Recent Comments
Prev 2181 2182 2183 2184 2185 2186 2187 2188 2189 2190 2191 2192 2193 2194 2195 2196 Next
Comments 109401 to 109450:
-
Ned at 05:37 AM on 2 October 2010Does Climate Change Really Matter?
2-3 C sounds like a little temperature change ... but that's misleading, because a small temperature change averaged over the entire globe is actually a huge change in the climate. For comparison, global temperatures at the last glacial maximum were about 8 C lower. So that 2-3 C is about a quarter to a third of the change between my home being in a comfortable temperate forest and my home being buried under 2000+ meters of ice. -
Doug Bostrom at 05:34 AM on 2 October 2010Does Climate Change Really Matter?
One of way of thinking of this, mfripp, is that if my house should burn down, I will not be able to comfort myself with the thought that my neighborhood did not noticeably warm up. Some of the problem is indeed with "wild weather"; presently there's an extra accumulation of something like 4000 petawatt hours/year of energy on Earth happening and unless it's really smoothly distributed the effects are expected to be noticeable in visibly dramatic and kinetic ways. That translates into things like this: For example, the "hundred year flood" was once something that you had better be aware of, but it was not very likely soon and you could get reasonably priced insurance. But the probability distribution function does not need to shift very far for the 100-year event to be occurring several times a century, along with a good chance of at least one 500-year event. -- NASA-GISS: 2010 — How Warm Was This Summer? Speaking of weather, Kevin Trenberth says: I find it systematically tends to get underplayed and it often gets underplayed by my fellow scientists. Because one of the opening statements, which I’m sure you’ve probably heard is “Well you can’t attribute a single event to climate change.” But there is a systematic influence on all of these weather events now-a-days because of the fact that there is this extra water vapor lurking around in the atmosphere than there used to be say 30 years ago. It’s about a 4% extra amount, it invigorates the storms, it provides plenty of moisture for these storms and it’s unfortunate that the public is not associating these with the fact that this is one manifestation of climate change. And the prospects are that these kinds of things will only get bigger and worse in the future. -- NCAR’s Trenberth on the link between global warming and extreme deluges The "vitriol" about convection is reflective of frustration with the idea that so much energy can be wished away. -
Ned at 05:32 AM on 2 October 2010Climate Change: Past, Present, and Future
philc writes: The bottom line takeaway is wait another 30-40 years and we will have a much better idea of what drives the climate. Actually, we've already got a pretty good understanding of what drives the climate. -
michael sweet at 05:31 AM on 2 October 2010IPCC Reports: Science or Spin?
The IPCC was founded by politicians who were trying to show that there was not a scientific consensus that AGW was a problem. The politicians thought that the scientists would not be able to reach a consensus and that nothing would have to be done. The reality is that QGW is so obvious that scientists quickly reached a consensus. We need to act to prevent future problms. -
NETDR at 05:30 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
RE: doug_bostrom [6] Posted: Lest anybody be confused by NETDR's rarefied treatment of ocean heat, here's a synopsis of the latest thinking on OHC measurements, "Robust warming of the global upper ocean" where the matter can further be discussed. ************ Lest anyone be confused by Doug’s study of ocean heat. The XBT which this study is based upon only goes 460 Meters deep[for most measurements] while the more accurate Argo buoys go 2 kilometers deep. The XBT’s are launched from ships and so are weighted toward warmer shipping lanes. There are 3000 Argo buoys which sample the whole ocean except under the ice packs. Which s more accurate ? The Argo buoys have found cooling since 2005. http://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/3M_HEAT_CONTENT/ There were several people who objected to my using 6 ° C for a doubling of CO2 which was taken from Dr Hansen 2008. He had a short term value of 3 ° C also if that is more pleasing. We aren’t warming nearly that fast either. The earth s a long way from being on track for even 3 ° C of warming in 100 years. The article The decade 2000-2009 was, globally, around 0.15 °C warmer than the decade 1990-1999." This projected warming would be 1.5 °C in 100 years which is not enough to spend tens of trillions of dollars to avoid. Don’t get me started on models. I coded them professionally and am less than impressed with “hindcasting”. It is a good start but only a start.. They have to insert a huge plug to insert natural cooling to account of the warming which isn’t happening according to predictionModerator Response: A more comprehensive discussion of OHC may be found here, "Robust warming of the global upper ocean."
As a general note to anybody making comments here on Skeptical Science, if you find yourself writing an extended comment on a specific avenue of inquiry, be sure it's posted in a place conducive to coherent, nonduplicative discussion of the particular research topic you have in mind.
Not to pick on NETBR in particular, but the above comment is an excellent example of producing an intractable salad of issues, each of which are deserving of separate discussion.
As always, the "Search..." box at upper left is your friend when it comes to locating opportunities to continue conversations as well as avoid rehashing issues in a myriad of different locations. -
Ned at 05:28 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
philc writes: We can't even get good solid measurements out of the current measuring network because measurements as little as 5-10km apart can be significantly different. That doesn't matter, because temperature anomalies are correlated over very large distances (hundreds of km). Nick Stokes showed that you can reconstruct the global temperature trend with as few as 60 stations. -
philc at 05:23 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
There is no point in trying to graft measured temps over the last 100 years to proxies collected over hundreds to thousands of years. The estimated proxy temperatures can't be calibrated with the measured "current" temperatures because none of the measuring points are co-located. None of the proxies are co-located either. We can't even get good solid measurements out of the current measuring network because measurements as little as 5-10km apart can be significantly different. We need much better current data. -
actually thoughtful at 05:17 AM on 2 October 2010An underwater hockey stick
Yay! Thanks for this paper based post (I enjoy all of them, but do appreciate a diet rich in peer-reviewed science!) -
Doug Bostrom at 05:15 AM on 2 October 2010Climate Change: Past, Present, and Future
Always worth remembering, while they may provide information on expectations, reconstructions of past climate do not presume to be explanations of what drives the climate. Philc, when you say no reconstructions of past temperature do not provide much usable information, what do you mean? Are you saying they provide no cues on likely boundaries? If your conclusion is that they show temperatures as generally having been constrained within a range of perhaps 0.6 degrees C, how is that not useful? -
CBDunkerson at 05:05 AM on 2 October 2010Does breathing contribute to CO2 buildup in the atmosphere?
johnd #44: "choosing an apple to make a point was perhaps not the best choice as it focuses on the fruit and not the tree." Last I checked, people do not eat trees. -
philc at 05:05 AM on 2 October 2010Climate Change: Past, Present, and Future
Interesting graph. Doesn't look much like this one: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/paleo/pubs/mann2008/mann2008.html The most notable conclusion I can make from all the paleo reconstructions of temperature is that none of them provide much usable information. All of them show that changes of ~.5-.6 degC over periods of 10 years or so are to be expected. The bottom line takeaway is wait another 30-40 years and we will have a much better idea of what drives the climate. -
MattJ at 04:54 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
This article is basically good, but it takes too long to state its 'thesis' in the proem, and its lack of vigor in stating the final conclusion reminds the reader of wilting plants. -
mfripp at 04:43 AM on 2 October 2010Does Climate Change Really Matter?
Sorry to break into the vitriol with a real question... But I do not understand. The implication of the main article is that the 2-3C temperature rise is not the main problem. As the article states, a small temperature change is not something to be bothered about. Instead, is the real issue with the increase in wild weather? Is the temperature rise simply a proxy for representing a bunch of other climatic events? I have to confess, I have never really understood why a small change in temperature could have such a big effect on civilizations. If, however, temperature was a proxy for storm energy, then this would be a different understanding. Thoughts? -
philc at 04:36 AM on 2 October 2010IPCC Reports: Science or Spin?
"The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC or FCCC) is an international environmental treaty produced at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro from 3 to 14 June 1992. The objective of the treaty is to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system." Since the IPCC was founded by the UNFCCC treaty, with the purpose of summarizing research into stabilizing "dangerous anthropogenic interference" with the climate Dr. Spencer's criticism is totally true. Scientific research does not assume a conclusion and then try to prove it. The IPCC reports are fundamentally UN-scientific simply because they presuppose the results. Look it up in the founding documents if you don't believe it. The IPCC is a political organization founded to promote the hypothesis that human emissions of C02 have caused dangerous changes to the climate. Case Closed!! It cannot produce and unbiased report simply by definition. -
ClimateWatcher at 04:24 AM on 2 October 2010IPCC Reports: Science or Spin?
"Sea-level rise is accelerating faster than the IPCC predicted." Sea level rise does not appear to be accelerating at all: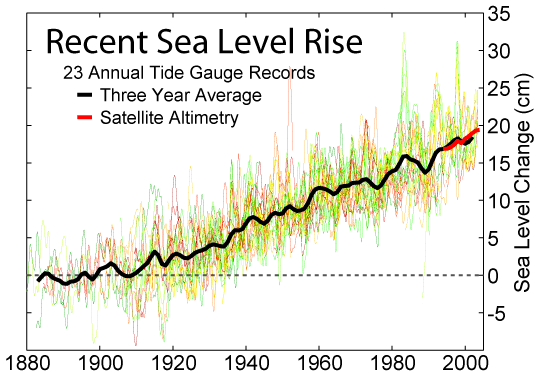 "Each Arctic summer, sea-ice is melting faster than average predictions in the last IPCC report."
Of course there is a dynamic loss of sea ice which explains much of the decline:
http://seaice.apl.washington.edu/IceAge&Extent/
See the movie:
http://seaice.apl.washington.edu/IceAge&Extent/Rigor&Wallace2004_AgeOfIce1979to2007.mpg
"The Arctic is experiencing a long-term loss of multi-year ice which is also accelerating."
Sea ice seems to have a 'memory' at a period which may exceed the duration of the satellite record. But given the unusual warmth in the Arctic during the 1930s, it's possible that such a similar decline occurred then. When sea ice is reduced, more heat escapes from the Arctic water and this would explain the 1930s anomaly.
The proximity of the Beaufort Gyre and the Arctic Throughflow set up a possible mechanism for this.
When the gyre dominates, ice spins around and accumulates. When the through flow dominates, ice is lost to the Atlantic and declines.
"Each Arctic summer, sea-ice is melting faster than average predictions in the last IPCC report."
Of course there is a dynamic loss of sea ice which explains much of the decline:
http://seaice.apl.washington.edu/IceAge&Extent/
See the movie:
http://seaice.apl.washington.edu/IceAge&Extent/Rigor&Wallace2004_AgeOfIce1979to2007.mpg
"The Arctic is experiencing a long-term loss of multi-year ice which is also accelerating."
Sea ice seems to have a 'memory' at a period which may exceed the duration of the satellite record. But given the unusual warmth in the Arctic during the 1930s, it's possible that such a similar decline occurred then. When sea ice is reduced, more heat escapes from the Arctic water and this would explain the 1930s anomaly.
The proximity of the Beaufort Gyre and the Arctic Throughflow set up a possible mechanism for this.
When the gyre dominates, ice spins around and accumulates. When the through flow dominates, ice is lost to the Atlantic and declines.
-
JMurphy at 04:19 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
ClimateWatcher, you would be more credible if you gave the whole quote, thus : Progress since the TAR enables an assessment that climate sensitivity is likely to be in the range of 2 to 4.5°C with a best estimate of about 3°C, and is very unlikely to be less than 1.5°C. Values substantially higher than 4.5°C cannot be excluded, but agreement of models with observations is not as good for those values. Which is not based on "those climate scientist [who] happen to be part of the IPCC", but a vast body of work given here : Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis 8.6 Climate Sensitivity and Feedbacks Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis 9.6 Observational Constraints on Climate Sensitivity Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis 10.5 Quantifying the Range of Climate Change Projections (I have also posted this over on the Climate Sensitivity thread, which is where this should be) -
JMurphy at 04:19 AM on 2 October 2010Climate sensitivity is low
ClimateWatcher (on another thread), you would be more credible if you gave the whole quote, thus : Progress since the TAR enables an assessment that climate sensitivity is likely to be in the range of 2 to 4.5°C with a best estimate of about 3°C, and is very unlikely to be less than 1.5°C. Values substantially higher than 4.5°C cannot be excluded, but agreement of models with observations is not as good for those values. Which is not based on "those climate scientist [who] happen to be part of the IPCC", but a vast body of work given here : Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis 8.6 Climate Sensitivity and Feedbacks Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis 9.6 Observational Constraints on Climate Sensitivity Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis 10.5 Quantifying the Range of Climate Change Projections -
archiesteel at 04:07 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
Sorry for continuing the off-topic discussion. I won't comment on it here any further. -
archiesteel at 04:06 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
@CW: 1.8 is not under low estimates, it is exactly on the low estimate. You've been trying to push that canard in a different thread, but it's still as false here as it was there. "Unless those climate scientist happen to be part of the IPCC, in which case they do. "likely to be in the range 2 to 4.5°C" "Values substantially higher than 4.5°C cannot be excluded"" No, they don't. These two statements are correct. You're simply trying to muddy the waters here. As far the broad-spectrum ORL showing an increase, that is also an indication that AGW is happening. In fact, it's well explained on this very web site. You should learn a bit more about the science before playing the role of contrarian, your errors are too easy to spot. -
DSL at 03:59 AM on 2 October 2010Newcomers, Start Here
CW, you're projecting on that critical thinking comment. You know the onset of warming is much more rapid now than for the HCO. You know that adaptation is more difficult in rapidly changing conditions. You know that human environmental restructuring was, compared to today, insignificant during the HCO. You don't know what the sea ice extent was for the HCO. You don't know whether or not summer sea ice disappeared for long periods of time during the HCO. Yet you still persist in shrugging off current conditions as "been there, done that, no major bio-change." Science doesn't agree -- 15-37% of species committed, by 2050, to extinction if present trends continue. The polar bear is probably already committed, even with significant mitigation efforts. Who cares? After all, for most people, a polar bear is a fantastic creature most will never actually see in its natural habitat. It might as well be something from Tolkien's imagination. yet a flippant attitude toward this top predator (well, "top" doesn't mean anything, since bacteria etc. will eat the dead body of the bear) suggests a flippant attitude toward dying and rapidly expanding species that will (and are) having a direct impact on every day human life. This warming is different--more akin to the rapid extinctions that punctuate the fossil record. It's not the pathetic, slow deaths of the woolly mammoth and sabretooth tiger. It's the discordant rapid loss and rapid expansion of habitat. -
dana1981 at 03:52 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
ClimateWatcher, I refer you to How do we know global warming is still happening, particularly the discussion of Earth's global energy budget and top of the atmosphere imbalance of 0.9 W m-2. -
ClimateWatcher at 03:47 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
dana1981 15. "Climate scientists almost never refer to 2xCO2 climate sensitivity as higher than 3°C" Unless those climate scientist happen to be part of the IPCC, in which case they do. "likely to be in the range 2 to 4.5°C" "Values substantially higher than 4.5°C cannot be excluded" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Climate_sensitivity Of course there is 'uncertainty' because there is uncertainty in the IPCC range and the observations are all below the low end of that range.Moderator Response: Unless you'd prefer your comments on this thread regarding specific features of climate science be deleted, you'll want to take each specific scientific problem you feel exists to the appropriate thread, as has already been suggested. -
JMurphy at 03:38 AM on 2 October 2010Newcomers, Start Here
I think polar bears are like 'hockey-sticks' to a certain type of so-called skeptic - if they can convince themselves that polar bears are going to be alright (because they were alright in the past, right ?), then that would be another final (final) nail in the coffin of AGW. Perhaps they should have an emblem of a polar pear playing hockey on lovely thick ice, with a big cheesy smile on its face. And a knowing wink - visible only to those who know the 'real' truth of AGW. -
Ned at 03:31 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
In addition to this back-and-forth about climate forcings, earlier in this thread Ken got very interested in the fact that, taking each decade on its own, neither the 1990s nor the 2000s had a statistically significant warming trend. Nor did the 1980s, nor the 1970s. That's right -- if you only look at ten-year periods, none of the past four decades has had statistically significant warming when taken on its own. But over the entire four-decade period, the warming has been very highly significant. The lack of a statistically significant warming trend at decadal time scales does not mean "global warming has stopped", any more than the lack of a statistically significant warming trend at weekly time scales means that "the seasonal cycle has stopped". I've done some simulations, using an underlying quadratic warming trend that matches the past four decades and rises smoothly to a very extreme warming of +6C (above 1970 values) in 2100. I de-trended the last decade's temperature record, and then added it to each future decade, thus giving each decade a similar kind of "noise" superimposed on top of an ever-increasing trend. The first decade where we would see a statistically significant decadal trend is the 2020s. In other words, it's not until 2030 -- nearly halfway through the period of 1970-2100 -- that we would have experienced a decade where there actually was a statistically significant trend within the decade itself. If you use the 1990s as a model for "noise", the 10-year warming trend first becomes significant in the 2010-2019 decade. So we could potentially see this in the 2010s, or it might not be until the 2020s. By the 2030s, pretty much any previous decade's "noise" would show a statistically significant 10-year trend. Thus, even with a strong underlying warming trend, you have to go through the fifth or sixth decade before you are able to detect a statistically significant decadal trend. I think this very nicely disposes of Ken's claims that the non-statistical significance of warming in individual decades is evidence that temperatures have "flattened". -
johnd at 03:31 AM on 2 October 2010We're heading into an ice age
Tom Loeber at 02:10 AM, Tom I tend to agree with you. Virtually nothing is discussed here about noctilucent clouds, I think because of the fascination with what occurs at the TOA which seems to be considered as being the tropopause. I think TOA is a misnomer anyway as it is actually more so the top of the weather with water vapour and CO2 extending above it as well as all the other gases that form the atmosphere. -
JMurphy at 03:23 AM on 2 October 2010We're heading into an ice age
Tom Loeber wrote : "Research noctilucent clouds. Me thinks they are purposely ignored due to their suggesting carbon dioxide build up leads to quick cooling of the globe." To state that they are being "purposely ignored" and finish up with a link to a NASA video about them, is a bit confusing. There is also a WIKIPEDIA page all about them, which shows lots of studies into them. Hardly "purposely ignored", surely ? As for your assertions about 'cold records' : Bolivia had their coldest temperatures in nearly 50 years and that, combined with low water levels due to drought (plus, possibly, disease), led to the massive loss of fish. Nature Parts of New Zealand have experienced cold and snow (perhaps the worst since the 70s), unfortunately at the same time as lambing is progressing - However, it is important to remember that many parts of the country have experienced benign weather at the same time, leaving many people wondering what all the fuss was about. NZ Met Service SMH Four gorillas died back in May in Rwanda : New Times If you were trying to prove that AGW is leading to more and more extreme events (albeit the cold ones not being as significant records as the hot or wet ones), then well done. Or were you trying to show something else...perhaps about a coming ice-age ? -
johnd at 03:04 AM on 2 October 2010Does breathing contribute to CO2 buildup in the atmosphere?
CBDunkerson at 23:27 PM, choosing an apple to make a point was perhaps not the best choice as it focuses on the fruit and not the tree. The structure of the tree enables CO2 to be sequestered into the tree itself and fixed below ground through the root system. Depending on the state of the soil to begin with, this and the buildup of organic matter in the soil itself can result in a permanent increase of carbon storage within the soil. If instead we focus on the trees, then we realise that the effects of global deforestation not only contribute in the short term a substantial proportion of the annual increase in atmospheric CO2 levels, but are impacting on the long term capacity to permanently lock up carbon in the soil on a large scale. -
tobyjoyce at 03:04 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
chriscanaris #10 said: "I suspect the AGW debate follows the time-worn Hegelian path of thesis, antithesis, & synthesis" Hegel was talking about philosophical ideas, not scientific ones. Besides Hegel was a lousy scientist - in his youth he published a book stating on philosophical grounds that there could not be more than seven planets. Scientific ideas usually survive on an "all or nothing" basis. There was no synthesis between Newton's and Einstein's theories. I suspect, though, you may be partially right. The denialists are pivoting from science (where they are losing badly) to politics, where they may even be winning. Look at the way the Tea Party has embraced denialism. "Alarmism", "radicalism" and "bringing politics into science" are becoming the main accusations. The Tea Party in power will either have to betray their constituents (which is possibly) or work out some sort of modus vivendi with science. A scientists vs politicians clash is possible, which will make the "science wars" of George Bush's terms look like a kiddies party. Some Tea Partiers are already threatening Congressional Investigations into climate science. So, if there is going to be a synthesis, it will have to be on the politics front. And the best hope is that Tes Partiers do not follow their rhetoric but are more reasonable than they seem. The other hope is that they lose. Given the demeanour of political denialism and the state of play in US politics, I am not optimistic. I know the above seems overly focused on American politics, but that is where the frontline is at, right now. -
Paul D at 03:04 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
chriscanaris: "The science is never settled." That doesn't matter. You still USE the science that you know. You don't hide it under the carpet pretending it never existed or sit around waiting for something better to come along. People didn't say, 'ha Newton, there are a lot of uncertainties because Mercury isn't explained, lets wait until someone else comes up with something better'. What we do, is take what we have got and act on it. -
Doug Bostrom at 02:56 AM on 2 October 2010Newcomers, Start Here
What amazes me are the passionate feelings contrarians bring to discussions of polar bear populations, how emotion seems to supersede rationality, leading to strange arguments simultaneously mixing anachronistic situations as well as contemporary phenomena to produce a sort of average result saying "the bears are ok." Apparently there's some sort of desperation to suggest that loss of habitat for polar bears is a neutral influence on their population, which seems unlikely. -
ClimateWatcher at 02:54 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
NETDR 9. "Ok if you want to say 3 ° C.." Maybe not. The thirty year trends from MSU, SST, and Land/Ocean indices are all at or below 1.7° C per century. Given that most of the IPCC scenarios indicate a deceleration of temperature trend, there's some 'splain'n to do. as to why the observations are not only below the mid range (3° C) but even below the best estimate for the low end scenario (1.8° C). -
Ned at 02:49 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
CBDunkerson makes a good point. Ken's conceptual model of the Earth system would make the climate amazingly sensitive to even a tiny sustained departure from equilibrium. If I understand correctly, he's holding outgoing longwave radiation constant, rather than letting it adjust to changes in atmospheric temperature. An Earth that functioned like that would probably be uninhabitable. -
Doug Bostrom at 02:45 AM on 2 October 2010We're heading into an ice age
Despite local variations, this past summer/winter (depending on where you are) was exceptionally warm in terms of the global scale, not exceptionally cold: 2010 — How Warm Was This Summer? The global scale is of course the significant scale of "Global Warming." Here's a nice roundup of recent work in noctilucent clouds as they relate to climate change, including a really nice photographic example of what they look like: Increase in Shining Clouds Highlights Climate ‘Weirding’. Not a peer-reviewed item but includes links to actual research. -
lord_sidcup at 02:40 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
The spin the GWPF is putting on the Royal Society guide is simply outrageous. It is worth noting that the GWPF has charitable status in the UK and as a result enjoys certain tax breaks and financial benefits. The GWPF stated 'charitable' objectives are: "TO ADVANCE THE PUBLIC UNDERSTANDING OF GLOBAL WARMING AND OF ITS POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCES, AND ALSO OF THE MEASURES TAKEN OR PROPOSED TO BE TAKEN IN RESPONSE TO IT, INCLUDING BY MEANS OF THE DISSEMINATION OF THE RESULTS OF THE STUDY OF, AND RESEARCH INTO A THE SCIENCES RELEVANT TO GLOBAL WARMING B ITS IMPACT UPON THE ENVIRONMENT, ECONOMIES AND SOCIETY C AND THE ABOVE-MENTIONED MEASURES" It seems to me they are actually doing the complete opposite of the above and are actively misleading the public. For some time I've wondered if there is a basis for complaining to the Charity Commission (the body that regulates charities in the UK) about the GWPF. Their status as an educational charity is dubious to say the very least. -
ClimateWatcher at 02:40 AM on 2 October 2010Newcomers, Start Here
The lack of critical thinking really does amaze me. The HCO exposed the polar bears to thousands of years of higher summer temperatures and much less sea ice. The polar bears survived just fine. They don't care. They won't hug you for buying a 'Leaf' ( which will likely be powered by coal anyway ) they will eat you because that's what they do. -
MarkR at 02:31 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
#9 NETDR: "Ok if you want to say 3 ° C so be it but when the scientists want to scare the public they use the higher number." This is a confusion between climate sensitivity and what is projected to happen. Let's say the shopkeeper tells you that an apple costs 3p, but if you buy 2 apples it will cost you 6p. Both of these are true, but the 2 numbers are different and 6p looks worse than 3p. The 3C figure is commonly quoted as the eventual warming if you double CO2 once. 6C is what we expect if we double CO2 twice, which is what is expected to happen under 'business as usual'. It gets even more complicated as 6C is the upper bound of warming by 2100 which includes us heading for 2 doublings of CO2 and the upper bound in the uncertainty of climate sensitivity (3 C is the best estimate, but models still calculate a good chance of up to 4.5 C) -
Rob Honeycutt at 02:15 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
NETDR... "Ok if you want to say 3 ° C so be it but when the scientists want to scare the public they use the higher number." No. I think you're hearing what you want to hear. Problem is you have to listen very closely to what scientists say because there is usually a lot of information imbedded in what and how they say things. Scientists are generally extremely careful to be accurate about what they say (i.e., Phil Jones' "no statistically significant warming"). What you are doing is EXACTLY what you are accusing scientists of doing, only in reverse. You are claiming 6C of warming isn't being seen in current trends, when no one even suggests that you would see them now. Slow down. Listen to what scientists are really saying. -
Tom Loeber at 02:10 AM on 2 October 2010We're heading into an ice age
Research noctilucent clouds. Me thinks they are purposely ignored due to their suggesting carbon dioxide build up leads to quick cooling of the globe. That makes Robert Felix' theory (if you can call it that) even more non-threatening to the robber-baron fossil fuel industries than the global warming theory but makes them both quite unlikely. Carbon dioxide leads to more methane thought to be the main source of the high altitude ice crystals of noctilucent clouds first noticed at the start of the industrial revolution and steadily increasing since then to record extent last year. There is research that suggests they block one percent of the incoming sunlight during the summer months when they peak. That is ten times more solar variation than what has been observed during humanity's existence in the sun's changes in output. It was just found that the mesosphere, where these clouds happen, is now coldest recorded. The jet stream is observed to be at record speeds as well as unusually low, blamed for both the floods in Pakistan and the heat wave in Russia. Recently, Bolivia had their worst environmental catastrophe as normally tropic areas plunged to record cold killing millions upon millions of wildlife and hundreds of people. Tens of thousands of sheep just died in New Zealand due to record cold. Wild gorillas in Rwanda Africa just died from record cold. Germany just saw the most recorded rain for an August. Canada is suffering significant crop destruction from record rains. If the record precipitation persists into the winter, it is liable to bury whole cities under snow and ice. Here is a video made by NASA on the noctilucent clouds: http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-8920558797349908992&ei=NfVUS-rYNJWUqAOzmfzEAw&q=noctilucent# "Are you tied to our destiny?" -
JMurphy at 02:08 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
Ken Lambert wrote : "Happy for you to point out the parts of my post #98 which are wrong JMurphy. Where do you want to start?" I see others more capable have already done so. I would like to add the following quote from your post, which is also wrong : Maybe all those 'scientists' out there who are working on their complex specialties miss the simpler minded basics. In fact, I had already pointed that out but you seem to have a blind-spot when your unsubstantiated beliefs are pointed out to you. -
MarkR at 02:03 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
#3 NETDR: I suggest reading a few of the articles on this site or elsewhere that try to explain the concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity and what this means for future temperature change. Climate sensitivity is a very technical term and in most cases we have reported equilibrium climate sensitivity - which can take a significant time to occur! We also have transient climate sensitivity, which is a bit more relevant and is less than the equilibrium value. Equilibrium says that if you double CO2, you'll eventually get 2-4.5 C warming, most likely 3 C. Your 6 C value comes from almost doubling CO2 twice by 2100, which we haven't done yet! Heating will probably accelerate from today's value. We have increased CO2 by 40%: aerosols approximately cancel out the other greenhouse gases but there are big uncertainties in the cloud effects so they might not be, or they might be partly cancelling out CO2. We expect about 1.4 C warming from CO2 eventually, but it takes time for this to happen. We have climate models that tell us how long we expect to wait, and current temperature change is well within the uncertainty bounds of current generation models - we are warming and the rate we're warming at does not contradict eventual 6 C warming if we double CO2 twice. -
CBDunkerson at 02:03 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
Ken #98: "Maybe all those 'scientists' out there who are working on their complex specialties miss the simpler minded basics." I'm afraid I may not be simple minded enough to follow this. "If the Solar forcing curve were to start not at (0,0) but say (0.1W/sq.m, 0) - a slight positive forcing, then the extra area under the curve would be offset positively by 0.1W/sq.m x 260 years x 365 days x 24 hours x 3600 seconds x surface area of Earth; which equals approx 4190E20 Joules." So... you're saying that if there was a 0.1 w/m^2 rounding error in the baseline solar irradiance figure for 1750 then that would act as an ongoing forcing, never reaching radiative equilibrium, for the entire subsequent 260 year period... and thereby explain a large portion of the observed warming? So... from this we should conclude that the MUCH larger radiative forcing from the enhanced greenhouse effect will ALSO continue to accumulate heat, with no slowdown, for at least another 260 years and therefor we can look forward to temperature increases of +6 C or more even without any further fossil fuel emissions. -
dana1981 at 02:00 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
NETDR, you are rejecting physics in your comments. There is still a net planetary energy imbalance (measured by satellites), so we know that there is more 'warming in the pipeline'. Climate scientists almost never refer to 2xCO2 climate sensitivity as higher than 3°C, so I have no idea what you're talking about. Perhaps you're referring to the warming projected by 2100, which may be as high as 7°C because atmospheric CO2 may rise well above 560 ppmv. -
JMurphy at 02:00 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
“There remains the possibility that hitherto unknown aspects of the climate and climate change could emerge and lead to significant modifications in our understanding.” Of course, and that is a classic crumb which has been thrown to the so-called skeptics, and perhaps why some of them are more keen on the Royal Society than previously, i.e. whereas previously the RS was part of the great big conspiracy, now they have apparently turned about-face and embraced denialism (according to the GWPF, anyway). Supposedly this no doubt means that scientists are slowly moving away from the lies they have previously been telling about AGW, because they aren't interested in the money and power anymore, but have developed a conscience thanks to great men like McIntyre, Watts, etc. Anyway, after that fantasy, here's another possible future : "There remains the possibility that hitherto unknown aspects of gravity and the theories of relativity and quantum physics could emerge and lead to significant modifications in our understanding." Anything is possible... -
Ned at 01:59 AM on 2 October 2010New temperature reconstruction vindicates ...
Ken Lambert writes: By definition all the AG forcings were zero in pre-industrial times (set at AD1750 by IPCC AR4). If you plot the AG forcings (heating and cooling) in W/sq.m on the vertical axis and time on the horizontal axis, you will start at (0,0) in AD1750. You're right, the forcing for GHGs in 1750 is 0 ... because we've chosen 1750 as a baseline! It's not because there were no greenhouse gases in the atmosphere in 1750, nor because they were at "equilibrium" in 1750. Likewise, if you choose a baseline of 1750 for solar forcing, then the solar forcing graph will start at 0,0 in 1750. Just like the greenhouse gas forcing graph. Do you really not understand the concept of "baseline", Ken? You are trying to force people to use an imaginary "equilibrium condition of the Earth" as the only acceptable baseline for calculating forcings. But you can't force (pun not intended) the entire scientific world to abide by your idiosyncratic redefinition of terms. -
Riccardo at 01:59 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
chriscanaris, what the guide says and you report here sound a little obvious. What I found in the new version of the guide is that they utterly fail to give useful information to the public. If this is the contribution of the skeptics i'd be happy to live without it. -
MarkR at 01:58 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
#2 HR: I've edited the first section. One of them is listed under the working group that produced the article (what I would call a co-author) and one of them as a contributor. I've changed the wording and now I hope it combines accuracy with succinctness. -
tobyjoyce at 01:51 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
I thought the RS report was ok, nothing spectacular but sound enough. Then I saw Joe Romm having a cow over it on his blog, so I thought again. But I think Joe is wrong on this one. The public are not clued into the nuances of denialism and will see it as an endorsement of the science of global warming. There is enough in the document to convince readers of the reality of global warming. -
chris1204 at 01:41 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
The RS document seems to have a substantially less forceful tone than its predecessors, which took a very polemic stance of debunking 'dangerous myths.' Much more prominence is given to uncertainties. For example, they state: “It is not possible to determine exactly how much the Earth will warm or exactly how the climate will change in the future. “There remains the possibility that hitherto unknown aspects of the climate and climate change could emerge and lead to significant modifications in our understanding.” Now if I posted a comment on those lines, I suspect many on this site might take issue with me given my role as one of a number or 'sceptics in residence.' I suspect the AGW debate follows the time-worn Hegelian path of thesis, antithesis, & synthesis. So-called sceptics increasingly acknowledge the basic physics and strive to educate their readership on the blogosphere. Warmists increasingly reach out to sceptics (and sometimes get tarred and feathered for their troubles). Nevertheless, we do not yet have synthesis or complete 'consensus.' Nor should we. The science is never settled. In the late 19th century, many believed that physics under the Newtonian paradigm had answered all the basic questions. That all changed in the early 20th century (no doubt, as a non-physicist, I may be grossly over-simplifying the history of relativity and quantum mechanics). Settled science however becomes a stagnant backwater. -
NETDR at 01:40 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
Dana [8] The point is that what you see is what you get. We have seen approximately the mount of warming expected without feedback. [Or less ] That isn't scary enough ! As far as the thermal inertia of the oceans that has been debunked by the "missing heat" arguments refereed to above. If it is hiding at the bottom of the oceans why do we care? When will it return is more germane ? The "long term" feedbacks Hansen refers to have the same problem. Where is the heat now? When will it return ? Ok if you want to say 3 ° C so be it but when the scientists want to scare the public they use the higher number. -
dana1981 at 01:32 AM on 2 October 2010Uncertain Times at the Royal Society?
NETDR - your numbers are wrong. I refer you to Quantifying the human contribution to global warming, which shows that we expect to see ~1.4°C warming from the CO2 we've already emitted, but have only seen ~0.8°C due mainly to the thermal inertia of the oceans. Rob Honeycutt - A study by James Hansen set 6°C as the *long-term* sensitivity to 2xCO2. This accounts for slow-acting feedbacks, as I discussed in a detailed look at climate sensitivity. However, the short-term climate sensitivity is in the 2-4.5°C range, most likely around 3°C. Thus NETDR's reference to the 6°C long-term senstivity is inappropriate and incorrect.
Prev 2181 2182 2183 2184 2185 2186 2187 2188 2189 2190 2191 2192 2193 2194 2195 2196 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























