Arguments
Arguments
 Software
Software
 Resources
Comments
Resources
Comments
 The Consensus Project
The Consensus Project
 Translations
Translations
 About
Support
About
Support


Latest Posts
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #06
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #6 2026
- The future of NCAR remains highly uncertain
- Fact brief - Can solar projects improve biodiversity?
- How the polar vortex and warm ocean intensified a major US winter storm
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #05
- Help needed to get translations prepared for our website relaunch!
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #5 2026
- Climate Variability Emerges as Both Risk and Opportunity for the Global Energy Transition
- Fact brief - Are solar projects hurting farmers and rural communities?
- Winter 2025-26 (finally) hits the U.S. with a vengeance
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #04
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #4 2026
- WMO confirms 2025 was one of warmest years on record
- Fact brief - Do solar panels release more emissions than burning fossil fuels?
- Keep it in the ground?
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #03
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #3 2026
- Climate Adam - Will 2026 Be The Hottest Year Ever Recorded?
- Fact brief - Does clearing trees for solar panels release more CO2 than the solar panels would prevent?
- Where things stand on climate change in 2026
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #02
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #2 2026
- UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
- Six climate stories that inspired us in 2025
- How to steer EVs towards the road of ‘mass adoption’
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #01
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #1 2026
- 2025 in review - busy in the boiler room
- Direct Air Capture
Archived Rebuttal
This is the archived Intermediate rebuttal to the climate myth "There is no consensus". Click here to view the latest rebuttal.
What the science says...
|
That humans are causing global warming is the position of the Academies of Science from 19 countries plus many scientific organizations that study climate science. More specifically, around 95% of active climate researchers actively publishing cli |
Oreskes and Peiser
Scientists need to back up their opinions with research and data that survive the peer-review process. A survey of all peer-reviewed abstracts on the subject 'global climate change' published between 1993 and 2003 shows that not a single paper rejected the consensus position that global warming is man caused (Oreskes 2004). 75% of the papers agreed with the consensus position while 25% made no comment either way (focused on methods or paleoclimate analysis).
Benny Peiser, a climate contrarian, repeated Oreskes' survey and claimed to have found 34 peer reviewed studies rejecting the consensus. However, an inspection of each of the 34 studies reveals most of them don't reject the consensus at all. The remaining articles in Peiser's list are editorials or letters, not peer-reviewed studies. Peiser has since retracted his criticism of Oreskes survey:
"Only [a] few abstracts explicitly reject or doubt the AGW (anthropogenic global warming) consensus which is why I have publicly withdrawn this point of my critique. [snip] I do not think anyone is questioning that we are in a period of global warming. Neither do I doubt that the overwhelming majority of climatologists is agreed that the current warming period is mostly due to human impact."
Doran 2009
Subsequent research has confirmed this result. A survey of 3146 earth scientists asked the question "Do you think human activity is a significant contributing factor in changing mean global temperatures?" (Doran 2009). More than 90% of participants had Ph.D.s, and 7% had master’s degrees. Overall, 82% of the scientists answered yes. However, what are most interesting are responses compared to the level of expertise in climate science. Of scientists who were non-climatologists and didn't publish research, 77% answered yes. In contrast, 97.5% of climatologists who actively publish research on climate change responded yes. As the level of active research and specialization in climate science increases, so does agreement that humans are significantly changing global temperatures.

Figure 1: Response to the survey question "Do you think human activity is a significant contributing factor in changing mean global temperatures?" (Doran 2009) General public data come from a 2008 Gallup poll.
Most striking is the divide between expert climate scientists (97.4%) and the general public (58%). The paper concludes:
"It seems that the debate on the authenticity of global warming and the role played by human activity is largely nonexistent among those who understand the nuances and scientific basis of long-term climate processes. The challenge, rather, appears to be how to effectively communicate this fact to policy makers and to a public that continues to mistakenly perceive debate among scientists."
Anderegg 2010
This overwhelming consensus among climate experts is confirmed by an independent study that surveys all climate scientists who have publicly signed declarations supporting or rejecting the consensus. They find between 97% to 98% of climate experts support the consensus (Anderegg 2010). Moreover, they examine the number of publications by each scientist as a measure of expertise in climate science. They find the average number of publications by unconvinced scientists (eg - skeptics) is around half the number by scientists convinced by the evidence. Not only is there a vast difference in the number of convinced versus unconvinced scientists, there is also a considerable gap in expertise between the two groups.

Figure 2: Distribution of the number of researchers convinced by the evidence of anthropogenic climate change and unconvinced by the evidence with a given number of total climate publications (Anderegg 2010).
Vision Prize
The Vision Prize is an online poll of scientists about climate risk. It is an impartial and independent research platform for incentivized polling of experts on important scientific issues that are relevant to policymakers. In addition to assessing the views of scientists, Vision Prize asked its expert participants to predict the views of their scientific colleagues. The participant affiliations and fields are illustrated in Figure 3.

Figure 3: Vision Prize participant affiliations and fields
As this figure shows, the majority (~85%) of participants are academics, and approximately half of all participants are Earth Scientists. Thus the average climate science expertise of the participants is quite good.
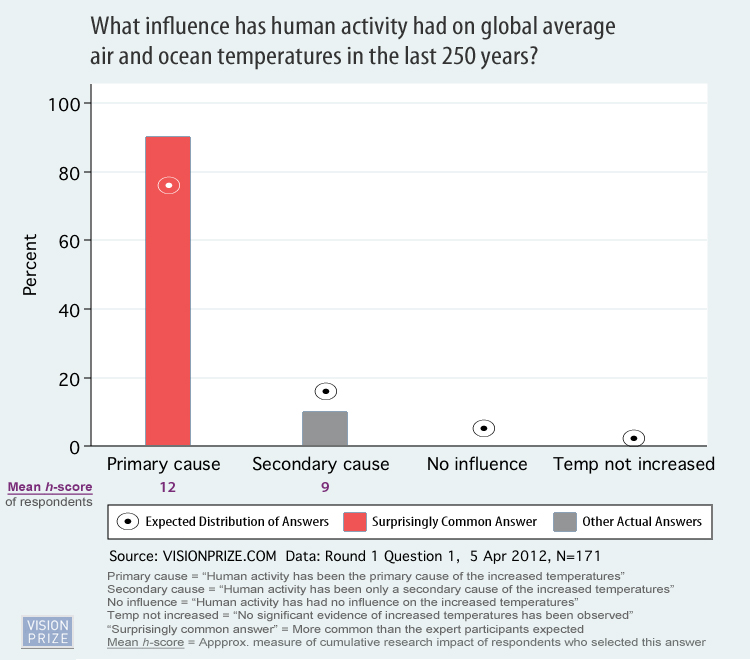
Approximately 90% of participants responded that human activity has had a primary influence over global temperatures over the past 250 years, with the other 10% answering that it has been a secondary cause, and none answering either that humans have had no influence or that temperatures have not increased. Note also that the participants expected less than 80% to peg humans as the primary cause, and a few percent to say humans have no influence - the consensus was significantly better than the participants anticipated (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Vision Prize answers and expected distribution to the question"What influence has human activity had on global average ocean temperatures in the last 250 years?"
Scientific organizations endorsing the consensus
The following scientific organizations endorse the consensus position that "most of the global warming in recent decades can be attributed to human activities":
- American Association for the Advancement of Science
- American Astronomical Society
- American Chemical Society
- American Geophysical Union
- American Institute of Physics
- American Meteorological Society
- American Physical Society
- Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society
- Australian Bureau of Meteorology and the CSIRO
- British Antarctic Survey
- Canadian Foundation for Climate and Atmospheric Sciences
- Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society
- Environmental Protection Agency
- European Federation of Geologists
- European Geosciences Union
- European Physical Society
- Federation of American Scientists
- Federation of Australian Scientific and Technological Societies
- Geological Society of America
- Geological Society of Australia
- Geological Society of London
- International Union for Quaternary Research (INQUA)
- International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics
- National Center for Atmospheric Research
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- Royal Meteorological Society
- Royal Society of the UK
The Academies of Science from 19 different countries all endorse the consensus. 13 countries have signed a joint statement endorsing the consensus position:
- Academia Brasiliera de Ciencias (Brazil)
- Royal Society of Canada
- Chinese Academy of Sciences
- Academie des Sciences (France)
- Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina (Germany)
- Indian National Science Academy
- Accademia dei Lincei (Italy)
- Science Council of Japan
- Academia Mexicana de Ciencias (Mexico)
- Russian Academy of Sciences
- Academy of Science of South Africa
- Royal Society (United Kingdom)
- National Academy of Sciences (USA) (12 Mar 2009 news release)
A letter from 18 scientific organizations to US Congress states:
"Observations throughout the world make it clear that climate change is occurring, and rigorous scientific research demonstrates that the greenhouse gases emitted by human activities are the primary driver. These conclusions are based on multiple independent lines of evidence, and contrary assertions are inconsistent with an objective assessment of the vast body of peer-reviewed science."
The consensus is also endorsed by a Joint statement by the Network of African Science Academies (NASAC), including the following bodies:
-
African Academy of Sciences
-
Cameroon Academy of Sciences
-
Ghana Academy of Arts and Sciences
-
Kenya National Academy of Sciences
-
Madagascar's National Academy of Arts, Letters and Sciences
-
Nigerian Academy of Sciences
-
l'Académie des Sciences et Techniques du Sénégal
-
Uganda National Academy of Sciences
-
Academy of Science of South Africa
-
Tanzania Academy of Sciences
-
Zimbabwe Academy of Sciences
-
Zambia Academy of Sciences
-
Sudan Academy of Sciences
Other Academies of Sciences that endorse the consensus:
Updated on 2013-04-16 by John Cook.
THE ESCALATOR

(free to republish)