Climate change could impact the poor much more than previously thought
Posted on 26 January 2015 by dana1981
It’s widely accepted that climate change will have bigger negative impacts on poorer countries than wealthy ones. However, a new economic modeling study finds that the economic impacts on these poorer countries could be much larger than previous estimates.
As a result, they suggest that we should be aiming to limit global warming to near, or perhaps even less than the international target of 2°C. This conclusion is in sharp contrast to current economic models, which generally conclude that the economically optimal pathway results in a global surface warming around 3–3.5°C.
Current economic models mainly treat economic growth as an external factor. In these models, global warming and its impacts via climate change don’t significantly affect the rate at which the economy grows. However, several economic studies have concluded that this is an inaccurate assumption, with a 2012 paper by Melissa Dell and colleagues taking the first stab at quantifying the effects of climate damages on economic growth.
The new study by Frances Moore and Delavane Diaz of Stanford University calibrates the climate ‘damage functions’ in one of these economic models (DICE, developed by William Nordhaus at Yale) using the results from the Dell paper. They grouped the world into rich and poor countries, finding that while the economies of rich countries continue to grow well in a warmer world, the economic growth of poor countries is significantly impaired.
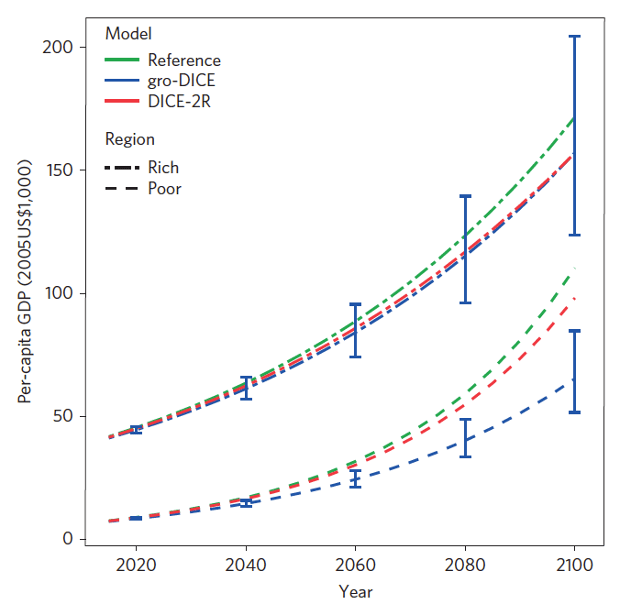 Per-capita GDP under a business-as-usual scenario for rich (top) and poor (bottom) regions for the reference (no damages) run (green), standard economic model (DICE; red), and DICE modified to account for climate impacts to economic growth (blue). Source: Nature Climate Change
Per-capita GDP under a business-as-usual scenario for rich (top) and poor (bottom) regions for the reference (no damages) run (green), standard economic model (DICE; red), and DICE modified to account for climate impacts to economic growth (blue). Source: Nature Climate Change
As a result, Moore and Diaz conclude that the economically optimal pathway could be very similar to the most aggressive scenario considered by the IPCC (called RCP2.6). In this scenario, human carbon emissions peak almost immediately and then decline until they reach zero around the year 2070.
Moore and Diaz find that if climate change does affect GDP growth in this way, then the best path for society would limit temperatures to between 1.6 and 2.8°C warming in 2100, with a best estimate of around 1.7°C warming.
The study estimates the impact on economic growth in poor countries if we continue on a business-as-usual carbon pollution and rapid climate change path:
The average annual growth rate in poor regions is cut from 3.2% to 2.6%, which means that by 2100 per-capita GDP is 40% below reference.
One challenge is that there are two factors that may contribute to the bigger impact of climate change on economic growth in poorer countries, and we don’t know which effect is bigger.
As poor countries are, on average, hotter than rich countries, they are exposed more frequently to damaging temperatures and therefore show higher sensitivity to temperature. Under this mechanism, the sensitivity of rich countries would increase as they warm. Alternatively, higher temperatures may be more damaging in poor countries because their economies are reliant on climate-exposed sectors such as agriculture and natural resource extraction, or because risk management options such as insurance or air conditioning are not as widely available. In this case we would expect the sensitivity of poor regions to warming to decrease as per-capita GDP increases.
In other words, poorer countries may have the resources to adapt to climate change as they become wealthier in the future. On the other hand, if their economic growth is sensitive to global warming mainly because they’re located in hotter parts of the planet, then their economies will struggle in a hotter future world.
The ‘social cost of carbon’ is an estimate of the costs of carbon pollution to society via climate damages. It’s an important number in terms of setting federal policy. In May 2013, the US government revised its estimate of the social cost of carbon from $22 per ton of carbon dioxide emitted to $37 per ton, to great consternation from the Republican Party. The new figure was based in large part on the average of the estimates from current economic models.
However, Moore and Diaz conclude that when accounting for climate impacts on economic growth, the social carbon cost rises to between about $70 and $400, with a best estimate of over $200 per ton. This suggests that even the new, higher US government estimate is too low. Frances Moore told me,
Our estimate of $200 per ton includes the assumption that there will be fairly rapid and effective adaptation to climate change impacts. If there is no adaptation, then the social cost of carbon is substantially larger. So its not an either / or choice between adaptation and mitigation policy.
The results of this study also suggest that estimates of the social cost of carbon to date have underestimated the already large uncertainty in its value. This suggests that climate policies should focus on risk management, as Delavane Diaz explains,































 Arguments
Arguments






























As documented in the following article, the leaders of the U.S. and India have just agreed upon a plan to simultaneously fighting warming and fighting poverty.
Obama & Modi Link Zero Carbon and Zero Extreme Poverty by John H. Cushman Jr., InsideClimate News, Jan 26, 2015
And this is how a Yaley Skull and Bonesman established an economic analysis pattern that would justify the use of outrageously high multi-generational discout rates. By asserting the kind of unlimited growth projections that were previously found only with the "Chicago Boys" who were advocating total economic dismantling of Chile under the ruthless dictator Pinochet.
If (when?) we reach 3.5 C of globally averaged warming, there will be only a small shadow of the former global human civilization since mass migrations, sea level rise and wars, famines and plagues have destroyed most of the global infrastructure.
Were these real impacts incorporated in the models, the reduction in global output would justify a negative discount rate. But you aren't going to get that from Yale.
jja,
I have an MBA and totally agree that the way many 'economists' value things and evaluate things is unrealistic and can even be shown to be irrational.
I prefer to state that it is unacceptable for anyone to benefit at the expense of others or in a way that harms others, and others includes future generations and other aspects of the robust diversity of life on this amazing planet. I add that helping others and striving to imrove the understanding of what is going on to improve the ability of humanity to advance to a sustainable constantly improving better future for all life on this amazing planet is among the most valuable things a person can do, contrary to what the current soicio-economic-political system values (encourages to be popular and profitable).