Recent Comments
Prev 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 Next
Comments 19551 to 19600:
-
Richard Stephens at 06:21 AM on 14 May 2017Citizens’ Climate Lobby - Pushing for a price on carbon globally
No, No, No. Taxing carbon does nothing to solve the problem ... it simply displaces it. Renewable energy is the only solution, but low oil pricing will defeat it. Don't tax carbon; tax oil imports! #TaxImportedOil
-
sauerj at 05:47 AM on 14 May 2017Citizens’ Climate Lobby - Pushing for a price on carbon globally
Thank you SkS on publishing this good update on the CCL organization!
Eclectic @2, very good points. I'll tag along: The wikipedia article on Carbon Tax also gives a good summary, global history, aspects of effective policies & list of endorsements. My Summary: Most of the global C-tax policies have not been nearly as effective as they could be, because they fail to meet the obvious requirements of an effective tax policy. For a C-Tax to be effective, it must be: a) comprehensive (on all FF's, at their source point, proportional to their CO2 footprint), b) have significant impact (at least 10% of GDP, CCL's $100/USton would be 22% of US GDP), c) do not subsidize impacted industries either directly or via tax deductions, which is likely reason the efficacy of most global C-taxes has not lived up to their full potential (subsidizing impacted industries is simply moving money in a circle; of course, the result falls short), and d) the tax must be progressive (i.e. all revenue must be returned to the citizens, and none to industry). On the latter point, only citizens should receive the dividend. They ultimately are the source of the markets. So, in terms of pure capitalistic economic principles, they should be the only sector to receive the dividend. In other words, no specific industry sector by itself is intrinsically endowed w/ capitalistic value except for those that serve basic human survival needs, which are typically publicly funded (water, education, civic order & security, etc). CCL's proposed policy covers these publicly funded sectors by stating that the citizen dividend would be taxed like any other income; this covers the sustinence of these intrinscially valuable sectors. To return the dividends to today's status-quo industries (and I would argue that such industries are already & invisibly subsidized today because the external or social cost of their processes is not included in their product costs), is to capitalistally circumvent the optimum cost vs value trajectory of the economy in a non-sustainable and, thus, injust direction (we would all agree on that statement).
I would agree that subsidizes may likely be necessary to aid in transitioning public utilities. That can still happen as a separate policy. CCL's proposal is, of course, not meant to be an exclusive, do-it-all policy solution. But subsidizing much beyond transitioning public utilities, I believe, would be less effective than RNCFD (revenue neutral carbon fee & dividend), because when subsidizing renewable processes, the selection of which processes to subsidize is limited to the presently known technologies and futhermore is easily politically influenced, resulting in less than optimum solution pathways versus the more effective use of free-market competition & ever organic human ingenuity to discover & develop ever new & better solutions. Instead, let the competitive force of the free-market drive the re-direction of investments away from the carbon-laden & thus less profitable industries, and toward the increasingly more profitable sustainable industries, thus driving the development of optimum R/D endeavors and the resulting commercial solutions.
In the industry that I work in (corn wetmilling for starch & syrup products), I can affirm to everyone that if there was a $100/USton tax, that the plants where I work would immediately implement 100% cogeneration using CCGT technology, thereby cutting our sizable carbon footprint in half (because with a proper C-tax, energy cost would go hand-in-hand with the processes carbon footprint). I believe my anecdotal story would be representative of what would happen all up & down the economy resulting in significant carbon reductions. However, if this transition was fueled instead by regulations or subsidy programs (which are also more administratively burdensome than RNCFD), who's to say if the ultimate & economically viable pathway to the highest degree of carbon emission reductions is, instead, a gradual phase-out of the entire corn wetmilling industry, or at the least, a complete shake-up of our product line. Because the policies of subsidies & regulations do not comprehensively result in "loading" the entire economy with the true cost of FF's (agriculture, other raw ingredients, shipping, packaging, etc, etc ... i.e. but only impact those processes that the subsidies are only directed to), industries like mine would still be partially subsidized (as they fully are now), due to not applying the full & comprehensive extent of carbon's future external costs into our process economics. This makes these other policies less effective in driving the optimum economic sustainable trajectory. On the other hand, RNCFD, by its nature in touching the whole economy, would most effectively force the economy toward optimum solutions and thus maximum carbon emission reductions.
-
BaerbelW at 05:02 AM on 14 May 2017Citizens’ Climate Lobby - Pushing for a price on carbon globally
Gingerbaker - have you checked out the REMI-study commissioned by CCE in 2013? Here is the link to the summary from where you can get to the full report:
-
dudo39 at 04:31 AM on 14 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
michael sweet, it is not a matter of "understanding how to read", its is a metter of having sufficient knowledge and understanding on the subject matter before even attempting to solve a problem or get some answers.
Statistics do not provide solutions: they may indicate how to express an educated guess or opinion [neither one is a fact].
So, it appears to be quite evident that when it comes to what is the net effect of water vapor, the fat lady has not sung as yet.
Yes indeed, we have to make the best decision we can with the information we have, which to me, it does not mean to make facts out of opinions to justify the decision.
-
Gingerbaker at 02:38 AM on 14 May 2017Citizens’ Climate Lobby - Pushing for a price on carbon globally
"Both approaches, used in parallel, seem most appropriate (don't you think?)"
First of all, I do not think both approaches would be available. At least in the U.S., enormous political capital would need to be spent to pass a carbon tax, and I think it is nearly certain that RE subsidies would be on the chopping block as the Republican price for any agreement.
I don't think that is surprising - incredibly, it is difficult to find staunch supporters of subsidies now even on the environmentalist side. I am constantly amazed at the libertarian bent of people interested in this issue. Do they think we should not spend government's money to give preference to RE? They are obsessed with phasing out RE subsidies, are constantly comparing costs of RE vs fossil fuels as if Keynesian economic theory should inform us on this issue. There is a theology about the free market at work here, which is gobsmackingly obtuse imho considering what we know about political corruption and its track record re RE these past thirty years.
Yet, we do know a few things. We know that every single penny spent on a RE subsidy actually builds the only thing that we truly need to solve AGW - RE infrastructure built and deployed. We know that with any of the zillion proposed carbon tax schema, there is zero guarantee that a dime will be spent actually building that infrastructure. We know from years of past experience with carbon taxes in place around the world, that, for the most part, they have been huge failures and do not result in new RE being built any faster than in places where there are not any carbon taxes. They are not even evaluated by that calculus.
Yes, a carbon tax seems like a good idea in a general, hazy Econ 101 sort of way And everyone seems to think a good idea, even if no one actually knows how it might actually work. But, if we spend more than five seconds thinking about it, carbon taxes do not hold up to scrutiny. Worse, they appear to me to be a guaranteed way to make people despise environmentalism. No one, in any schema I have seen, is going to be rebated exactly what they have paid. In most scenarios, despite initial promises, it turns out that half the people will be paying in more than they will be rebated. Combine that with a steady drumbeat in the anti-environmentalist echo chamber, and we are going to see the carbon tax as the most despised boondoggle ever devised. With zero results to show for it. The public is going hate us. There lies doom.
I'll tell you what we DO have evidence of success for: government mandates and subsidies. China is actually accomplishing their part in solving AGW. They don't have any need for the vaguaries of a carbon tax - a mixture of mandates and subsidies is building RE more successfully than the total grand sum of free marketeerism has accomplished over the past three decades.
I would also like to point out to you that twice in your reply to me you have couched the issue of carbon taxes only in relation to "private investors". The majority of electric utilities in the U.S., however, are publicly-owned co-ops or nonprofits. And a giant question that nobody addresses is to what extent should the electric sector remain in public hands? How can we justify the idea of a for-profit paradigm when sun and wind are free and the total expenditure for a brand new RE system would cost us only about seven years of current U.S. fossil fuel spending - which could be payed off in less than a decade while the longevity of RE systems looks to be 0.5 to 1.5 century?
Please note that a carbon tax is antithetical to providing RE power at the lowest possible cost. By making FF more (regressively, btw) expensive, we provide no incentive to keep RE prices low - quite the opposite.
We have an opportunity to build ourselves an egalitarian energy system which could deliver energy at such low cost to us we really could take the meters off the wall. Instead, we are doing everything we can, it seems, to transfer our public utility system into private hands, and set ourselves up for paying maximum prices for energy forever. We really can do so much better than that.
-
citizenschallenge at 22:55 PM on 13 May 2017What Does Statistically Significant Actually Mean?
Dikran valuable article, quite informative, in fact mind-boggling. It helps an uninitiated, such as myself, appreciate the depth of cumulative complexity. It also underscores the reason real experts have spent decades and life times dedicated to studying this. It'll make a handy reference. Thank you for taking the time to tackle the near impossible task of explaining statistical significance to dummies. :- )
peter
-
Eclectic at 22:09 PM on 13 May 2017Citizens’ Climate Lobby - Pushing for a price on carbon globally
Gingerbaker : surely the mechanisms of carbon tax and targeted subsidies are so very different, that in asking which is more "effective", you are trying to make an apples & oranges comparison. You would need to carefully define an agreed definition of "effective" — particularly in relation to short medium and long-term time scale. Additionally, the two approaches are not exclusive (and probably a good case could be made for using both together, to differing degrees at different locations around the world, according to physical circumstances and perhaps political/cultural circumstances as well).
There is a further difficulty, in that a competent carbon tax system has not had much of a trial so far : and thus it is premature to judge effectiveness. Common sense and general economist opinion both indicate that a carefully constructed carbon tax (with or without "dividend") would be reasonably efficacious — provided that it is politically "locked in" and gradually from a low base ramped up at a rate which is well-understood and gives private investors the full certainty they need in order to make their plans for construction of facilities (and phasing out of old plant).
Direct intervention with RE constructions gives the benefit of moving things faster, but needs to be well flagged/publicised to give private investors ample time to make their own best plans to integrate into the future national infrastructure.
Both approaches, used in parallel, seem most appropriate (don't you think?) .
-
Gingerbaker at 18:56 PM on 13 May 2017Citizens’ Climate Lobby - Pushing for a price on carbon globally
Is there a shred of evidence - a single shred - which shows that any carbon tax has been more effective than targeted subsidies at actually getting new RE infrastructure built?
-
jgnfld at 13:21 PM on 13 May 2017What Does Statistically Significant Actually Mean?
Another point w.r.t. significance that is often misused (naively or deceitfully) is examining a series then cherrypicking a local min or local max as the start point for a supposedly "new" and "independent" analysis. This can drastically bias the raw probabilities given by various stats procedures.
By picking a local min in a descending series we can see false "recoveries" in, for example, ice extent records. Alternatively, by picking a local max in an ascending series we can see false "pauses"--or even "cooling periods"--in, for example, temp records. In both cases the reported probabilities have little to do with the actual probabilities when corrected for the cherrypicks.
-
Tom Curtis at 11:48 AM on 13 May 2017What Does Statistically Significant Actually Mean?
The comments by Bob Loblaw @3, and Mammal_E @1 show how important it is to be clear in what you are testing. If we are testing to see if a coin shows heads (or tails) on both sides, the most reliable statistical test is to look at one side, then look at the other.
If we want to test to see if it is weighted to favour one side over the other, and absent precise measuring devices, the best test is to flip it repeatedly to see if there is a bias in the results. In this instance a two tailed test is appropriate because we do not know whether it is biased towards heads or tails, but we would not test against the probability of a particular sequence of heads or tails, but a particular frequency of heads or tails given that a weighted coin will not always turn up the lighter side.
If we want to test to see if an umpire, or group of umpires are cheating in favour of a particular team in the coin toss, we would use a single tail test against the actual sequence of calls by the captain of the team. The test will be against the probability of that sequence turning up given the number of sequence calls (ie, the number of call sequences by all captains in the competition).
-
Tom Curtis at 11:31 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Bob Loblaw @10, I think Art Vandalay was trying to allude to Watt's surface stations project. The idea is that introduction of a cement slab or other artificial structure to the immediate vicinity of a meteorological station will contaminate the trend information. While direct IR absorption by the thermometer does not have any impact on that, it is certainly possible that such degradation of the site might have an effect. Indeed, the effect was quantified in Fall et al (2011). They state in the abstract:
"This initial study examines temperature differences among different levels of siting quality without controlling for other factors such as instrument type. Temperature trend estimates vary according to site classification, with poor siting leading to an overestimate of minimum temperature trends and an underestimate of maximum temperature trends, resulting in particular in a substantial difference in estimates of the diurnal temperature range trends. The opposite‐signed differences of maximum and minimum temperature trends are similar in magnitude, so that the overall mean temperature trends are nearly identical across site classifications. Homogeneity adjustments tend to reduce trend differences, but statistically significant differences remain for all but average temperature trends. Comparison of observed temperatures with NARR [NorthAmerican Regional Reanalysis] shows that the most poorly sited stations are warmer compared to NARR than are other stations, and a major portion of this bias is associated with the siting classification rather than the geographical distribution of stations. According to the best‐sited has no century‐scale trend."
It should be noted that for the primary point of comparison with satellite data, ie, daily mean temperatures, the "... overall mean temperature trends are nearly identical across site classifications".
You have shown that Art Vandalay was wrong in assuming site degradation would effect thermometers by IR radiation to any significant degree, but it does effect local air temperature which is measured at the site.
Finally, I will note that homogeneity adjustments in the surface temperature record are conceptually equivalent to the adjustments made to the satellite record to ensure consistency between the records from different satellites. The major difference is that in the surface record, the adjustment is not checked against the records of one or two other satellites, but against multiple nearby thermometer records, making the adjustment far more reliable.
-
Bob Loblaw at 10:43 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Art Vandelay's description of the effects of a radiation shield is not correct. In addition to eliminating the heating effect of the sun, you also want to eliminate the normal surface IR imbalance.
Under most conditions, IR is a net loss by the surface - the surface emits more than it receives from the sky. This might be close to zero with low overcast, but with clear skies the net loss will be well over 100 W/m2. Overall, net IR cools the surface. We do not want this effect on our air temperature measurement.
The thermometer has an energy balance. If we look at the gain or loss of energy by the thermometer, there are three terms. The sum of the three tells you whether the thermometer is losing or gaining energy.
- Net radiation (solar + IR)
- Thermal heat gain/loss with the air
- Evaporative loss to the air (water evaporates from the surface of the thermometer, consuming latent energy which cools the thermometer).
You need to end up as close as possible to net radiation = zero, so you want solar gain = 0 and net IR = 0. You need to keep the thermometer dry to eliminate evaporative cooling. Then the thermal gain/loss depends on whether the thermometer is warmer, cooler, or the same temperature as the air. If warmer, the thermometer will lose energy to the air and cool. If cooler, it will gain enery from the air and warm. At balance, the thermometer is equal to air temperature and neither cools nor warms, which is what we want. Now we have a measurement of air temperature.
The temperature is then referred to as "dry bulb temnperature". Why? Because if we add water to the mix, we add evaporative cooling. With evaporative cooling the thermometer cools below air temperature, until the heat gain from the now-warmer air exactly balances the rate of heat loss by evaporation, and a stable temperature is reached. That temperature is called the "wet bulb temperature", and it is a fundamental way of measuring the humidity of the air (in combination with the dry bulb temperature).
Even if net radiation is not exactly zero, ventilation using a fan reduces its effects. Big thermometers are worse than small thermometers. In fact, if you use a fine-wire thermocouple (diameter typically 0.001"), then you don't even need a radiation shield or ventilation. Such thermocouples are not particularly robust, though.
Art's speculation about LWR variables contaminating climate data is off base, as far as radiation shields are concerned, because the radiation shield isolates the thermometer from the surrounding net IR fluxes, just as it isolates it from the solar fluxes.
-
Bob Loblaw at 10:18 AM on 13 May 2017What Does Statistically Significant Actually Mean?
Yes, but the sequences HHHT, or THHT are both equally unlikely, too - in fact any single sequence of four tosses has the same probability of 0.0625 (with a fair coin).That's how we figured out 0.0625 - there are 16 different sequences of four tosses, each with equal probability (1/16), all equally "extreme".
If you had a coin that constantly repeated the sequence THHT, then even though you get 50% heads and 50% tails over a long period of time, you would still be playing in a rigged game. If you bet on the basis that each toss was independent/random, then the person that rigged the coin and knew the pattern would be able to take your money.
Four heads in a row or four tails in a row gets our attention because we see a pattern - and our brains think that pattern is significant, even though it is quite possible with a fair coin. Because we see a pattern, we think it is more significant than it really is.
...which is why we should use statistics.
-
HK at 07:25 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Nigelj #7:
"The "law of large numbers" would probably cancel out some of the biases in the surface record, because of so many thermometers."
Indeed! Tamino demonstrated that point very clearly in his blog post Warts and All six years ago. There is an impressive correlation between the temperature trends in five large gridboxes in Europe when using raw data only!
-
michael sweet at 07:09 AM on 13 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
Dudo39,
I am sorry, I thought that you understood how to read a scientific report.
It is very rare for a scientist to make a definitive statement as you request. There is always the possibility that new data will be uncovered that results in something unexpected, even though that possibility is very low. Instead, scientists often speak in terms of probabilities. In the Climate field, lay people have objected to numerical descriptions of data (for example saying there is a 95% chance something will happen) so the terms likely (>66%), very likely (>90%) and extremely likely (>95%) are used (IPCC definations).
It is difficult to get an exact value for cloud feedback so research continues on this topic. In simple terms, for clouds the data indicate that clouds are not a large negative feedback. It is most likely that clouds are a small positive feedback. Clouds will not prevent overheating caused by AGW. Clouds might make warming worse. A scientist would not make absolute claims about clouds because the research is not yet done.
Many things in life are not definite. If I go for a drive in my car I might not come back. We have to make the best decision we can with the information we have.
-
chriskoz at 06:45 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Kevin@5, knaugle@4,
Indeed. The noise of the linear regression residual (be it random or red noise of ElNino signal) - in fact linear regression itself does not represent the data variability across th etimespan shown -is not the subject of this OP. The subject is the biases from imprecise modeling of TLT temperature. When TLT is partially contaminated with TLS (and stratosaphere temp is supposed to fall) then we have a trouble obtaining accurate ands unbiased TLT data. That bias (and bias from satelite drift and trouble combining data from differrent sateltes) is a bigger problem than whether random noise and ElNino red noise. Thermometers place in Stephenson boxes don't suffer from orbital decay if the boxess stand steady.
-
nigelj at 06:38 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Art Vandelay mentions that the sun screens around thermometers can still radiate lw radiation, and I think he is also referring to the urban heat island effect?
I thought these things were well known uncertainties and dealt with, and also relatively small biases. I thought the raw data was adjusted to ensure these sorts of things didn't bias temperatures upwards? Am I right? They are easy enough things to quantify, more so than problems with satellites.
In comparison the satellite data seems to be full of controversies about possible biases and uncertainties, from what I read over at RC, so are more of an unknown quantity.
It's also important to realise problems with sun shading for thermometers would either be constant over the decades, so unlikely to distort an actual changing temperature trend, or if the sun shades have been improved, this would obviously improve the accuracy of the trend. Neither would cause a warming bias to the trend.
The "law of large numbers" would probably cancel out some of the biases in the surface record, because of so many thermometers.
-
william5331 at 06:19 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
If anything the warming is greater than we measure. Sound strange? We should be estimating how much warmer the earth is compared to where we should be if we were slowly sliding into a glacial as we should have been. Apparently the interglacial most similar to our present one in terms of the Milankovitch cycle is the one that occured 400,000 years ago.
-
Dikran Marsupial at 04:48 AM on 13 May 2017What Does Statistically Significant Actually Mean?
Mammal_E indeed, good point.
-
Mammal_E at 02:19 AM on 13 May 2017What Does Statistically Significant Actually Mean?
"The probability of a test statistic at least as extreme as that observed is called the "p-value". In this case, there is no more extreme result than four heads in a row if you only flip the coin four times, so the p-value is just the probability of getting four heads in four flips"
— Not quite. There is another equally extreme outcome (4 tails) which should be considered to generate a 2-tailed p-value — the probability of getting FOUR OF THE SAME RESULT (4 heads OR 4 tails) in four flips = 0.0625+0.0625 = 0.125. Now, a result of 4 tails might not rouse suspicion (because it works against the other team's interests), but that is not really relevant to the test of whether the coin is fair. -
dudo39 at 00:35 AM on 13 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
michael sweet, I stated "The link does not give a definitive statement....": which word don't you understand?
Your statement is iffy and indefinite....
-
Kevin C at 00:07 AM on 13 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Knaugle: I'm afraid that's not a very good indication of the uncertainty in the temperature estimates. The uncertainty given by the temperature plotter is a measure of the 'wiggliness', or more precisely the deviation from linearity. So what it is actually telling you is that the satellite data are more wiggly.
While uncorrelated errors in the data would contribute to wiggliness, so can other things, and worse the long term biases of the kind which might be present in the MSU data may not. So for example a simple drift over time won't show up in the uncertainty at all, but will lead to a substantially wrong trend.
What you can infer from the larger uncertainty in the trend tool is that the satellite data are more strongly influenced by El Nino. Which also reduces their usefulness in detecting long-term trends (unless you do an analysis to remove the impact of El Nino), however this has nothing to do with errors in the dataset. -
knaugle at 23:40 PM on 12 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
It's true that there are errors everywhere in measured data. But not all errors are equal. Is it just scatter? or bias? or what? Kevin Cowtan's page at Univ. York is interesting in that it shows at least the scatter part of each of the main data sets.
University of York, Temperature Plotter
Note that the nominal uncertainty of the warming rate calculated by the HadCrut4 and GISTEMP data for the past 30 years is ±0.06 °C/decade, whereas the uncertainty of the RSS 3.3 TLT set is ±0.09 °C/decade and UAH 6.0 TLT is ±0.11 °C/decade. While the satellites are showing lower warming rates, it also appears they are struggling to achieve a consistent measurement as it is.
-
michael sweet at 22:21 PM on 12 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
Dudo39,
Did you read the intermediate tab at the link you were given? It states that it is difficult to exactly determine the effect of clouds. It is most likely that the effect of clouds will be a positive feedback (possibly a large positive feedback) and that it is very unlikely that there is a large negative feedback from clouds. There is a small chance that clouds have a small negative feedback. A more recent lecture is attached that I did not view but probably addresses your questions.
Overall climate feedbacks are positive. It is very unlikely that clouds will bail us out and cause warming to be small.
-
dudo39 at 13:15 PM on 12 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
steveingbg, a simple mention would be sufficient for me. The link does not give a definitive statement, say as to what is the net effect, of an increase in cloud coverage, on the thermal balance of the biosphere. I would say that clouds act like a greenhouse gas by blocking infrared radiation from the earth day and night, and reflect [and block?] incoming solar radiation [during the day, of course]: the key point is to determine what is the net effect of clouds on the thermal balance....
-
Art Vandelay at 12:26 PM on 12 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
There are errors associated with land and sst measurements too of course. In fact, a thermometer enclosed within a pseudo solar shielding box near ground level is really only a means of attaining an approximation of air temperature - because the solar shield converts some short wave radiation into LWR, and additionally, the ground and surrounding area also radiate (LWR). The consequence of this is that LWR viariables can contaminate climate data if they change over time.
-
Bob Loblaw at 08:16 AM on 12 May 2017Is the climate consensus 97%, 99.9%, or is plate tectonics a hoax?
In the case of "plate tectonics denial", if the theory of plate tectonics had said that fossil fuel extraction would cause an unheralded increase in the rate of plate movements, and this would lead to huge increases in earthquake activity and great damages to many populated areas close to fault zones (hi, California!), with huge impacts on society as me know it, would this have led to corporate funding of plate-tectonic-denial think tanks? Would companies like Exxon have invested large amounts of money to deny the science in order to protect their business, as they have with anthropogenic climate change?
Fortunately, plate tectonic theory made no such predictions, so corporate interests did not react that way, but how has the fossil fuel industry reacted to claims that fracking causes earthquakes?
-
Tom Curtis at 08:07 AM on 12 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
Also of interest. A significant revision of the amount of the Earth's surface covered by forest. The news article says of Professor Andrew Lowe, one of the papers authors:
'He said if the newly discovered forests are protected, they could provide information about how trees "fix" carbon, and prompt a re-evaluation of the global "carbon budget".
"We know that forests sequester huge amounts of carbon, so increasing the area of forest globally helps explain additional carbon sequestration opportunities that are available," Professor Lowe said.'
It probably will result in a reevaluation of the total carbon stored in forest systems, but is unlikely to lead to a reevaluation of the change in the amount stored IMO. That is because the later is constrained by isotope data.
-
Bob Loblaw at 08:05 AM on 12 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
Using satellite-measured microwave radiation to try to determine atmospheric temperatures is affected by what is called "the inversion problem". I can't quickly find a definitive discussion of it, but a quick search produced this paper that mentions it in the abstract:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002240737890136X
The inversion problem can be summarized as this:
- radiation transfer theory is quite capable of taken a known set of atmospheric conditions (temperature, pressure, chemistry, etc.) and giving quite accurate estimates of the resulting radiative fluxes.
- Going the other way - taking radiation measurements and trying to use a model to determine atmospheric conditions (in this case, temperature) - is much more difficult. The problem is usually "ill-conditioned" - there are a lot of unknowns, and the model can be made to fit the measurements fairly well with a wide variety of closely-related input parameters that may or may not be known accurately.
- For example, if my model says A+B=C, and I know A and B, it is easy to estimate C. On the other hand, if I measure C and don't know much about A and B, then it's really hard to say I know B with certainty. If B is what I am interested in, and I can find an independent way to know or estimate what A is, then I can learn about B by measuring C, but my estimate of B is highly dependent on how well I do with A.
All the "corrections" to Spencer and Christy's results over time can be described as modified attempts to constrain the results based on improved understanding of either the models or the approximations needed to overcome the inversion problem. Spencer and Christy's track record - of having others find problems that need fixing - does not do them a lot of credit. Follow the link to the Grauniad's story to see the graph of Spencer and Christy's sequence of corrections to their work.
-
JWRebel at 07:23 AM on 12 May 2017More errors identified in contrarian climate scientists' temperature estimates
The most important point about the satellite data is that it is an attempt to model atmospheric temperatures. Once fully mature, this would be an invaluable tool to model temperatures throughout all strata of the atmosphere. Like all complex modeling, there is always room for incremental improvements on the basis of advances in the data and theoretical insights.
The opposition often articulated between climate models and "the satellite data" completely skips the problem that all "raw" data must be integrated and interpreted within a framework (model) to tell us anything useful.
-
scaddenp at 07:20 AM on 12 May 2017Industrial-era ocean heat uptake has doubled since 1997
Eclectic - CC was just repeating a common myth. This states that only visible-wavelength radiation penetrates into sea (as you state), but infrared only penetrates a millimetre if that. Ergo, increasing infrared cannot heat the ocean. This is a fallacy, missing the full nature of energy interactions in the system. CC was pointed to resources explaining it but appears to be incapable of comprehending any experimentally proved physics which undermines his/her cherished position. Once someone prefers their misinterpretation to observational evidence, there is little point in further discussion.
-
Tom Curtis at 00:32 AM on 12 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
Here is a new CSIRO techonology that could be a game changer for emission free transport. Essentially the technology splits hydrogen of from ammonia. That means renewable energy can be used to extract nitrogen from the air, and hydrogen from water, combining the two to make ammonia. Ammonia can then be used as a liquid (and hence easy to transport and store) fuel. Finally, this technology would allow the hydrogen to be split of and burnt as fuel, leaving emissions of N2 and H2O rather than the NO2 and H2O which would result from burning the ammonia. Needless to say, NO2 is a powerful greenhouse gas.
-
Eclectic at 17:59 PM on 11 May 2017Industrial-era ocean heat uptake has doubled since 1997
ConcernedCitizen @11
You overlook one point.
Heat from the sun arrives mostly as visible-wavelength radiation (colloquially called "light").
As a scuba-diver, I can assure you that this radiation penetrates well down into the sea-water.
Could this account for the ocean heat uptake?
Moderator Response:[DB] The user in question has recused themselves from further participation in this venue.
-
ConcernedCitizen at 17:40 PM on 11 May 2017Industrial-era ocean heat uptake has doubled since 1997
You have all missed the point. The IPCC uses the term "Ocean heat uptake" to account for the difference between ECS and TCR. This is in respect of CO2.
This is reflected in such statements as"90% of global warming is going into the ocean"
If "global warming" is the energy from CO2, then clearly this is impossible since the energy from CO2 penetrates ~0.006 cm of the ocean skin (this is well known physics).
The only action, as measured by the SAGE COARE experiments) is a resopnse a few CM deeper which is due to retained shortwave. This was in any case tiny, something like 0.02C per 100 wm^-2 increase in LW.
So what is the response to increased LW? The oceans retain a tiny amount of heat from SW. This reduces sensible heat flux from the ocean to the air while the ocean is warming.
Once warming stabilises and sensible heat flux is restored the air assumes its correct temperature.
This is the only way in which the air temperature increase can be delayed, but it isnt by ocean heat uptake, since the flow of energy is not into the ocean, thus the IPCCs explanation for the terms ECS and TCR is fundamentally wrong.
As for HKs comments, you can't balance ocean heat flux in a 24 hour time frame. Turbulent mixing, ie the near dissapearance of the cool layer, happens only at wind speeds. However such wind speeds also increase evaporation, so even if the cool layer shrinks from 0.5 mm to 0.05 I would expect and absorbed LW to be lost immediately in latentent heat flux. If anyone has any data similar to SAGE COARE for higher wind speeds it wold confirm this.
Moderator Response:[DB] "it isnt by ocean heat uptake, since the flow of energy is not into the ocean"
Incorrect. You have been advised of this fallacy on your part multiple times, including multiple interventions by the moderation staff. Given that you are here to simply prosecute an agenda of ideology and not to further your understanding of the science in question, you will be given no further opportunities to waste the time of others in this venue.
-
Eclectic at 15:22 PM on 11 May 2017Study: to beat science denial, inoculate against misinformers' tricks
Haze, have a closer look at Curry's blog.
She posts her own reflections on climate matters, plus some selected scientific studies (with spin), plus some articles containing nonsense — these articles she says she includes because they are "interesting" but she distances herself from the idea that she might be endorsing them. Go figure !!
The comments columns have much nonsense in them : the attraction here is for deniers who are wishing to vent, but do not wish to associate with the vitriolic morons as found at WUWT etc.
There are few (if any!) other such denier-oriented websites, where the more genteel deniers can have their say in congenial company. That, I suspect, is one of the great attractions of the Curry blog.
-
Susan Anderson at 14:15 PM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
Tom Curtis@23, final bit about models, that is very helpful. Thanks. I get a bit cross-eyed at times with all the technical material, since a real layperson has to figure out what to believe and sciencey arguments are all over the place. It's also one of the few times I've seen falsifiability mentioned where it isn't used to obfuscate, show off, or go off on a complicated tangent with some group that really wants to focus on the philosophical side.
-
scaddenp at 13:45 PM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
Wonder how a civil engineer would like rejection of a project proposal with objections like:
"Your design uses concrete and I bet that was pushed on you by all those concrete firms who will make money if we accept it".
"I havent the faintest idea how you can assess the strength with all those different materials being used so your factor of safety must be wrong."
"I've heard steel goes runny 50 years and I you havent accounted for that".
-
nigelj at 13:28 PM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
SkepticalCivil Engineer @24
I don't see how loss of jobs to countries with low environmental standards or poor labour laws relates to climate science, or in some way reduces the need to reduce emissions. It's a political and economic issue, and remember while globalisation has some problems as you mention, it has provably bought many benefits. It's just a whole entirely different issue needing resolving separately from the climate issue.
I also dont believe anyone has ever claimed climate models are perfect or perfectly account for every possible variable. I mean its just a strawman claim. All predictions have error bars that reflect the uncertainties that are around exact climate sensitivity and various regional factors. However climate science is highly certain CO2 is the main cause, and has ruled out solar changes and the like.
The real test of any model or theory is predictive ability, and the models have done well so far as below. The fact the models are doing well is proof the uncertainties you claim exist are not significant enough to undermine the models. Im a lay person with a very decent education, and I take nothing for granted, but I just think the evidence we are altering the climate and are the most dominant cause by far is now overwhelming.
-
scaddenp at 13:06 PM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
Can I also recommend "The big picture" for fast look at the problem. Note also that we can measure the increase in surface irradiation from CO2. The ocean heat content is way to estimate the radiative imbalance.

The surface temperature rise and heating is what we expect from the net forcing (sum of all the things positive/negative affecting the energy balance). If you dont want to accept GHG warming, what do you propose happens to the irradiation of the surface? Hopefully you are not a conservation of energy denier.
-
scaddenp at 12:52 PM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
SCE - I struggle with the apparent logic "I suspect the motives of some countries therefore the scientists in all countries are wrong". This motive-based style of reasoning is an appalling way to assess the validity of science. Please to spend some time on this site so you are not working from such a terribly low base of understanding.
And frankly the diagnosis of where the "push" is coming from is based on what information? So far you seem to be relying on appallingly inaccurate source of information on which to base your opinions. Looking at Paris and earlier conferences, I would say the most desparate push is coming from countries most affected - but as I say, this is largely irrelevant to the science. USA, Europe, Japan would be the biggest contributors to our science.
Just because you dont know something does that mean noone does? The models dont attempt to predict weather, are poor at regional prediction and have no skill at even decadal level prediction. However, they are very good at studying the energy balance on earth which is what ultimately determines climate.
It seems you are also still stuck in the notion that AGW is somehow all climate models. Why not look at all the other ways of investigation (eg the first few chapters of the WG1).
Instead of look for a blog commentator response on the models, why not just read the chapter in the AG5?
If you want to propose some alternative to current theory, then you need an alternative source of energy to be heating the earth. With solar flat or down, Milankovich going negative, its a tough job. Try spending some time with the "Climate changed before" myth (top left). The Arguments button, taxonomy is also a very good way to navigate this site and get answers to questions.
On the other hand, if your skepticism is motivated by ideology or group identity, I very much doubt that anything you read here will change your mind. Can I suggest that in advance you think hard about what is the data that would convince you when examining an aspect of the science? It is the standard scientific way of overcoming our biases.
-
Haze at 12:02 PM on 11 May 2017Study: to beat science denial, inoculate against misinformers' tricks
I just watched the video clip featuring Bill Nye the science guy. No doubt amusing to some but giving entirely the wrong message. Look for yourselves. The"denier" is asked why he denies climate change and gives a concise, clear, straightforward and readily understandable answer "the science isn't in yet". John Oliver then turns to the "climate scientists" who produce a babble of sound in which nothing can be distiguished. How does this help their cause? Humorus? Debatable. Informative? Definitely not
A significant sentence in the piece under discussion is " I asked lead author John Cook how these findings can be implemented in the real world where misinformation about subjects like climate science and vaccines is pervasive."
The primary interest of the MSM is earning money by selling advertising everything else is secondary. A piece headlined "Climate Change is a Scam" attracts heaps of interest. All the WUWT and JoNova readers say "Yeah bro, right on!" while the readers of Real Climate and Skeptical Science "No way bro, the evidence shows that that ain't so". This sells papers and/or attracts viewers but above all gets publicity which attracts advertisers.
And on a slightly different tack, I agree that JoNova and WUWT are attractive to the wider community as their content makes little demand on the intellect. That however is not the case with Judith Curry's "Climate etc" so why does it garner so many comments?
-
Susan Anderson at 11:39 AM on 11 May 2017SkS Team - Marching for Science around the globe
Terrific! Good signs too. Thanks.
-
SkepticalCivilEngineer at 10:52 AM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
scaddenp @22 & Tom Curtis @23
One of the reasons why I posted here is because I am not a climate scientist and welcome the insight that I might find on this site. I have tried not jump to any unwaranted conclusions but see the big push for alternative energy comming from the same industrial countries that have a reputation for having weak environmental standards themselves. Those lower standards and higher profit margins is one of the many reasons why production in the United States has moved overseas.
In response to the statement: "Those, in contrast, who reject models are really insisting that their theories should be allowed to remain vague, and prediction free" : I'm not sure how to go about realistically building a model that incorperates all the changes to coastal lands over the centuries and what effect that might have had on weather patterns, cloud cover, the ocean's temperature, and the planet as a whole. I don't think that allows my theory to remain vague, and prediction free, it just makes me a skeptic of the models that are presented as though they account for everything. I am still asking the question what don't we know and how much of that unkown is causing the problem. What do the models not account for what assumptions do they make? There is Warming, the planet is changing again, it has changed before. Is CO2 the only reason?
-
Tom Curtis at 08:08 AM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
SkepticalCivilEngineer @21:
1) The most commonly cited source of CO2 concentration data is the Mauna Loa station, which is on top of a very tall mountain in the middle of the Pacific. However, that is not the only remote station detecting CO2 concentrations. Here are the locations of various CO2 concentration data stations:

As you can see, they are overwhelmingly from remote locations, and the ones commonly cited (those in black, plus Cape Grimm, the CSIRO station in Tasmania) are all remote. There are also multiple partially overlaping CO2 records from ice cores. The records from a significant proportion (possibly all) of those CO2 recording stations, plus four ice cores are shown in the famous pump handle video. If you want data from approximately the same location, just compare the four ice core records shown, which are all from Antarctica, with the South Pole data.
2) The change in carbon stores in various reservoirs was shown by the IPCC AR5 in this diagram:
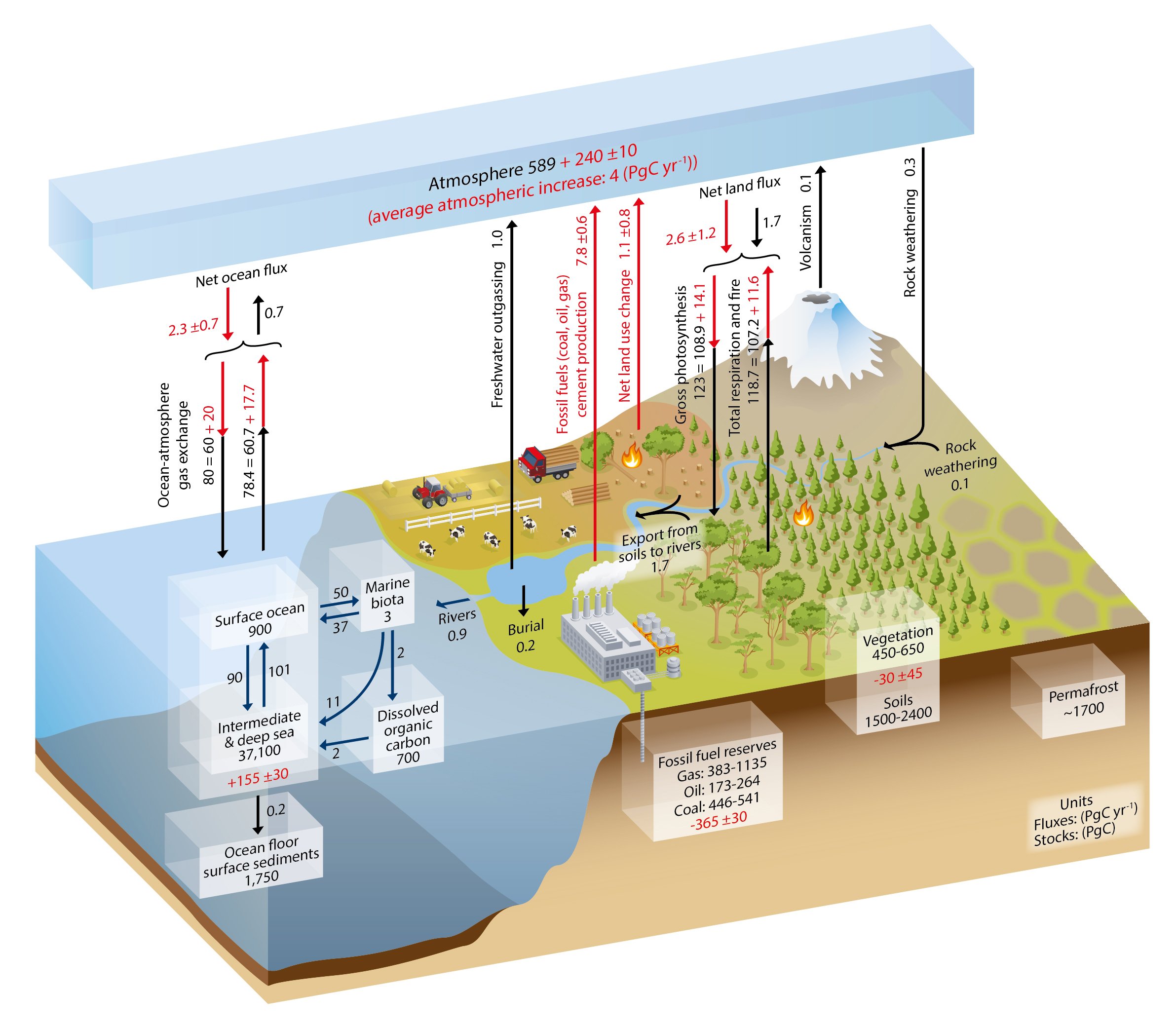
This data was determined by a combination of direct observation and counting of inventories, and cross checked by isotope data. For this discussion, the important thing is that the amount of the increase in the atmosphere (240 PgC) represents 57% of the industrial emissions, ie, emissions from fossil fuels and cement manufacture:

It follows that the 155 PgC increase in the oceans represents 37% of that increase. There is just no plausible scenario in which nearly 37% of our oil and gas production has been lost as fats, oils, and greases washed into the ocean. That is quite apart from the fact that oils, fats and greases are largely insoluble so that in water, they eventully (after their surface scum is broken up), form insoluble sludges gathered in low points in the ocean.
Most fertilizers are nitrogen based rather than carbon based, and do not enter into the equation at all.
3)
"My therory to this question is that because the cost to fix these problems will be borne by the wealthiest 2% of people who are the land owners and future land developers. It is much easier for them to sell electric cars for a profit then invest in groundwater replenishment systems which have no profit other than environmental."
I will note, firstly, that that theory is a conspiracy theory, and needs to meet a very high evidentiary bar before we would trust it; and that climate scientists are not paid sufficiently highly to be in that 2%, or anywhere close. Nor do they typically profit from sales of electric cars or solar panels (although some may have individual small investments in that area). Given that the people warning us of the danger are not in the group you say are running the scam, your theory falls at the first hurdle.
4)
You are correct that models are not evidence. This is a point I wish was made much clearer, and it is a genuine ground of criticism of climate scientists that they are not clearer on this point. What climate models are is algorithms that predict the consequences of changes in atmospheric composition given our best current theories on radiation, energy transfer, conservation of momentum etc. More correctly, they provide approximate predictions because, due to limits of computation, they must approximate based on average responses across fairly large scale cells. Further, as the best way to make those approximations is not known, the prediction is best considered to be the mean of the predictions of the various methods tried (ie, the ensemble mean).
We need models to make more than very rough predictions about what would happen given a particular increase in GHG concentrations, or solar forcing, etc. Without models, the falsifiable content of climate science would be very small, and limited to general claims about rising temperatures plus a few other things. With models, the falsifiable content is greatly enlarged.
Two things are important about this. First, when somebody says, "climate models are evidence that XYZ", they should really be saying, "our best theories predict that XYZ". That is still important knowledge, because it means the evidence behind those best theories (which is very substantial) also combines to predict XYZ.
Second, if you don't have a climate model of your theory, your not even in the science game when it comes to climate science. It means you have not expanded on your theory sufficiently to generate predictions that can be compared with reality. Unless your disagreement with climate science is very particular, on a subtle point; where the predictions can be checked without reference to a full model, your not even doing science (or at best, your alternative climate science is as undeveloped as standard climate science was at that and the end of the 19th century).
Paradoxically, this means the use of climate models represents a strong commitment to empiricism. It is an attempt to expand the types of data which can be used to falsify the theory, and to narrow the range of values within that data which will falsify the theory. Those, in contrast, who reject models are really insisting that their theories should be allowed to remain vague, and prediction free (ie, not science at all).
-
scaddenp at 07:41 AM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
SCE - tried looking for some answers by say reading the IPCC WG1 report? Or even the summary for policy makers?
"Much of the climate change debate" - not much "debate" in published science - only attempts to seed doubt by misinformation sources.
"usually in favor of spending money" - when facing a potential threat what do you expect peoples response to be? The belief that scientists must be motivated by some money-making scheme appears to be a case of projection to me. Where do you see the science being influenced by money?
"keep hearing about these glacial air bubbles that show CO2 levels increasing by 50% in the last 65 years." Wonder where you "keep hearing" that? CO2 levels are measured directly at multiple stations all round the globe - the continuous Mauna loa record goes back to 1958 - spot measurements much longer. Ice core is a way to extend that record back nearly 800,000 years and funnily enough most ice cores are from Greenland or Antarctic. Furthermore cores from diametrically opposite position deliver the same gas composition record.
Again if you read the IPCC report you would find the numerous papers that have quantified the effect of land-use change and it contribution to AGW. (small, negative, but not insignificant compared to GHG).
Does it seem to fair to you that the cost of fixing the problem should by borne by those who created the problem? If you dont fix it, then those who have contributed the least to problem are those who will bear brunt of its effects. (eg see here).
"A mathmatical model is not evidence of anything unless all the assumptions made are correct and the parameters can be measured and predicted with 100% accuracy." No parameter can be measured with 100% accuracy but yet we find mathematical models in physics extremely useful. The modern world relies on them every single day.
However, GCMs are not proof of climate theory, but they are the best we have for predicting what the consequences of various policy options will be - far ahead of examining entrails or assuming nothing will change. The question to ask is "are they skillful at predicting climate - ie the the 30 year average" and yes they are - remarkably so.
I can suggest you do a lot more reading of the actual science before leaping to unwarrented conclusions.
-
nigelj at 07:24 AM on 11 May 2017Study: to beat science denial, inoculate against misinformers' tricks
Why do certain climate denialist websites get a lot of posts? One reason is they often publish quite provocatively worded articles. It's human nature to be attracted to that sort of rhetoric.
But writing very provocative or even outrageous or "alternative" facts, and getting some readers, doesn't make them true.
I think genuine research scientists and websites like this have to be careful not to get fooled into descending to the same low, inflammatory level, although its still good to have some colour and be prepared to be angry occasionally, if an issue really deserves this
Like M Sweet says, denialist websites also allow people to get away with obvious non scientific, or generally irrational rubbish (or things with a grain of truth that are then twisted into more than they really are). Its a place for the children to play, without fear of being genuinely scrutinised or having to admit they made an error.
But people tire of this garbage eventually. We all like reading conspiracy theories a bit, but they get tiresome very fast, and we want the facts from real scientists doing the research.
-
Tadaaa at 06:41 AM on 11 May 2017Study: to beat science denial, inoculate against misinformers' tricks
the trick is to be wise to their tactics
all the top denier points are effective because they have a kernal of truth
by that I mean, they are in themselves true statements - hence can be defended
but in reality red herrings and irrelevant
so we have - C02 is a traces gas, the climate has always changes, no rise in temps for XX years
all "true", but irrelevant to the science of AGW
I was at a dinner party the other day when this subject was briefly discussed, one guest brought up the "pause" meme
i immediatly shot back with - "why do you expect tempuratures to go up in straight lines"
march and be colder than feb or Jan, April can be colder than Feb, but July (volcano eruptions apart) will always be warmer than Jan, Feb or March
"tempuratures do not go up in straight lines - it would actually be odd if the did"
you could see the cogs in his brain wirring - then he changed the subject
-
SkepticalCivilEngineer at 05:16 AM on 11 May 20172017 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #18
My first post is skeptical.
Much of the climate change debate is wheather man made CO2 is the main culprit for rising tides, melting glaceres, and higher acidity in the ocean. Coincidentally proponents of this cheering squad are usually in favor of spending money on new electrical cars, new solar pannels, and alternative energies. This changing of the energy guard ushers in new money and new profits. Unfortunately I believe their arguments are more about the money than the environment. Furthermore I don't believe they really seem cite specific sientific evidence.
For example I keep hearing about these glacial air bubbles that show CO2 levels increasing by 50% in the last 65 years. What is not clear about this information is how many data sets are there that show this phenominon and is the air trapped in the bubbles being compared to air at the same location today on a really good air quality day or a particularly bad air quality day.....or is it being compared to air above a poluted city like Beijing China? The air bubble arguments just seem very lacking to me right now..... I vow to look more at this evidence.
Whcih brings me to what concerns me. Why aren't more people talking about the changes in coastal lands and metropolitan areas have undergone in the last 2 centuries? California's Central valley used to be a swamp until it was dredged and sent out to the ocean. All the water that used to rain on the LA basin used to be absorbed into the ground. Now becasue of farming, manmade development, impervious hardscapeing, and storm facilities much more rain water water goes directy into the ocean than ever before in history. That rain water takes with it the fats, oils, greases, and fertalizers that might also be the cause the higher acidity in the oceans. This has happend in costal lands and metropolitan areas all over the world. Why isn't man made develoment, farming hydromodifcation, and storm water facilities given more of the blame for global warming?
My therory to this question is that because the cost to fix these problems will be borne by the wealthiest 2% of people who are the land owners and future land developers. It is much easier for them to sell electric cars for a profit then invest in groundwater replenishment systems which have no profit other than environmental.
I would like to finish this comment by making a statment about climate change models . A mathmatical model is not evidence of anything unless all the assumptions made are correct and the parameters can be measured and predicted with 100% accuracy. I don't see how this is possible with any climate model predicting weather, cloud patterns, development, and other naturally occuring phenominons that have changed the earth many times in the past.
When someone says the model predicts "such and such" I immedeatly want to ask does the model take into account
"this, this, this, and this?" -
Evan at 00:04 AM on 11 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
ubrew12, interesting story and comment. Whereas UV blocker actually does block UV rays from reaching us, I think you will agree that what you mean by "block" was the tree returning as much infrared radiation to you as you were sending to it. I know this is a subtle point, but it will help people understand what controls climate change to understand that what is often viewed as "static" is really a game of give-and-take that is in balance. If you get as much as you give, the system appears to be static. Sit under a tree or out under the stars and you are giving up the same amount of infrared radiation, but under the stars you are getting much less in return than the trees have to offer.
-
ubrew12 at 23:36 PM on 10 May 2017SkS Analogy 3 - The Greenhouse Effect is Like a Cloudy Night
I used to backpack in the Sierra Nevada mountains. In the summer on cloudless nights, above 9,000 ft, it was definitely more comfortable to sleep next to a tree rather than out in the open, even if it somewhat robbed your view of the amazing stars. The tree served as an infrared blocker, and definitely kept me warm and cozy compared to lying out exposed under the stars.
Prev 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























