIT. This is where CRUTEM 4 comes from.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 06:45 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC... I hope you are aware that Idso and Scafetta represent a very small fraction of researchers who hold such position. Both of them are very well known to all the regulars at this site. In such, you're attaching yourself to a position that is extremely unlikely to be correct.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 06:39 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC @24... You can disagree all you like, the fact remains that "None of these bodies...endorsed ice age predictions in the 70's." John is referring to scientific bodies. You've yet to show us one of the bodies that endorsed that position.
-
NecktopPC at 06:29 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt@20
Thank you - and I'll certainly be cautious, to avoid 'running afoul of the moderation policies.
Moderator Response:[JH]
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can be rescinded if the posting individual treats adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
NecktopPC at 06:16 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt@18
I disagree with you on the accuracy of Mr. Cooks comment, that's all - and I have been working on providng some refrences, which are helping to substantiate the inacuracy of his statement, and or story here.
RE: "thus far you've not linked to any specific science on global cooling in the 1970's."
I am doing my best at providing information (circa 1970s) which has, included the names of scientists, and the organizations of which they were associated with, at the time, i.e. NOAA & NCAR (thus far) and the association (ice age) that have been mentioned together with global cooling.
By the way; I have read Peterson's paper, and perhaps you have read Idso's paper as well - "The Climatological Significance of a Doubling of Earth's Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentration"
There is another, which is more on topic of the sun and its effects on climate, as per Dr. Roberts - the paper is by Scafetta - "Empirical evidence for a celestial origin of the climate oscillations and its implications"
-
Rob Honeycutt at 06:05 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
No. I merely let you know how policy is applied here to everyone. I was trying to help you so that you could make your points without running afoul of moderation policy.
-
NecktopPC at 06:01 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt@19
I'm not "Playing the potential victom" at all. You blatantly threatened me @14 - and you speak about conduct unbecoming?
I don't know?
Moderator Response:[PS] Please stick to topic. Any discussion of moderation is offtopic. Further offtopic discussions by either of you will be deleted.
-
NecktopPC at 05:58 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt@14
On one hand, you asked me a couple times, what my point is, or was, and now your alluding to me 'repeatedly making the same point'.
What point is that then?
And now you seem to be adopting the stance of an adlescent, whom, when they can't have things their way, they try to break the other persons computer, or simply grab their little network and run off, with all the cords becoming unplugged (banned).
RE: "And note ahead of time that moderation complaints also get deleted."
I'll be certain not to complain about any moderation actions.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:55 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
"The science was, and remains evident, regarding global cooling in that period."
And isn't it interesting that, even though we'd come through a period of cooling from 1940-1960, most scientists were more concerned about the challenges we face in relation to global warming due to emissions of greenhouse gases.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:52 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
"If you wish to delete my comments, or have RobP do so, becuse it upsets the policies of your website, then that is totally up to you and your colleagues; isn't it?"
Playing the potential victom is rather unbecoming. Plenty of people come to SkS and strongly argue their points without problem at all, even when they go against the scientific consensus position, as long as they play by the rules. That's not about getting upset. It's about keeping the conversations here polite and constructive.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:49 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC... John Cook's comment is accurate. Your references do nothing to refute that. You provided a link to a paper by Roberts that discusses agriculture and food supply in a cooling world. As I stated, Roberts worked with Sagan and others on at least two separate issues related to potential global cooling. Nuclear winter and human emissions of aerosols. Roberts was also very active, as was Sagan, in research on global warming.
You state that, "The science was, and remains evident, regarding global cooling in that period." But thus far you've not linked to any specific science on global cooling in the 1970's.
I would highly suggest you check out a paper by Peterson 2008, The Myth of the 1970s Global Cooling Scientific Consensus. PDF
Moderator Response:[PS] Yes, please do read Peterson. Note that it is incumbent on posters to produce evidence to back claims. Peterson produces strong evidence against a consensus on cooling. In my opinion, you either need to redefine consensus or find something better than Peterson that produces the opposite conclusion.
-
NecktopPC at 05:49 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt@11
No worries!
-
NecktopPC at 05:47 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt@12
My point was being made from the start. There were scientists (Hansen included) who realized, from studies, surveys and or data, that the globe was cooling, and many of them referenced this global cooling, to a possible (prediction) return to an ice age.
And I point out @9 that this was the consensus coming from NOAA (one of two, that existed back then) as well...global cooling.
-
NecktopPC at 05:40 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
"NecktopPC @6... If your comment was not intended to be related to a "...predicted ice age in the 70's" then it would be off topic and thusly should be deleted - Rob Honeycutt@10"
I might remind you, that it was a comment made by Mr. Cook, which read: "None of these bodies (at least the ones that existed back then) endorsed ice age predictions in the 70's."
The term ice age prediction, is simply alluding to the fact or science which showed global cooling - and if the globe continues to cool, then it could very well be expected, that there may be a return to another ice age.
I have been on topic, of global cooling, and for the period in question, from the start of my first comment here, and have shown where the information which I have provided, makes references to, or uses the words ice age - call that 'prediction' if you will, but lets not turn this into word semantics.
The science was, and remains evident, regarding global cooling in that period.
If you wish to delete my comments, or have RobP do so, becuse it upsets the policies of your website, then that is totally up to you and your colleagues; isn't it?
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:31 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Yes. That's pretty standard netiquette, and it's applied here equally to all commenters. Please also take note of the policies related to off-topic, ad hominem and sloganeering (repeatedly making the same point). Those are the ones that most often get people banned. And note ahead of time that moderation complaints also get deleted.
-
NecktopPC at 05:27 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt...I did notice that there was a "RobP" in brackets before the moderetor's comment - and thanks for the heads up on where your comments (updated) policy is located - and as I suspected; upper-case lettering, is viewed by your policy makers as shouting.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:24 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC @9... So, is there a point you want to make?
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:23 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
My mistake on the NOAA/NCAR mix up.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:21 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC @6... If your comment was not intended to be related to a "...predicted ice age in the 70's" then it would be off topic and thusly should be deleted.
-
NecktopPC at 05:21 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt...You stated in your comment to me at 01:02 AM the following: "You note that Roberts is one individual and not the entire NOAA"
I never associated Dr. Roberts with NOAA, but rather, the "National Center for Atmospheric Research".
But speaking of NOAA, the first in the list of bodies, as it was mentioned in this story, by Mr. Cook; here is an interesting achived article that speaks of a 'cooling climate', as opposed to a warming one, and with conotations toward that of ice ages. A Dr. Murray Mitchell of "NOAA" conducted a survey (study) which revealed a cooling of the earth's surface temperature, by half (0.5) of a degree. This being between 1945 and 1968.
And a study released by two (2) "NOAA Scientists" noted that the amount of sunshine reaching the ground in the Continental U.S. had diminished by 1.3 percent between 1964 and 1972.
And the word "Climatologists", is mentioned in this little story, about Science.
URL: http://denisdutton.com/newsweek_coolingworld.pdf
-
Rob Honeycutt at 05:17 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC... It wasn't me that moderated your post. It was RobP. If you look directly above the text box where you write your comments you will see a sentence with an embedded link stating...
"Political, off-topic or ad hominem comments will be deleted. Updated Comments Policy..."
-
NecktopPC at 05:03 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt...Can you provide a source to your comments "policies" that I may be able to review them, thus being able to know in future, how to avoid any breaches.
I hope that by me using a TLA (three letter acronymn, e.g. BTW) in upper case, was not adding to anymore unnecessary work for you.
-
NecktopPC at 04:49 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt...I have read the document (paper as you put it) and I never stated that it was "a paper about ice age predictions".
RE: "t's a paper about agriculture in the face of a cooling climate"
Exactly - and in the story, it does mention the following: "The Earth may have entered a new "little ice age."
Now; there were other scientist whom were involved in the study of the climate (weather, space, oceans, sun, etc, etc.) and articles written in science magazines as well, that were hinting at a return to an ice age...predictions if you will.
RE: "I honestly don't see that you have any point."
I would not have expected a different response.
BTW: the only reason for me having put certain words of my last post in upper case, was merely a means for me to supply emphasis - I guess I could have used the bold or underline feature however.
I find to be of a cynical nature, that moderators quickly assume that someone is shouting, or being rude, when using upper case lettering - that's a very insecure attitude in this business.
So what degrees in particular, does make a climate scientist?
-
jmath at 04:49 AM on 3 February 2016Climate scientists' open letter to the Wall Street Journal on its snow job
The simplest way to put this is that over the last 70 years since 1945 there has been between 0.3 and 0.6C temperature change depending on if you look at the homogenized land record produced by GISS (0.6C) or the satellite record, the unhomogenized land record, perfect thermostats, weather balloons or sea surface temperatures as recorded by ARGO buoys (0.3C). In either case this is the result of pouring in approximately 30% of the CO2 of a doubling. Since CO2 acts logarithmically this is closer to 40% of the effect we expect to see from another 200ppm of CO2. So, the amount of change is another 0.4-0.7C between now and 2100 depending on if you want to depend on homogenization being able to continue to produce double the temperature change than the rest of the measuring apparatus can show. That's simply a fact. To expect anything more would be unscientific. There is no basis to say temperatures will accelerate for the next 80 years compared to the last 70 years especially as it will be difficult to maintain the growth of CO2 output needed to keep the linear growth in co2 concentration and increasing heat.
-
JPostma at 04:48 AM on 3 February 2016Joseph E. Postma and the Greenhouse Effect
Their cooker even had a double-pane of glass for cover, so the temperature with a GHE should have skyrocketed to above 200C.
-
JPostma at 04:39 AM on 3 February 2016Joseph E. Postma and the Greenhouse Effect
TSI peaks at 1410, yes, and the difference of the average TSI from now to then is, what, 0.5 W. So, hardly an inflation - use 1409.5 then. The temperatures where they used reflectors to increase the internal flux are not relevant to a test of the greenhouse effect. And the result of 126C without relfectors is still well below the 182C which would be required if the cooker has an IR emitting cover. 126C is also easily within experimental effects such as having absorption occuring on the shaders, geometrical concerns of the device (the cooker isn't a simple plane), etc.
Herschell's 115C is still well within a no-GHE result, as we expect something closer to 182C with a greenhouse effect.
The values you cite are all hovering around a no-GHE result close to the temperature of the insolation-only expectation. Nowhere near the 182C required for a GHE. All a cooker needs to do is to add another cover layer (or more) to increase their internal GHE, and boost their internal temperatures far, far beyond the insolation-only values. None do.
-
Tom Dayton at 04:36 AM on 3 February 2016'If the world ends in 2100, we’re probably OK'
jmath, Apple did not introduce the cell phone. The rest of your screed is just as incorrect.
-
jmath at 04:33 AM on 3 February 2016'If the world ends in 2100, we’re probably OK'
While it certainly is seemingly useful to consider things like periods after 2100 it is impractical to consider really 20 years into the future with any reliability for virtually anything. Prediction is hard. People in the climate business should be more aware of that than anyone. Who would have guessed 20 years ago that practically all the energy from the excess CO2 could be stored in the ocean below 300M for 20 years while man poured 57% of all the CO2 ever poured into the atmosphere in. Certainly none of the climate scientists thought such a thing was possible. No computer models predicted this. So, even when considering nature one can be drastically surprised by the way nature works. If you look 20 years ago in any field you will see a fantastical amount of change that was impossible to predict 20 years ago. It is hard to believe that it was 2007 when apple introduced the cell phone. It has been only 8-9 years since and we cannot imagine life without them. 20 years ago we were utterly dependent on middle east oil to run the US economy and suffering trade debt of 800 billion/year to Arab and other oil economies. Today the US debt related to oil is under $300 billion and falling rapidly. Arab nations are eating up their surpluses rapidly.
One of the big problems with estimating something like co2 in 2100 is technological. The rate of change in cost of solar is fairly constant price decreases which show the price to go below the price of coal/oil in 10-20 years maybe less. Many developments in progress are very significant. Other technologies for energy production are in development. The rate of all technological development is on an exponential curve. We just discovered the CRISPR virus and the means to use it to modify DNA reliably. It has already been used in clinical trials. In 20 years we will see dramatic improvements in medicine as we unlock both the epigenetic code and are able to engineer at the micro level new materials and cheistry of all types including new materials twice as strong as any previously known material, the ability to make computer memories that are terabytes in size and as fast as RAM yet persistent without power like SSDs. We now have 1152 qubit quantum computers and our AI is able to recognize faces and other objects almost as well as humans can. We have the first self-driving cars. Elon Musk landed a rocket ship back on Earth after deploying cargo in space. In the meantime we have saved animals from extinction, raised the living standard of hundreds of millions of human beings and reduced starvation dramatically. I could go on. It is just very difficult to say what will happen in 85 years considering the confluence of all the factors above and all the unknowns.
The assumption of CO2 rising to 2100 at an exponential rate is already in question. Total CO2 production peaked last year and is expected to be flat this year as well. It may already be that we are on a slowly decelerating trend of CO2 increases. A prediction of exponential growth in anything is problematic. It has been the undoing of many predictions. The fact that is it is near impossible to maintain a systematic growing CO2 output for 85 more years in the face of all this. So, by 2100 it is unlikely we will have CO2 levels above 500 in my opinion and we will be on a downward trend most likely. That's my prediction simply based on what seems like what is the most probable evolution of technology.
I think there are many things to worry about the future however CO2 is by far the smallest of all worries. We are producing smart machines, genetic abilities, micro materials, nano materials, huge changes in jobs and livelihood, distribution of wealth and populations. There is a lot to think about but global warming has to be one of the silliest concerns imaginable. The simplest argument I have is that temperature is uncorrelated with growing wealth and improved condition of man or animals. The more wealthy man has been we have been able to take care and care about the environment more. So, better economic conditions short term are more likely to result in improved conditions for the planet. The chinese for instance need to be wealthier so they can afford to clean their environment. if they stay poor they will kill themselves with pollution. no amount of telling them to clean up the environment will work until they get wealthy enough to afford to clean it up. They may be at that point right now. We are learning about the environment in exponential ways. I am confident we will figure out how to save it but the worst thing to stifle our ability to learn and fix the environment would be to stifle growth or development. It is a catch-22 in a sense but this is the only way forward.
-
MA Rodger at 04:21 AM on 3 February 201610 Indicators of a Human Fingerprint on Climate Change
POJO @94.
I'm not entirely sure what you mean by "backed away" and "opt back in." They are not terms I have met in scientific papers. AR5 Section 2.4.1.2 is titled Diurnal Temperature Range so DTR is still a subject under discussion by the IPCC, as ever. Perhaps the question should be asked as to why there are no DTR analyses plotting out global DTR time-series post-Vose et al. (2005)? Is there a difficulty with such analysis? Indeed, why do your graphs present data that is clearly contradictory to that presented by Vose et al. (2005)?
-
Rob Honeycutt at 03:42 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
NecktopPC... If you'll read the paper you originally posted, it's not a paper about ice age predictions. It's a paper about agriculture in the face of a cooling climate. Roberts did work with people like Carl Sagan on the issue of nuclear winter. There were a few papers out at the time about the potential for cooling the planet through human aerosol emissions. Those are both reasonable issues to consider in terms of impacts on agriculture and food production.
I honestly don't see that you have any point.
Relative to the relevant degrees held by SkS contributors, that hardly matters because contributors are reporting on science that is produced by climate scientists.
-
NecktopPC at 03:01 AM on 3 February 2016They predicted an ice age in the 70's
Rob Honeycutt...You chose to dispel the information by a noted climate scientist, associated with the 'National Center for Atmospheric Research" - that organization was mentioned by the story here - and perhaps it serves to fit with your personal opinions or narrative...who knows?
RE: "First off, he's an astrophysicist, not a climate scientist."
Yes; an astrophysicist who's work spans decades of studying the influences of the sun on weather and climate.
Your impression on what makes a climate scientist is obviously also skewed - and your choice of providing a link to the story carried by the the New York Times, only confirmed that Dr. Roberts was in fact, viewed as a climate scientist - its in the headline itself.
Roberts was a founder of the Department of Astrogeophysics at the University of Colorado and took a personal research interest for many years in the study of influences of the sun on weather and climate - https://aas.org/obituaries/walter-orr-roberts-1915-1990
There is an enormous of amount of information on Dr. Roberts on this wikipedia website - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walter_Orr_Roberts
And we have the American Meteorological Society (AMS) recognizing Dr. Roberts - https://www2.ametsoc.org/ams/index.cfm/about-ams/ams-awards-honors/lecturers/lecturers-list/the-walter-orr-roberts-lecturer/
There are many individuals (almost all) on the "Skeptical Science Team" who are not listed as having specific degrees in climatology (only one); they hold degrees in other studies.
Have you realized, that the head (chairman) of the IPCC, is an economist...has a degree in?
So what is a climate scientist?
Moderator Response:[Rob P] All caps removed. All caps are a breach of the comments policy & are tedious to correct. Any further breaches may result in the entire comment being removed.
-
knaugle at 02:55 AM on 3 February 2016Fox News Republican debate moderators asked a climate question!
@Elmwood #2
I do think it is not cap and trade that was the problem in Europe, but rather how they set it up. Also, European anti-nuclear sentiment, as in the USA, doesn't help. Seems to me that many fear what is imagined "might" happen over what certainly will happen.
-
knaugle at 02:51 AM on 3 February 2016Fox News Republican debate moderators asked a climate question!
I find it interesting that the USA dealt with acid rain in the early 1990s with a GOP endorsed cap-and-trade approach. As I recall the economy in the 1990s did fairly well. However now the GOP says the exact same approach will destroy the economy.
www3.epa.gov/captrade/documents/ctresults.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acid_Rain_Program
It is interesting how the only thing that has changed really is the political dogma of the times.
-
Tom Curtis at 01:49 AM on 3 February 201610 Indicators of a Human Fingerprint on Climate Change
POJO @92 and @94, seems intent on creating a fiction about the IPCC discussions of DTR. According to his mythology, the IPCC supported "the DTR story" up to, and including the Third Assessment Report (TAR), but thereafter withdrew that support. In fact, the IPCC discussion of DTR has been nuanced throughout. This, from the First Assessment Report (FAR) we have:
"Because the ocean has a large heat capacity, diurnal temperature variations in the ocean and in the overlying air are considerably muted compared with those over land and, from a climatic point of view, are likely to change little Over land, diurnal variations are much less restricted so the potential for relative variations in maximum and minimum temperature is much larger Such relative changes might result from changes in cloudiness, humidity, atmospheric circulation patterns windincss or even the amount of moisture in the ground Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to assess variations of maximum and minimum temperature on a hemispheric or global scale However in the regions discussed below, multi-decadal tiends of day-time and night-time temperatuies have been studied and do not always appear to be the same"
Discussion clearly focusses on the multiple possible causes of changes in DTR, and notes that hemispheric and global data is not availabe. From that it follows that they cannot have been pushing "the story" POJO attributes to them.
The Third Assessment Report concludes its discussion of DTR by saying:
"Minimum temperature for both hemispheres increased abruptly in the late 1970s, coincident with an apparent change in the character of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon, giving persistently warmer sea temperatures in the tropical central and east Pacific (see Section 2.6.2). Seasonally, the strongest changes in the DTR were in the boreal winter (−0.13°C/decade for rural stations) and the smallest changes were during boreal summer (−0.065°C/decade), indicating some seasonality in the changes. Preliminary extensions of the Easterling et al. (1997) analysis to 1997 show that the declining trends in DTR have continued in much of North America and Asia.
Figure 2.3 shows the relationship between cloudiness and the DTR for a number of regions where long-term cloud cover data are available (Dai et al., 1997a). For each region there was an increase in cloud cover over the 20th century and generally a decrease in DTR. In some instances the correlation between annual cloud cover and annual DTR is remarkably strong, suggesting a distinct relationship between cloud cover and DTR. This would be expected since cloud dampens the diurnal cycle of radiation balance at the surface. Anthropogenically-caused increases in tropospheric aerosol loadings have been implicated in some of these cloud cover changes, while the aerosols themselves can cause small changes in DTR without cloud changes (Hansen et al., 1998 and Chapter 6)."
The strong trend in DTR from the 1970s is attributed to a change in the ENSO regime. The effect of cloudiness is discussed extensively, and some attention is also given to aerosols. Again we have the nuanced discussion we expect from the IPCC.
In short, the only thing that has changed in the IPCC accounts prior to AR4, and after is the addition of more data allowing a better characterization of the trends and uncertainties.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 01:35 AM on 3 February 2016'If the world ends in 2100, we’re probably OK'
Johnb,
I share your concern about the merits of geoengineering 'solutions' to the climate change issue. My concern is that they will be 'popular and profitable' rather than be thoroughly understood and legitimately justified.
nigelj,
I understand that Humans are not 'wired to ignore the future or not care about others'. Lots of marketing research results (and what is presented by Susan Cain in “Quiet: The Power of Introverts in a World That Can't Stop Talking”; and Naomi Oreskes' and Eric M. Conway's “Merchants of Doubt”), clearly show that some humans can easily be impressed and be encouraged to care about personal short term desires to the detriment of others or the future.
Most aboriginal cultures developed the understanding that they must live as part of nature and limit their actions to ensure they only made things better for future generations (did not make things worse).
Competition to get more of a limited opportunity for desired personal benefit (not needs, just desires) can obscure or even erase that type of understanding and awareness. It made many aboriginal groups fight each other.
And the ability to 'win' by deliberately misleading others, or through created authority and the force it can exert when being misleading fails, makes things worse. This was proven by most of what was done by the European conquerors as well as many other horrible examples of abuse of power and authority (including things happening today).
The detrimental consequences of competition in a game that allows uncaring selfish people who would abuse their freedom to get away with unacceptable actions, including misleading marketing, is repeatedly proven by every successful delay of the research into, and dissemination of better understanding of, how to advance humanity to a lasting better future for all when that better understanding is likely to be contrary to the interests of people who got away with becoming more fortunate, wealthier and more powerful.
That is the best explanation I am aware of for what can be seen to be going on, not just regarding climate science related to rapid recent global warming and the resulting climate change.
Human nature is not the problem. The problem is clearly people who understand how to manipulate human nature and abuse that understanding to impede the advancement of humanity to a lasting better future for all. And they do it because that future would have them be perceived as 'comparatively less of a winner' even if they too would be better off in that future.
This leads many people to desire to not want to understand climate science. And if they must, they prefer to only talk about what things might be like 85 years from now, and deliberately understate the expected future consequences of their personal short-term interests and pursuits.
This counter-productive way of thinking (counter-productive from the perspective of the advancement of humanity to a lasting better future for all), also leads people to believe they are justified in doing economic assessments of their perceived 'value of lost benefit by the most fortunate in the current generation' for comparison to their 'perceived costs of the consequences on others in the current and future generations (limited to the next 85 years)' and justifying what they want to get away with by claiming the perceived benefit a portion of humanity would need to give up today (as those having to give up the opportunity to benefit figure it) is more than the costs to all others including future generations (as those having to give up the opportunity to benefit figure it and limit it). This way of thinking is totally irrational and clearly inappropriate. It is like a person wanting to do something they personally consider to be a $1000 benefit and justifying it by figuring that the cost to their neighbour is less than $1000. Yet it is the way the US Government and many other powerful groups like to think about this issue.
So there are far more unacceptable ways of thinking and acting than 'limiting the thoughts to what things may be like 85 years from now'. And they are being exposed by the fight against climate science. It is a very 'enlightening issue'. Hopefully it can help change what has been going on so that humanity has a better chance of advancing (rather than developing a steady stream of ultimately unsustainable and damaging technological changes selected based on popularity and profitability that are incorrectly perceived to be advances).
Prev 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























