Recent Comments
Prev 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1606 1607 1608 1609 1610 1611 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 Next
Comments 80401 to 80450:
-
BBD at 04:26 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Mark Harrigan 123Still - I like this debate. At least it focuses on what the options are to move forwards and Mark's contribution is certainly a positive one
Not if it's wrong, and being used to push energy policy in the wrong direction. Tom Curtis asks me above (114): Why the bitter and unenlightening attack on renewables? I think this is unreasonably harsh, but then I would. However, if TC had read my original comments when I joined the thread, he would understand why I have a problem with renewables advocacy. It is fantastically dangerous to energy policy (see #69 and above, where Hansen's warning to President Obama is discussed), and it is going to cause an energy policy disaster in the UK (see #72). It will cause an energy policy disaster everywhere in due course, if not stopped, but I happen to be in the UK where I can see what is going on (eg #98; #99). What such activism is not going to do is displace coal significantly from the global energy mix. Which means it is as dangerous from a climate perspective as scepticism. We need to get past the all-consuming anti-nuclear bias and accept the unpalatable facts as they stand. Then formulate energy policy that makes sense. -
jmsully at 04:22 AM on 4 July 2011Great Barrier Reef Part 1: Current Conditions and Human Impacts
Dr. Hoegh-Guldberg, I was wondering what you thought of this article: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3053361/ recently published in PLoS One which analyzes the AMIS data to come to the conclusion that there is no widespread decline in coral coverage. My initial thought was that it focused on too narrow a question, but otherwise seemed OK. Of course this is being used by denialists to claim that "coral reefs are OK! Nothing to worry about!", but I'd be interested in your take. -
BBD at 04:12 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
dana1981 See SPM p19:More than half of the scenarios show a contribution from RE in excess of a 17% share of primary energy supply in 2030 rising to more than 27% in 2050. The scenarios with the highest RE shares reach approximately 43% in 2030 and 77% in 2050.
Teske is the outlier. The report points to ca 30% RE by 2050. I don't want to argue about this sort of thing; it's pointless. The press release grossly misrepresented the actual report. Which was both exceptionally stupid of the IPCC, and unforgivable. -
dana1981 at 03:52 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
BBD - not sure what you mean about SRREN. It examined 164 different scenarios, up to 77% renewable production by 2050. Mark - in response to your #1, I don't think there's enough wind turbines installed in any single country to test that load management. Regarding #2, it would depend on how much the gas turbines were fueled by natural gas vs. biofuel, for one thing. How many gas turbines would be necessary would depend on the breakdown of the rest of the power grid mix. But remember that even natural gas has significantly lower CO2 emissions than coal, and these gas turbines are proposed to operate as peak load power, only used when there is insufficient wind and solar energy to meet demand. Solar PV costs have been declining quite rapidly, as well. They're expected to become as cheap as coal power (without subsidies, and excluding coal external costs) within the next decade. -
BBD at 03:50 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Mark Harrigan #123 Good to see some critical thinking ;-)1) Have there been any actually implementations of this sort of load management model implemented on any serious commercial scale (as opposed to modelling)? [No] 2) Just how much "peak load" gas type generation will be needed in a given annual scenario and how much CO2 might they produce (for example as a % of today's Australian emissions assuming the same generation requirements as today). In other words if we could wave a magic wand and switch on Mark's proposal tomorrow what would that do to emissions?
Perhaps an even earlier question to ask than your (2) is: what kind of gas turbine can be brought up from cold shutdown to full operating capacity fast enough to respond to peaking demand? And why, in countries such as the UK, can't we have some? Instead, we are obliged to compensate for wind intermittency with gas turbines permanently running because they cannot otherwise respond quickly enough to allow grid balancing? Needless to say, this cancels out any emissions saving from UK wind. And it might do worse. Consider this statement by someone who knows what they are talking about:One of Britain's leading energy providers warned yesterday that Britain will need substantial fossil fuel generation to back up the renewable energy it needs to meet European Union targets. The UK has to meet a target of 15% of energy from renewables by 2020. E.ON said that it could take 50 gigawatts of renewable electricity generation to meet the EU target. But it would require up to 90% of this amount as backup from coal and gas plants to ensure supply when intermittent renewable supplies were not available. That would push Britain's installed power base from the existing 76 gigawatts to 120 gigawatts. Paul Golby, E.ON UK's chief executive, declined to be drawn on how much the expansion would cost, beyond saying it would be "significant". Industry sources estimate the bill for additional generation could be well in excess of £50bn.
-
Patrick 027 at 03:42 AM on 4 July 2011The Planetary Greenhouse Engine Revisited
(PS of course liquid water coexists with vapor over a range of temperatures, but the vapor phase is in a mixture in such familiar conditions. If the vapor phase were chemically pure, then the vapor pressure would be the pressure that the liquid is at as well.) -
Patrick 027 at 03:38 AM on 4 July 2011The Planetary Greenhouse Engine Revisited
Re Michele - The cooling effect occurs within the isothermal sinks because the conversion heat->EM radiation, in effect, is a phase transition... That last term - maybe part of the problem? Granted, energy is changing forms and so that could be considered a phase transition, but when I here 'phase transition', I generally think of a substance or mixture changing from a solid to a liquid and/or to a gas, etc., or various changes between different crystal structures. Sometimes I think this may also involve changes in chemical equilibria (I think in some cases a liquid may react with a solid to form a different solid during a phase transition in which each solid is a different substance (though with dissolved impurities); it certainly can involve solid vs liquid vs gas solubility. For a pure substance, generally (so far as I know) such physical phase transitions occur isothermally (if provided they are also isobaric) - meaning that the two or more phases only coexist in equilibrium at a single temperature (for a particular pressure). And any latent heat involved must be given off or taken up at that point. However, in mixtures, it can often be the case that a phase transition occurs gradually. This may be punctuated by some isothermal (if isobaric) phase transitions (for example, if I remember correctly, the point at which the remaining liquid freezes into two different solids in a eutectic phase transition (this can happen because two substances may be miscible as liquids but only have limited solubility in each other as solids)), but in between there are spans of temperature in which different phases coexist, with proportions varying gradually - the phases will generally have different compositions that vary with temperature and the composition of the whole is maintained by changing the mix of phases. This is commonly the case between a liquid and solid phase. In a phase diagram, this is illustrated with lines/curves, I think they're called the solidus and the liquidus. Other interesting terms - peritectic, syntectic, etc. And of course, chemical equilibrium varies gradually (although maybe sometimes quickly) over a span of temperature. Anyway, none of this really is quite the same as changing the form of energy from a difference in vibration/rotation mode to a photon. Each type of transition behaves according to the relavent physics. Photons don't 'boil off' a material like steam from liquid water at a single set temperature. -
Mark Harrigan at 03:07 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Haven't read all the posts here but would like to ask when Mark Diesendorf says "There are a number of renewable energy technologies which can supply baseload power. The intermittency of other sources such as wind and solar photovoltaic can be addressed by interconnecting power plants which are widely geographically distributed, and by coupling them with peak-load plants such as gas turbines fueled by biofuels or natural gas which can quickly be switched on to fill in gaps of low wind or solar production." 1) Have there been any actually implementations of this sort of load management model implemented on any serious commercial scale (as opposed to modelling)? 2) Just how much "peak load" gas type generation will be needed in a given annual scenario and how much CO2 might they produce (for example as a % of today's Australian emissions assuming the same generation requirements as today). In other words if we could wave a magic wand and switch on Mark's proposal tomorrow what would that do to emissions? Despite the proselytising of Wind, data I have seen suggests it's load factor is about 1/3 of gas or coal. I have even heard it alleged that sometimes lots of Wind can lead to increased emissions because it can displace other forms of renewables and the need for the back up generators can cause problems - but I confess I don't know how reliable that allegation might be. So how many wind plants would be needed and how widely distributed would they need to be on a well connected grid to achieve the model parameters Mark sets out? Is this practical in Australia? The problem with Solar Thermal, as I see it and by Mark's own admission, is that it is simply not a commercially viable technology yet. A 20 Megawatt plant that can only operate less than 3/4 of the year is hardly inspiring. Solar PV remains grossly expensive in terms of the cost per tonne of carbon offset and I'm yet to hear of any Solar PV plants in commercial operation producing more than 100MW. Given that Australia currently has well over 50GigaWatt generating capacity it's hard for me to see how we can replace that so easily with the alternatives on offer - at least not very quickly within our financial means and not with the relatively poor grid interconnection available today. I have to confess, as much as I might find it appealing, I am sceptical about Mark Diesendorf's approach as being practical or affordable in the near to medium term. Still - I like this debate. At least it focuses on what the options are to move forwards and Mark's contribution is certainly a positive one -
BBD at 02:50 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Tom Curtis Your points 1 - 4 are entirely reasonable. Your apparent belief in the ability of renewables to displace coal significantly by 2050 is not. You have not justified your position, so you have effectively lost this debate. Your misreading of Hansen's letter is obtuse. End of. WRT nuclear safety, I find your position untenable, and your reasoning misleading. You obviously don't take well to criticism:Anyway, this will be my last post responding to you. You have demonstrated a complete unwillingness to enter into rational debate, to the extent that you have several times completely ignored my clear statements and tried to set me up as as strawman. You have also repeatedly repudiated the burden of justifying your claims when challenged. I get enough irrationalism on this site from the deniers. I don't need another source as well.
Oho. I see. Fine, off you go then. ( -Snip- ).Moderator Response: (DB) Inflammatory snipped. -
Tom Curtis at 02:00 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
BBD @114, I repeat:"I still think the letter contains good sense - all of it. But I have to wonder, seeing you have introduced Hansen as an authority why you are ignoring those sections that I have highlighted? Why the bitter and unenlightening attack on renewables?"
(emphasis added) So, as explicitly stated, I introduced highlighting not to "reveal the true meaning" of Hansen's quote, but simply to emphasise those parts of it which obviously you find uncomfortable, and which contradict the line you are pushing. Further, no body can ever reveal the "true meaning" of a quote by adding emphasis. Adding emphasis changes emphasis, and by doing so changes the meaning. That is why people who are concerned about accuracy of quotation always note when they add emphasis, and your failure to do so shows that accuracy in conveying Hansen's meaning is not a concern of yours. In fact, you clearly attempt to distort his meaning when you say "... when renewables fail to deliver on the hype (as Hansen clearly believes is likely)...". Indeed, Hansen's "carefully worded" message states that "Energy efficiency, renewable energies, and an improved grid deserve priority ..." (my emphasis). When you remove your heavy handed emphasis it is clear that as much generation of electricity that can be done by renewables should be done by renewables. However, he clearly thinks that nuclear is better than coal and that we should not put all our eggs in one basket. And let me emphasise again, and for the third time, I think Hansen's advise is good. All of it, or at least all of it that letter, except for the discussion of the Carbon Tax where I am indifferent between broad means of pricing carbon (but not about implementation). My preferred policy is: 1) Place a price on carbon that increases incrementally on an annual basis (whether by tax or emissions trading I do not care); 2) Remove broad prohibitions on nuclear power except for occupational health and safety, and security regulations; 3) Implement regulations guaranteeing that waste disposal does not place any additional risk on later generations; and 4) Let the market sort it out. Apparently that is too anti-nuclear a position for you. Anyway, this will be my last post responding to you. You have demonstrated a complete unwillingness to enter into rational debate, to the extent that you have several times completely ignored my clear statements and tried to set me up as as strawman. You have also repeatedly repudiated the burden of justifying your claims when challenged. I get enough irrationalism on this site from the deniers. I don't need another source as well. -
BBD at 01:50 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
dana1981 Careless writing; apologies. J&D do indeed claim that renewables can replace nuclear as well as fossil fuels. And their treatment of nuclear is egregious. Not something I'd focus on, if I were you ;-) But to your point: what difference does it really make? All high-renewables energy scenarios claim the same thing. All fail to make a convincing case. Interestingly, I wonder why the main conclusion of the SRREN report - ca 30% renewables by 2050 - is so far at odds with J&D? Had meant to ask earlier but it slipped my mind. -
Mark Harrigan at 01:33 AM on 4 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
Thanks Dikram for those points. I think your point about 1970 onwards is the most compelling since this is indeed the relevant AGW period. As for your comment about "honesty" - I agree the paper shows no dishonesty. But I don't think it is "naive". If you had been following Mr Cox's tactics on the ABC and other blogs you might question whether he is always entirely forthright in his approach. He is actually a lawyer - not a trained scientist. He wrote an article once on Drum (http://www.abc.net.au/unleashed/44734.html) about how there had been a challenge to the Australia/New Zealand tempetarure data, implying some sort of conspiracy on the part of BOM people in New Zealand. He made it out as if this was independent challenge from credible sources. What he failed to disclose directly in the article was that he was actually one of the prime architects of the challenge (in his capacity as secretary of the Climate Sceptics)- which didn't come from reputable client scientists at all. He also published the link to his "paper" on Drum in response to a challenge to submit a piece of peer reviewed science that invalidated AGW. Somehow he conveniently neglected to mention that it hadn't actually been published. In other words he has an avowed political agenda - it not simply a naive approach or lack of self-scepticism -
Dikran Marsupial at 01:30 AM on 4 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Tom Curtis Counting events is not the only way in which you could determine whether the return period has changed. For instance, you could model the distribution of observed rainfall at a particular location as a function of time, using perhaps the methods set out in the paper by Williams I discussed in an earlier post. You can then see the trend in the return period by plotting say the 99th centile of the daily distributions. This would be a reasonable form of analysis provided the extreme events are generated by the same basic physical mechanisms as the day-to-day rainfall (just with "outlier" magnitudes), rather than being cause by a fundamentally different process. Alternatively extreme value regression methods might be used. -
Tom Curtis at 01:19 AM on 4 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Eric (skeptic) @218, you seem determined to exclude yourself from the discussion as completely irrelevant. To see what I mean, consider this definition of a severe thunderstorm:"In Australia, for a thunderstorm to be classifi ed as severe by the Bureau of Meteorology, it needs to produce any of the following: • Hailstones with a diameter of 2 cm or more at the ground • Wind gusts of 90 km/h or greater at 10 m above the ground • Flash flooding • A tornado.
That come from the joint CSIRO BoM 2007 report on Climate Change,which then goes on to make predictions about cool season tornadoes and the number of hail days expected per annum. I have seen other prediction in Australia for AEP rainfall events of 1 in 20 for various periods. From memory it was an expected 30% increase for the top 5% of one hour events, and a 5% increase for the top 5% of one day rainfall events by 2030. The twenty year return peak rainfall for one hour at one Toowoomba station (Middle Ridge) is about 60 mm, with about 80 mm, ie 25% higher. For another (USQ) they are about 55 mm and 75 mm respectively, ie, 36% higher. So in terms of rainfall intensity, and the fact that it involved a flash flood, Toowoomba was exactly the sort of event about which predictions where made. Now, the question is, was Toowoomba's flash flood a 1 in 100 event, or has it now become a 1 in 20 year event (as is predicted for around 20 years from today). The only way you can find out is by counting the number of relevant events. You, however, have carefully contrived your definition of "extreme event" so that it does not count exactly the sort of events we need to track to see how the AGW prediction is bearing out. In doing so,of course, you have contrived your definition to include events about which there is no explicit AGW prediction in the near term (or in many cases the long term), and which occur far to rarely for any sort of statistical analysis. What that amounts to is an attempt to remove your beliefs from empirical challenge. It also means your discussion on this thread is irrelevant because you have carefully chosen to avoid discussing the type of events about which AGW has made its predictions. -
dana1981 at 01:09 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
BBD - J&D is essential to a claim that wind, water, and solar alone can displace 100% of fossil fuels and nuclear. It's not essential to claims that renewables can significantly displace coal. I haven't had a chance to read the links about that paper, but this is an important distinction to make. -
dana1981 at 01:05 AM on 4 July 2011Glickstein and WUWT's Confusion about Reasoned Skepticism
andreas - I would agree with you, except Glickstein didn't propose a carbon tax for the economic benefits. He proposed it purely as a capitulation because he felt the 'warmists' have succeeded in convincing the public and policymakers that some action is necessary, and he would prefer a tax to cap and trade. It's not that he thinks a carbon tax would be beneficial, he just thinks it's not as bad as cap and trade. So I think the description in the post is valid. -
Dikran Marsupial at 00:44 AM on 4 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Eric, would you say that an event that is sufficiently dramatic that it only happens once in a thousand year is an extreme event? The return period is a measure of the "extremeness" of an event; the threshold return period that demarcates extreme from non-extremes depends on the nature of the application. The same is true of statistical significance tests. The 95% threshold is often used to indicate an event sufficiently extreme that it is difficult to explain by random chance. However what people often forget is that Fisher himself said that the threshold depends on the nature and intent of the analysis. Expecting a single threshold that is right for every aplication is unreasonable in both cases. As to the additional effects such as area, event duration etc. These are conditioning variables on which the return period depends. They are already taken into account in the analysis. For instance, what is the return period for 12" of rain falling in some particular catchment in Cumbria in August. If the events you are discussing are "dime a dozen" then by definition they have a low return period, and hence would not be considered extreme according to their return period. That is the point, the return period is self-calibrating to the distribution of events at the location in question. -
Tom Curtis at 00:38 AM on 4 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Norman @200:"On both links you posted, the 1 and 2 levels on the charts are not considered disasters. Loew & Wirtz call the first two "small and moderate loss events" the next four levels are various degrees of disaters. Munich Re lists the higher levels as catastrophes and not disasters but the meaning would be the same."
I wondered about that from the slides to which you linked, so I looked a bit further for clarification and found Löw and Wertz, who say:"The Munich Re global loss database NatCatSERVICE divides natural disasters into six damage categories based on their financial and human impact, from a natural event with very little economic impact to a great natural disaster (see Figures 3). The combination of the number of fatalities and/or the overall loss impact ensures that each event can be categorised with one or two of these criteria. The limits of overall losses are adjusted to take account of inflation, so it is possible to go back into the past if new sources are available."
(My emphasis) That wording strongly suggests that category 1 and 2 events are included in the database as natural disasters. That the events are described in a continuum of increasing severity reinforces that interpretation, with 1 (small scale loss event) and 2 (moderate loss event) being followed by 3 (severe disaster). If level 1 and 2 events are not included, we have to wonder why no minor or moderate disasters ever occur in the world. You also have to wonder why an event with 9 fatalities (level 2) is not worth calling a disaster. I know insurance agents are widely considered to be heartless, but that is going to far. If you disagree with that assessment, may I suggest you contact either Munich Re Geo or the NatCatService for clarification.
The map you looked at only shows the United States as having more than 650 natural disasters in the period 1980-2004. Chile is shown as having from 51 to 150, the second lowest category. The reason different countries have different numbers of natural disasters varies. The US has a large number in part because of Tornado Alley. Australia, in contrast, has relatively few (351 to 650) partly because it is so sparsely populated. In contrast, it is almost certain that Africa shows very few catastrophes (outside of South Africa) because of poor reporting. UN agencies, aid agencies and other NGO's only become involved in and report large natural disasters. Many African governments are dysfunctional, and western media ignore all but the largest catastrophes in Africa, and often ignore those as well. Wether they like it or not, this inevitably introduces a bias into Munich Re's figures for Africa and (probably) South America and former Soviet Block nations. Because of that bias, although I quote the headline trends for simplicity, I only employ trends that are reflected in North American and/or European figures where these selection biases do not apply. Indeed, because reporting from Africa and South America is so low, any distortion they introduce to the overall figures is slight. Consequently this bias is unlikely to distort trend data very much, but it does make international comparisons of limited value, and mean the total figures understate the true number of natural disasters significantly. Of more concern are China, SE Asia and former Soviet Block nations where there may be a significant trend in increased reporting over time. Again the figures are not large relative to the total trend, and none of these regions show an unusual trend when compared to Europe or North America, but it is something to be aware of. The important point,however, is that global trends are reflected in European and North American trends where these reporting issues are not a significant factor."I looked back at your post 116 on the thread "Linking Extreme Weather and Global Warming" where you posted the Munich Re Graph. I guess the graph shows about a 55%increase in 25 years in number of disasters (about 400 in 1980 to 900 in 2005, and annual rate of 2.2%) Here is a link on the yearly rise in home prices. National average was 2.3% but some areas were at 3% and more. A yearly rise of 2.3 in a home's value (not to mention the items in the house) will get you a 57.5% increase in value in 25 years. The value of property rose at a faster rate than the disaster rate. But the biggest thing is there incremental choices they picked for determining a disaster. From 1980 it was $25 million. In 1990 it was $40 million. In 2005 it was $50 million. The overall rate of determining a disater rose 50% in 25 year or at a rate of 2% a year. From 1990 to 2005 the rate of increase would only be 1.3% a year. The criteria to become a disaster was rising at a much slower rate than property values."
First, it is important to note that the categories are inflation adjusted. That is, the threshold levels are stated in inflation adjusted figures. The changing threshold is therefore only introduced to adjust for increased wealth in society. Second, adjustment is carried out be two methods, by fixed stepwise adjustment as reported by Löw and Wertz, or by linear interpolation as reported by Neumayer and Barthel. In the stepwise approach, the levels for a Major Catastrophe are $85 million from 1980-1989, $160 million form 1990-1999, and $200 million from 2000 to 2009. For linear interpolation the figures are linearly interpolated between $85 million in 1980 and $200 million in 2009. In the graphs contrasting all disasters with major disasters, it is the Neumayer and Barthel method that is used. The Munich Re graphs either show all disasters (category 1 to 6) of Devastating and Great Natural Catastrophes (category 5 and 6), or Great Natural Catastrophes (category 6). Both of the later have to few events for effective statistical analysis of any trend due to global warming. Using property prices as an index of overall wealth is probably as good as you'll get for a simple comparison. So, to see how the Neumayer and Barthel adjustment fared, I compared their interpolated threshold to an index based on an exponential 2.3% (average value) and 3% (high value). Of immediate interest is that 85*1.03^29 is 200, give or take, so the endpoints preserve there values to within 0.15%. This means the middle values would overstate the relevant threshold by up to 9.5% using the 3% inflator, thus understating the number of natural catastrophes. But, the average price rise was 2.3%, not 3%. Using the average price rise as the inflator, the 2009 threshold should be 165 million dollars, and the 2010 threshold should be 168 million. That is, using the average increase in US property prices, the Munich Re threshold overstate the threshold in later years by as much as 21.5%. The effect of this is that Munich Re would be understating the number of disasters in 2009 and 2010 relative to 1985. The rarety of these events, and the large variability of damage done means the understatement of the number of major disasters will not be anywhere near 20%, but it is an understatement, not an overstatement as you conjectured. -
Dikran Marsupial at 00:31 AM on 4 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
Mark, note that some arguments are stronger than others, for instance the test used to detect the step change may still be reasonable, even if the noise is non-Gaussian, but in such circumstances it is up to the authors to convincingly demonstrate that it is O.K. (for instance by testing it using synthetic data where the noise is statistically similar to the real data). They would have to do more than just remove ENSO, even after that is done, a linear trend model over a complete century still isn't a reasonable model, given what we know about climate of the 20th century, so it would still be a straw man. If they wanted to demonstrate that there really was a step change in 1997 that was evidence against AGW, they would have to limit the analysis to the period where mainstream science actually says CO2 radiative forcing was dominant (e.g. approximately 1970 onwards). For any test, the null hypothesis ought not to be known to be false apriori. If they wanted to show it wasn't just ENSO they would also have to use data that had been adjusted for ENSO. As it is well known that ENSO affecte climate (especially Australian climate), showing ENSO is responsible is nothing new. If the want to say it is PDO, this is more of an oscillation that modulates ENSO, so a step change model isn't really appropriate anyway. I don't think there is evidence that the analysis isn't honest, just naive (from the climatology perspective) and lacking in self-skepticism. -
BBD at 00:23 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Tom Curtis Just a general reflection: it would be constructive if you actually read my original posts here in full rather than creating an artificially distracting fuss about a couple of paragraphs. We could start with the various critiques of Jacobson & Delucchi's contentious claim that we can transition globally to 100% renewables. Funny how the critical response to J&D was greeted by absolute silence here. Especially since it is absolutely essential to any claim that renewables can significantly displace coal. -
Eric (skeptic) at 00:20 AM on 4 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Hi Dikran, the wikipedia article on return period does not offer any criteria on what is extreme. In fact it assumes that "extreme" or other threshold event has already been defined, then simply offers an estimation of likelihood in any year or years. One cannot assume the event is extreme just because the likelihood is low using that formula. There are a lot of factors that need to be considered, some of which I mentioned above, such as the event duration and areal extent. For example flash floods are much more common than river basin floods because the areal extent is smaller along with the event duration. My own location in Virginia is hilly enough to have flash floods mainly from training thunderstorms. The probability for any single location is low but much higher considering the large number of potential flash flood locations. Truly a dime a dozen. Meanwhile the major river that I live on shows no trend in extreme floods (1942 is the flood of record, see http://www.erh.noaa.gov/er/lwx/Historic_Events/va-floods.html) Tom, on your point 1, the fact that Munich Re defines tornado events in some arbitrary way does not invalidate my point about areal extent and event duration. On your point 2, the Moscow heat wave qualifies as extreme by my criteria and not just barely. However the blocking pattern that enabled the heat wave is a natural phenomenon and makes the probability of the extreme event higher. The mean and standard deviations of heat waves are higher in blocking patterns which makes extreme heat waves more likely. Independent of that, AGW makes extreme heat waves more likely. The Towoomba flash flood was indeed not extreme. The Brisbane flood had 1 in 2000 rainfall over a very small areal extent, not uncommon and not extreme. The more widespread rain was borderline extreme as you point out and fell on saturated ground. There were complications of measurement of river levels with damming in place. That damming may mask an extreme event by lowering levels downstream. Urban hydrology may exacerbate an event causing it to have river level extremes which would not have otherwise existed. Damages and economic losses were exacerbated by poor zoning. IMO the Brisbane flood was a somewhat borderline extreme weather event creating an extreme flood due to a variety of factors. -
Ken Lambert at 00:19 AM on 4 July 2011Uncertainty in Global Warming Science
KR #81 "However, we have the track record of global temperatures, and a decent record of forcing changes both natural and human. We can see when the climate is gaining or losing energy over the last few hundred years. Global temperatures have gone both down and up over that period, which immediately tells us that we've seen forcings both above and below equilibrium - that the area under the forcing curve has gone both positive and negative." Please expand on the 'cooling' we have seen over the last 'few hundred' years and the reasons for same. S-B is a fourth power function of T so you would see most of the effect in the last 50 years or so. -
BBD at 00:12 AM on 4 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Tom Curtis 114 Thanks for the amusing attempt to forcibly alter Hansen's meaning. Good try. Now, let's go back to the true sense of the letter:Energy efficiency, renewable energies, and an improved grid deserve priority and there is a hope that they could provide all of our electric power requirements. However, the greatest threat to the planet may be the potential gap between that presumption (100% “soft” energy) and reality, with the gap filled by continued use of coal-fired power. Therefore it is important to undertake urgent focused R&D programs in both next generation nuclear power and carbon capture and sequestration. These programs could be carried out most rapidly and effectively in full cooperation with China and/or India, and other countries. Given appropriate priority and resources, the option of secure, low-waste 4th generation nuclear power (see below) could be available within a decade. If, by then, wind, solar, other renewables, and an improved grid prove that they are capable of handling all of our electrical energy needs, then there may be no need to construct nuclear plants in the United States. Many energy experts consider an all-renewable scenario to be implausible in the time-frame when coal emissions must be phased out, but it is not necessary to debate that matter. However, it would be exceedingly dangerous to make the presumption today that we will soon have all-renewable electric power. Also it would be inappropriate to impose a similar presumption on China and India. Both countries project large increases in their energy needs, both countries have highly polluted atmospheres primarily due to excessive coal use, and both countries stand to suffer inordinately if global climate change continues.
Hansen's carefully worded caution to President Obama is that there is no need to debate about whether renewables can displace coal. Rather, we should get on with R&D including Gen IV nuclear and when renewables fail to deliver on the hype (as Hansen clearly believes is likely) we can still get on with the over-arching business of decarbonising the energy mix and attempting to stave of climate disaster. I do think you need to mull this over carefully. It's terrifyingly important, and wishful thinking about renewables is starting to look like a serious impediment to good energy policy-making. So serious that no less than James Hansen wrote an open letter to the President warning him about it. -
BBD at 23:58 PM on 3 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
Tom Curtis 113From 101: a) 64.6 trillion kWh of electricity produced by nuclear; b) 2 INES 7 events; Therefore, c) 1 INES 7 event per 32.3 trillion kWh produced by nuclear; From 69: d) 11.5 Terrawatts of clean energy capacity required; Or e) 100 trillion kWh of electricity if produced at peak capacity; Or 50 trillion kWh of electricity allowing for a peak to zero capacity cycle everyday; So F) An expected 1.5 IES 7 events per annum if fossil fuels are replaced by nuclear at current safety standards.
Sophistry old chap. You seem to have forgotten that the Chernobyl and Fukushima events were caused by abysmally poor design and afflicted plant many decades old. So your projection breaks. Amusing, coming from someone who repeatedly says things like this:Again you are throwing up a wall of numbers without carrying it through to an actual analysis, just as you did on your first full post on the topic.
Your pop at Brook omits one inconvenient fact: nobody died at Fukushima. But do carry on with the anti-nuclear propaganda anyway.I don't care whose numbers they where, you quoted them, and you drew an implication from them. Therefore either you defend them, or you withdraw the implication.
The 'implication' - which is actually a blindingly obvious logistical problem - speaks for itself. And I can tell that you don't like that at all. Either stop fulminating about Griffith's numbers or rebut them.You do not get to both disavow the "evidence" and retain it as bolstering your argument, at least not if your purpose is rational discussion or analysis rather than propaganda.
As I have said, I have provided a great deal of practical input on this thread. Not propaganda. In responses here I seen nothing that supports the claim that renewables will play a significant role in displacing coal from the global energy mix. If there is bias, denial and zeal anywhere, it is coming from the pro-renewables lobby. -
BBD at 23:45 PM on 3 July 2011A Detailed Look at Renewable Baseload Energy
JMurphy #112 You are transparently anti-nuclear. It is evident from the tone and content of your responses. Why deny it? You do not seriously address the points I raise at 101, so I will return the discourtesy. However, the INES 7 ratings for Chernobyl and Fukushima are puzzling. I invited you to refresh your memory on the facts concerning Chernobyl, but evidently you haven't yet had time. When you do get a minute to review the evidence, you can see for yourself that the INES 7 rating for Fukushima may have been an over-reaction. After all, Fukushima has caused no fatalities, and resulted in no life-threatening exposure to radiation. Odd, isn't it? You close with this:The fact that you try to lessen the seriousness, speaks volumes.
This is incorrect and strategically dishonest, which is in line with much else you say here. As time is limited, I do not think there is much point in continuing this exchange. -
Mark Harrigan at 23:42 PM on 3 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
Oops - for "show that a linear trend is still valid" I should have said - "show that a FLAT trend is still valid". I wish they could show such a thing - I'd love to discover AGW isn't a real problem! I wish it wasn't! But wishing doesn't make it so and good scientists don't fall for the "is/ought" fallacy. So I am betting they won't and can't. -
Mark Harrigan at 23:38 PM on 3 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
@#104 - Thanks Dikram. Really appreciate your comprehensive reply. I think this just about knocks it on the head - it's good to have such a clear, albeit somewhat arcane and technical, discussion. In summary I would argue this paper can be safely dismissed because #1) After two years it hasn't been published - suggesting a problem with its acceptance #2) It has been submitted to a forecasting journal which, whilst reputable and purports to cover climate forecasting, does so as only as one out of a long list of forecasting topics which are predominantly economic and social in nature (in other words it's light on hard science) - which means there is actually very little climate science expertise within the journal #3) It contains no physics or science arguments what-so-ever as to what may actually be the mechanisms it purports to reveal or forecast. The above 3 really make it clear it is hardly a paper about climate in the first place #4) It's approach is statistically invalid since the test it applies assumes a gaussian noise distribution in the data when that is not the case (due to the multiple impacts of noise from cyclical drivers of climate of different periods and variabilities) #5) It's approach is invalid on the physics of climate because of the above #6) It's invalid on the physics anyway since it is established beyond reasonable doubt that increased atmospheric levels of CO2 produce an increased green house effect #6) It's approach is statistically invalid because of the multiple hypothesis testing problem - i.e. it is highly likely to generate false positives in the statistical analysis of the data - especially when it ignore the underlying physics - in other words the so-called linear trend they forecast is likely to be plain wrong #7) It fails to remove the effects of things like ENSO and volcanos from the data in order to analyse the temperature effects of increasing CO2 in the atmosphere - particularly egregious when the ENSO of 1997/98 was known to be one of the largest ever #8) It actually fundamentally fails to address the central tenet of AGW - that increasing levels of human generated atmospheric CO2 are contributing to a warming of the planet independent of other (natural) factors sufficient to cause substantial climate change that will most likely be deleterious. have I missed any? If they want to come back on any of that all they have to do is re-analyse the data accounting for ENSO etc (as per your graph) and then show that a linear trend is still valid and is not a false positive - and of course get that accepted in peer review. If they were honest scientists that's what they'd do. I hope I get the chance to put that to them :) -
neilrieck at 22:41 PM on 3 July 2011Roy Spencer on Climate Sensitivity - Again
Not sure how many people know that the industry sponsored deniers were at it again in Washington D.C. (June-30 to July-1) climateconference.heartland.org The usual suspects include: Roy Spencer, Harrison Schmitt, Willie Soon, Anthony Watts, S. Fred Singer, to only name a few -
Dikran Marsupial at 22:41 PM on 3 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
@mark The central limit theorem does indeed suggest that the averaging of temperatures at stations at different location means that a Gaussian noise model is appropriate, but only for a particular time point. To see why this is the case, imagine some AM radios that are affected by mains hum. Each will have a noise component that is due to the electronic components in the radio, these are independent, so the noise for the average signal over many such radios will have a corresponding Gaussian component. However, the mains hum on all the radios will be in phase and will be reinforced in the averaged signal, and will have the same [scaled] distribution as the mains hum measured at any one of the radios. Another way of looking at it, cyclical data is easily confusable with data containing a step change, but how likely is it to see a cyclic pattern in Gaussian white noise? A lot less likely than in data with autocorrelation or cyclical noise. You are not being at all dense, the central limit theorem is hardly stats 101! I checked the archive at the Journal of Forecasting, it hasn't been published yet. For the multiple hypothesis testing issue, there are standard methods to deal with this, but they are generally overly optimistic or pessimistic. What I would do is generate a large number of model runs using a GCM where the only forcing was from CO2 and see how many produced a non-significant trend at some point during a 40 year period via the models internal variability. The forty year period is chosen since worries about global warming began to gain acceptance in the early 70s, the test is "at some point" because we are asking if cherry picking is the issue, so the "skeptics" would make the claim as soon as such a period ocurred. Easterling and Wehner (who Stockwell and Cox claim to refute) did almost that, in that they looked at model output and found that decadal periods of little or no warming were reproduced by the models (although opf course the models can't predict when they will happen). This means that the observed trend since 1995/8 is completely consistent with model output. Easterling and Wehners' result shows that cherry picking is a possibility; it isn't necessarily deliberate cherry picking, but the skeptics have never performed an analysis that shows the ressult is robsut to the multiple hypothesis testing issues. For the removal of ENSO, see the Fawcett and Jones paper mentioned in the intermediate version of this article. If you just look at the data: you can see there isn't much evidence of a step change in 1997 if you account for ENSO.
The real problem with the paper is the straw man of a linear centennial trend. AGW theory doesn't suggest a linear centennial trend is reasonable, so showing a model with a break-point is statistically superior to something that AGW theory does not predict is hardly evidence against AGW.
I also remember some comment about solar forcing being better correllated with temperatures than are CO2 concentrations, and conclude that CO2 radiative forcing is not significant (or words to that effect). However, that is another straw man, the mainstream position on AGW does not say that co2 radiative forcing is dominant on a centennial scale (and that solar forcing is responsible for much of the warming of the 20th century). This is both a straw man and a false dichotomy, it isn't one thing or the other, but a combination of both. Reviewers at the Journal of Forecasting might not be suifficiently familiar with the climatology to spot that one.
What I am basically arguing is that statistics should be used to gain knowledge of the data generating process (in this case climate physics). If you ingore what is already known about the data generating process and adopt a "null hypothesis" (e.g. linear centennial trend) that is known a-priori to be incorrect, then statistical methods are likely to be deeply misleading. It is a really good idea for statisticians to collaborate with climatologists, as together they have a better combination of climate science and statistical expertise than either has on their own. This paper, like McShane and Whyner (sp?) and Fildes and Kourentzes, is an example of what happens when statisticians look at climate data without fully immersing themselves in the climatology or getting their conclusions peer-reviewed by climatologists.
you can see there isn't much evidence of a step change in 1997 if you account for ENSO.
The real problem with the paper is the straw man of a linear centennial trend. AGW theory doesn't suggest a linear centennial trend is reasonable, so showing a model with a break-point is statistically superior to something that AGW theory does not predict is hardly evidence against AGW.
I also remember some comment about solar forcing being better correllated with temperatures than are CO2 concentrations, and conclude that CO2 radiative forcing is not significant (or words to that effect). However, that is another straw man, the mainstream position on AGW does not say that co2 radiative forcing is dominant on a centennial scale (and that solar forcing is responsible for much of the warming of the 20th century). This is both a straw man and a false dichotomy, it isn't one thing or the other, but a combination of both. Reviewers at the Journal of Forecasting might not be suifficiently familiar with the climatology to spot that one.
What I am basically arguing is that statistics should be used to gain knowledge of the data generating process (in this case climate physics). If you ingore what is already known about the data generating process and adopt a "null hypothesis" (e.g. linear centennial trend) that is known a-priori to be incorrect, then statistical methods are likely to be deeply misleading. It is a really good idea for statisticians to collaborate with climatologists, as together they have a better combination of climate science and statistical expertise than either has on their own. This paper, like McShane and Whyner (sp?) and Fildes and Kourentzes, is an example of what happens when statisticians look at climate data without fully immersing themselves in the climatology or getting their conclusions peer-reviewed by climatologists.
-
Mark Harrigan at 22:19 PM on 3 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
@ Sean 103 Thanks - while these links don't explicitly address Cox's paper and the statisticaly validity (or otherwise) of their approach they do remove the effects Dikram was pointing out. The challenge then to Cox and Stockwell would be to analyse again based on this and see if they could still find the break points. On a visual inspection of the graphs in the links I suspect not. Please ignore #101 - I must have hit submit when I meant to hit previewModerator Response: [Dikran Marsupial] #101 deleted, done the same myself more than once! ;o) -
SEAN O at 21:55 PM on 3 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
Mark #102 Tamino at Open Mind has looked at these issues in these two threads: http://tamino.wordpress.com/2011/01/20/how-fast-is-earth-warming/ http://tamino.wordpress.com/2011/01/06/sharper-focus/ -
jatufin at 21:52 PM on 3 July 2011Great Barrier Reef Part 1: Current Conditions and Human Impacts
Never visited Down Under, but I think the three things we Europeans have in our mind, when we first think about Australia are: The Big Red Rock, The Sydney Opera House and The Great Barrier Reef. The rock will probably be fine for eons to come, the opera house will cope with future as any man made object. But if GBR would came to its end due human actions, that would be a sin future generations will never forgive us. -
Mark Harrigan at 21:38 PM on 3 July 2011It hasn't warmed since 1998
@kdkd - I know what you mean about the IPA but that doesn't count as a valid refutation. Even though the IPA is populated with ideologues who far too frequently see things only through the prism of their free market ideology that doesn't make everything they say wrong. @Riccardo - thanks for that - I was told it HAD been published - that was certainly the claim by the Cox supporter and Cox himself posted a link to it on the Drum (ABC) (as per mine above) to the paper as if it "were" published - typical of his dissembling approach. But you are correct - I can find no reference to it in any of the indexes for this journal. That in itself is telling enough as it is now almost 2 years since it was submitted. In my own days (long past) of publishing in the field of Atomic Physics it could sometimes take 12 months or so from submission to publication. But two years suggests there are some issues with acceptance. I should have checked this before. But I'm not sure your other comment is entirely fair. I agree any physics is absent and I accept Dikran's comments on the poor statistics (as I'm not the expert there) but I'm not sure you can claim that their only conclusion is that local temperatures are sensitive to nearby ocean. Perhaps I've misread it but I gathered they were looking (purportedly) at Australian temperature data and using that as basis to dispute local warming (i.e. saying they can show a statsitically valid trend based on the Chow test that it may be flattening) @Dikran - thanks for your comprehensive statistical refutation - I'm afraid I don't have the statistical expertise that you do - If asked I would have thought sum-of-squares errors was a fair anough approach (which is what you would expect in econometrics). But would you elaborate further? I understand what you mean about physical processes - as climate/temperature outcomes are a function of many different factors each with their own cycles and forcings and ENSO of course being a big one. But given that temperature data (what they are analysing) is ultimately data that is averaged over many sources why isn't it by definition normally distributed? I'm sorry if I'm being a little dense - is it because each of the "drivers" has it's own statistical/natural "noise" and this creates a non-gaussian distribution of noise when the (average) temperature data is considered? Do you know of anyone who has looked at the data after tyrying to remove the effects of ENSO etc? I very much take your point about the "multiple hypothesis testing problem" - some thing I wasn't familiar with before but based on your explanation and a bit of my own secondary research can see how "false positives" might abound in an area like this. Are there any simple tests that can be used to identify the likelihood of this? I do find their comments about breakpoints to be not unreasonable - although I note they make no real statement about what possible physical processes may be causing them. Perhaps the most compelling argument (against this paper) is actually that they offer no fundamental physical reason behind their so called flattening. If I were to have a stab at trying to understand what is going on here based on the statistical arguments you have presented I might have speculated that you can get large maxima and minima in any data that is the physical outcome of many cyclical processes that operate on different periods merely because from time to time the cyclical maxima co-incide in time. The danger is then that you "cherry" pick these points. You have to remove these other cycles to get out any linear drivers underneath the data. I think that is sort of what you are arguing? Regardless - thanks all for your responses. Any more welcome but at least I feel now that we can point out not only that Mr Cox is on shaky ground - but also why. Cheers -
JMurphy at 20:01 PM on 3 July 2011Arctic icemelt is a natural cycle
With reference to DB's moderator response above, I would be prepared to try to get something written (if only for my own future reference) but I would need to be able to find all previous references to the St Roch on SkS, because I think quite a bit of relevant information is already there - it just needs to be gathered together and researched in more detail. Is there any way of gathering this information ?Response:[DB] Short answer: There's no easy way to find a comprehensive listing in all the SkS comments. A search of various terms will bring up a listing of blog posts containg the terms, but one is still forced to then hunt-and-peck through the sometimes length comment threads.
If you are interested in doing it, it would be easiest (from a manhours perspective) to start from scratch.
A good starting point for research:
-
Tom Curtis at 19:48 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Berényi Péter @215, my figures for the Brisbane flood are based on the SEQWater report on the flood, and in particular on the Rainfall Intensity Graph for Lowood: and Helidon:
and Helidon:
 The graph plots the peak rainfall recorded for each duration at the two sites. The dashed lines show the Annual Exceedance Probability, with the highest shown being the white dashed line with an AEP of 1 in 2000. AEP's of greater than 1 in 2000 are not plotted because there is insufficient data after a century of recording to determine the values with any accuracy. You will notice the recorded rainfall intensity for periods between about 6 and 24 hours (Lowood) and between 1.5 and 24 hours (Helidon).
The claim in relation to the Toowoomba storm is based on the Insurance Council of Australia's report on the event, which states:
The graph plots the peak rainfall recorded for each duration at the two sites. The dashed lines show the Annual Exceedance Probability, with the highest shown being the white dashed line with an AEP of 1 in 2000. AEP's of greater than 1 in 2000 are not plotted because there is insufficient data after a century of recording to determine the values with any accuracy. You will notice the recorded rainfall intensity for periods between about 6 and 24 hours (Lowood) and between 1.5 and 24 hours (Helidon).
The claim in relation to the Toowoomba storm is based on the Insurance Council of Australia's report on the event, which states:
"Short-term rainfall data are available at nine raingauges in and around Gowrie Creek catchment. At six of these nine gauges, rainfall severities were greater than 100-Years ARI for rainfall durations of 30 minutes to 3 hours. At another gauge, rainfall severities were greater than 50- Years ARI. Readings at the remaining two gauges were far less severe (less than 20-Years ARI)."
So, while I did just use the probabilities from a normal distribution in determining the Standard Deviation, that just means, if anything, that I have overstated the SD which would strengthen my point, not weaken it. Your criticism may be valid with regard to the Moscow heatwave where I have relied on Tamino's analysis. The 1 in 10,000 figure assumes a normal distribution. Tamino calculates the return period using extreme value theory as 1 in 260 years. However, the Moscow Heat Wave was a significant outlier on the tail of the QQ plot.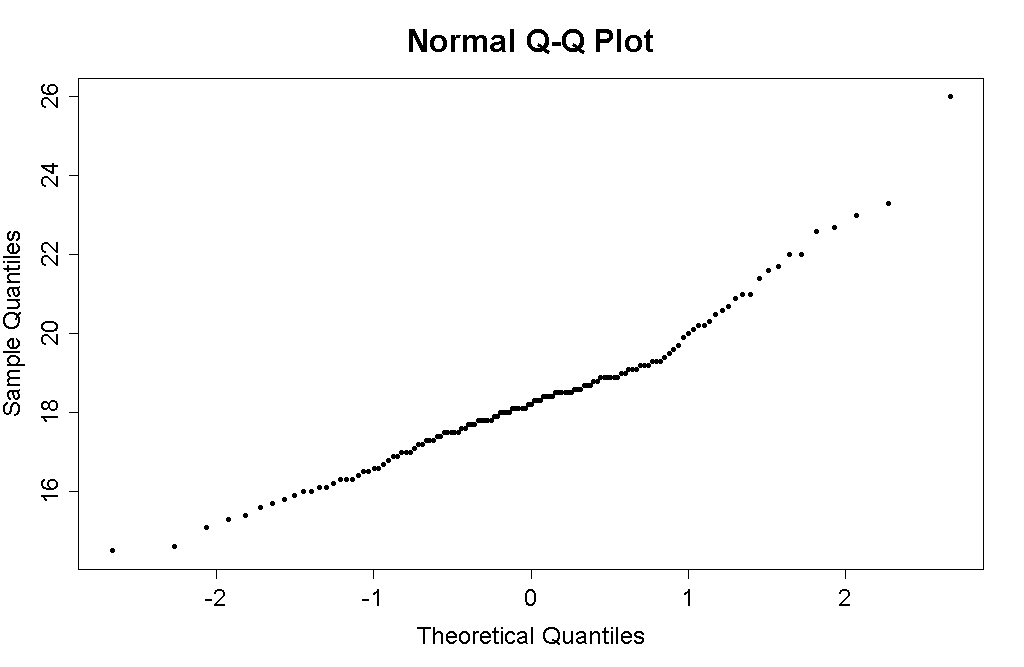 Assuming that extreme value theory or normal distributions can be used to calculate the probability of extreme outliers is a fallacy equivalent to assuming that you have a chance of rolling 13 on two loaded six sided dice. Consequently the most that can be said about the Moscow heat wave is that its AEP was not less than 1 in 260 assuming global warming; and not significantly less than 1 in 1,000 assuming no global warming, but possibly not physically realisable in the absence of global warming.
Using the best value, AEP 1 in 260 would have, again, strengthened by case against Eric's definition. If you have a problem with my using conservative values relative to my argument, let me know. Then I too can argue like a denier.
While on the topic, I disagree with Dikran about defining extreme events by return intervals. It is in fact the best practise. However, the prediction of more extreme events from global warming is not a prediction restricted to events of a certain return interval. Further, not all data sets, and in particular Munich Re's data set is not easily classified by that basis. The definition of extreme is therefore relative to a particular data set, with the only (but very important) provision that the definition of extreme used is one for which the prediction of AGW holds.
Assuming that extreme value theory or normal distributions can be used to calculate the probability of extreme outliers is a fallacy equivalent to assuming that you have a chance of rolling 13 on two loaded six sided dice. Consequently the most that can be said about the Moscow heat wave is that its AEP was not less than 1 in 260 assuming global warming; and not significantly less than 1 in 1,000 assuming no global warming, but possibly not physically realisable in the absence of global warming.
Using the best value, AEP 1 in 260 would have, again, strengthened by case against Eric's definition. If you have a problem with my using conservative values relative to my argument, let me know. Then I too can argue like a denier.
While on the topic, I disagree with Dikran about defining extreme events by return intervals. It is in fact the best practise. However, the prediction of more extreme events from global warming is not a prediction restricted to events of a certain return interval. Further, not all data sets, and in particular Munich Re's data set is not easily classified by that basis. The definition of extreme is therefore relative to a particular data set, with the only (but very important) provision that the definition of extreme used is one for which the prediction of AGW holds.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 19:11 PM on 3 July 2011Glickstein and WUWT's Confusion about Reasoned Skepticism
Here is an example of the level of commentary at WUWT. Read it and weep (or laugh (or both)) "Phil – Visible Light cannot and therefore does not convert to heat the land and oceans of Earth. That comes from bog standard traditional science which I have outlined above. I have also gone to some considerable effort to show that “absorb” is used in different contexts, the context of “absorb” here is in the difference between Light and Heat electromagnetic energy. In this context, Visible is not absorbed to convert to heat as the AGWScience Energy Budget KT97 claims. Because it cannot. It physically cannot. It physically does not. It is Light. Light energies are used, affect, react with matter in a completely different way from the Thermal Infrared electromagnetic wave carrying Heat. Re my: ” These are LIGHT energies, which are REFLECTIVE, in contrast to HEAT energies which are ABSORPTIVE.” More nonsense there is no such distinction. But I’ve just given you the distinction. You don’t have any distinction in AGWScience fiction, because you’re one dimensional., you don’t have differences between properties of matter and energy. Read the wiki piece I gave about how real Visible light waves/photons act in the real world. Read the links to the pages on luminescence etc. That information has been gathered over considerable time by a considerable amount of people who have done real work and real thinking exploring the differences between Light and Heat energies. The myriad applications of this knowledge are in real use by real people who all live in our real world. That there is a difference is a CATEGORY distinction in REAL TRADITIONAL SCIENCE. mods – i THINK THE INTERFERENCE IS KEY STROKE HACKING. aND IT’S BLOODY Iirritating. " Lol (TeeHee (Jesus Wept!)) -
Dikran Marsupial at 19:04 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Berényi Péter While you are correct that some weather parameters are non-normal (for frontal precipitation a gamma distribution is approapriate, for convective rainfall an exponential distribution is the use model), you have not established that the distributions are not sufficiently heavy tailed for Tom's argument to be qualitatively incorrect. However, the point is moot as the statistical definition of an extreme event is based on the return period, not the standard deviation. -
Berényi Péter at 18:50 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
#214 Tom Curtis at 17:20 PM on 3 July, 2011 As another example, the rains causing the Brisbane flood had an Annual Exceedance Probability of 1 in 400 for the whole event, and for the peak rainfall of 1 in 2000. That works out as lying between 3 and 3.5 standard deviations from the mean. Right, a 1 in 2000 event is 3.29053 standard deviation (which is indeed between 3 and 3.5). But only if the phenomenon examined follows a normal distribution. However, it is well known that probability distribution of weather/climate parameters are very far from being normal, in this domain so called fat tail distributions prevail. This fact leads to risk estimate distortions. Therefore your analysis does not make sense in this context. -
andreas3065 at 18:25 PM on 3 July 2011Glickstein and WUWT's Confusion about Reasoned Skepticism
@ dana I'm almost ashamed in defending Glickstein, but I think you are wrong with this: "to support a carbon tax when you have just finished arguing that carbon emissions are a net benefit is intellectually incoherent." It's not necessarily a contradiction. You can deny climate science and propose a carbon tax because of economic benefits e.g. by reducing oil imports. See for example Revkin's post about Charles Krauthammer "A Conservative's case for a Gas Tax" (http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2011/06/24/a-conservatives-case-for-a-gas-tax/). And BTW there would be also a political benefit, because it would help to take some pressure out and would help to delaying tougher climate policies. Krauthammer's version is more intelligent, because he avoids ridiculous claims about climate science. Krauthammers approach is interesting. Should I criticize him of doing a good but using the wrong reasons? If you accept WUWT being not a science blog but having a political agenda, then you could find some coherence in all this craziness. -
Tom Curtis at 17:20 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Eric (skeptic) @210: 1) The point about the size of the event is valid but irrelevant. Specifically, the events under discussion like those catalogued by Munich Re, where a tornado outbreak over three days spawning 300 tornadoes counts as a single "event". 2) Your definition of extreme sets to high a bar. Take for example the Moscow heat wave of 2010, with an expected return interval, which lay just above 4 standard deviations above the mean for July temperatures, giving it an Annual Return Interval on the assumption of a normal distribution of 1 in 10,000 years. According to your proposed definition, that only just qualifies as extreme. As another example, the rains causing the Brisbane flood had an Annual Exceedance Probability of 1 in 400 for the whole event, and for the peak rainfall of 1 in 2000. That works out as lying between 3 and 3.5 standard deviations from the mean. This is a flood that sent twice the amount of water down the river as when Brisbane got hit by a cyclone in 1974, and as much as for Brisbane's breaking flood in 1893 (also cyclone related), but this was just from a line of thunderstorms. But according to you it is borderline as to whether it should count as extreme. Or consider the Toowoomba flood. The rainfall for that flood had an AEP of just over 100, equivalent to a standard deviation of just 2.6. Consequently Toowoomba's "instant inland tsunami" does not count as an extreme event for you. The clear purpose of your definition is to make "extreme events" as defined by you so rare that statistical analysis of trends becomes impossible. You as much as so so. In your opinion, " true extremes have small numbers of events which make it difficult to perform trending". But that is as good as saying your definition of true extremes is useless for analysis. In contrast, an event with an AEP 2 SD above the mean (a 1 in twenty year event) is certainly extreme enough for those caught in the middle. Further, those events are predicted to increase in number with global warming. So why insist on a definition of extreme which prevents analysing trends when the theory we are examining makes predictions regarding events for which we are able to examine trends? Why, indeed, is global warming "skepticism" only ever plausible once you shift the spot lights posts so that the evidence all lies undisturbed in the darkness. -
Dikran Marsupial at 17:17 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Norman wrote: "I am only questioning the collection of severe weather events of 2010 and using this as proof that the warming globe is causing an increase in extreme weather that have caused more destruction and will continue to get worse as the planet continues to warm." It isn't proof, it is corroborative evidence. In science you can't prove by observation, only disprove, and constant calls for proof of AGW (which is known to be impossible, even if the theory is correct) is a form of denial. A warmer world means that the atmosphere can hold more water vapour, and thus there will be a strengthening of the hydrological cycle. A consequence of that is likely to be an increase in extreme weather in some places. Thus an increase in weather extremes is what you would expect to see if AGW is ocurring, but it isn't poof. If you think that is not good science, then it is your understanding that is at fault. That warm air holds more water vapour is observable to anyone with a thermometer and a hygrometer, compare humidity in summer months and in winter months. That water vapour has to go somewhere, as water is constantly being evaporated from the oceans by the suns heat. More is evaporated in warm condisions than in cold. Thus more evaporation means more rain. It really isn't rocket science. -
Dikran Marsupial at 17:01 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Eric Extreme events already have a good statistical definition, namely the return period, for instance an event might have a return period of 100 years, in laymans terms, a "once in a hundred year event". This definition has the advantage of automatically taking into account the skewness of the distribution. The small number of events does not pose a serious problem in estimating changes (trends) in return times. There is a branch of statistics called "extreme value theory" that has been developed to address exactly these kinds of problems. If you have a statistical background, there is a very good book on this by Stuart Coles (google that name to find tutorial articles). -
Tom Curtis at 15:58 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
Norman @192, several comments: 1) The graph is not directly comparable as the CEI graph uses a 1 in 10 year definition of extreme, while Kunkel shows 1 year, 5 year and 20 year return intervals. 2) The graph you indicate only shows the period to 2000. From the data from CEI, the period 2001-2010 shows a higher frequency of one day, 1 in 10 year return period precipitation events than does 1991 to 2000, which probably means it is equivalent to 1895-1900 for 1 year and 5 year return events, but less than 1895 - 1900 for 20 year return events. It is however hard to be sure as no direct comparison is possible (see above). 3) The first interval on the graph, and the only interval to exceed 1991-2000 and presumably 2001-2010 in any category (except for 1981-1990 five day duration/ 20 year return interval) consists of only six years. It is probable that has the full decade been included the values would have been reduced, possibly significantly so. It is, of course, also possible that they would have increased them. If the four excluded years had followed the mean of the entire record, then the 1 day/ 1 year return value would have been approx 12.6%, the 5 year return value would have been 11.4%, and the 20 year return value would have been around 28.8%, values lower than or equivalent to those for 1990-1991. That would mean they are also lower than the 2001-2010 values. These three considerations suggest we should treat the 1895-1900 data with considerable caution. That the period is also the most likely to be adversely effected by poor station quality, and/or record keeping, only reinforces that caution. For example, one explanation for the different patterns between 1 day, 5 day and 30 day records (see below) may simply be that records were not taken at consistent times in the early period, thus inflating single day values without altering multi-day values. A six hour delay in checking rain gauges could easily inflate daily values by 50% or more. Having urged caution, however, I will take the data at face value (because it appears to counter my case rather than support it). That is, I will treat the data conservatively with respect to my hypothesis. Doing so, I proceeded to check the whole paper. What struck me is that though Figure 3 (extreme one day precipitation events) shows very high values for 1895-1900, that was not the case for 5 day and thirty day events (figures 4 and 5). For 5 day events, the 1895-1900 figures where less than the 1991-2000 (and presumably also 2001-2010) in all categories. The same is true for 30 day events, but in that case the number of 1 year and 5 year return events where much less than those for the 1990's. Assuming the data is genuinely representative of the decade 1891-1900, that indicates that the high number of extreme rainfall events in that decade has a distinct cause form those of the 1990's and presumably 2000's. If they had the same cause, they would show a similar rainfall pattern to the most recent decades. The difference in causation may be something common to the two periods, along with some factor present in the recent decades but not in the 1890's. More likely it is entirely distinct in that the only thing truly common between the 1990's high rate of extreme precipitation and the 2000's even higher rate is high global temperatures. In any event, the data presented ambivalently confirms the notion that the most recent period is unusual. Confirms because in two out of three periods, the 1990's and presumably 2000's represent the highest frequency of heavy rainfall events, while in the third (1 day events) the 1890's are similar but neither conclusively greater nor less than the 2000's. The data certainly disconfirms the notion that some periodic oscillation is responsible for both the rainfall extremes in the 1890's and over the last two decades because of the distinct causal antecedents. Now, having given you what I consider to be a fair analysis of the data, I am going to berate you. Firstly, drawing attention to the 1 day return interval without also mentioning the different pattern for the other durations is without question cherry picking (yet again). It is cherry picking even though you where responding to a comment about 1 day duration events because it was relevant in general, and definitely relevant to your hypothesis because it undermined it. (The original comment was not cherry picked in that the CEI data only includes the 1 day interval.) Further, your analysis was shoddy in that it made no mention of the confounding factors. That's par for the course in blog comments, but it is shoddy analysis. It is particularly so from somebody who is so scrupulous in finding confounding factors in data that does not suit you. In fact, it shows you are employing an evidential double standard (yet again). All of this is exactly what I would expect from a denier in sheep's clothing. But if by some extraordinary chance you are what you claim to be, you can't afford that sort of shoddiness. You need to look out for the confounding factors yourself, and always treat the data conservatively, ie, assume it has the worst characteristics for your preferred hypothesis. Otherwise you will just keep on proving the maxim that the easiest person to fool is yourself. -
Phila at 15:53 PM on 3 July 2011Google It - Clean Energy is Good for the Economy
I will continue to disagree with the premise that a doubling of co2 will result in a min of 2.0C temp rise. I'm sure you will, come hell or high water. As the old gag says, "you can't reason a man out of a belief he didn't reason himself into." In other not-very-surprising news, the rest of us will continue to get our information from experts who know what they're talking about, instead of non-experts who are proudly spinning their wheels in an ideological rut. -
Eric (skeptic) at 14:59 PM on 3 July 20112010 - 2011: Earth's most extreme weather since 1816?
My 2 +/- 2 cents on trends in extremeness is that true extremes have small numbers of events which make it difficult to perform trending. The extremes need to be more tightly defined than is the case above (some of the head post examples are extreme, some are not and some are ill-defined or not commonly measured). Tom's proposed definition up in post 110 which is two standard deviations from the mean for rainfall needs to be tightened up IMO. The extremeness will depend on the coverage area, time interval for the mean, and the distribution of that particular random variable. A normally distributed variable will have a relatively straightforward definition of extreme, 3 SDs in many cases and 4 SDs in most cases as long as the time period and arial extents are large enough. Here's an example of extreme rainfall events http://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/pdf/10.1175/1520-0493(1999)127%3C1954%3AEDREAT%3E2.0.CO%3B2 e.g. 10 SDs above the daily average in an Indian monsoon due to the skewness of the distribution making outliers more common than a normal distribution. The Tennessee floods mentioned above had a large area of 1 in 1000 probability so qualifies as extreme. In contrast the 2010 Atlantic season described above as "hyperactive" is not a strong statistical outlier (12 versus 7 +/- 2 hurricanes with some right skew) -
Camburn at 14:13 PM on 3 July 2011Google It - Clean Energy is Good for the Economy
actually thoughtful: This thread is about the implimentation of a carbon tax and what some percieve to be the results of said implimentation. I disagree with the projected results. I have demonstrated changes that are occuring without a carbon tax. I will continue to disagree with the premise that a doubling of co2 will result in a min of 2.0C temp rise. As far as spending, all on and off budget items, being balanced in 2 fiscal years by eliminating the Bush Tax Cuts and the increase in medicare payments, well....you are totally wrong. -
JoeRG at 12:39 PM on 3 July 2011It's the sun
KR First is that natural variability means that on a short time scale (5-10 years) 'climate' models can only give an approximation of the 'weather', where on 20-30 years they do an excellent job of looking at trends. It's not a miss unless the observations go outside the envelope of model predictions, the orange and blue bands representing the multiple-run envelope.. Therefore the fit with anthropogenic forcings is quite good. If you didn't notice, the two peaks I mentioned are begin and end of a trend that lasted about 35 years and that, after removing the noise of ENSO effects, was as straight as a temperature trend could ever be. So I didn't speak about a short time effect but about a significant climatic scenario. Besides, it is a good example for underestimation of natural forcings, especially the solar forcing. Given that the forcings are to describe as a function like in comment #845 by scaddenp, the function for the natural forcings is: (nat)Temp = Func(Sun, Albedo(clouds), Aerosols(vulcans)). Looking at the conditions shows that in this period the albedo is to assume as nearly constant and the aerosols were slightly lowering with only a very small change after 1915. So the solar forcing remained as the main driver of the occured trend. As well, if only the natural forcings were considered, this trend should have been continued until 1963 because there were no significant changes. This leads to your next statement: Third, 'global dimming' shows up in both model and measurement data as change to a downward trend around 1940. I think your statement regarding that is unfounded. Excuse me, but where is it? In the measurements clearly, but where in the models? Given the circumstances that no natural forcing had changed that far that the trend could have been stopped (in the period from '45 until '63) results in the conclusion that anthropogenic forcings were at work in the manner of global dimming. This would mean that natural forcings must have caused higher temperatures as anthropogenic forcings in this time. But this never happens in the models. Summarized: We have a model that 1) doesn't consider significant trends, 2) underestimates natural forcings and 3) shows wrong values of anthropogenic forcings. Sorry, but 'excellent' is something different. Finally, as to models - they are an important tool for teasing out the contributions and effects of different forcings, as well as a good check on our understanding of the physics involved. Such models give the impression that the physics are not well understood, at least in the climate science. Second, given recent higher grade measurements of forcings, the post 1950's fit is accordingly better in the models. Not quite. Forcings are calculated based on measured physical values and observed conditions. I suggest you read the Models are unreliable thread if you have such concerns about the use of models as tools. I didn't mean to go too far off topic, but this model that you've presented is a proper example for an analysis how underestimated solar activities are in the climate models. As I see it, because of false trails that exist (and that are powered by such bad models), the research in possible amplifications of solar forcings is too little to get a better understanding. For example, as I told before the magnetic field of the Earth weakened by 10% in the last century while the solar magnetic flux nearly doubled. I found only a view studies about this influence on climate, but most of them were made by persons that you would call a 'denier'. In the IPCC documents I found nothing at all, regrettably. As well, an influence of number and intensities of solar flares is possibe (and can of course explain the unusual hard rise in the OHC in 2003). But as long as only the last 35 years of solar activity are considered (as in the 3 topics and the IPCC reports) there will be probably no change in research. And that is not only a 'miss', it is truly a mess. -
actually thoughtful at 12:11 PM on 3 July 2011Throwing Down The Gauntlet
Camburn, The problem with your analysis is you are focusing on the wrong problem. While you are correct that oil will become fairly scarce in the next 2 decades, natural gas and coal are very plentiful. The chart below (source:http://www.eia.gov/dnav/ng/hist/n3010us3M.htm) shows you the cost of natural gas - it spiked in 2008, but is now back to 2005 levels.
Once oil prices start their inevitable rise, the world will be at a crossroads - do we convert to natural gas and coal for transportation? Or do we get off the fossil fuel roller coaster. At this moment, even with President Obama's leadership, the politics of the extreme right in the USA will not allow the rational choice. This is a HUGE problem.
So it is important to solve the right problem. You have us solving a fuel shortage - that is not the problem.
The problem is CO2 - which says eliminate coal first, then other fossil fuels as soon as possible. I am in favor of a full court press to eliminate any fossil fuel I find in my life. I think being carbon free is the most patriotic thing you can do.
As for China - PLEASE! let's bring the debate above kindergarten "but so-and-so did X" - let's get our house in order, then profit like bandits helping the other countries (see Germany as but one example).
This is why it is critical to focus on the ACTUAL problem - which is warming due to CO2 - so you don't end up with bizarre policy solutions that have no relationship to the problem (with your model you could end up with the US government actually supporting "clean coal" - what could be a dumber policy!?
Moderator Response: [Dikran Marsupial] adjusted width of image
(source:http://www.eia.gov/dnav/ng/hist/n3010us3M.htm) shows you the cost of natural gas - it spiked in 2008, but is now back to 2005 levels.
Once oil prices start their inevitable rise, the world will be at a crossroads - do we convert to natural gas and coal for transportation? Or do we get off the fossil fuel roller coaster. At this moment, even with President Obama's leadership, the politics of the extreme right in the USA will not allow the rational choice. This is a HUGE problem.
So it is important to solve the right problem. You have us solving a fuel shortage - that is not the problem.
The problem is CO2 - which says eliminate coal first, then other fossil fuels as soon as possible. I am in favor of a full court press to eliminate any fossil fuel I find in my life. I think being carbon free is the most patriotic thing you can do.
As for China - PLEASE! let's bring the debate above kindergarten "but so-and-so did X" - let's get our house in order, then profit like bandits helping the other countries (see Germany as but one example).
This is why it is critical to focus on the ACTUAL problem - which is warming due to CO2 - so you don't end up with bizarre policy solutions that have no relationship to the problem (with your model you could end up with the US government actually supporting "clean coal" - what could be a dumber policy!?
Moderator Response: [Dikran Marsupial] adjusted width of image -
Patrick 027 at 11:33 AM on 3 July 2011The Planetary Greenhouse Engine Revisited
In the same vein as my 57, see fig 10 from source in 53. It is a global annual average. It shows solar heating generally almost in balance with net LW cooling. However, I think it may be showing the part of solar heating via chemical latent heat at the point where the chemical latent heat is released. Hence the location where solar radiation is absorbed may not be the same, althouth I think it has a similar general pattern in the lower mesosphere. Anyway, that's a bit different than conduction/diffusion of sensible heat and though circulation may be involved, it wouldn't be necessary to bring fluxes into balance there (temperature would adjust as necessary to bring net LW cooling into balance with the others). There is an interesting descrepancy between the cooling and heating rates higher up - I'll have to look again but I think it may not be balanced by conduction/diffusion; perhaps there is a fingerprint of convection in the global average? But a reminder that this is forced motion, not locally spontaneous. -
dana1981 at 11:00 AM on 3 July 2011Glickstein and WUWT's Confusion about Reasoned Skepticism
Chris - there's a forehead slapper. I guess being 40 years behind the times is an improvement over being 100 years behind the times. He also had a great barrier reef decline denial post, which mentioned Ove H-G, which is nice timing, because I'm about to publish a post by Ove H-G on exactly that subject.
Prev 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1606 1607 1608 1609 1610 1611 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























