Recent Comments
Prev 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 Next
Comments 7501 to 7550:
-
Odium at 20:41 PM on 27 October 20202020 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #43
I prefer a Trump reelection, the sooner we get close to a "point of no return" scenario the better, at least then, we could have a real informed discussion on a global scale.
Also it's not that i don't appreciate the bashing, but China emitted 2020 close to double the CO2 (10.06GT vs 5.41GT) not that one should take those number all to seriously as there is no sure way to independently verify whether national governments are telling the truth about their own emissions. And i honestly don't think that the worlds factory will stop pumping CO2 into Atmos, just becouse Trump didn't get re-elected. On the other hand, I'm pretty confident that a Biden Presidency would just motivate them to increase it even more.
Moderator Response:[DB] The latest full-year data are through 2018, with 2019 data still provisional. By definition, 2020 is incomplete. The US is by far the leader in both cumulative and per-capita emissions and thus by far the single biggest portion of the overall problem. Discussions on politics must also be tangential to climate change.
-
Eclectic at 19:41 PM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
Boston745 , your "observations and associations" are just personal anecdotes. Not scientific evidence. They seem to be your "feelings". Contrarians have all sorts of "feelings" ~ often mutually contradictory. That's one of the reasons why they can't get their act together.
Yes, those "qualified scientists" (who are very, very, very few) do deserve to be completely dismissed, since they completely fail to provide any valid evidence to overthrow the mainstream climate science. They talk hot air ~ empty rhetoric.
Instances : Drs Lindzen, Spencer, Curry - failed ideas or vague blather based on religious beliefs. No actual backing from scientific observations. And even they don't bother to advocate "magnetospheres and cosmic rays".
Boston745 , have you other "qualified scientists" who are contrarian enough to disagree with the mainstream science - and what is their substantive evidence that they are right and the mainstream is wrong? And why haven't they published it? Major scientific journals would be enthusiastic & delighted to publish some really cutting-edge ground-breaking stuff ! But the contrarians can't come up with anything valid.
Genuine science exists in the collective summary of peer-reviewed scientific papers in reputable journals - it does not reside in fruitcake blogs such as WattsUpWithThat. (If you wonder why I use the label fruitcake, then just go and read through WUWT. )
-
boston745 at 18:02 PM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
You failed to address a single observation Ive made. You completely dismiss qualified scientists who disagree with the mainstream. And you put your faith in climate models that do not factor in things like clouds nor weakening magnetosphere. I'm sorry but it doesn't seem like you're after honest dialog.
Atmospheric scientists have learned a great deal in the past many decades about how clouds form and move in Earth's atmospheric circulation. Investigators now realize that traditional computer models of global climate have taken a rather simple view of clouds and their effects, partly because detailed global descriptions of clouds have been lacking, and partly because in the past the focus has been on short-term regional weather prediction rather than on long-term global climate prediction. To address today's concerns, we need to accumulate and analyze more and better data to improve our understanding of cloud processes and to increase the accuracy of our weather and climate models.
Moderator Response:[DB] Sloganeering and moderation complaints snipped. Merely repeating a refuted assertion without citing credible sources to support your claims is sloganeering. Models do indeed factor in cloud effects. By definition, surface weather and climate are a product of phenomena and physical processes occurring primarily in the troposphere, with some effects occurring above the tropopause in the stratosphere. A weakening magnetosphere or changes in magnetic field strength or polarity have no effects on surface climate because, essentially, air is not ferrous. As for moderation complaints:
"Moderation complaints are always off topic and will be deleted"
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can and will be rescinded if the posting individual continues to treat adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Moderating this site is a tiresome chore, particularly when commentators repeatedly submit offensive or off-topic posts. We really appreciate people's cooperation in abiding by the Comments Policy, which is largely responsible for the quality of this site.
Finally, please understand that moderation policies are not open for discussion. If you find yourself incapable of abiding by these common set of rules that everyone else observes, then a change of venues is in the offing.Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
Eclectic at 17:30 PM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
Boston745 , you really should educate yourself by reading the large amount of scientific information available here on the SkS [SkepticalScience] website ~ included are links to peer-reviewed papers in respected scientific journals, and summaries given by NASA, NOAA, the American NAS, the UK Royal Society . . . in short, by all the peak scientific bodies internationally. No exceptions. Yes there are a few qualified scientists who disagree with the mainstream science ~ but those few "contrarian" scientists have only their opinions (They don't have any facts to back their opinions. They are just hot air.)
I reckon you're pulling my leg regarding: "I know it's not CO2 though".
Barking up the wrong tree . . . could be worse! Like: just barking . . . and no tree in sight.
-
michael sweet at 17:22 PM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
Scaddenp:
Thanks for the reference. Exactly what I wanted to know. As expected, scientists have figured out a complex evolution of mountains in the ocean.
-
Eclectic at 17:06 PM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
Hal Kantrud @857 , the wording of your second sentence is awkward, since it seems to suggest a steady rise in ocean levels during our most recent millennia. Surely that was not what you meant to say. As expected, the very modern temperature spike has led to a sea level rise.
Yet the 4-5000 previous years have been cooling ( roughly 0.7 degreesC) and, as you would expect from basic physics : more cooling overall means more land ice mass and therefore less ocean mass. Does less ocean mass necessarily mean lower sea level globally? MA Rodger's post #843 shows an almost flatline sea level for the last 2000 years . . . but as you have seen discussed, there are many factors & difficulties of measurement ~ so the illustrated "flatline" should be viewed as a rough approximation (and we get into comparing different criteria and even definitions of exactly what is meant by "global Mean Sea Level" and Relative Sea Level). However, that's all "past history" ~ and the problem we now have to tackle is the current & future sea level rise and associated CO2 problems.
Bob Loblaw @856 , thank you for that almost psychedelic picture of the world. I see that it is a model output, so I shouldn't look for granular detail along the coasts!
-
Eclectic at 15:27 PM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
Boston745 :
With or without nuclear explosions, the Earth's magnetic field has negligible effect on climate. Magnetic "reversals" are also of trivial importance. The magnetosphere is very useful in protecting the planetary atmosphere from (geologically) rapid ablation . . . and useful for (partly) protecting your DNA from cosmic ray damage. Another plus, is producing the beautiful auroral lights displays . . . and helping ham-radio operators etc with their long-wave communications. But that's about it. You are barking up the wrong tree.
Likewise, with the idea of cosmic rays somehow altering climate. There's lots of empirical evidence (plus experimental evidence) that the cosmic ray effect on climate is approximately zero [see the appropriate thread ~ linked at #37 above]. Forget about the cosmic-ray / climate connection. It ain't there. You are completely wasting your time on these things.
-
boston745 at 15:22 PM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?

In this animation, the blue lines indicate a weaker magnetic field, the red lines a stronger one, and the green line the boundary between them, at 10-year intervals from 1910 to 2020. The field is weakening over South America, and the red area over North America is losing strength
The Magnetic Field Is Shifting. The Poles May Flip. This Could Get Bad.
Moderator Response:[DB] Please limit image widths to 450.
Earth’s magnetic field is powered by fluid movements in the Earth’s liquid iron outer core, a convective flow called a geodynamo and is powered by gravity and the rotation of the Earth itself. The solid iron inner core inhibits polarity reversals, with the result that such reversals seldom happen, even on geologic timescales.
https://www.nasa.gov/vision/earth/lookingatearth/29dec_magneticfield.html
https://neptune.gsfc.nasa.gov/gngphys/index.php?section=411
https://istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/earthmag/dynamos2.htm
https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/msl/multimedia/hassler02.html
https://websites.pmc.ucsc.edu/~glatz/geodynamo.html
http://news.mit.edu/2010/explained-dynamo-0325
While the Earth's magnetic field is weakening a bit and its magnetic axis is shifting somewhat, magnetic field polarity changes have no effects on climate on the timescale of human lifetimes because air isn’t ferrous. The effects on hand-held compasses are insignificant. For purposes of electronic navigation, changes in the position of the magnetic poles are constantly updated in navigational databases.
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/news/tracking-changes-earth-magnetic-poles
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/news/world-magnetic-model-out-cycle-release
https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/GeomagneticPoles.shtml
https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/faqgeom.shtml
"The last time that Earth's poles flipped in a major reversal was about 780,000 years ago, in what scientists call the Brunhes-Matuyama reversal. The fossil record shows no drastic changes in plant or animal life. Deep ocean sediment cores from this period also indicate no changes in glacial activity, based on the amount of oxygen isotopes in the cores. This is also proof that a polarity reversal would not affect the rotation axis of Earth, as the planet's rotation axis tilt has a significant effect on climate and glaciation and any change would be evident in the glacial record."
And
"The science shows that magnetic pole reversal is – in terms of geologic time scales – a common occurrence that happens gradually over millennia. While the conditions that cause polarity reversals are not entirely predictable – the north pole's movement could subtly change direction, for instance – there is nothing in the millions of years of geologic record to suggest that any of the 2012 doomsday scenarios connected to a pole reversal should be taken seriously."
https://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/2012-poleReversal.html
https://science.nasa.gov/science-news/news-articles/earths-magnetosphere
"Reversals take a few thousand years to complete, and during that time--contrary to popular belief--the magnetic field does not vanish. "It just gets more complicated," says Glatzmaier. Magnetic lines of force near Earth's surface become twisted and tangled, and magnetic poles pop up in unaccustomed places. A south magnetic pole might emerge over Africa, for instance, or a north pole over Tahiti. Weird. But it's still a planetary magnetic field, and it still protects us from space radiation and solar storms."
https://www.nasa.gov/vision/earth/lookingatearth/29dec_magneticfield.html
Answers to many other related questions on that subject can be found here:
https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/faqgeom.shtml
-
boston745 at 12:49 PM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
I understand that cosmic rays aren't germain to the articlr directly. However a weakened magnetic field allows more CR energy in. Its possible that the nuclear testing accelerated that weakening.
The problem with compartmentalization by article topic is that no 1 thing is causing global warming. Multiple factors are at play. Thus its difficult to discuss.
The earths orbit around the sun has brought the earth as close to the sun as it gets in a 400,000 year cycle. Thus the earth is receiving about maximum solar radiation. With a weaker field, more solar radiation gets through and thus more absorption.
Cloud cover is also a factor, which is impacted by moisture in the air, aerosols, & CRs. Clouds can reflect energy or keep radiation in like a thermal blanket.
-
Hal Kantrud at 12:05 PM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
Eclectic thanks for pointing that out. I just noted what looked like quite a marked temperature drop during the last 6000 years pre-spike was accompanied by at least a fairly steady rise in ocean levels. So the sea level data is questionable.
Since the Antarctic ice has stayed relatively stable, it looks like the temperature drop and recent rise has has so far involved only the smaller (less than continent-size) ice sheets. This would be expected if the smaller sheets were thinner, partly above the sea, and assisted by human agriculture, deforestation, and industrialization, as these occurred almost exclucively in the N. Hemisphere because of greenhouse gas emissions. Is an estimate of the proportion of these gasses attributed to the three human activities available? I know even a rough estimate would be extremely complicated because plants use CO2 and N, as well as sequester them, plus we might know little about the extent of hydrocarbon extraction during the last 200 years, forest utilization, etc., but I bet it could be done.
I have read that the entire subarctic zone continues to lift upwards after the glacial ice maximum and subsequent melt. Are there studies showing the contrubution of each to ocean depths?
-
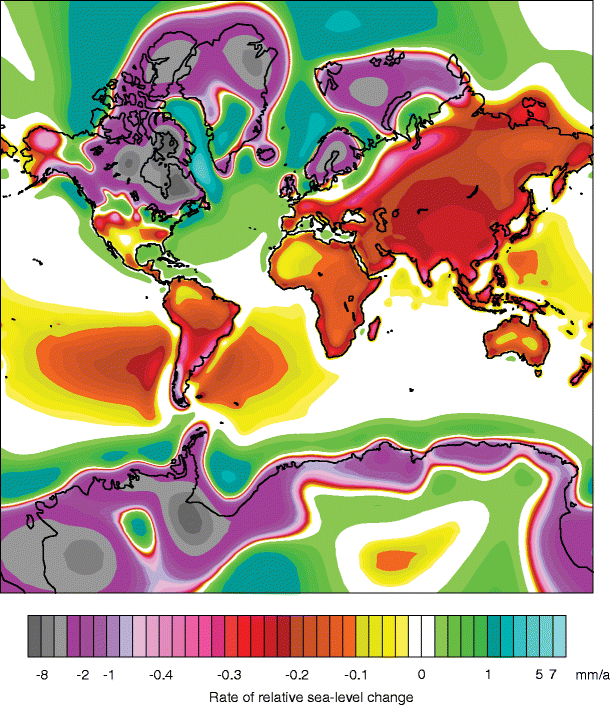
Bob Loblaw at 11:40 AM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
It looks like MA Rodgers image in comment 850 does work if you drop the as=webp part of the URL:
-
boston745 at 11:04 AM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
BTW a decreasing magnetic field means increased cosmic radiation. Cosmic radiation can increase cloud cover, increase hurricane strength, and even lead to massive polar air moving to lower latitudes .
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/12/171219091320.htm
https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014AdSpR..54.2467V/abstract
Moderator Response:[BL] If you want to argue cosmic rays, it is on-topic on this thread:
https://skepticalscience.com/cosmic-rays-and-global-warming.htm
Please read the Basic, Intermediate, and Advanced tabs, and make sure you follow the Comments Policy.
-
boston745 at 10:44 AM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
Why would you remove my post about what chemtrails really are? A combination of airplane aerosol emissions with cosmic rays. A natural phenomenon caused when increase cosmic radiation is incoming from outside our solar system or our sun.
Moderator Response:[BL] Moderation complaints are a pretty fast way to get things deleted.
General Warning
Thank you for taking the time to share with us. Skeptical Science is a user forum wherein the science of climate change can be discussed from the standpoint of the science itself. Ideology and politics get checked at the keyboard.
Please take the time to review the Comments Policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
boston745 at 06:27 AM on 27 October 2020How much has nuclear testing contributed to global warming?
Did nuclear testing cause current warming trends? Stop looking at the energy released and look at the impact of the energy.
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2017/space-weather-events-linked-to-human-activity
Simply put, HANT impacted the magnetosphere in ways they are still trying to understand and was classified until recently. There's a reason this has been classified for the last 50 years.
The magnetosphere is weakening folks and maybe accelerating. Thats established science. That means greater amounts of radiation is able to penetrate into the atmosphere. What happens when you increase energy input of an object? It heats up. It also means more potential cloud cover. Clouds were thought to increase cooling, well thats true but clouds can also increase warming. Clouds can work as either a reflective blanket or thermal blanket depending on type. Consider for a minute the desert. It absorbs the most energy heating up. It also releases that energy into space which is why deserts experience biggest temperature swings. Add cloud cover, less energy gets in but also less energy escapes. Studies have shown that we are experiencing surface warming but cooling troposphere which correlates with an effect clouds can do. Hold energy in reflecting incoming energy back to space.
Moderator Response:[DB] Space weather is not surface weather. That NASA link does not support your claims.
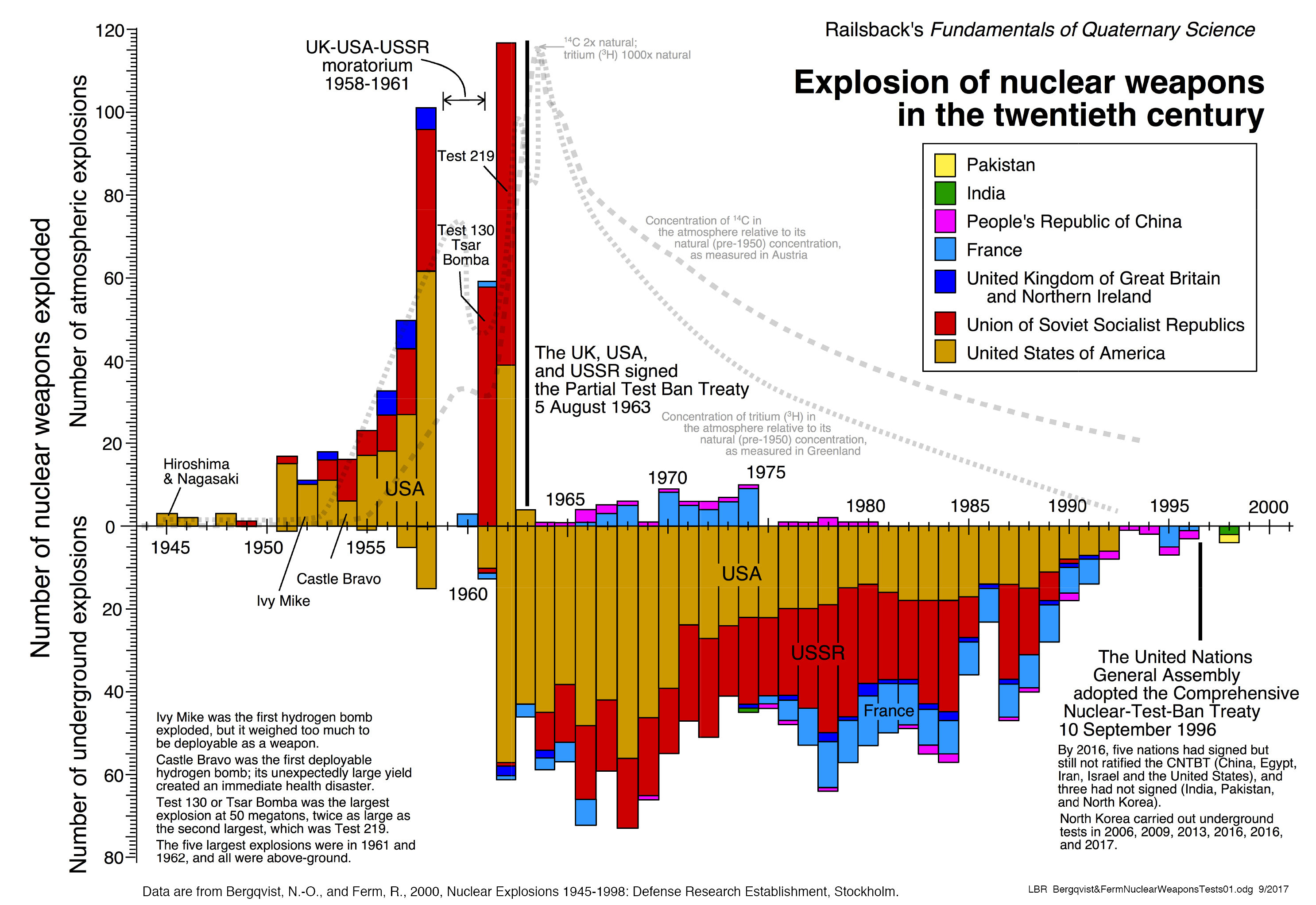
From 1945-2009 there were 2,402 surface and underground nuclear weapon tests. Of those, 527 were conducted above-ground. Of those, some 458 were conducted in the first 20 years of nuclear weapons testing.
Looking at those peak years of testing, the forcing from those 20 years of peak tests of the nuclear weapons on the Earth came to about one eight-millionth of a Watt per square meter (8 x 10-6 W m-2) of power.
For comparison, the 1.8 Watts per square meter (1.8 W m-2) of CO2 radiative forcing as of 2011 generates approximately twenty nine billion, trillion Joules of energy (29 x 1021 J) over the Earth's surface in a single year, or more than ten thousand times as much energy in a year than the entire combined nuclear weapons program of the world had generated in those 20 years.
http://railsback.org/FQS/FQSNuclearWeaponsTesting01.jpg
http://www.johnstonsarchive.net/nuclear/nuctestsum.html
http://www.unscear.org/docs/reports/2008/09-86753_Report_2008_Annex_B.pdf
http://www.laradioactivite.com/site/pages/RadioPDF/unscear_artificielle.pdf
https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/aggi/ -
scaddenp at 05:32 AM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
Michael - see here perhaps. This is hydro-isotasy at work as opposed to rebound from weight of ice. Extra weight of water from ice melt deepening the ocean basins, dropping sea level slowly.
-
michael sweet at 03:45 AM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
A long time ago someone at SkS suggested that sea level in the Pacific ocean peaked about 3-5,000 years ago and then went down about 1.5-2 meters. This explained how atolls formed and why they have coral rock above current sea level.
I do not see this change in MARodgers graph at post 843 but it seems consistant with his post at 850. Is sea level change the current understanding of how atolls came to be above current sea level? (Most atolls in the Pacific have 1-2 meters of coral stone at their core which cannot form above sea level. Sea level could have changed more than that.)
-
One Planet Only Forever at 03:18 AM on 27 October 20202020 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #43
nigelj,
The following is my current understanding of the problems faced by efforts to develop sustainable improvements for the future of humanity. Better understanding a problem, and the desired outcome, is one of the most important steps in developing sustainable solutions, as every Engineer is very aware.
Regarding reactions to climate science and climate change information and misleading claims, a major difference between the USA and NZ is probably that, relative to NZ, the USA has more powerful wealthy people who have their wealth and power because of fossil fuels. They would lose status if the changes of how people live that are required to limit the climate change harm done to future generations are actually achieved. Increased awareness and understanding of the need to meet the Paris limits makes these powerful wealthy people more likely to lose their status. And that threat of losing their perceived status causes some of them to mentally 'lose it' and double down on harmful misleading marketing rather than striving to honestly change to be less harmful and more helpful.
Other possible reasons for the difference regarding harmful populism in the USA and NZ could be:
- The USA is the least Socialist of the supposedly more advanced nations. I use 'supposedly' because it highlights that 'impressions of advancement' may be misleading. Increased wealth or increased technological development that does not result in sustainable improvements of the living conditions for the poorer portion of the population is not 'advancement'.
- The USA, since its foundation, has been a nation of Anglo Saxon Colonists pursuing ever expanding Superiority for 'Their Tribe' relative to all 'Others' (the reason I pointed to "White Fragility" as a book to read). Books like "The End of the Myth" by Greg Grandin present an accurate and unflattering history of the formation and expansion of the USA (violent disregard for Others is a powerful part of the USA's history). And many Americans are still powerfully motivated by their collective lack of social development on acceptance of diversity and the related need to systemically more equitably treat the diversity of humanity.
- In the USA the 'pursuit of freedom' has been about the more freedom for powerful wealthy property-owning people (with property including Other people) to become more powerful and wealthier (small government having no role in regulating economic activity, not limiting the harm it does). It includes protection of the ability of likely unjustly acquired wealth to be passed to children who may be even less deserving of having that wealth and power. The wealthier a person is the more helpful and less harmful to Others that person needs to be, or the advancement of society is slowed or reversed.
- The USA has a 2 party system which makes it easier for the greedy and intolerant people to gather together and claim that 'The Other is the enemy'. And the history of the USA explains why the 2 Parties in the USA substantially share the objective of protecting the wealth of the wealthy. However, currently the Democrats are leaning towards being more Socially Sharing and Caring due to their party including the Social Democrat thinking. Multi-party systems may make people more aware of diversity rather than seeing things as Black-White Us-Them. In Canada there is only one party heavily focused on promoting greed and intolerance, the merged Right-Wing Conservatives. There used to be a Progressive Conservative Party that was centrist, but it disappeared when it merged with social conservatives and increased appeals to greed (which used to be in fringe parties). The inability of the hard Right-wing Party to get along with a diversity of Other Parties may make more people aware that it is the uncooperative party that is the problem, rather than a 2 party system where 'The Other' can always be blamed.
Another difference between the USA and NZ is that the Separation of Church and State has been removed by the current Republican pursuit of popular support from fundamentalist religious groups, because there is such a large population of fundamentalist evangelical religious people (and those people appear easily inclined to believe conspiracy theories about 'Those Others - Their Enemies').
A related difference between the USA and NZ may be that the USA has also amplified the power of wealth in government. It is clear that democracy requires a separation of Wealth and State (read Thomas Piketty's "Capital and Ideology") so that the State can act as the Responsible Governor of what is going on to limit harm done and help develop sustainable improvements for the least fortunate.
In summary, Social Democracy that effectively limits the influence of Religion and Wealth on the actions of Government may powerfully inoculate populations against populist autocracy. Note that anti-Socialism is part of the misleading marketing attacks by the greedy and intolerant portions of many populations that have joined forces to try to win the power to do as they please. Selfish people are more inclined to be harmful to Others, and less inclined to be helpful to Others. They easily dislike the idea of being 'forced to share and care by Government'. Any government that would do that is part of the 'Others'. They want the freedom to 'Win higher status any way they can get away with'. To them 'Harm Done is justified by Benefits Obtained'.
Closing back to climate change and climate science. The belief in conspiracy is strong in people who have developed preferred beliefs that are contradicted by expanded awareness and improved understanding of how to be less harmful and more helpful to Others. To maintain their perceptions of status and related beliefs, they accept anything that appeals to them, including the ability to declare themselves to be the Victims - of conspiracies, which requires the belief that there is no Objective Reality as a basis for Common Sense, every belief is equally valid - because of the barage of falsehoods they have developed a liking for but have been unable to make sense of.
-
Bob Loblaw at 01:16 AM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
Eclectic:
A direct link to MA Rodger's figure is:
I notice that it is formatted to display is as a webp object, which might be breaking things for you if that format is not supported in your browser. It seems to be a Google format. YOu might try dropping the "as=webp" part.
As for isostatic rebound: keep in mind that it is a local effect. The crust is depressed where ice weighs on it, and rebounds when ice is removed. Areas around the ice do the opposite - they flex upwards when the ice pushes downwards, and move back down when the ice is removed. Think of what happens when someone places an object on a waterbed.
Interpreting sea level changes due to glaciation is rather complex, and evidence is difficult to find.
-
Eclectic at 00:14 AM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
Correction :- not Peltier (2002) , but Khan et al. (2015) as per link in #850
-
Eclectic at 00:05 AM on 27 October 2020Climate's changed before
MA Rodger @850 ,
sorry, but your diagram [relative sea level map] is not loading for me. (And yes, Nigelj, I have tried 3 computers!! ) I will take a stab, and presume the diagram is from Peltier (2002) .
If I understand you correctly, then relative sea level (disregarding the "short term" alterations from thermal volume effect and total mass change) during the Holocene interglacial . . . ought to receive a major influence from isostatic rebound of subpolar land regions, as well as from the more general land "rebound" secondary to oceanic siphoning. And both of these rebounds should produce a late-Holocene fall in relative sea level (i.e. measured at shore-lines). Perhaps excepting special cases like southern Britain.
To all of which, we can add in some extra fall secondary to late-Holocene cooling that reduced ocean temperatures and also deposited more ice on land ~ an amount of ice presumably rather less than the 30-meter deposit I mentioned in last paragraph of #849 . . . (a deposit too marginal to really decrease the land rebound).
I guess the whole question comes back to the nett result on "Mean Sea Level", from all these various factors. In view of all the difficulties in local measurement of millennial changes, I am not surprised by the scatter of results from different studies on this topic.
Almost - but not quite - it is enough to feel some sympathy for that remarkable outlier, the (recently) late Dr Moerner.
-
MA Rodger at 20:27 PM on 26 October 2020Climate's changed before
Eclectic @849,
In the past, I do recall SLR free of significant tectonic movement being claimed as a good indicator of global SLR and that it usually concerns Australian data but I'm not sure such claims usually attach to late Holocene SLR. Lewis et al (2008) and indeed Lewis et al (2013) and Lewis et al (2015) are concerned with the late Holocene and more so the Australian record than establishing a global record. And their findings are not so clear cut although a significant drop in sea level post-7,500y bp has been established. The 2013 paper concludes:-
"A clearer understanding of past sea-level changes and their causes is urgently needed to better inform our ability to forecast future changes. A concerted effort is required ... to address the issues of whether there have been oscillations of the sea surface and if so, of what magnitude. The pattern and rate of fall from the Holocene highstand to modern levels, and of the contributions of the various factors to this change, both global ‘eustatic’ or ‘steric’ components and local geophysical, tectonic and land instability issues also need to be addressed."
The work to unravel the late Holocene global SLR record is far from complete and I see no evidence of the Australia (Oceania) data providing a short-cut to providing a conclusion. Thus, the conclusion from, for instance, Khan et al (2015):-
"Far-field Relative SL records exhibit a mid-Holocene highstand, the timing (between 8 and 4 ka) and magnitude (between <1m and 6 m) of which varies among South America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania regions."
And on the reasons:-
"The Relative SL signal of many far-field locations is characterized by a mid-Holocene sea-level maximum, or highstand, at the time meltwater production decreased. The fall in Relative SL to present is due to hydro-isostatic loading (continental levering) and a global fall in the ocean surface due to both hydro- and glacio-isostatic loading of the Earth’s surface (equatorial ocean siphoning). Perturbations to Earth’s rotation driven by mass redistribution also cause Relative SL changes in far-field regions to depart from the eustatic value. These processes occur during the deglacial period but are not manifested in far-field RSL records until the early to mid-Holocene because the eustatic signal is dominant prior to this time. Far-field locations are characterized by present-day rates of Relative SL change that are near constant or show a slight fall (<0.3 mm/a) in [rate of] Relative SL (Fig 1)."
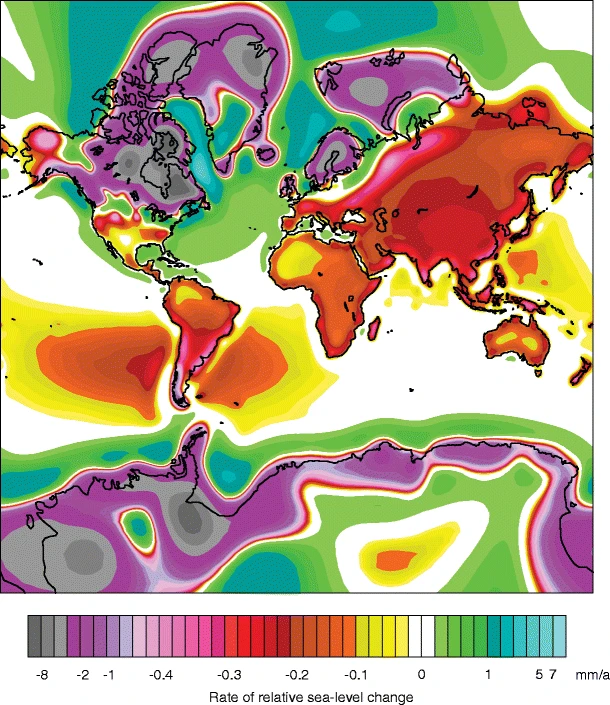
-
takamura_senpai at 17:18 PM on 26 October 2020The Debunking Handbook 2020: Debunk often and properly
People say what is profitable/gainful, NOT they realy think. USA produce more CO2 than whole Africa + S America + ...much more, if we look on goods which USA consume. Latin America + half Africa + others is a USA colonies, so MUST produce huge CO2, they must supply USA with many things.
For example: Brasil paid > 1 trillion to USA in last 20 years, and debt is higher and higher - colony. -
nigelj at 15:49 PM on 26 October 20202020 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #43
OPOF, I have a copy of Post Truth, by Evan Davis so that is another one to add to the list.
Your explanations sound quite good, although I'm still puzzled why we haven't seen quite the same extent of problems in NZ, ( we have seen some and it is growing a bit) but it may partly relate to geography and size and location, in that we are very small and very reliant on trade and international alliances which does open the mind and make people more tolerant of 'foreigners' and international organisations, and very aware of what happens in other countries. Fake news and xenophobia finds it harder to gain traction in that sort of environment.
America is so large it's almost self contained, and certainly trades less on a per capita basis than us, all of which might create a little bit of a bubble where fake news can gain traction along with anti foreigner sentiments, and if you tap into that racial dimension with appropriate falsehoods and emotive rhetoric, you pretty much have people under your control. We have had politicians like that and our share of xenophobes, but they are getting less and less traction. It was actually a free trade agreement with China around 2006 that got us through the GFC, and people are grateful.
-
Eclectic at 13:34 PM on 26 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
RedBaron @22 ,
thanks for that info. I did see that a charge would not be made until 28 Oct . . . but I wasn't clear whether that applied only to donations which were in excess of the official target. The wording was a touch ambiguous ( I thought ). I am guilty of overthinking the wording.
BTW my original computer has still shown the defective pop-up window on the Experiment.com website. Perhaps my software is not as up-to-date as I had believed. All the same, it might be worth dropping a word to the site Administrator, to check that the donation "mechanism" is functional for a wide range of operating systems (both ancient and modern) ~ if such is possible in a secure way. Every fishing line should have a hook on it!
2nd BTW ~ and thanks, RedBaron, for the Widow's Mite tale you had mentioned earlier. No reply from Mr Keithy, I see.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 13:24 PM on 26 October 20202020 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #43
nigelj,
What is happening in the USA is a massive effective misleading marketing campaign that appeals to people who believe they should be masters of the world, or at least the masters of their part of the world, or at least the masters of what is believed in their part of the world (or more likely aspiring toward as much of the above as they can get away with).
Post-truth or some version of it is discussed in many books. And many of them were written decades ago about how Lenin and Hitler openly told falsehoods and bombasted their way to steamroll evidence-based understanding, common sense, out of the minds of many to establish popular belief in what they claimed.
The onslaught of nonsense that appeals to a gut-reaction, first impression, emotion-triggered type of response over-whelms the ability of many people to figure out what is actually verifiable common sense. People feeling a little less successful than they believe they should be are easily led to believe they are being cheated by 'Others'. And in the USA, white or english-speaking or evangelical-christians or men (or any combination) are feeling cheated out of their Perceived Right to forever continue, strengthen, and expand their rule over Others in their part of the USA, all of the USA, and around the world. And another group that is easily triggered is greedy people who want more status relative to Others any way they can get away with. That greedy group has figured out how to appeal to the first group to get more support for their fight against the rapid ending of fossil fuel use.
The first book I read about the attack on 'Reason' and 'Evidenced based understanding' was Al Gore's "The Assault on Reason". More recent books on the topic of post-truth include Masha Gessen's "Surviving Autocracy" and Michiko Kakutani's "The Death of Truth".
Other books about the current state of affairs in the USA include "On Tyranny" by Timothy Snyder, and "White Fragility" by Robin DiAngelo.
The problem is not because of Trump. The problem in the USA has been developing towards something like Trump becoming President for a while now.
-
RedBaron at 11:55 AM on 26 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
@20 Eclectic,
Your card won’t be charged unless the project is fully funded.
-
nigelj at 11:44 AM on 26 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Eclectic @20, I made a donation some hours ago and having read your comment I just checked my credit card account, and payment not registering either, so its probably a delay. I think it can take a day or two sometimes.
I'm a bit like Scaddenp, so a bit sceptical about the whole soils issue, but I think basically its because more information is needed, and experiments like this help. Its a worthy cause.
-
Eclectic at 09:01 AM on 26 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Nigelj @18 ,
thanks - I have now tried another computer, and possibly successfully!!
Mine is an all-Apple household, so I figured (in my klutzy way) that simply shifting to another Apple would make no difference. But quite wrong. The second computer brought up Scott's webpage, and the pop-up window this time appeared to be perfectly conventional & fully functional in accepting details (including credit card). So now I have donated - possibly. I say possibly, because Scott's webpage shows a coincidental contemporary uptick in his total . . . but my credit card account shows no deduction yet.
I shall keep an eye out - I hope it's just some electronic "lag effect".
-
scaddenp at 07:15 AM on 26 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
I should clarify that I am not in anyway involved in the experiment except as one of the donars. I have been very skeptical of the experimenter's claims made on this site in the past but the weight of evidence provided by him has convinced me that:
a/ should his hypothesis be correct, then his methods could make very useful contributions to mitigating global warming (with plenty of environmentally useful addition as well)
and
b/ this hypotheses has promising supporting evidence and deserves further experimental testing. The proposed experiment and the conditions of experiment.com should provide useful evidence.
-
nigelj at 05:07 AM on 26 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Eclectic, I just signed up for red Barons website ok. Suggest you try using another web browser or computer.
-
Eclectic at 22:33 PM on 25 October 2020Climate's changed before
MA Rodger @847 ,
thanks for that information. Re late Holocene MSL decline, I must confess I was relying on memory of seeing (several years ago) a graph of the Holocene highstand declining by 1-2m during the most recent 4-5000 years, as the global temperature reduced by around 0.7 degreesC. As you say, I might have been rather faultily recollecting something which lacked land "rebound" compensation.
On the other hand ~ a quick googling turns up SE Lewis et al. (2008) showing an eastern Australian fall in MSL of 1-1.5m over the period 7000-2000 BP. Eastern Australia (excluding Tasmania) had very little burden of ice sheet at the last glacial maximum (to rebound from) . . . and Australia has been tectonically relatively stable, as well ~ so it is a useful basis for Holocene MSL trends.
I think I may be misunderstanding your IPCC reference where: "Ocean volume between about 7 ka and 3 ka is likely to have increased by an equivalent sea level rise of 2 to 3 m." If the lagging effect of Holocene warming produced a likely 2-3m MSL rise over the period about 7000-3000 BP . . . is that inconsistent with a 1-1.5m MSL fall in the last 3000 years? [Assuming some fuzziness/uncertainty in the Lewis et al. dating]
As a matter of interest, I did a quick back-of-envelope calculation: indicating that for a 1m fall in MSL, the depth of ice on Greenland/Antarctica would need to increase by about 30m. This ignores oceanic thermal contraction and glacier expansion in non-polar regions.
-
MA Rodger at 19:50 PM on 25 October 2020Climate's changed before
Hal Kantrud @845,
There is certainly a timelag between temperature rise and ice loss and with big ice sheets the lag can also be big (but not necessarily). The current level of AGW is put at 1ºC and the sea level rise so far at 20 or 30 cms. Yet the anticipated sea level rise per 1ºC AGW is put at 230cm over a period of a couple of millenia. But additional to that 230cm/1ºC is Greenland which maintains its ice sheet solely becuse its summit is high up surrounded by cold atmosphere. It is anticipated that somewhere between 1ºC and 2ºC of AGW, the summit of Greenland's ice will drop into an unstoppable melt-out as the summit decends into warmer atmospheres, this adding a further 600cm to sea level over perhaps ten millenia. I say "unstoppable" in that it would require a return to ice age conditions to stop the melt and build the summit back up into colder airs.
Regarding the chopping down of woodland, this is globally not New World.
-
MA Rodger at 19:34 PM on 25 October 2020Climate's changed before
Eclectic @844,
I'm not sure where you get the metre drop in late Holocene sea levels. There have been dropping sea levels in some locations through the late Holocene but that is due to isostatic rebound caused by the redistribiution of mass - melted ice sheet flowing into tropical seas. The accepted wisdom as I understand it is still as per IPCC AR5 Ch5 5.6:-
"Ocean volume between about 7 ka and 3 ka is likely to have increased by an equivalent sea level rise of 2 to 3 m."
"For the past 5 millennia the most complete sea level record from a single location consists of microatoll evidence from Kiritimati that reveals with medium confidence that amplitudes of any fluctuations in GMSL during this interval did not exceed approximately ±25 cm on time scales of a few hundred years. Proxy data from other localities with quasi-continuous records for parts of this pre-industrial period, likewise, do not identify significant global oscillations on centennial time scales."
-
RedBaron at 19:07 PM on 25 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Keithy,
One of the donors lost her farm when the Russians annexed Crimea. As recently as 6 months ago she was struggling to avoid becoming homeless when Corona hit, having her whole family disrupted and nearly "refugee status" around Kiev, an already poor country before the war. And I never asked her for a dime, just showed her the work I am doing to help farmers back when I first designed this, before the corona delay. She told me back then she was almost in tears to think people she never even knew were working so hard to help people they don't even know. So clearly this isn't about being "rich". I was even embarrased that she donated. I wished she would have told me, so I could have stopped her. But you know how farmers are, stubborn to the core.
The whole point of a crowd funding science is to have lots of people donate really small amounts, so that no single person needs to dig deep at all. And then the science is open sourced for all to benefit. In this case there were a few bigger donors and I am eternally grateful and amazed. But that tiny donation from a displaced farmer who lost almost everything she owned so recently, touched me more than I have words to express.
I will bet my bottom dollar Scaddenp was just frustrated, as most of us here are, by the lack of people realizing how important mitigating AGW is.
My friend from Crimea knows first hand how quickly our lives can change through forces out of our control. I am pretty sure that's the sort of motivation the whole world needs to think about, as about 80-90 % of the World's population is in danger zones from unmitigated AGW, whether from coastal flooding, droughts and fires, or war.
There is another group of farmers that know all too well what's in store for us all. Maybe you heard of them?
The Ominous Story of Syria's Climate Refugees
So please don't be too hard on Scaddenp. We are all in this together.
-
Keithy at 17:20 PM on 25 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
@ 12: scaddenp, Who are you to be disappointed? The world doesn't owe you anything --> especially when you consider it gave you everything.
How ungrateful are you for being so rich by mistake?
Moderator Response:[BL] You are pushing the envelope in inflammatory rhetoric. Tone it down.
Skeptical Science is a user forum wherein the science of climate change can be discussed from the standpoint of the science itself. Ideology and politics get checked at the keyboard.
Please take the time to review the Comments Policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
Eclectic at 13:55 PM on 25 October 2020Climate's changed before
Hal Kantrud @845 , your first paragraph is crossed-up.
As the planet cools 0.7 degreesC during the past 5-ish millennia, more land ice forms, and so the sea-level falls. MA Rodger's graph (above) is a broadbrush illustration of sea-level, yet data fuzziness does not illustrate the small fall (roughly in the region of 1 maybe 2 meters in the past few thousand years).
As far as I have gathered, the broad scientific opinion favors a return to atmospheric CO2 level around 350 ppm. Incorporating carbon into deeper soil is a worth goal, but probably will be too slow (and limited) to achieve a negation of all the recent & continuing fossil fuel usage.
-
Hal Kantrud at 12:06 PM on 25 October 2020Climate's changed before
Thanks. To narrow down, the graphs show temperatures dropped during the last 6 millenia, while sea levels rose about 2m. One would think sea levels would rise, so is there a time lag working here?
CO2 increased during this period till the recent spike. There is no data on NH4 and SO2, but I thought this mix tended to prevent reflection of the sun's rays and thus increase temperatures.
I am not convinced that 'cutting trees' in the New World was as important a source of human CO2 emissions as the switch of grasslands from the production of perennial grasses to annual crop plants and domestic animals. Forest soils are notoriously poor in carbon and most is sequestered in the trees themselves, whereas perennial grasslands sequester most carbon deep underground while evolving in cycles of frequent fire and intense herbivory. Soils dominated by grasses have always been the first to be heavily exploited for food production ("the land of milk and honey") and were where our staple foods such as wheat, rice, barley, etc., were domesticated. So to seriously tackle the problem of high CO2 levels, it would be more efficient to seed perennial grasses, whose root systems remain the only viable net CO2 sink. Trouble is those areas are the source of most of our food!
-
Eclectic at 10:44 AM on 25 October 2020Climate's changed before
Hal Kantrud , I would like to add a few disparate points which may be of interest to you. (And you may already have come across some of them.) As always, I shall be grateful if MA Rodger (who is extremely well-informed on climate matters) sees fit to make any corrective comment!
1. The term "BP" / bp stands for Before Present, but does not mean "up until right now this year of [2020]". BP is a convention used by the paleo scientists to standardize the reference to past ages - whether centuries, millennia or mega-years [ma]. BP at point zero is taken as year 1950.AD
Some "contrarians" have not been aware of this convention (for instance the slightly-contrarian scientist Loehle has had to go back and correct some of his work, because he was initially unaware of the paleo convention).
Hal, this paleo convention is enormously important, since there has been a huge rise in global surface temperature since 1950. Even today, some Denialist blogsites are publishing graphs which misrepresent reality, and are showing a graph's final temperature as 2000.AD or 2010.AD . . . when the original graph only went up to 1950.AD . . . and worse, the denialists have sometimes doctored or airbrushed-out the most modern temperatures. Sometimes this deliberate deception is outright concealed - and sometimes the deception is camouflaged under the term "Adapted from [a certain scientific paper]" .
Another small point is that some of the ice-core temperatures are recorded up until around 1855.AD , since later/shallower levels of ice are unrepresentative of their ambient conditions.
[You will have noticed how almost all science-deniers are still falsely (and vehemently) asserting that both the Holocene Maximum and the MWP were hotter than 2000.AD and current years.]
2. The Holocene Optimum [sometimes called Holocene Maximum] was roughly 8000 years ago, but as MA Rodger rightly points out, the Maximum was more of a plateau of roughly 5 millennia. Over the succeeding 4 or 5 thousand years, the temperature has dropped roughly 0.7 degreesC as part of the background cooling which would eventually lead into the next glaciation. But AGW has intervened - with global temperature rising like a rocket in the past 100-200 years (dare I say like the end of a Hockey Stick?) Hockey Stick is yet another term which causes Denialists to choke on their cornflakes.
As a consequence of the natural cooling down from the Holocene Maximum, the global sea level has reduced by about 1 or 2 meters . . . and that fall should have continued onwards as we slide into the next glaciation. Except for the modern AGW-caused rise in sea level, a rise which is slow but accelerating.
3. Each glaciation cycle of the past 800,000 has been subtly different, owing to differences in the variations of the Milankovitch cyclings. That makes it difficult to predict when the next glaciation would have occurred in the absence of human influence. One figure I recall seeing, is the next chilly glaciation being due in roughly 16,000 years. So we humans have plenty of time to fine-tune our climatic effects before any threat of severe glaciation! (Some denialists maintain that the "New Ice Age" was due in a few centuries from now . . . and our anthropogenic CO2 has fortuitously been raised only in the nick of time... )
4. I won't comment on your point of interest about the New World grasslands. The changes there would be quite minor in the overall picture.
-
nigelj at 07:14 AM on 25 October 20202020 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #43
"We have the Trillion Trees program. We have so many different programs. I do love the environment (says Trump)”
Trump does not have a one trillion trees programme. America does not have a one trillion trees programme. Its all spin. Trump is just joining something called the "global one trillion trees initiative" which is funded by many countries. in terms of Americas contribution it mostly amounts to planting some extra trees in the USA on conservation land.
Its also "tokenism" because the actual planting plan in the USA is a small part of the solution to climate change. Politicians often have token programmes to try to keep everyone happy, things that sound nice and dont cost too much or ruffle corporate feathers. Some references on the tree planting programme here and here.
We have just had a general election in New Zealand. A centre left leaning Party won, and the centre right party lost in a landslide. The interesting point is the leader of the losing Party was a little bit like Trump in style and personality, although the policies were different except for her very dismissive attitude to climate change and other environmental problems. There is some good evidence that most people are not too impressed with her style (polling and commentary) and perhaps her position on climate change.
Given all this and other evidence, I doubt Trump would get more than 5% support in NZ or Australia. I simply dont understand whats going on in the USA, and how anyone could support a leader who has been so ineffective on really crucial things, and who gets so many facts wrong, regardless of whether the leader leans left or right.
-
MA Rodger at 22:21 PM on 24 October 2020Climate's changed before
Hal Kantrud @842,
To address your three requested points of clarification/confirmation.
(1) The only actual continent-sized ice sheet is Antarctica and that remains unaltered in size through an interglacial and through a glacial maimum. The glacial maximum see the growth of ice sheets across the northern half of N America, Greenland and N Europe. The Greenland ice sheet has survived the present interglacial but was melted out in the previous one.
The impact of small wobbles in global temperature is not significant within this process as the temperature change is small and it doesn't last very long. The ice melt is a slow process. Thus, while global temperatures stopped rising 10,000 years ago, the melt continued strongly for a further 2,500 years and less strongly for another 4,000 years, this shown by the sea level record.

(2) Your timings are a little off. After the Holocene peak temperture (best considered as a plateau 10,000y to 6,000y bp), global temperature has been dropping but only to the equivalent of 11,000y bp. 13,000y bp would have you back in the Younger Dryas event when it was very cold.
(3) The CO2 record from ice cores does show previous interglacials with CO2 (& CH4) levels falling quickly from the peak of the interglacial. This is not the case for the present interglacial when CO2 (& CH4) levels are shown to rise not fall. This has led to some interesting work setting out the idea that the activities of mankind are responsible for this early rise, for CO2 perhaps dating back to 8,000y bp (& 5,000y bp for CH4).
While this work remains speculative, the CO2 (& CH4) levels through this interglacial would act to slow the drop back into a glacial maximum.
The unprecedented CO2 levels likely now top the CO2 levels seen 3 million years ago (this was back when N America was joined S America at Panama and initiated the Arctic ice) and are thus uprecedented in 13 million years, thus back to a time when weathering of the newly-formed Himalayas caused reducing CO2 levels.
....
And addressing your main question which concerns the CO2 levels of the last few centuries rather than those of the late stone age because any increase pre-industrial cannot be the result of fossil fuel use.
According to the Global Carbon Project, the anthropogenic CO2 emissions since pre-industrial amount to some 650Gt(C) of which 450Gt(C) results from fossil fuel use and 200 Gt(C) due to Land Use Change, but note this is mainly cutting trees down not "the conversion of New World grasslands".
-
Eclectic at 15:50 PM on 24 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Sorry, RedBaron, but I still can't access via Sign In. The pop-up window does not allow me access to email & password fields. Very strange.
I see at the bottom right corner of the [experiment.com] Home page there is a field where I can request the regular newsletter emailed - but I am not wishing to enrol for the newsletter.
RedBaron, you probably can't do anything to raise my IQ to something above moron status. But it may be worth your while to contact the experiment.com Administrator, to see if there is some attention needed to the pop-up window that I mentioned. ( I shall check back in a few days to see if the Home page has altered.)
-
Hal Kantrud at 13:23 PM on 24 October 2020Climate's changed before
Thanks. So we are in a period of the current Ice Age where continent-size ice sheets cover land at the poles. While waiting for the next Ice Age, we experience cooling periods, (phases) but these are too small to significantly increase the size of the continental ice sheets. Does this imply that the warming periods or phases will not significantly reduce the size of the ice sheets?
Am I correct in reading the graphs that during the Holocene, Earth reached peak temperatures about 8000 YBP and has since cooled down to temperatures reached about 13,000 YBP, but during the last 200 years has spiked to levels far above those observed during the Holocene peak?
Can I also say that atmospheric CO2 levels followed an opposite pattern, slowly increasing during the last 8000 years, only to spike upwards during the last 200 years to unprecedented highs?
My main question concerns the latter. What portion of the recent spike in CO2 can be attricuted to the conversion of New World grasslands to agriculture and pasturage and what portion can be attriubted to the increased use of hydrocarbons worldwide?
-
RedBaron at 04:18 AM on 24 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Eclectic,
I am not exactly sure what you mean, but if you follow the page you will see this at the top right: Discover Start a Project Sign In
Click "Sign in" and it will ask for an email and a password, or you can use facebook if you want.
Fill them in click log in and it will sign you in. Then you can go to my project and click "Back this project".
-
One Planet Only Forever at 00:57 AM on 24 October 2020What does the global shift in diets mean for climate change?
RedBaron@28,
Agreed. Pursuing Sustainable Development, which humanity needs to pursue in order to have a lasting improving future, aspires to develop the most sustainable ways of living. That involves doing everything more sustainably, endlessly pursuing better ways of doing things.
The less fortunate seldom have the luxury of choice and have limited ability to learn about their choices. The more fortunate have 'No Good Excuse'.
Differences in the impacts of the ways of growing different foods should be the basis for the choices that more fortunate people make. The more fortunate a person is, the more helpful and less harmful their choices should be required to be (the ball and chain of being more fortunate is the obligation to Be Better).
A related point is that unnecessary over-consumption, like eating more than 100 g of meat in a meal or eating meat in 2 meals a day, needs to be ended. The less fortunate have no role to play in that effort. That one is totally on the more fortunate. And the more fortunate a person is the greater the expectation, or requirement, for them to actually be Better Examples that way (that ball and chain of more responsibility for the more fortunate to be less harmful and more helpful).
-
Eclectic at 20:41 PM on 23 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Scaddenp, I wish to donate funds, but am running into an obstacle.
As a computer klutz, I don't recognize what I am doing wrong. There were some earlier problems I had, a couple of weeks back. But now that you have reminded [us] to donate, I find a new problem :-
when I click on the donating field, up pops a window with : "LOG IN"
plus [second line] : "Don't have an account yet? Sign up."
Unfortunately, the LOG IN [etc] announcement almost fully overlaps the first field below it - and I cannot access the first field. ( I can access the email field and the password field which are below that. )
Is there some extremely simple mistake I am making? Do the experiment.com people need to re-jig their layout? (Worse - are other potential donors getting frustrated and abandoning the attempt?)
[ Mine= ancient Apple desktop, but with up-to-date software, I believe. ]
-
scaddenp at 07:43 AM on 23 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
Hm. I am disappointed with funding so far. This is an interesting experiment that deserves your support. Advertise it on your facebook etc. people.
-
RedBaron at 07:19 AM on 23 October 2020What does the global shift in diets mean for climate change?
Like most foods, rice is similar. It's not rice that is the problem, but how we raise the rice that matters.
The System of Rice Intensification (SRI)…
… is climate-smart rice productionIt's not meat that matters, but how we raise that meat. Rice, wheat, meat, timber, you name it. There are right ways to raise it and wrong ways to raise it.
“Yes, agriculture done improperly can definitely be a problem, but agriculture done in a proper way is an important solution to environmental issues including climate change, water issues, and biodiversity.”-Rattan Lal
-
One Planet Only Forever at 06:17 AM on 23 October 2020What does the global shift in diets mean for climate change?
nigelj@26,
I agree that lots of people 'rely' on rice for basic food needs.
I would say that the more fortunate people 'choosing' to eat rice may be more helpful regarding climate impacts, and other impacts, if they reduced their rice consumption and replaced it with lower impact alternatives.
With global population still increasing, increased areas for rice cultivation would be a concern from a climate and biodiversity impact perspective (and other impacts). And reducing the extent of areas already under rice cultivaton would, like reducing areas needed for cattle raising, be helpful from a biodiversity perspective.
-
RedBaron at 14:32 PM on 22 October 2020A Skeptical Science member's path to an experiment on carbon sequestration
For those considering funding this trial, I thought it might be useful to post a more formal link to the hard science supporting the reprint of now defunct Australian Farm Journal article. Here you can find the methods, scope, and results supporting Dr. Christine Jones claim for a CO2e sequestration rate of 5-20 tonnes CO2e /ha/yr "under appropriate conditions".
The role of grazing management in the functioning of pasture ecosystems
And here is a published paper from the US confirming a similar rate.
I should caution though. While the first one did include both grazing alone and pasture cropping, the second by Teague was only comparing various grazing strategies and did not include any cropping at all, nor was it a long term study either.
Since I am cropping only and only simulating grazing with a mower and compost, I really don't know what the rate of carbon sequestration I will find will be at all. I am as curious as the rest of you. Also the scope of the trial I designed is quite limited. I designed this to be potentially useful for those farmers wishing to help mitigate AGW by changing agricultural methods and become eligible for carbon credit payments. So the audience I am mostly looking at is not PhD's, but just ordinary farmers. So my scope is very modest.
If funded of course all this and more will be added to the lab notes section.
I would think that it would take a much more expensive trial and a formal team of full time research scientists to follow up if the results I find are interesting and/or significant. But the results I find should be useful "in the field" for actual action mitigating CO2 rise in the atmosphere.
We will see?
And the link for those who haven't been there yet.
What is the rate a new regenerative agricultural method sequesters carbon in the soil?
-
Eclectic at 12:10 PM on 22 October 2020Climate's changed before
MA Rodger @835,
Thanks. Yes, I had heard that the "frozen Thames" events had occurred even during the Medieval Warm Period (though those are never mentioned by Denialists).
I was interested in the "meme" of Thames freezings being held up as an example of the world-chilling severity of the Little Ice Age. And as I was saying to Hal Kantrud (who seems just starting out on learning about climate science) . . . the main point to remember is that the LIA and the MWP were pretty small beer compared with earlier climate changes.
As you yourself know very well, the LIA is greatly misrepresented by the climate-science Deniers :-
(a) Firstly, they exaggerate its severity ;
(b) Secondly, they falsely claim that our modern rapid warming is (somehow) "just a rebound from the LIA" .
(c) Thirdly - with amusingly unintended irony - they claim that the huge temperature excursions of MWP & LIA make the modern warming look insignificant . . . and yet at the same time they claim that the planet's Climate Sensitivity is so very low that we need not be concerned about the "slight" warming effect of anthropogenic CO2 emissions. Superb!
MA Rodger, you might not have seen it . . . but on one of the Denialist blogs recently, a particular Denier asserted that (by his calculation) Earth's Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity was around 0.4 degreesC. Improving on that, he then (based on the negligibly-small rise in CO2 which he attributed to humans) calculated that, of the modern warming, only 0.02 degreesC was human-caused. To repeat: 0.02 degreesC. Not a misprint. (Ah, who needs to pursue comedy, when so much is freely available on the Denier blogs! )
Prev 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 Next































 Arguments
Arguments