Recent Comments
Prev 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 Next
Comments 37051 to 37100:
-
grindupBaker at 06:41 AM on 28 April 2014Global warming since 1997 more than twice as fast as previously estimated, new study shows
VictorVenema #1 "those adjustments are huge". Hang on, those adjustments are huge for that region and obviously of great interest in knowing who is computing best, but offhand I think they look negligible as a global adjustment (the underlying topic). My assessment is only based on my eyeballing GISTEMP-Cowtan & Way graphic and estimating ranges of differences and areas but it's a low order of magnitude. I have 0.8Mk2 @ -1C<=>-2C, 1.0Mk2 @ 0C<=>-1C, 8.5Mk2 @ 0C<=>-0.3C and 8.5Mk2 @ 0C<=>+0.8C (GISTEMP a warmer anomaly for this one). I compute -0.0025C, -0.0010C, -0.0025C and +0.0066C as global equivalents for a net effect on GMST of +0.0006C (Cowtan & Way showing this much less global warming than GISTEMP) but my final quantity detail is not significant and might be incorrectly signed because I used the graphic, not data, and minimal effort so what it indicates is only that it's negligible as a global adjustment.
Per 2013-11-13 post, the Cowtan & Way paper regarding HadCRUT4 (on which this post is an interesting aside) noted HadCRUT4 at +0.046°C per decade GMST anomaly, NASA at +0.080°C per decade, the C&W kriging and hybrid data sets at +0.11C and +0.12°C per decade. That's the one with global adjustments are huge .
-
Mal Adapted at 05:00 AM on 28 April 2014Climate's changed before
Autumnleaves's comment brings to mind Charles Darwin's observation that "ignorance more frequently begets confidence than does knowledge".
The response by Tom Curtis was outstanding.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 04:12 AM on 28 April 2014How global warming broke the thermometer record
Kevin C @5.
Rather than a key point being that short term trends are not a good basis for drawing conclusions, I suggest that the best understanding requires all possible factors to be well understood. That means the process of developing the best overall understanding of what is going on requires the constant investigation into, and improvement of, the understanding of each potential factor.
That is understood in a community of people genuinely interested in constantly pursuing increased understanding. However, this issue faces challenges from a group of critics desperate for it not to be better undestood by the general population. And the general population contains many people eager for any excuse not to better understand this issue. Many people will fight against any indication that it is unacceptable to benefit from burning fossil fuels.
What is most important is to constantly point out that the improvement of understanding that develops confirms (does not contradict) the unacceptability of massive burning of fossil fuels, regardless of the popularity of that activity among those who want to benefit from it. It can be added that CO2 impacts are only part of the troubles and impacts created by the fighting over the right to benefit most from burning fossil fuels.
-
Doug Hutcheson at 17:00 PM on 27 April 2014The consequences of climate change (in our lifetimes)
Peter says AGW does not alarm him, but (to paraphrase) the human reaction to the threat is alarming. I have to agree, with the caveat that I am alarmed by what AGW could do to our civilisation and, by inference, to our population. If our current cereal producing areas go out of production, what guarantees do we have that we can migrate our food plants as we migrate toward the poles? Sure, the cool areas may become warm enough to support our current prey organisms (plant and animal), but what will happen to plants adapted to a different day length, for example?
Will we see any concerted action before large numbers of people become alarmed enough to apply political pressure? I don't think so.
At the very least, the C in CAGW should stand for 'Concerning'.
-
Doug Hutcheson at 15:48 PM on 27 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
A very informative post, thank you.
Although I, too, would deplore the human suffering from weather extremes caused by a massive El Nino, it might at least cause some doubt about the veracity of AGW to be removed, at least in minds open to reason. A nasty jolt to our civilisation now, might just wake up some who are, currently, peacefully asleep at the wheel.
-
Tom Curtis at 15:39 PM on 27 April 2014Climate's changed before
Autumnleaves @405, first a technical point. I do not believe in evolution. Evolution is not something I put my trust in as though it were a deity. Rather, I believe that modern living things have evolved from earlier forms through a process of random mutation and natural selection; and that all life currently on Earth share a common ancestor, which lived certainly more than a billion years ago, and possibly more than three billion years ago; and that all life share a first common ancestor that lived around four billion years ago. These are scientific claims having very little religious implication.
Second, your objection is specious because it does not take into account the pace at which evolution proceeds. Fixing a new genotype takes thousands to billions of generations. If there is little selective advantage, the time taken on average is the inverse of the size of the population (ie, currently 7 billion years for humans). The greater the selective advantage the shorter the time, but that selective advantage is measured in reduction in population size. For very rapid evolution, populations must teeter on the edge of extinction.
That fact creates a major problem when many species must evolved rapidly at once. Species are massively interdependent on each other in an ecological network. The near extinction of a few species can create large risks of exinction in their own right. The near extinction of many species simultaneiously means that very many of them will go extinct.
Further, the rapid rate of evolution I am describing depends on the existence of a large reservoir of genetic variability within a species that typically exists. Rapid evolution reduces this variability. After it is exhausted, evolution can proceed no faster than the rate of introduction of new, beneficial genes by random mutation, a much slower process. Given that following a period of very large selection pressures for very many species, species will need to adapt not just to the new environmental conditions but to the new ecological conditions, that means recovery from such large selection pressures will be very slow and extinctions consequently more likely. Indeed, it is worse than that. Humans have placed other organisms under massive selection pressures due to ecological changes over the last century, which will have already greatly reduced genetic variability in most species, limiting their ability for further adaption.
Finally, the impact of BAU global warming mirrors in impacts, but exceeds in pace, that of the End Permian mass extinction which saw the exinction of 90% of marine Genera. We know, therefore, that living things cannot, in general adapt to the current rate of environmental change is sustained over the next 100 plus years. The question among ecologists, SFAIK, is no longer whether or not the comming centuries will mark one of the greatest mass extinctions the Earth as seen, but only whether it will be comparable to that which killed of the dinosaurs, the Permian mass extinction, or something worse.
-
Autumnleaves at 15:05 PM on 27 April 2014Climate's changed before
I'm not an expert on global warming, so I won't attempt to argue with anyone about that. What I am wondering is why you are worried. Since from your article you obviously believe in an old earth ("hundred thousand year cycle", "last 700 thousand years", etc.), then I am assuming you also believe in evolution. If evolution is true, than life must be adaptable enough to survive global warming, or there is no way it would have survived in the past!
-
JIm Steele at 15:05 PM on 26 April 2014Climate Change: Years of Living Dangerously
‘Years of Living Dangerously’ shouts climate fire! But, data says their shouting is simply noise. The documentary uses talented celebrities who are totally ignorant of the entire climate issues. Read my debunking of the first 2 episodes.
http://wattsupwiththat.com/2014/04/25/years-of-living-dangerously-shouts-climate-fire-but-data-says-their-shouting-is-simply-noise/
and
http://wattsupwiththat.com/2014/04/14/exploiting-human-misery-and-distorting-the-science-an-environmentalists-critique-of-years-of-living-dangerously/
Moderator Response:(Rob P) - Your post links to a paper entitled: Warming and Earlier Spring Increase Western U.S. Forest Wildfire Activity - Westerling et al (2006). And includes this graph, which you even highlight in your post, illustrating a long-term increase in wildfire activity in western US forests:
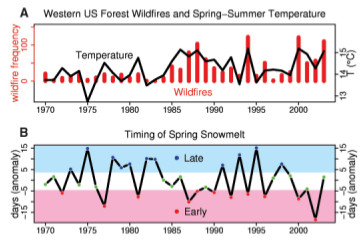
Their abstract states:
".........We compiled a comprehensive database of large wildfires in western United States forests since 1970 and compared it with hydroclimatic and land-surface data. Here, we show that large wildfire activity increased suddenly and markedly in the mid-1980s, with higher large-wildfire frequency, longer wildfire durations, and longer wildfire seasons. The greatest increases occurred in mid-elevation, Northern Rockies forests, where land-use histories have relatively little effect on fire risks and are strongly associated with increased spring and summer temperatures and an earlier spring snowmelt."
This is effectively what Years of Living Dangerously seems to be getting at - the long-term increase in wildfire activity is a result of global warming.
-
Riduna at 09:44 AM on 26 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Wili @ 7
Another factor which may contribute to a strong El Nino are increased Chinese efforts to reduce their chronic air pollution. Every success they have in doing this increases solar radiation reaching the surface, adding that little extra to global surface temperature.
-
Kevin C at 04:45 AM on 26 April 2014How global warming broke the thermometer record
Paul: If you look in Appendix A of our report here you'll find some plots, but more importantly links to the plots from both GHCN and Berkeley Earth, both of which are very informative. Berkeley's Google Earth station browser in particular is a very powerful tool.
When it comes to differences with Berkeley, the questions become much harder. There are some localised differences in Antarctica - it comes down to Berkeley's better station count versus our use of the satellite data - that's an interesting question for further study. There are also some mid latitude differences which are not so localised so will be harder to track down.
While we're now pretty confident that GISTEMP is running a bit cool over the last few years, I really wouldn't want to have to pick between our results and Berkeley. Berkeley is a very impressive piece of work.
There are some further potential biases which neither Berkeley or us have assimilated with yet. Currently we are both using ocean temperatures from HadSST3, which is actually rather similar to ERSST3 over the study period, despite ERSST not including the engine room corrections. If ERSST4 shows a signficantly higher trend then the SST guys would have to fight it out as to who is right, but it would be another potential small upward adjustment.
Also, the air temperature over sea ice question isn't closed. While extrapolating from land temperatures is better than ignoring them or using SSTs, it doesn't capture everything. The reanalyses tend to show faster warming between the pole and the Chuckchi sea - you can see it in the GISTEMP-MERRA plot above - and this is completely inaccessible to the station record. While we show similar trends to MERRA in the Arctic, the other reanalyses show faster warming. The Antarctic ice will similarly be an issue, although if it is linked to ice cover the sign might be different.
Having said that, one of the key points of our work is that short term trends are not a good basis for drawing conclusions. Weeding out the biases illustrates the problem, and may mitigate it somewhat, but short term trends are always going to be dominated by much larger factors such as volcanoes and El Nino.
-
keithpickering at 03:44 AM on 26 April 2014How global warming broke the thermometer record
Great work, Kevin, and it answers a question I've had for a long time.
-
Doug Bostrom at 03:33 AM on 26 April 2014How global warming broke the thermometer record
The trends in the Arctic adjustments are shown in Figure 4, and show a basin-wide pattern of downward adjustments.
After years of reading mutterings by pseudoskeptics over NASA being involved in a conspiracy to adjust temperature records upward as part of an insidious global plan to turn us all into communists, I can't help but chuckle at reading that.
Somebody forgot to install Das Kapital into the software producing temperature statistics. The responsible party will surely be punished as soon as a chemtrails dispenser disguised as a commercial airliner can be dispatched to their location.
-
pauls at 02:54 AM on 26 April 2014How global warming broke the thermometer record
Nice work. Just a suggestion for illustrating the point: could you plot some example station time series with the adjusted and unadjusted versions compared?
Have you developed any ideas on the small 1997-2012 global average trend difference from Berkeley Land+Ocean?
-
VictorVenema at 01:56 AM on 26 April 2014How global warming broke the thermometer record
That is interesting and those adjustments are huge. Will read the report.
The story has even been picked up by Science Magazine (pay walled).
News & Analysis
Climate ScienceClimate Outsider Finds Missing Global Warming
Eli Kintisch
Major climate data sets have underestimated the rate of global warming in the last 15 years owing largely to poor data in the Arctic, the planet's fastest warming region. A dearth of temperature stations there is one culprit; another is a data-smoothing algorithm that has been improperly tuning down temperatures there. The findings come from an unlikely source: a crystallographer and graduate student working on the temperature analyses in their spare time.
-
AndrewDoddsUk at 19:29 PM on 25 April 2014The consequences of climate change (in our lifetimes)
Re: 6, It's interesting..
The Late Cretaceous is noted for very high sea levels compared to today - it seems that the whole ocean went over to thermohaline based circulation and warmed up significantly. Most currently inhabited areas were underwater in huge 'epicontinental' seas.
It's worrying that all other things being equal, the blue line on the graph for 2011 puts us at or around the point where no ice sheets are stable - certainly not the GIS and WAIS.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 18:47 PM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
wili @7
The yearly increase in CO2 can jump around a bit - even modest changes in the rates for the major natural sources and sinks can have a big effect. So I would wait several years before calling such a large rate increase. That said the economy is picking up after the GFC so there could be some increase in the human emission rate. Too early to tell.
-
AndrewDoddsUk at 18:17 PM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
This is confusing my brain for a couple of slightly irrelevant reasons..
First, a large el-Nino event that blows away previous temperature records by a large margin would quiten doen the whole 'hiatus' hubbub. But that's scare comfort given the likely impacts. So on humanitarian grounds I want it to be a dud.
Second, there's a kind of Murphy's law involved.. everyone in the climate blogosphere is anticipating a big el nino.. but it's still possible that it'll fizzle out. Especially if people keep going on about it..
It's a bit like following the Arctic sea ice. It's a kind of addiction seeing if records are going to be set again this year.. but you know that the best thing that could happen is a sea ice recovery. And you also know that the moment you stop clicking 'refresh' on cryosphere today and forget about it, we'll have open water at the North Pole.
-
billthefrog at 18:10 PM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
And the moral is... "never post on SkS just before going to bed after an evening spent slurping real ale with old university chums!"
OPOF @ 10 & 11
Thanks for the f/b
I totally agree with your la Nina comments in #11. What I had been trying to convey was that, despite the significant upwelling of cold deep water in the Eastern Pacific during 98/99, the temps were still remained very elevated for the time.
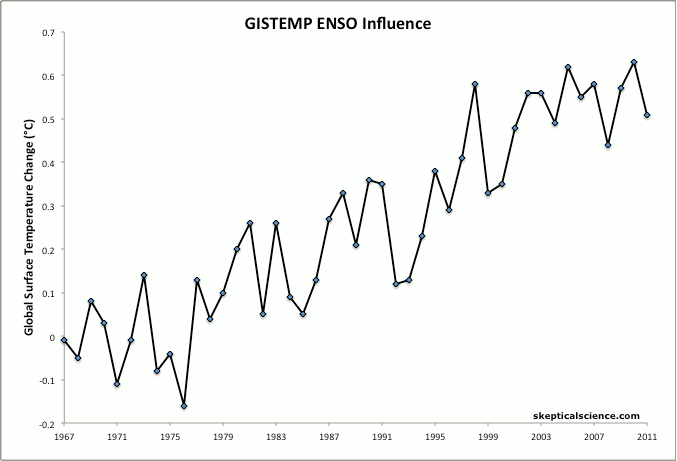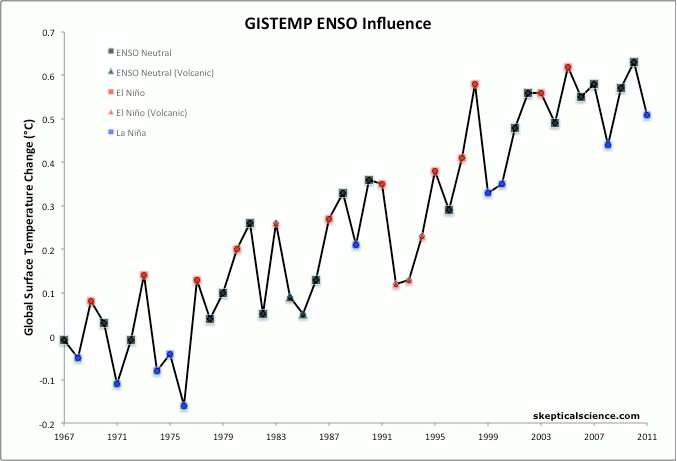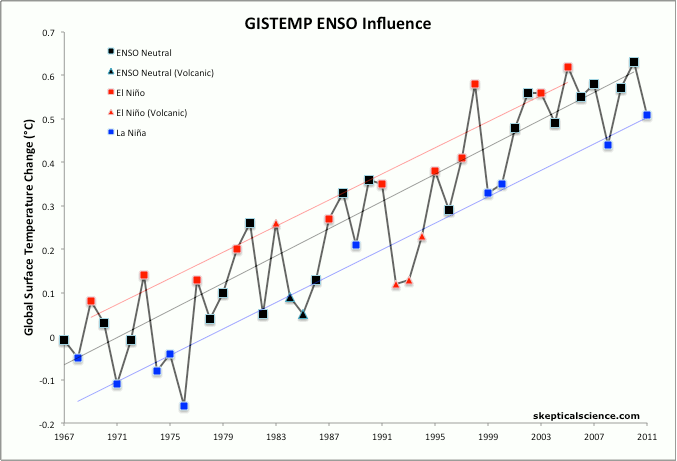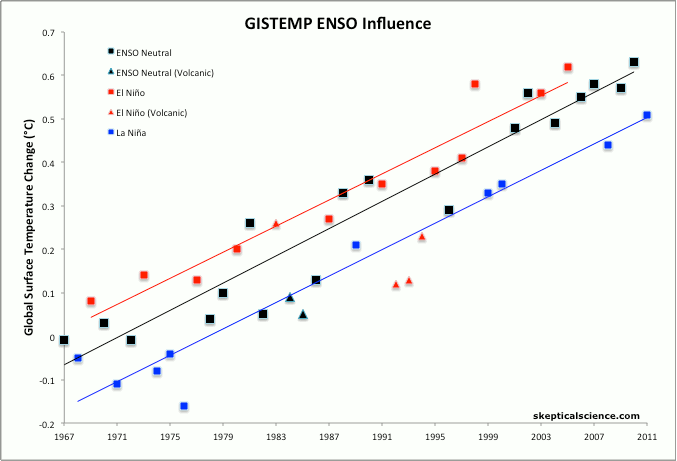
SkS has (somewhere) a graphic with annual global temps filtered into 3 categories: la Nina years, el Nino years and ENSO neutral which (I think) really explains the idea far better than words.
Cheers me dears Bill F (Oh look, it's getting near opening time again.)
Moderator Response:[DB] Try here:
-
One Planet Only Forever at 14:39 PM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Bill @8,
A better explanation for the sharp drop of global average temperature in 1999 from the 1998 peak was the rapid formation of a significant La Nina condition in mid-1998 (as you would see in the NOSS ONI table at:
http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ensoyears.shtml.
However, I agree that 1999 and 2000 remained high compared to the previous temperature history even though a strong and long acting La Nina had developed.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 14:33 PM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Bill@8.
You are interpretting the ENSO/ONI information correctly. The warm El Nino effect typically starts in one year and continues into the next year.What Rob@3 points out can also be seen. The global average surface temperature increase lags behind the formation of the warmer El Nino ocean surface. It takes time for the warmth from the equator to spread its effect to a larger area of the globe.
So 1997 was a record compared to the previous temperature history, but the bigger bump of that El Nino was in 1998.
As I indicated in my earlier post, this greater bump of the second year is seen in most of the El Nino periods.
-
billthefrog at 10:06 AM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Oops!
Paragraph 2 of my comment above should have read...
"... increasingly IMprobable with each passing year..."
See what I mean about each passing year????
-
billthefrog at 10:01 AM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Kevin @1
We seem to be looking at different data as regards the assertions in your opening paragraph. When I look at the ENSO data provided by NOAA, (http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ensoyears.shtml) the “super el Nino” seems to pretty well straddle both 97 and 98. If I am looking at the wrong dataset, or if I am managing to misinterpret it, can you (or any one else) please point me in the right direction?Regarding temperatures, if I am reading the data correctly (increasingly probable with every passing year) each of the three main terrestrial datasets (HadCRUT4, NCDC, Gisstemp LOTI) all seem to show 1997 as having been a record year for global (land + ocean) temps – albeit very briefly. Similarly, 1999 at the time ranked either 3rd or 4th (again very briefly) in each of these datasets.
The fact that 1997 was a record breaking year has simply been forgotten by many owing to the way it was summarily eclipsed in 1998. The two year rise (96-98) is unparalled in both the gisstemp and NCDC datasets, and is the second biggest (behind 1876-78) in the HadCRUT4 dataset. Similarly, although 1999 now seems relatively “cool”, it wasn’t really at the time. The huge drop from 98 to 99 was due to the fact that 98 was such an outlier, rather than any chilliness inherent in 1999.
If the timing is right (note the "if") then I think another outlier of the scale of 1998 could easily appear sometime in the not-too-distant future.
That is NOT a prediction for this year, just a thought for the future.
Cheers Bill F
-
wili at 05:31 AM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
"Week beginning on April 13, 2014: 401.53 ppm
Weekly value from 1 year ago: 397.52 ppm" http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/weekly.htmlSo there's been a rise of over 4 ppm for last week over the same week last year.Is that going to be the new rate of increase--4ppm/year? Or is this a seasonal blip above the longer term rate of ~1.5 to 2.7ppm/year we've seen in so far this century?
ftp://aftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/products/trends/co2/co2_gr_mlo.txt
Note that the only reading in annual increase above 2.7ppm before this century was 1998 at 2.93. This, of course, was the year of the last Super-El-Nino. If we are moving toward a new Super-El-Nino this year, I would expect the annual increase this year to be considerably above 3ppm--maybe even well above 4, since we are already seeing this level of rise with the El Nino not quite officially started yet?
-
robert way at 05:18 AM on 25 April 2014Wave goodbye to the stadium wave - global warming still caused by humans
Although the stadium wave is undoubtedly an incorrect hypothesis - I consider the counterintuitive result of the recent Mann et al (2014) study to require greater scrutiny. In particular this result does not
The issues with the method are related to the input parameters of the energy balance model he uses, the accuracy of the forced components used and finally the lack of any spatial figures. IF this method is appropriate then he should be showing a spatial amplitude map and it should have the same spatial pattern as would be expected based on theory behind the mechanisms. This is somewhat a glaring omission. I think he provides a compelling case that the detrended AMO is inappropriate but I think his solution is theoretically appropriate but in practice is not sufficiently justified based on the paper. I also did not like that he cited Booth and other aerosol forcing AMO studies without citing their rebuttals which were compelling. The argument that the AMO was positive during the 1990s and is negative currently is at odds with the spatial distribution of temperature changes over that period - particularly in the Labrador Sea. In this area the temperatures are warming faster than projected by GCMs and were faster during the mid-century and cooler during the 1970-1995 section. This temperature history for one of the main nodes of the "amo" is at odds with the history implied by Mann's version. I suspect many of the experts on the physical mechanisms behind the AMO will disagree strongly with his new reconstruction of this index.I think any "new definition" of an AMO needs to be supported by more than just time series analysis - there needs to be a physical understanding of the underlying mechanism. A point made in Climate Dynamics last year. Did they check to make sure these results made sense with respect to the underlying mechanism? Did they relate it to salinity and sea ice ? As a mode of NH temp variation it is possible there is some relation to this index - however the AMO which is traditionally referred to by authors was not cooling over the past 15 years.
-
bjchip at 01:41 AM on 25 April 2014Ice age predicted in the 70s
Please correct the caption to figure 1
Figure 1: Number of papers classified as predicting global cooling (blue) or warming (red). In no year were there more cooling papers than warming papers (Peterson 2008).
Of these 15 years, 14 had more warming than cooling papers
Looking at the data on the bar graph it appears that there is one year (1971) in which there were 2 cooling papers to the single warming paper.It may be insignificant, but it is an error. A suggested correction.
-
keithpickering at 01:15 AM on 25 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Rob,
I'd also like to draw your attention to a completely mathematical treatment of ENSO prediction, based on (elliptical) Mathieu functions rather than (circular) sine waves. You can find it here:
http://contextearth.com/2014/02/21/soim-and-the-paul-trap/
-
Tom Curtis at 23:10 PM on 24 April 20142014 SkS Weekly Digest #16
A close look at responsible investment in coal:
h/t to Coby Beck
-
Tom Curtis at 19:09 PM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Poster @11, I based my comment on the link which you provided in support of your claim that "There is discussion elsewhere ... that a significant comment in the IPCC report was not included by Mr Nuccitelli".
As it happens, the article to which you linked did not discuss Dana's article (not even in comments). Nor did it mention the figures you quoted, instead stating misleadingly that "..strong climate policies would be more expensive than claimed as well – costing upwards of 4% of GDP in 2030, 6% in 2050, and 11% by 2100". The first of those figures lies outside the 95% confidence interval of the costs of mitigation. All are the rounded upper bounds of the 95% confidence interval so that Lomborg in effect argues that the IPCC states the costs will be equal to or higher than (upwards of) the upper bound of the 95% confidence interval of the IPCC stated values. Given that he quotes the 84% (+/- 1 stdev) range for costs, this biased presentation looks like straight forward, and intentional deception. (Apparently, however, something you do not, or at least did not have a problem with, while having a problem with Dana's correct figure.)
In any event, as you did not draw the figures you quoted from your cited source, it was a reasonable assumption that you drew them from your sources cited source, ie, table SPM.2, or the text which states:
"Under these assumptions, mitigation scenarios that reach atmospheric concentrations of about 450ppm CO2eq by 2100 entail losses in global consumption—not including benefits of reduced climate change as well as co‐benefits and adverse side‐effects of mitigation19—of 1% to 4% (median: 1.7%) in 2030, 2% to 6% (median: 3.4%) in 2050, and 3% to 11% (median: 4.8%) in 2100 relative to consumption in baseline scenarios that grows anywhere from 300% to more than 900% over the century. These numbers correspond to an annualized reduction of consumption growth by 0.04 to 0.14 (median: 0.06) percentage points over the century relative to annualized consumption growth in the baseline that is between 1.6% and 3% per year."
So, to summarize, based on the information you gave it was a reasonable assumption that your knowledge of the figures came directly from the IPCC report, and hence came with a direct statement of the near equivalence of Dana's figure.
-
Poster9662 at 16:55 PM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Thanks Dana for your rapidreply, it is appreciated. Tom Curtis@9, no I didn't already know and furthermore I'm not charging Mr Nuccitelli with anything at all. Others have done that and it is that I was asking about. I very much appreciate that Mr Nuccitelli had the courtesy to answer my questions both civilly and rapidly. His attitude is markedly and refreshingly different from the attitudes of others in the blogosphere dealing with Climate Change.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 15:07 PM on 24 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
ktam @1,
There is a correlation between the SOI and the El Nino that can be seen when you compare the values of each. A consistent strong negative monthly SOI was the start of the 1997/98 event. But noteable El Ninos have formed with fluctuating SOI values at this time of the year.
The following site presents a table of monthly updated averaged SOI values.
http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/current/soihtm1.shtml
And this one presents the monthly updated tracking of the ONI (El Nino/La Nina)
http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ensoyears.shtml
When an El Nino forms it generally gets established by midyear and extends into the following year.
Also, the change to negative SOI occurs in advance of the El Nino forming (as mentioned by Rob @3, and as presented in the article).
And the year after the formation of the El Nino is often the one that gets the biggest temperature increase above the ENSO Neutral condition.
Reviewing the NASA/GISS land-ocean average temperatures alog with the ONI:
- 1997/98 El Nino created the 1998 bump.
- 2009/10 El Nino bumped 2010 more than 2009
- 2006/07 bumped 2007 more
- 2004/05 bumped 2005 more
- 2002/03 bumped both years but it also got established a couple of months earlier than the others I mentioned and started with more consistent negative SOI monthly averages.
This one, if it forms, could create a bigger 2015 bump or a big bump of both years.
How big the bump will be will depends on a number of difficult to predict factors, so it is a "watch for it" situation as mentioned in the article.
-
Tom Curtis at 11:51 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
TonyW @6, in fact costs of mitigation will be greater if it is unexpectedly difficult to integrate renewable energy into the future energy equation. The middle section of table SPM.2 (see my post @9) deals with that issue, and shows that the cost of "limitted solar/wind" penetration in the market will increase the cost by 6%. Far more concerning is the 138% cost if Carbon Capture and Storage proves untenable (as is widely believe by many at SkS). However, even with that increase, fully calculated the cost of not mitigating will exceed the cost of mitigating to keep temperatures below 2-3 C. Further, there is a real risk of catastrophic effects from warming that raise the expected cost of unmitigated warming well above any reasonable estimate of the cost of mitigation.
-
Tom Curtis at 11:41 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Poster @7, the table Lomborg refers to is this Table SPM.2:

You will notice (and I suspect, already knew) that Dana quoted the compounding cost for restricting CO2eq rises to 450 ppmv, for which you quote the values at 2030, 2050, and 2100. For comparison, the compounding cost at 2030 is 1.2%, at 2050 it is 2.4%, and in 2100 it is 5.5%. That is, it underestimates the cost for the earlier years, but over estimates the cost in the later periods. In all years, however, it is not statistically significantly different from the specific values.
Your charge is that Dana incorrectly claims that WG3 does not mention annual losses, but Dana is correct. It does not give the annual values for any other than the three years stated. That only allows a direct comparison if the year in which the global temperature increases to 2.5 C above recent values is one of those three years. In order to make a direct comparison, the IPCC would need to report the costs for each level of temperature increase, correlate that to the specific years to give a cost in each year, and provide a cost in each year for mitigation, and then integrate the two. Indeed, done properly they would repeat that several thousand times in a monte carlo procedure allowing for potential error in estimates of temperature increase, cost at a given temperture and costs of mitigation to generate expected costs of the options - a procedure which would show higher expected costs from global warming than simply comparing mean values.
Finally, the cost due to an increased temperature is simply a raw cost. That cost, "the equivalent of less than one year of recession" according to the Lomborg article you linked to, can be expected to have its own impact on economic growth - but does not include any such impacts. Logically it cannot include such impacts as it is a cost at a particular temperature without refference to the year in which it occurs, or temperature trajectory over time to that year. Consequently the actual cost of not mitigating will be that 0.2-2% plus any impacts on economic growth from from the raw impacts. As, by Lomborg's own admission, the impact at 2.5 C is comparable to a years recession, and that impact will be felt every year, that means with BAU by the end of this century the impact of global warming will be equivalent to being in permanent recession - ie, a complete stagnation of economic growth.
As Lomborg's own words show, he is simply playing the old game of comparing incomparables, and hiding the actual costs of global warming.
-
dana1981 at 11:03 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Poster @7 - the criticism is ridiculous because I had included the figures in question in the Lomborg quote immediately preceeding the second Lomborg quote in question.
That said, I didn't explain the apples and oranges point well - Christian @4 and Tom @5 have hit on the key point, and I've revised the post to clarify it and also included it in the myth rebuttal now linked at the bottom of the post. That being, limiting global warming to a further 2°C is not 'no action', it requires substantial mitigation efforts. Lomborg tries to sweep this under the rug by only looking at costs in 2070, ignoring the accelerating costs thereafter if we 'do nothing'. Not to mention that the 2% is likely an underestimate and the 6% likely an overestimate, as the IPCC explicitly stated.
This is why you need to go beyond the numbers in the IPCC reports and look at models like PAGE to determine the economically optimal path, and they conclude it's around 450-500 ppm CO2, which is a scenario that requires substantial mitigation.
-
Poster9662 at 10:35 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
There is discussion elsewhere (http://tinyurl.com/oxthlrc) that a significant comment in the IPCC report was not included by Mr Nuccitelli. The section in question gives assessments of median values of annual economic loss in 2030 0f 1.7%, 3.4% in 2050 and 4.8% in 2100. In his comments Mr Nuccitelli noted that the IPCC report did not mention annual economic losses when clearly it does. Can Mr Nuccitelli explain why the relevant data that disagrees with his comment was not mentioned? Is he being unfairly maligned? My comment is not off topic, is not political, is not ad hominem and gives the relevant reference so seems to meet the standards set by Skeptical Science.
-
TonyW at 08:39 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
I don't think it's possible to estimate either the cost of mitigation or the cost of not mitigating. The idea that all fossil fuel use can stop with only a slight hit to growth seems bananas. It would take an unreasonable step of assuming that alternative energy sources (and resources for other non-energy use of oil, gas and coal) can fairly smoothly slot in for the fossil fuels, at whatever level the global economy "needs" at whatever scale is required. This seems nonsensical. Not that we shouldn't mitigate given that a world of 3C warmer (or even 2C warmer) would appear to become unliveable in many places (including some island nations wiped out). We're already seeing damaging effects of climate change.I think we need to concentrate on the impacts of unmitigated warming, for why we don't want to get there, whatever the cost. In the end, economic growth has to stop on a finite planet (and the limits appear to be getting very close), so the costs of mitigation, in terms on the impact on growth is not a good way to look at the issue. In any case, if serious mitigation does get underway (something I'm not holding my breath for), it will soon become clear that it will be a bigger burden on the global economy than these low estimates. At that point, mitigation actions would cease unless the case is iron-clad for why we have to continue with such efforts to avoid an even worse ending. -
Doug Bostrom at 08:34 AM on 24 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Entirely apart from the matter of climate change, my understanding of El Niño seems quite a lot better than it was a few minutes ago. Thanks!
-
Rob Honeycutt at 04:04 AM on 24 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
Kevin @1... But surface temps usually lag by about 6 months, so if we see an El Nino this summer or fall, we'll likely see a corresponding rise in surface temperature starting in 2015.
-
phaeretic at 03:53 AM on 24 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
The included chart of the BOM's 30 Day Moving SOI is out of date by over two weeks. The one you posted is showing a value of -12.3, but for the past couple weeks, that value has been steadily climbing and after topping out at +2.2 a few days ago, it currently sits at +1.9. The latest is available here:
http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/enso/#tabs=SOIModerator Response:(Rob P) Yes, I'll update that later on today - the post was written a few weeks ago. I updated the first GIF animation, but forgot about the SOI image.
A new burst of westerly winds has started up within the last 4-5 days, so it would be expected to shift the SOI sharply negative once again, and push the subsurface warm water to the surface when the new kelvin wave reaches the east. Typical transit time from Papua New Guinea to the South American Pacific coast is about 2 months.
-
ktam at 02:47 AM on 24 April 2014Is a Powerful El Niño Brewing in the Pacific Ocean?
I think it needs to be made clear that even if we have as signficant event as the 1998 El-nino it is less likely to have such a dramatic impact on the calendar year temperature record as the impact looks to be spread across 2 calendar years. The impact of the 1998 El-nino was almost perfectly timed with the calendar year, as can be seen when you notice that 1997 and 1999 were both relatively cool.
A new temperature record is quite possible as it is during any El-nino event nowadays, it just wont be a stand out record in the way that 1998 was.
Kevin
-
frankbr at 01:23 AM on 24 April 2014Debunking Climate Myths from Politicians
I hope you extend your database to include Australians. " Maurice Newman, the chairman of the Prime Minister's Business Advisory Council discusses climate change and says that there is little correlation between carbon dioxide and the warming of the planet."
http://www.abc.net.au/lateline/content/2014/s3990190.htm
"MAURICE NEWMAN: They all come up with flawed methodologies. So we don't pay any attention to that. We know that there are a whole host of scientists out there who have a different point of view, who are highly respected, reputable scientists. So the 97 per cent doesn't mean anything in any event because science is not a consensus issue. Science is whatever the science is and the fact remains there is no empirical evidence to show that man-made CO2, man-made emissions are adding to the temperature on earth. We haven't had any measurable increase in temperature on earth for the last 17.5 years. If you look back over history, there's no evidence that CO2 has driven the climate either. So I know that this is a view which is peddled consistently, but I think that the edifice which is the climate change establishment is now starting to look rather shaky because mother nature is not complying."
" I just look at the evidence. There is no evidence. If people can show there is a correlation between increasing CO2 and global temperature, well then of course that's something which we would pay attention to. But when you look at the last 17.5 years where we've had a multitude of climate models, and this was the basis on which this whole so-called science rests, it's on models, computer models. And those models have been shown to be 98 per cent inaccurate."
-
Tom Curtis at 01:00 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Christian Moe @4, strictly it should be compared to the costs of warming at BAU (RCP 6.0 or 8.5) minus the costs of warming to 1.4 C. 1.4 C because temperatures are referenced to 2000 levels (strictly, 1986-2005) rather than to preindustrial levels (taken as 1850-1900) in the report, so that the 2 C target relative to pre-industrial levels often quoted becomes a 1.4 C target relative to 2000. That then becomes complicated because the costs sited are strictly for 2.5 C relative to 2000. That compares to projected temperatures of 2.2 +/- 0.5 C (1 SD range) in 2080-2100 for RCP 6.0; and 3.7 +/- 0.7 C for RCP 8.5.
So, for RCP 6.0, estimated costs are slightly less than those stated in the report. For RCP 8.5, they are greater than the estimate by an amount larger than the estimated costs are greater than the costs at the 2 C above pre-industrial mitigation target - so that overall the costs cited are an underestimate of the cost of not mitigating. That is because costs increase more than linearly with increased temperatures. Worse, the costs estimates are more likely to underestimate costs than to over estimate them (according to the IPCC), which I consider a considerable understatement. Further, temperature projection risks are greater on the high side than on the low side. Therefore the expected value of the risks is substantially understated in any event.
So, you are correct in your intuition, but because of the poor composition of the reports on these relevant points, direct comparison is simply impossible.
-
Christian Moe at 00:04 AM on 24 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
OP: The challenge is that these two numbers aren't directly comparable. One deals with annual global economic losses, while the other is expressed as a slightly slowed global consumption growth.
Even more basically: The WG3 estimate is essentially about the mitigation cost of limiting warming to roughly 2 °C. Shouldn't it be compared to the losses from the warming that mitigation avoids, then? That is, shouldn't it be compared to the losses that would be incurred due to warming beyond 2 °C, and not at about 2 °C, which is what WG2 estimates?
-
JohnB6223 at 19:51 PM on 23 April 2014Toward Improved Discussions of Methane & Climate
This has got to be the most confusing article I (a layperson) have ever read on SkepticalScience.
Having carefully read Chris Colose's critique of Natures article "Vast Costs of Arctic Change", and the many informative comments that follow, it appears that there are many countering views.
Can the interpretation of such a wealth of data be so indecisive on the likelihood of catastrophic methane emmision from the Arctis's thawing permafrost and warming oceans?
I have followed the excellent articles presented on Arctic News for some time, and have always found their graphics and data to be most informative, objective and (apparently?) of the highest quality.
Paul Beckwith has responded to SkepticalScience (dated 9 Aug 2013) here, in which he appears to raise many valid points of dispute.
He opens with this para:
Paul Beckwith: The above two paragraphs set the tone of this discourse. AMEG (Arctic Methane Emergency Group) is unjustly framed in this introduction as a fringe group using such terms as “overhype”, “beyond realm of plausibility”, “overblown scenarios or catastrophes”, “planet-wide emergency”. This is the complete opposite of the truth...Could SkepticalScience revisit this ussue please, to clarify what appears to me to be many valid points of interpretive disagreement.
-
Harry Twinotter at 19:44 PM on 23 April 2014Skeptical Science consensus paper voted ERL's best article of 2013
Well done, an excellent pay back for the hard work.
I noticed Maurice Newman (chairman of the Australian Business Advisory Council) disputed the "concensus" figures on ABC Lateline last night - it's good to be noticed. -
chriskoz at 19:32 PM on 23 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Riduna@2,
As is the case in long term policies, the sense of Lomborgs' advocacy depends on the point of view. Lomborgs takes a point of view that only the economy until 2070 does matter anything beyond is not worth considering. Considering that most of us will not be alive at the date in question (I certaqinly won't), the issue becomes more of inter-generation ethics rathrer than economics. It was nicely (although rather vulgarily) described in Australia's Coal Policy to which Lomborgs undoubtedly subscribes.
-
Timothy Chase at 15:07 PM on 23 April 2014Skeptical Science consensus paper voted ERL's best article of 2013
Congratulations! I believe this is well-deserved.
Given the role of free market ideologies in all this, I believe it is worthwhile to keep in mind the following points:
- The fossil fuel industry receives massive subsidies.
- Power utilities are typically government regulated monopolies, and both solar and wind that generates power sold back to the grid offers a more decentralized approach - an approach that is already supported by some libertarian and tea party groups.
- Carbon taxes can be revenue neutral, and with an "across the board" approach in which carbon taxes are entirely offset by reductions in other taxes there is no reason why they can't be implimented on a local level while the regions that apply them remain competitve with those that have yet to do so. (British Columbia seems to be doing quite well at $27.88 per ton with corresponding reductions in income tax.)
Personally? I was a libertarian of sorts (Objectivist, actually, for about a decade and a half), and I am still quite sympathetic towards that sort of world view. I also recognize industrial climate disruption as the single greatest issue facing humanity of our time. Failing to address it will make people impoverished and desperate, and the freedom of the individual tends to be greatly discounted under such conditions.
-
Riduna at 10:30 AM on 23 April 2014Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
Dana – Lucid as ever. That’s quite a fruit salad you’ve got there, apples, oranges and bananas.
And talking of bananas, I have never been able to understand Lomborgs’ persistent preoccupation with the strange notion that its not only OK to do nothing when it comes to mitigation but desirable. Rather like his misplaced advocacy for global warming and claim that increased CO2 emissions are beneficial for us - at least until 2070.
Clearly, both contentions are nonsense, unsupported by climate science and unsupportable by economics, or for that matter common sense.
-
Climate dollars and sense – preventing global warming is the cheap option
I've had this very discussion on a few of the pseudoskeptic blogs (such as here), pointing out that mitigation is far less expensive than adaptation to climate change under a Business as Usual (BAU) economic strategy. And that if the pseudoskeptic is concerned about economic consequences, BAU is probably the worst choice possible.
The usual responses are sputtering (often accompanied by links to something by Lomborg, whose work has issues such as discussed above) or changing the subject. Sigh.
-
jsam at 23:43 PM on 22 April 2014Skeptical Science consensus paper voted ERL's best article of 2013
Better than a bloggie, I guess. :-)
Well done all. -
CBDunkerson at 21:33 PM on 22 April 20142014 SkS Weekly Digest #16
The objection that distributed solar users get to use the electricity grid while paying less than other customers (or nothing if they generate more power than they use) is theoretically valid. The 'proposed solutions' to this 'problem' have all been utter nonsense.
As Michael noted, ALEC was pushing for monthly fees of between $50 and $100 in Arizona. At those rates we'd have to believe that a majority of every electric bill goes to grid maintenance rather than power generation. Even the $5 monthly fee Arizona settled on is almost certainly more than the utilities are spending on grid maintenance... $5 * ~100 million residential households in the U.S. = $500 million per month. That'd work out to $6 billion per year spent on grid maintenance, and that's not counting non-residential customers.... yet most of the U.S. grid equipment is more than a century old and huge sections go offline for weeks every time a major storm rolls through.
The reality is that actual grid maintenance costs are miniscule. The utilities should split out a flat charge (I'm guessing less than a dollar per month) to apply to every customer and reduce the cost per unit of electricity accordingly. Nice simple solution to the 'problem' requiring no legislative action at all. They aren't doing that because the 'problem' is purely a pre-text for attempts to place absurd extra charges on solar. If they succeed then they will simultaneously slow the growth of solar and steal profits from people who do install solar power on their homes.
That being said... there is now a real chance that in a few more years the cost of solar and/or electricity storage will have fallen enough that customers will be able to go off grid entirely and still save money. Either solutions like that or states which refuse the 'maintenance charge' nonsense will lead to solar becoming extraordinarily successful in some areas... which will eventually result in voters demanding the same nearly everywhere.
Prev 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 Next































 Arguments
Arguments