Recent Comments
Prev 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 Next
Comments 31801 to 31850:
-
billthefrog at 01:31 AM on 10 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
@ Stephen & Doug et al
As I only did Chemistry in First Year (and that was a long, long time ago) I am struggling to keep up with the subtleties here. Would I be correct in thinking that this represents a good example of le Chatelier's Principle in action?
If memory serves, an over-abundance of one of the components in an equilibrium-type reaction would tend to force the equilibrium point in the opposite direction. Hence, this would act as a sort of negative feedback and consequently would somewhat compensate for the initial over-abundance.
Am I understanding this correctly?
Cheers Bill F
Moderator Response:[Rob P] - I would recommend you read the OA not OK series (left hand column of the page). Part 7 deals with Le Chatelier's principle.
I do wonder, however, if this series may be slightly revised as some stage because equation 1 is very confusing for most. A naive interpretation could be that increased bicarbonate in the ocean, as a result increased CO2 dissolved in seawater, might be expected to aid biological marine calcification, rather than hinder it.
Bicarbonate is indeed a source of calcification, but it looks like marine calcifiers convert the bicarbonate ion to carbonate in order to form calcium carbonate structures by pumping hydrogen ions out of internal chambers where this calcification takes place. The decrease in the number of hydrogen ions raises the pH of the calcifying fluid considerably and this is what enables the building of the shell or skeleton. There's much more it than that of course, but that's the basic gist.
The concentration of carbonate ions represents an energy gradient upon which calcification must operate. More carbonate ions and less bicarbonate ions make calcification easier, and less carbonate ions and more bicarbonate ions (as in OA) makes shell formation more difficult - the organism has to work harder, pumping more hydrogen ions out of the calcification chamber in order to reach the required level of carbonate saturation.
So, well before carbonate undersaturation is reached (i.e. seawater becomes physically corrosive to calcium carbonate forms), ocean acidification will affect growth rates in many marine organisms.
-
slowtojump at 00:24 AM on 10 January 2015A detailed look at Hansen's 1988 projections
I would like to see these graphs updated to 2015 and have the discussion again.
-
Doug Mackie at 17:12 PM on 9 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
siloch @28: umm you get deposits like the cliffs at Dover.And then those deposits weather (OA not OK post #6).Increased CO2 in atmosphere leads to increase in acidity of rain, leading to increased weathering of rocks. (Calcification is a source of CO2, weathering of rocks is a sink). Appendix 1 shows this process alone is sufficient (in absence of other processes, see caveats) to remove all CO2 from atmosphere in 3,000-4,000 years.Read the rest of the OA series and then get back with questions. -
Tom Curtis at 16:29 PM on 9 January 2015There is no consensus
amhartley @652, there are several rebutals of various denier talking points regarding Cook et al 2012. This is the most general, but this one is also worth looking up.
-
ubrew12 at 14:48 PM on 9 January 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #2A
"Limiting global warming means forgoing vast fuel reserves - study by Kate Kellen, Reuters" I couldn't get this link to work.
I got it here, and the BBC is also reporting it here.
Moderator Response:[JH] Link fixed. Thank you for bringing this glitch to our attention.
-
amhartley at 11:19 AM on 9 January 2015There is no consensus
Thanks, MA Rodger & JH, for the input. I had a hunch Epstein was himself misrepresenting things, but as a statistician—rather than a climate scientist--I might not be able to debunk all of his claims. However, if the experts at SKS were to publish, routinely, rebuttals of claims like those, I can imagine those rebuttals could help others like me to both understand the truth & communicate it more widely.
-
wili at 08:47 AM on 9 January 2015Economics supports immediate action on global warming
Some good points here, but conventional Neo-Classical economics is not going to get us there--in fact, it is precisely what we have to jettison as soon as possible if we are going to start the process of building a civilization that is not set on destroying the living planet and the systems that support it. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GCkCVFI3934#t=824
-
Stephen Baines at 05:27 AM on 9 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Slioch @28
I'm not a real chemical oceanographer, but I'll take a stab at this. Doug can correct the specifics later. I'd be interested to hear his opinion as I sometimes have to teach this stuff.
You have to think of the combined ability of both the ocean and the sediment to store carbon from the atmosphere when answering this question. By producing calcium carbonate, a calcifying organism is removing a Ca2+ ion from solution by bonding it to a carbonate ion. That has two effects.
First, it removes the Ca2+ ion from solution and places it in sediments. By reducing the base cation concentration in the ocean, this reduces the total amount of bicarbonate and carbonate ion in solution within the ocean at equilibrium. With respect to the atmospheric CO2, this transfer is stealing from Peter to pay Paul.
Second, calcification is not an efficient way to use Ca to store C away from the atmosphere, at least relative to having dissolved calcium ions. In calcium carbonate, you store one mole of C (as CO32-) per mole of bivalent Ca. When dissolved in the ocean at current pH, univalent bicarbonate (HCO3-) is the most abundant form of dissolved inorganic carbon at current pH. To maintain charge balance, two bicarbonate ions are in kept solution for every dissolved bivalent Ca ion.
So yes, the sudden appearance of a massively calcifying organism would increase atmospheric CO2 by moving removing more storage capacity from the ocean than it adds to the sediments. Therefore some of the huge reservoir of carbon stored as dissolved bicarbonate and carbonate in ocean water would be free to equilibrate with the atmospheric reservoir of CO2. The exact effect would vary a little depending on the pH, chemistry and temperature of the ocean. The effect becomes more neutral as you consider pHs above current levels because dissolved carbonate becomes more abundant.
Of course, it's a hypothetical example, as such an organism would find it increasingly difficult to calcify as the ocean pH became more acidic and carbonate became less abundant in ocean water. Also, we have not discussed the secondary effect of calcium carbonate production on storage of organic carbon. That is a different kettle of fish entirely.
-
MA Rodger at 19:49 PM on 8 January 2015There is no consensus
The Forbes story amhartley asked about @650 is rather strong in its assertions. It asserts that Cook et al (2013) involves "egregious misconduct" and was "a deliberate misrepresentation designed to intimidate the public." These claims are backed up by a mis-description of the Cook et al method and the comments of some well-known scientists - Richard Tol, Craig Idso, Nicola Scafetta and Dr. Nir Shaviv, this last one being a not-so-well-known climate change denier compared with the other three.
Moderator Response:[JH] The author of the Forbes article is Alex Epstein, founder of the Center for Industrial Progress and author of The Moral Case for Fossil Fuels. As a Forbers contributor, Epstein states, "I write about the environmental benefits of industrial progress." I guess we know which side his bread is buttered.
-
Slioch at 18:43 PM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Thanks to Stephen and Doug for their posts. I have a friend arriving soon for several days and I know that once she's here thoughts about ocean acidity (or anything else for that matter) will recede from my mind, so I will have to study your posts and possibly come back much later. I've read the first four parts of OA not OK and it is all very straightforward, except for the subject in dispute (the answer to which, I suspect, may turn out to be a question of time scales), but I will have a look at the rest once I have the opportunity.
Meanwhile, if I may, could I pose a question:
Suppose we have an Earth in which oceans and atmosphere are more or less at equilibrium and in which atmospheric CO2 and oceanic dissolved inorganic carbon is not changing very much over the long term (in other words an Earth in which no great volcanic or mountain building activity is occuring and no naked ape is chucking fossil carbon into the atmosphere like there's no tomorrow). Into this unchanging world a new lifeform evolves that causes the deposition and sequestration of huge quantities of calcium carbonate on the ocean floors. What then happens to the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere over time?
Moderator Response:[Rob P] - A scenario similar to that which you propose most likely did happen in Earth's past. Given the information provided by Doug Mackie & Stephen Baines, what do you think would happen?
-
Doug Mackie at 14:16 PM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Siloch: Stephen Baines is correct about the importance of speciation. See the speciation fig.3 (below) in part 8 of OA not OK series and the step through to make your own figure in Appendix 2 of the book we did (link someone?) .

To counter denialists it is important to be rigorous. I mean no disrespect but your simplified eqn @6 was misleading and incorrect. Why give them a chance to misunderstand and misinterpret?It is worth recalling that it is not 'acidity' per se that is the problem for CaCO3 dissolution. Instead the key point is that changing [H3O+] causes a change in [CO3=] and it is this change in concentration of carbonate that causes problems. Adding CO2 to atmosphere causes CO2 to enter ocean. This increases total dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in the ocean but decreases the fraction of DIC that is carbonate ions. (See parts 15 and 16 of the OA series).
Moderator Response:[Rob P] - pic & link provided.
-
sauerj at 12:17 PM on 8 January 2015Pope Francis plants a flag in the ground on climate change
I'd like to see the following 'points spelled out in Francis's encyclical:
1) Basic Background Content: Well worded, convincing and comprehensive explanation of the science and, from there, man's only moral response toward a truly sustainable culture.
Other ideas to make the encyclical even more effective:
2) Announce that the Vatican would divest from FF's and strongly request all catholic dioceses to do the same.
3) Announce that the Vatican will develop plans to become FF free by year 20XX. And, request all catholic dioceses to start tracking & publishing parish, school & hospital carbon footprint, and develop plans to reduce usage and stick to their plans.
4) Announce that Vatican will sponsor a blue-ribbon panel of scientists, policy leaders and climate knowledgeable clergy to issue global strategical recommendations on how the catholic church can best make meaningful and effective long-term impacts on mitigating and reversing the current unsustainable trend of AGW.
5) Announce that Vatican will hold multi-year inter-faith conferences with representatives from all religions on developing multi-religious plans on mitigating climate change.
6) Announce 'Year of the God's Creation' with expectation that dioceses hold seminars, youth activities, novenas, special liturgical prayers, etc. to awaken & motivate our responsibilities towards the world's future generations.
7) Promote Pray & Constant Diligience: Indicating that the Pope & all Catholic leaders should promote constant focus & pray on the subject. -
amhartley at 10:47 AM on 8 January 2015There is no consensus
This story
came up yesterday, about the consensus; I wonder if it deserves a response?
Moderator Response:[RH] Hotlinked url.
-
Dcrickett at 09:37 AM on 8 January 2015Pope Francis plants a flag in the ground on climate change
#1 shoyemore: Thanks for bringing that Hayhoe interview to our attention; just now I finished reading it. And more thanks for selecting the quote, which captures well the essence of the interview.
…David Collins
-
chriskoz at 08:47 AM on 8 January 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #1
Oil slump stalls sector projects
Not a word about Keystone (or other unconventional oil projects) but I think Obama will face easier decision to ban it in such environment. Eventually, there will be no economic incentive to dig Canadian tar sands (American fracking has essencialy beaten it) which is (unfortunately for human intelligence) stronger than any env incentives discussed on this and not only site.
-
Stephen Baines at 08:00 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
I should mention that many people have the mistaken idea that to be consumed, CO2 must be converted to a particulate form, like a plant or rock. But, from the point of view of water chemistry and the interaction of the ocean with the atmosphere, the speciation of dissolved inorganic carbon is extremely important.
The vast majority of ocean carbon is as bicarbonate, so more dissolved inorganic carbon as bicarbonate in the ocean means less CO2 in the atmosphere, given a closed budget. Less inorganic carbon as bicarbonate means more CO2 in the atmosphere. By removing base cations, the precipitation of calcium carbonates reduces the amount of dissolved bicarbonate in the ocean, and thus reduces the total amount of CO2 the ocean can absorb.
-
Stephen Baines at 07:38 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Slioch,
Understood. But the equation you presented is not the actual reaction that would take place if you added CO2 to the ocean.
When CO2 dissolves in water at pH 8 it largely dissociates to bicarbonate ions and protons. The release of the protons actually causes equation 3 in your post @19 above to want to run the opposite direction than you have it, because the increased acidity shifts the carbonic acid-bicarbonate-carbonate equilibrium away from carbonate and toward bicarbonate and carbonic acid. So it should read..
1) H2O + CO2 + CaCO3 ==> Ca++ + 2HCO3-
If you add that to the equations involving hydration of aqueous CO2 to form carbonic acid and the subsequent dissociation of most of the carbon acid to bicarbonate given a pH~8, you get
2) 2H2O + CaCO3 + 2CO2 ==> H+ + 3HCO3- + Ca++
Actually, the reaction mostly occurs after the aqueous CO2 has equilibrated with bicarbonate, so...
3) 2H+ + CaCO3 + 2HCO3- ==> H+ + 3HCO3- + Ca++
they are stoichiometrically equivalent, but the net effect (after reequilibration) is closer to the latter under current pH. Calcite dissolution has the net effect of removing protons and, thus, lowering acidity. It also consumes CO2. Calcite formation does the opposite.
So, Segalstad is wrong on two counts. If the Ca was to bind to anthropogenic CO2, it would force reaction 1 to run backward, which would actually increase the CO2 in the oceans, not decrease it. This would perforce increase acidity after equilibration with bicarbonate. You are also essentially removing basic cations (Ca++) and alkalinity in the oceans and decreasing the equilibrium concentration of bicarbonate, and therefore the capacity of the ocean to absorb CO2 and store it as dissolved inorganic carbon.
Second, adding CO2 would actually tend to retard formation of calcium carbonate anyway. So it's pointless to say that enough dissolved Ca is present to bind the bicarbonate, because if anything calcium carbonate will be dissolving with more CO2, causing Ca++ concentrations to rise further in the future. You'd have to add an unimaginable amount of base to the ocean to do what Segalstad is suggesting. It's kind of like saying there is enough dissolved gold in ocean water to make everyone rich and then wondering why we aren't all rich.
What is true is that there is enough calcium carbonate in the ocean sediments to largely neutralize athropogenic CO2 dissolved in seawater, but that process is much slower than release of CO2 has been and will take thousands of years to complete.
-
Slioch at 05:18 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Stephen @ 21
Take a look back at the origin of this discussion of ocean chemistry. It began at #6 when I used that equation to counter Tom Segalstad's false assertion that ""the upper 200m of ocean water contains enough dissolved calcium to bind all anthropogenic CO2 as precipitated calcium carbonate ... without effecting the ocean's pH". It seems to me that claiming that increased CO2 will not increase ocean acidity is an important falsehood to counter, and that equation is a simple way of so doing.
(for info. on Tom Segalstad see, for example, http://www.desmogblog.com/tom-segalstad )
The equation 1. presented in the OA not OK article does not obviously address that issue, and the subsequent discussion was on a separate issue.
-
Firgoose at 03:46 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
On a more serious note, assuming that the graph shows seawater pH for surface layers, can one presume that the change in the graph since about 2000, being reminiscent of changes in the temperature graphs, is similar in being caused by more CO2 being pushed to deeper levels?
-
Firgoose at 03:38 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Have the deniers missed an easy reuse of a broken trick? Eyeballing that Station Aloha graph from 2000 (or, if it were clearer, maybe even the magical 1998?), it's clear that there's been a hiatus(!) in the seawater pH decline. In fact, if you choose your points carefully, has it actually risen? ;o)
-
Stephen Baines at 03:38 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Slioch
The problem is that, while your equations are right in terms of stoichiometry, presenting the overall equation that way gives the incorrect impression that that increasing CO2 will lead to increasing calcium carbonate production. In fact the opposite will happen in the short term because increasing CO2 shifts the pH in a direction that shifts the H2CO3, HCO3, CO3 equlibrium away from CO3 and toward H2CO3. This will tend to make the conditions needed to form CaCO3 rarer in the ocean.
Typically the reaction involving calcium carbonate formation it is considered separately from the reaction involving hydration of CO2 to H2CO3 because the equlibrium concentration of HCO3 and CO3 in the ocean is largely determined by the base cation concentration (the alkalinity) and pH, while the equilibrium CO2 concentration, on the other hand, is largely determined by temperature and atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Together, these two reactions allow the calcium carbonate pool in the ocean to act as a buffer for pH in the very long run. As CO2 rises, calcium carbonate dissolves, consuming protons and consuming CO2 in the process to make bicarbonate ions. As base cation concentrations increase or CO2 decreases, calcium carbonate is formed, producing protons and CO2.
Its a pair of reactions that are way too slow to keep up with changes due to anthropogenic emissions however.
-
wili at 02:16 AM on 8 January 2015Five bits of research that shaped climate science in 2014
wrt #4:
Dr. Francis has a new paper out with more evidence of this trend.
New metrics and evidence are presented that support a linkage between rapid Arctic warming, relative to Northern hemisphere mid-latitudes, and more frequent high-amplitude (wavy) jet-stream configurations that favor persistent weather patterns. We find robust relationships among seasonal and regional patterns of weaker poleward thickness gradients, weaker zonal upper-level winds, and a more meridional flow direction. These results suggest that as the Arctic continues to warm faster than elsewhere in response to rising greenhouse-gas concentrations, the frequency of extreme weather events caused by persistent jet-stream patterns will increase.
iopscience.iop.org/1748-9326/10/1/014005
So one more study to add to the series. How many more of these would it take for the "Maybe" at the end of #4 to fade away?
(Thanks to Sigmetnow at neven's Arctic Sea Ice forum for this link and text.)
-
One Planet Only Forever at 01:31 AM on 8 January 2015Things I thought were obvious!
dklyer@64,
I agree and have some things to add related to the erroneous results of the models of the likes of Milton Friedman. Often these people attempt to predict the future using an economic theory/model with a fundamantal presumption that the people making decisions, particularly the most powerful in leadership roles, would be highly averse to doing something that had a potential negative future consequence. That type of thinking would be the equivalent of a global climate theory/model that was based on human burning of fossil fuels not creating CO2 and that CO2 is not a greenhouse gas. The results of such models would never be accurate. And as long as those fundamentals of the theory/model do not change every attempt to 'add accuracy' will fail to produce meaningful helpful results.
I recall that Alan Greenspan (past Chairman of the US Federal Reserve) essentially said 'he had no idea that powerful wealthy people would ever do anything that was potentially damaging' when the US Congress asked him about why he did not foresee the damaging consequences of reduced fiscal regulation that produced the 2008 global tragedy.
The biggest global threat is the indifference many pursuers of profit, power and pleasure have regarding the helpfulness of their acions. Many such pursuers never try to be guided by a desire to help develop a sustainable better future for all life on this amazing planet (See footnote). That indifference to being helpful is a reality that is excluded from most economic models and is the reason the likes of Alan Greenspan fail to anticipate how wrong their 'leadership' is. Though indifference to being helpful is the major problem, the biggest trouble makers are the pursuers of personal power, profit and pleasuer who will deliberately do unhelpful or harmful things in pursuit of what they want. Any economic theory/model that fails to include the existence and potential for success of those type of people is destined to be wildly inaccurate.
This brings me to the evaluation of cost-benefit regarding action on the issue of global warming and climate change. Even people claiming to want to be helpful fail to properly evaluate the cost-benefit of climate change action. The proper evaluation needs to be one that ensures all actions of a current generation produce a sustainable better future fopr all. Evaluations that compare the 'cost/benefit to some in the current generations' against 'cost/benefit to future generations' are fundamentally incorrectly evaluating the acceptability of action by a current generation. Even if a current generation was to determine that the 'costs - lost opportunity to benefit' they evaluated were a match for the 'costs' they evaluated a future generation would face it is unacceptable for a current generation to impose costs onto a future generation, no matter how much benefit the current generation gets. It would be acceptable for a current generation to personally expend their own effort and profit to fully avert future costs, but even that would only be a neutral position, not a helpful development. And that type of balance case is prone to erroneous evaluation by people in a current generaton who are inclined to overstate the costs to the current generation and understate what needs to be done to create the minimum acceptable result of current generation activity, a neutral future condition that is not negatively affected by what the current generation did.
Foot Note - Fairly full disclosure. Referring to the recent reports of a climate change related encyclical being developed by Pope Francis, I am not Roman Catholic so I have not developed or acquired this attitude because of being aware of and adhering to the Roman Catholic position. I believe that there is a spiritual connecton between all life on this amazing planet. And I believe that the Old Testament (the Hebrew Bible) included some very good 'understandings' of how to live that needed to be updated (Leviticus chapters 11 through 15 provide advise about how to avoid food poisoning, how to deal with mold, and a few other helpful things that appear to be scientifically developed even though they are presented as 'rules from God'. And I consider Jesus to be a very wise person who provided important updates of the Old Testament. And I believe there are even more updates that are coming to be understood. Even though I do not believe in God and am an Engineer (and also have an MBA) my values appear to be very well aligned with the most progressive Christian and Muslim sects who are 'evolving their set of values rather than strictly adhering to interpretations of older documents'.
-
Slioch at 00:24 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Sorry, I must have clicked the paste button twice. The three equations added together should have been:
2CO2(g) + 2CO2(aq) + 2 H2O + Ca++ + 2HCO3- ==> 2CO2(aq) + 2HCO3- + 2H+ + CaCO3(s) + CO2 + H2O
-
Slioch at 00:19 AM on 8 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Thanks to the moderator for providing the links to the 'OA not OK' articles.
There is nothing therein that contradicts my previous posts and, once again, the assertion that calcification is a source of CO2 rather than a sink is simply wrong.
Tom Curtis (@18) has helpfully posted the relevant equation from OA not OK above, but, I'm sorry, Tom, you clearly do not understand what you are writing about.
I posted the OVERALL equation (neither you nor I have shown the mechanism of the numerous reaction steps , nor is that necessary) with respect to the precipitation of solid calcium carbonate from an aqueous solution containing calcium ions (you will note that in in both of my previous posts on this subject I referred to an "overall" equation). The overall equation provides a summary of the overall changes in constituents in that process, and, as I have stated previously, indubitably shows that the process consumes CO2 (and reduces pH).
The equation that you show, from the 'OA not OK' site, is an INTERMEDIATE equation from which, on its own, no conclusion can be drawn about OVERALL changes. (The 'OA not OK' site's assertion that calcification produces CO2 is simply wrong)
Hopefully this should become clear from the following:
The question is: "does the precipitation of solid calcium carbonate from a solution containing calcium ions a) cause an absorption of CO2 and b) cause a reduction in pH (ie an increase in hydrogen ions). The following shows that the answer to both questions is "YES".
Your equation shows bicarbonate ions being consumed. What is the source of those bicarbonate ions? They come originally from gaseous CO2 dissolving in water. The intermediate steps are as follows: (note: I will write all these equations as 'one way' equations, though they are in fact equilibria, since I am considering the process leading to precipitation of the product CaCO3).
Equ1. 2CO2(g) ==> 2CO2(aq)
That CO2(aq) then produces bicarbonate ions:
Equ.2 2CO2(aq) + 2 H2O ==> 2HCO3- + 2H+
(I've doubled those equations since we need 2HCO3- below)
If those bicarbonate (HCO3-) ions then react with calcium ions, then it as shown in the equation that you (and 'OA not OK') post:
Equ3. Ca++ + 2HCO3- ==> CaCO3(s) + CO2 + H2O
If we then ADD those three equations together, we get the overall equation:
2CO2(g) + 2CO2(aq) + 2 H2O + Ca++ + 2HCO3- ==> 2CO2(aq) + 2HCO3- + 2H+ + 2HCO3- + 2H+ + CaCO3(s) + CO2 + H2O
Cancelling leads to the overall equation:
CO2(g) + H2O + Ca++ ==> CaCO3(s) + 2H+which is what I gave in the first place (@6) and which shows that CO2 is absorbed and hydrogen ions produced (lowering pH) in the process.
I hope that is now clear.
Moderator Response:[Rob P] - Calcification is a source of CO2 - as Doug Mackie has already pointed out. It seems a few people with chemistry backgrounds get this wrong, so you have plenty of company. There is a great deal of scientific literature on this. For example see the Royal Society Report on Ocean Acidification (2005):
"The formation of CaCO3 leads to an increased CO2 concentration in the water. This apparently counterintuitive behaviour arises because two ions of bicarbonate (HCO3 – ) react with one ion of doubly charged calcium (Ca2+) to form one molecule of CaCO3, which leads to the release of one molecule of CO2. Some of this released CO2 is converted to bicarbonate by the buffering process, outlined above and in Annex 1. Under current conditions, for each molecule of CO2 produced during calcification about 0.6 molecules are released, potentially to the atmosphere, while the rest is taken up by the bicarbonate-carbonate buffer (Ware et al 1992)"
And that would be this from the OA not OK series:

-
Tom Curtis at 22:26 PM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Slioch @17:
1) Rather than using the OA not OK button, which just leads to the results of a search, try Part 1 and Part 2 of the summary of the OA not OK series, following further links for the more detailed discussion.
2) From Part 1, we can link through to the first post of the series which shows the following equation:
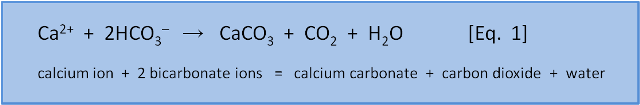
That shows calcification, as a reaction between Ca2+ and 2HCO3- is clearly a source of CO2 rather than a sink. Part 1 of the series also contains the crucial advise that:
"A basic principle is that chemical equations must be balanced. That is, they have the same number and types of atoms on both sides. Counting up we see on both the left and the right are 1 calcium (Ca), 2 hydrogen (H), 2 carbon (C), and 6 oxygen (O) atoms.
However, not all balanced chemical equations are valid chemical equations. The trick of chemistry (Oh! there's that word again) is in knowing if a particular balanced equation is valid."
Taking that advise, we can note that while you can write alternative equations that balance, that does not show that they are the preffered reaction (ie reaction spontaneiously occuring at the greatest rate) in given conditions. If the reaction is biological mediated, the equilibrium constraints which you ignore become even more stringent in that biologically mediated reactions often have only one pathway.
3) From the summary of part 5, we also learn that:
"Equations 7-9 describe reactions of the inorganic carbon in seawater. The balances between these equations mean 91% of carbon is in the form of bicarbonate (HCO3–), 8% as carbonate (CO32–), and less than 1% is found as CO2 and H2CO3."
That is, 91% of inorganic carbon is in the form found in equation 1, giving a strong reason why that is the preffered reaction and your equations show very slow subsidiary reactions if that. That your equations require the simultaneious interaction of three molecules would further lower the rates unless there are reasonably stable intermediates (in which case please break the reactions apart to show the intermediate steps).
-
Slioch at 21:22 PM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
14. Doug Mackie
Your 'OA not OK' button does not appear to work, so I have no idea to what equations you refer, but it is certainly not correct to state that "calcification" (if by that you mean the conversion of dissolved calcium ions to solid calcium carbonate) is a source of CO2. That is simply impossible.
If you can post the equations to which you refer I can answer your query.
Incidentally, there is an alternative (though equivalent, due to the H+ + OH- <=> H2O equilibrium) overall equation for the production of solid calcium carbonate that may be written thus:
Ca++ + CO2 + 2OH- ==> Ca++CO3-- + H2O
This also, of course, shows the process to involve absorption of CO2 (ie it is a sink for CO2), which is indubitably the case.
Moderator Response:[KC] The button links to a list of posts on ocean acidification, rather than the articles directly - that's not very intuitive. Doug was referring to the first four posts (ignoring the introduction) from the bottom of that list. Here are the direct links for you:
- OA not OK part 1
1 July 2011 by Doug Mackie - OA not OK part 2: Thermodynamic duo
5 July 2011 by Doug Mackie - OA not OK part 3: Wherever I lay my shell, that's my home
8 July 2011 by Doug Mackie - OA not OK part 4: The f-word: pH
10 July 2011 by Doug Mackie
- OA not OK part 1
-
Michael Whittemore at 20:59 PM on 7 January 2015A Relentless Rise in Global Sea Level
Thank you for all the replys
-
Michael Whittemore at 20:55 PM on 7 January 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #1A
Thank you for the information.
-
Rob Painting at 17:36 PM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
"These variables encompassed pH values more acid than those considered likely to be extant in 2100"
Yes, I don't think this has been communicated particularly well by the scientific community.
There is no point comparing say the upwelling region of the California Current system with the projected average global pH and saturation state in 2100 because local marine organisms may be periodically exposed to conditions exceeding those right now. What the experiment should be simulating are projected local future conditions. In some instances this may be equivalent to atmospheric concentrations exceeding 3000 ppm.
Clearly there are serious limitations to lab experiments because marine life in the real ocean generally doesn't have ocean pH and carbonate saturation state suddenly ramped up to maximum volume. But on the other hand, exposing only adult populations, which are typically less vulnerable, isn't realistic either. That's where studies of naturally acidified marine environments are useful. With a few exceptions, most marine calcifiers typically don't fare too well.
-
william11409 at 16:47 PM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Rob Painting I must have misunderstood the paper but I certainly got the impression that the authors had looked at the conditions to which the various species were exposed and at the variables in pH conditions to which these species were exposed. These variables encompassed pH values more acid than those considered likely to be extant in 2100. This is what the Scripps Institute of Oceanography said about the paper "In some of their study areas, they found that the decrease in seawater pH being caused by greenhouse gas emissions is still within the bounds of natural pH fluctuation. Some areas already experience daily acidity levels that scientists had expected would only be reached at the end of the 21st Century". In the example you give the area was one in which upwelling of colder more acidic sea water occurs. Perhaps this also had an impact. I'm not trying to blame Feely and Sabine for anything Wallace did or said although their attitude as reported doesn't seem particularly pleasant. Still I don't know what Wallace's attitude to them was like. They may have been hacked off with his approach.
-
jygan at 16:33 PM on 7 January 2015They changed the name from 'global warming' to 'climate change'
I believe that some people also use "climate change" because they feel that "global warming" invites the misconception that warming would occur uniformly and univerversally around the world. I've also heard "global weirding" and "climate chaos," neither of which is entirely accurate either (since even unusual or catastrophic effects have their causes). I suppose any term can be open to misinterpretations, and we've just got to do our best to avoid or correct those.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 15:18 PM on 7 January 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #1
wili,
Like you I am more curious about, and learning more about ENSO.
The latest update on the Australian Bureau of Meteorology website indicates the current strength of the SOI and Nino 3.4 are not maintaining El Nino levels, but they are close. From the tabs on the webpage you can view a variety of information including the latest Nino region sea surface averages.
Though the SOI and the Nino 3.4 are a little below the El Nino threshhold, both the SOI and Nino 3.4 are higher than they were during the months near the end of 2013. So there may be some new monthly record global averages in the early part of 2015.
Also, the ENSO evaluation indicates that the various models they review indicate that there is potential for El Nino conditions to develop, but it is not likely that a strong El Nino event will develop.
-
scaddenp at 14:52 PM on 7 January 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #1
Ingvar.
Deleted for accusations of fraud, repeating your previously debunked claims, sloganeering and off topic. You seem to either unable or unwilling to understand responses to you in the past.
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can and will be rescinded if the posting individual continues to treat adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Moderating this site is a tiresome chore, particularly when commentators repeatedly submit offensive, off-topic posts or intentionally misleading comments and graphics or simply make things up. We really appreciate people's cooperation in abiding by the Comments Policy, which is largely responsible for the quality of this site.
Finally, please understand that moderation policies are not open for discussion. If you find yourself incapable of abiding by these common set of rules that everyone else observes, then a change of venues is in the offing.
Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter, as no further warnings shall be given.
-
PhilippeChantreau at 14:36 PM on 7 January 2015Satellites show no warming in the troposphere
8000 to 15000 meters does not really describe lower troposphere, in my understanding. It sounds more like the tropopause height.
-
MEJ at 12:33 PM on 7 January 2015Satellites show no warming in the troposphere
Thank you all so much for the feedback. A lot of great information. I particularly like the moving graphic on surface temperature.This is proving to be a VERY complex issue to get my head around. It has struck me that I may be comparing apples with oranges.
The SkS graphic is specifically comparing Surface and Satellite temperatures. Three sets of data are being compared. 'Direct Surface Measurements' (Blue Line) and two sets of Satellite(?) data from UAH (Red Line) and RSS (Green Line). In respect to 'Surface Temperature' and I presume once certain adjustments are made they show a very close correlation.

My limited understanding is that if I take a temperature measurement at a ship on the Pacific Ocean (Surface Temperature) then fly up to the Lower Troposphere some 8 to 15 Klms above my position the Temperature measurement will be cooler.
So can I compare Carl Mear's graph of Temperature Lower Troposphere with a graph based on Surface Temperature data?
-
Doug Mackie at 12:16 PM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
slioch @6: Your eqn wrong. Calcification is a SOURCE not a sink for CO2.
Better to use our eqns 1 and 4 from the OA not OK series. (Click 'OA not OK' button to left). -
shoyemore at 05:11 AM on 7 January 2015Pope Francis plants a flag in the ground on climate change
An Evangelical Christian view here from Professor Katherine Hayhoe, lately one of Time's "100 Most Influential People":
Guernica Magazine talks with Katherine Hayhoe
It’s a common perception that science and religion are mutually exclusive. But there are many scientists who would consider themselves to be spiritual people. Not only that, but in the case of climate change—a scientific issue with strong moral implications and difficult decisions to be made—it’s essential to connect the science to our values. And for many of us, our values come from our faith.
A simlar view to that of the Pope - but the interview is well worth reading in full.
-
Rob Painting at 04:56 AM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Trying to blame Wallaces' ignorance of rather basic science on Feely and Sabine is rather amusing though.
"From this it may be that ocean acidification may be less deleterious than currently believed"
That's just wishful thinking. The near-collapse of the US North Pacific oyster fishery due to the die-off of larval oysters from too corrosive seawater highlights the rather obvious flaw in your reasoning. And when we look at the geological record, many marine calcifiers went extinct in the past when the oceans acidified at rates much slower than present-day.
The one of the greatest problems with most laboratory-based ocean acidification experiments is that they don't actually simulate conditions that marine organisms face throughout their lifecycle. That was the problem with the larval oysters - they are actually exposed to conditions much more corrosive than consideration of atmospheric CO2 alone would suggest, and their early lifestages are a time of great vulnerability to carbonate saturation state (corrsiveness of seawater).
So quantification of actual conditions that marine organisms face is essential if one wants to accurately forecast how they might respond to ocean acidification. The Hofman paper is right about that.
-
scaddenp at 04:43 AM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
This is why we have peer-review. The data is made available for the use of scientists with the appropriate domain-knowledge and expertise to be able to use it. This does of course also mean that amateurs with an agenda can use it. If Wallace had tried to publish however, expert reviewers would have immediately pointed out the issues to him. But then I doubt Wallace is really interested in ocean pH, only in ammunition to support a viewpoint based on political values.
-
Satellites show no warming in the troposphere
ginunn - Also note that CO2 is not the only driver of climate. Nobody with even a basic understanding of the science would argue for a simple monotonic linear increase in temperatures in the presence of multiple forcings and internal climate variation.
-
Not pHraud but pHoolishness
william - Apart from the 'blaming the victim' issue of putting the onus of pseudo-skeptic misunderstanding on the scientists, Feely and Sabine did tell Wallace about the issues with data coverage; he apparently followed by impugning their science and motives. Not IMO honorable behavior on Wallaces part.
The data coverage issues of past ocean sampling are well known to those familiar with the science - hence there is little reason to repeat common knowledge in the field in every paper.
-
william11409 at 02:10 AM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Jim Eager @ 9 fair enough but dodgy or incomplete or not spatially or temporally homogeneous or whatever, I am surprised Feely and Sabine made no reference to these data even if only to explain why they chose not to use them. I think they should have done and had they done so, none of this would have eventuated thus denying sceptical blogs another so called "example of sharp practice" with which to regale their readers.
And as an aside, a more recent paper published in PLoS One in 2011 using direct measurements of ocean pH, has shown marine species that are regularly exposed to much greater changes in pH than those forecast for the future and that some species currently are exposed to pH levels more acidic than those forecast for 2100 (http://tinyurl.com/6t9fjly} The paper is also summarised at https://scripps.ucsd.edu/news/1875 From this it may be that ocean acidification may be less deleterious than currently believed.
-
Jim Eager at 00:55 AM on 7 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
William, try reading for comprehension: the older data are not dodgy, the data are simply incomplete, plus dissolved CO2 concentration is not spacially or temporaly homogeneous. Not taking those facts into account is what is dodgy.
-
Composer99 at 00:00 AM on 7 January 2015Satellites show no warming in the troposphere
ginunn:
Regarding your second comment, in point of fact temperature increase is linear with logarithmically increasing CO2: climate sensitivity, you may recall, measures global mean surface temperature increase per doubling of atmospheric concentration of CO2.
-
mitch at 23:58 PM on 6 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
William:
The CO2 data for the oceans are not unreliable, just very incomplete. NOAA put them out because they are valid measurements. The measurements have been made well at least since the 60's and probably longer. The problem is that there is an attempt to create a global record by simple averaging of available data--this is not a smart way to go about producing an average where pH can vary by large amounts depending on the strength of upwelling. I
I guess I get irritated with people that are opposed to funding the monitoring effort but then claim that we cannot determine the trend. If one thinks that there is no trend, there should be more funding to show that, not less. Since 2000, funding for environmental science at the US National Science Foundation for environmental science has dropped by about 20%. -
ginunn at 23:19 PM on 6 January 2015Satellites show no warming in the troposphere
The lines drawn on the graph exclude initial data that would appear to produce a flatter interpretation. The second point is that if you are arguing for a linear increase, it suggests a problem trying to correlate against CO2 increase which is non linear.
-
Esop at 22:40 PM on 6 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
Hmm. Does this mean that the deniers are moving away from their inaccurate claims about temperatures and over to other topics. Wonder why.
-
PhilippeChantreau at 19:47 PM on 6 January 2015Things I thought were obvious!
Tom Curtis @ 60. My comment about the exanding Earth theory was tongue in cheek. Don't be too literal. My "phew" of relief should have indicated that much. Nonetheless, it is telling that Casey appears to treat said "theory" as worthy of rational exmination and comes to the well thought out conclusion that it is not well supported, as if the alternative had any chance to ever contend. In fact, his tone about the subject suggests that the jury could possibly be out again, some day. Open minded doesn't mean fill your mind with garbage. Casey tries hard to give the appearance of being open minded.
-
Slioch at 19:31 PM on 6 January 2015Not pHraud but pHoolishness
3. Rob Honeycutt
Perhaps Wallace has been fooled by the sort of nonsense that Tom Segalstad writes here:
https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B74u5vgGLaWoM0FaOUxrZ21FSmM/edit?pli=1
where he claims that, ""the upper 200m of ocean water contains enough dissolved calcium to bind all anthropogenic CO2 as precipitated calcium carbonate ... without effecting the ocean's pH" (p.818)
Segalstad is wrong.
The overall equation for the reaction of CO2 with calcium ions to produce solid calcium carbonate is as follows:
CO2 + Ca++(aq) + H2O ==> Ca++Co3--(s) + 2H+(aq)
The reaction produces hydrogen ions (2H+aq). You CANNOT precipitate solid calcium carbonate by combining aqueous CO2 and calcium ions WITHOUT at the same time producing hydrogen ions, and thereby reducing pH. (Of course, the H+(aq) + OH-(aq) <==> H2O ( K = c.10^-14 ) equilibrium is simultaneously maintained, but there is still an overall increase in hydrogen ion concentration)
Prev 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























