Recent Comments
Prev 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 Next
Comments 59601 to 59650:
-
muoncounter at 10:30 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip K#23: "It is not obvious to me that ..." You're entitled to your opinion, but not your own facts (although this isn't the thread for GHG mitigation arguments). Doc Ford#33: "... combat any perceived effects of short-term climate change through the use of air-conditioning," Ah, the 'let 'em get air conditioning' response. One can almost hear an echo of the fabled line of Marie Antoinette in that: 'The poor have no fans.... ' As usual, there is a more complicated response to consider: ... cold adaptation is usually more difficult physiologically for humans since we are not subarctic animals by nature. We do not grow dense fur coats nor do we usually have thick layers of fat insulation like polar bears. Despite this reality, more people die from heat than cold in the United States every year. Those who succumb are usually babies left in locked cars on hot days and the elderly poor who cannot afford air conditioning. The effect of heat on our bodies varies with the relative humidity of the air. High temperatures with high humidity make it harder to lose excess body heat. As for the glib assurance 'we can quickly adapt,' some can, others can't: Heat-related deaths among high school and college football players in the United States nearly tripled between 1994 and 2009, according to a new study. -
dana1981 at 10:30 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip @32 - I do reckon that improved technologies and deployment and communication will continue to improve, but firstly that does not support your argument that a higher frequency of heat waves would be beneficial, nor do I think those advances will keep up with the increased heat wave frequency caused by global warming. The reasons it's not a good thing are 1) in the meantime you get events like the 2003 European heat wave and 2) the costs of adaption are not low, and particularly difficult for poorer regions to cope with. Doc Ford @33 - nobody claimed that global warming proves human-caused global warming. Causation is discussed in many other posts on this site if you'd like to learn about the subject (i.e. see here and here and here). Regarding the myth that mitigation will be costly, see here. These myths are off-topic in this post. -
Chip Knappenberger at 10:12 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
dana1981 (#30), You say, "already adapted" but I gave you three examples of cities which in matter of only a couple of years, were able to take measures to reduce the impacts of heat-waves. Adaptations, in many cases, are fairly straightforward. Also, earlier in our discussion, you made a point that you thought that some of the adaptations that were taking place (which were responsible for the declining high temperature sensitivity trends over time) were not being driven by climate change. Don’t you reckon that such trends (e.g., improved medical technologies, heat watch/warning systems, etc.) will continue? Adaptation to heat takes place somewhat spontaneously, as well as being in a direct response to an increased threat of heat waves. It proceeds gradually over time perhaps accelerated by a wake up call. The net result is a declining sensitivity to heat waves. It is hard for me not to view this as a good thing. -Chip -
Tom Curtis at 10:05 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
First, to clear up some confusion (william @25; grypo @28), Knappenberger is not talking about the biological adaption of the human race, but about changes in behaviours to better cope with high heat levels. Such changes include (but are not limited to) stopping strenuous work, staying in shaded areas, drinking plenty of fluids, immersing yourself in water, and air conditioning. As Dana and others point out, such adaptations come at a cost, both in increased electricity and water requirements, and in lost economic productivity. What I find odd about Knappenberger's argument is that it shows no recognition of the scale of the problem. Below is a chart comparing a range of temperatures experienced over the 20th century with those expected by the end of the 21st century with Business as usual: The image was made by taking Lindzen's image of annual station averages from about 1850-1990 and superimposing a copy of itself in red with a 4 degree higher mean. As can be seen, what we are looking at is current record breaking years becoming the long term mean.
This graph understates the issue in two ways. First it is a graph of annual averages, and the divergence from the mean of heatwaves will be greater than that for annual averages. Second, as Hansen has shown, the standard deviation of temperatures is increasing so that the maximum temperature and frequency of extreme heat events is increasing faster than the mean.
So, what we are looking at is the current economic cost of adaption becoming an ongoing, daily cost year in year out, plus an exponentially increased cost of adaption to future heat waves.
The image was made by taking Lindzen's image of annual station averages from about 1850-1990 and superimposing a copy of itself in red with a 4 degree higher mean. As can be seen, what we are looking at is current record breaking years becoming the long term mean.
This graph understates the issue in two ways. First it is a graph of annual averages, and the divergence from the mean of heatwaves will be greater than that for annual averages. Second, as Hansen has shown, the standard deviation of temperatures is increasing so that the maximum temperature and frequency of extreme heat events is increasing faster than the mean.
So, what we are looking at is the current economic cost of adaption becoming an ongoing, daily cost year in year out, plus an exponentially increased cost of adaption to future heat waves.
-
sidd at 09:41 AM on 25 April 2012Levitus et al. Find Global Warming Continues to Heat the Oceans
I am impressed by Fig. S5 The amount of heat accumulating in (mostly) the 0-700m layer north of 70 degrees in the Atlantic over 50 yr. is on the order of 5e21 J this is a trend of 1e20 J/yr i note that melting 300GT/yr ice as indicated by PIOMASS is a heat sink of that order of magnitude. sidd -
dana1981 at 08:25 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Again Chip, cities which are already adapted to heat waves and variability aren't the issue. It's the cities which are unaccustomed to high temps, but which will see ever-more frequent heat waves which are the problem. As grypo @28 notes, while cities will eventually adapt to the increase in hot weather, in the meantime people will die until they are prepared for the changing climatic conditions. This will particularly be a problem in developing nations where adaption will be more of a challenge, since the necessary adaption measures cost money. -
Don9000 at 08:13 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Thank you Daniel--I have in the past managed to find a few items via google searches--usually from government sites, but hadn't thought to go through the authors. I find it a bit odd, to say the least, that the author can make even a pre-press version of the article available in this way, when the host publication takes the approach it does. Oh well! Ours is not to wonder why . . . -
Chip Knappenberger at 08:04 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
dana1981 (#27) "global warming may very well lead to greater temperature variability, and certainly more heat waves." That may be true, but 1) Zanobetti et al. did not look at heat waves (but the studies I listed above did), and 2) in the Zanobetti study, the cities in climates with the greatest amount of summer temperature variability were the cities whose populations were the least sensitive to temperature variations. So, it follows that if temperature variability increases, then the population's sensitivity to it should decline--just as I expect will happen as heat waves become more frequent. As Zanobetti et al. note, "there is strong evidence of adaptation to usual temperatures." -Chip -
grypo at 07:39 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
This is probably the first time I've ever heard a suggestion that we sacrifice lives in hopes that adaption down the line will save some lives used as an anti-mitigation argument. This type of thought process is rather dangerous. I would hope it gets ignored. The logic gets even more tortured when saying that attempting to prevent these initial outcomes is dangerous (as in the EPA). Let's all try and imagine this type of thought process being used all types of these situations. We can do better than this. I guess we should learn that they will say almost anything. -
dana1981 at 07:36 AM on 25 April 2012Levitus et al. Find Global Warming Continues to Heat the Oceans
ribwoods @1 - thanks, typo corrected. -
dana1981 at 07:36 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip - global warming may very well lead to greater temperature variability, and certainly more heat waves. -
Eric (skeptic) at 06:58 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
As clearly spelled out in the OP there are two topics in this thread, short term mortality attribution and long term extreme heat impacts. It would be nice if everyone clearly specified which topic they are referring to. (most appear to be addressing the short term attribution issue) Also, needless to say, carbon mitigation economics, regulations, etc is off topic. IMO I think cost of heat adaptation is a separation issue too, but JMO. -
Flakmeister at 06:39 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
This goes with #9... http://www.stsci.edu/institute/conference/faint-sun/posterList -
Flakmeister at 06:29 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Opps... I may have mispasted things... http://www.yomiuri.co.jp/dy/features/science/T120420005829.htm This concerns the suns field becoming quadrapolar... -
william5331 at 06:28 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip is of course, absolutely correct. If we have heat wave after heat wave, the human population will, over time, become adapted to higher temperatures. What he forgot to mention is that this process involves cutting off the non-heat-tolerant part of the population. In other words lots of deaths. Evolution is a remarkably fast process when you apply heavy selection pressure. Look at how fast we have changed wolves into everything from Pekaness to Rotweilers. Has anyone asked the heat intolerant tail of the population if they agree to this process. -
Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip Knappenberger - Your discussion of Jacobson 2010 is primarily an emphasis on uncertainties. But please note that uncertainties cut in both directions - these CO2 related issues (particulates, ozone, local heat) may just as well have much worse effects as much better. Christidis et al 2010 shows that adaptation is reducing both heat and cold related mortality, which is good. But using adaptation to claim that heat events do not increase baseline heat related mortality on those grounds is merely pushing the cost off to adaptation. The discussion over whether GHG emissions regulations would be effective is another discussion, and I would suggest taking a look at: Northeast USA Carbon Pricing Benefits Exceed Costs The economic impacts of carbon pricing Monckton Myth #11: Carbon Pricing Costs vs. Benefits where these are discussed. The overwhelming conclusion of the studies that I have seen is that GHG mitigation is immensely less expensive, to the point of being quite profitable, than adaptation/fixing it afterwards. I realize that you are part of an advocacy group, and that the general thrust of New Hope is towards reducing regulations (as per the group publications) - but even if adaptation reduces the impact of heat event mortality, it's going to be more expensive overall than avoiding the heat increases in the first place. -
Chip Knappenberger at 05:54 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
muoncounter (#21), Whatever you or I may feel about the need for "regulations," at the very least, we would want them to be effective. It is not obvious to me that GHG emissions regulations in the U.S. would be when it comes to mitigating climate change. -Chip -
nealjking at 05:52 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Something bothers me about the paper that says that increased levels of CO2 will drive the foraminifera extinct: As I recall, the lifecycle of foraminifera (specifically the creation of their exoskeletons from the CO2 in the ocean; and the deposit of these exoskeletons at the bottom of the oceans; eventually being compressed into limestone) is the principal means of removing CO2 from the atmosphere/ocean/biosphere, and is denoted as "the biological pump". If the biological pump breaks, we'll be stuck with excessive amounts of CO2 for a lonnnggg time. Are these different foraminifera that we're talking about, or are we kicking the football out of the stadium? -
Chip Knappenberger at 05:36 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
dana1981, Thanks for your response and the discussion. Zanobetti et al. looked at temperature variability. And they did not look at trends over time. So, their results are only tangential to the current discussion. You are correct that in the series of Davis et al. work we did not specifically examine what was prompting the U.S. population in major cities into becoming less sensitive to extreme high temperature events. However, other papers have suggested that decreased heat-related mortality in subsequent heat-waves (after particularly deadly ones) was directly related to adaptation measures put into place in response to the threat of heat-waves (see the Fouillet paper I mentioned above, or, Tan et al. 2006, or Palecki et al., 2001). And the measures were shown to be effective in reducing heat-related mortality. So, I think it quite reasonable to assume that in the face of increasing frequency and severity of heat waves, that adaptations will take place—and the evidence suggests (to me at least) that there is a good chance that these adaptations will be effective. With the probable net impact of reducing heat-related mortality in a standard population (i.e. after changes in demographics/age structure have been accounted for). -Chip -
muoncounter at 05:33 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
ChipK#19: Your opinion piece certainly pokes holes in Jacobson's model, but does not offer any new data of its own. Hardly a strong reference. My colleague Pat Michaels refers to this as the EPA’s “whack-a-mole” strategy—while effort is concentrated on trying to beat down one of its pesky and ill-founded CO2-regulating proposals, the EPA pops up another and another and another. Basically you've said 'let's not regulate because we don't like regulations.' All of Jacobson’s reported changes, with the exception of the transient existence of the CO2 dome itself, are only detectable in computer-model world, where all other factors are controlled for and each model in each step is presumed correct. So like all good deniers, your advice is to do nothing, wait and see. In this case, the signal we're talking about will emerge when people start dropping in the streets. Oh, I forgot, they can just 'adapt.' -
philipm at 05:26 AM on 25 April 2012Global Surface Temperature: Going Down the Up Escalator, Part 1
I don't agree with Muller that no one cares what journalsts said 10 years ago. What about the global cooling prediction in the 1970s that was more in the media than the scientific literature? -
dana1981 at 04:56 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
I think the argument itself is faulty. Heat-related mortality may be (or may have been in the past) declining in certain areas as those cities implement various measures to address the problem, but you haven't shown that they implemented those measures because of the increased heat wave frequency. Morevoer, most of your references are to very specific and small areas. Zanobetti at least looked at 135 different US cities and found a different story. Really what you've shown is that if cities implement measures to reduce heat mortalities, they will reduce heat mortalities. You haven't shown that a higher frequency of heat waves will lead to fewer heat mortalities. And again there's the problem of the cost of those measures, and the cost increases as the frequency of heat waves increases. -
Chip Knappenberger at 04:24 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Lionel A (#13): No doubt that there will be short-term hardships for places where heat-waves are currently rare. But once adaptation measures start to be adopted, the sensitivity of the population to extreme heat declines rapidly (see Fouillet et al. for a European example) Dana1981 (#14), All of the papers I referenced support my argument that the sensitivity to heat-related mortality has generally been declining. I am very aware of Kalkstein et al.’s opinion about heat-related mortality in the future, but I don’t think that it fully takes into account the power of adaptation which is apparent from observed trends. As to observed trends, Kalkstein et al. say “Our results generally show a reduction in EHE-attributable mortality rates since 1996.” Dan Bailey (#15): I credit all the decline in heat-related mortality to adaptation! muoncounter (#17): Here is my opinion about Jacobson 2010. jibal (#16, #18), Obviously, you are free to judge my arguments/argument style as you see fit. -Chip -
jibal at 04:04 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
This dialog between Mr. Knappenburger and blogger "TokyoTom"(self-described as "a right-leaning enviro-libertarian"), in which Mr. Knappenburger freely participated, and agreed to have published on the web, in informative about the usefulness of his research to those seeking the truth (see principle #2 in "A Code of Conduct for Effective Rational Discussion"): http://mises.org/Community/blogs/tokyotom/archive/2008/04/02/update-on-science-advocacy-and-pat-michaels-correspondence-with-chip-knappenberger.aspx -
ribwoods at 03:44 AM on 25 April 2012Levitus et al. Find Global Warming Continues to Heat the Oceans
Typo in the first sentence under "Consistent with Meehl's Hiatus Periods": "plateu" should be "plateau". -
muoncounter at 03:40 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Let's not leave out Jacobson 2010, as heat is not the only factor in increasing mortality. Jacobson found that domes of increased carbon dioxide concentrations – discovered to form above cities more than a decade ago – cause local temperature increases that in turn increase the amounts of local air pollutants, raising concentrations of health-damaging ground-level ozone as well as particles in urban air. Similarly, Jacobson 2007 found ... increased water vapor and temperatures from higher CO2 separately increase ozone more with higher ozone; thus, global warming may exacerbate ozone the most in already-polluted areas ... About 40% of the additional deaths may be due to ozone and the rest, to particles, which increase due to CO2-enhanced stability, humidity, and biogenic particle mass. I really like the 'adapt and do it quickly' philosophy. -
jibal at 03:23 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip, I suggest that you familiarize yourself with http://www.limbicnutrition.com/blog/resources/a-code-of-conduct-for-effective-rational-discussion/ because you're failing to adhere to most of these principles, notably in this case the rebuttal principle. -
Daniel Bailey at 02:23 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip's shotgun approach (a gentler term than the link-vomit term that comes so readily to mind) still lacks any cogent analysis. Conspicuous by its absence is the recent work of Christidis et al, which looked at: 1. The trends of the changes (if any) in Cold-Related-Mortality (CRM) and Heat-Related-Mortality (HRM) 2. To see what portion could be explained by human adaption (if any) and what could be attributed to climate change (if any) Causes for the recent changes in cold- and heat-related mortality in England and Wales Nikolaos Christidis, Gavin C. Donaldson and Peter A. Stott Climatic Change Volume 102, Numbers 3-4 (2010), 539-553, DOI: 10.1007/s10584-009-9774-0 Synopsis: "Cold related mortality among people aged over 50 in England and Wales has decreased at a rate of 85 deaths per million population per year over the period 1976–2005. This trend is two orders of magnitude higher than the increase in heat-related mortality observed after 1976. Long term changes in temperature-related mortality may be linked to human activity, natural climatic forcings, or to adaptation of the population to a wider range of temperatures. The need for a formal statistical tool when one attempts to make attribution statements that link impacts of climate change to possible causes is clear. A less stringent approach could be very misleading. For example, it would be easy to compare the recent decrease in cold-related mortality with the increase in temperature and make the seemingly logical assumption that fewer people have died because of milder winters. Our work, however, shows that this is not the case. Here we employ optimal detection, a formal statistical methodology, to carry out an end to end attribution analysis. We find that adaptation is a major influence on changing mortality rates. We also find that adaptation has prevented a significant increase in heat-related mortality and considerably enhanced a significant decrease in cold-related mortality. Our analysis suggests that in the absence of adaptation, the human influence on climate would have been the main contributor to increases in heat-related mortality and decreases in cold-related mortality." (Emphasis added) -
dana1981 at 02:02 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
Chip, it would help if you actually point out which of the papers you reference are supposed to support your argument. For example, Kalkstein et al. specifically say they don't know how increased heat events as a result of global warming will impact heat mortalities. You also reference Davis et al. (2003) which I addressed in the post above. There's also the problem of the costs of the necessary adaptions to cope with increased heat waves. Somehow people who argue that mitigating global warming will be expensive seem to forget the costs of adapting to global warming if we fail to mitigate it. -
Lionel A at 02:02 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
So let me see Chip (@12) all these people just couldn't be bothered to adapt quick enough. Now don't forget that 'rubber meets the road' not only in cities. I realise that US cities in particular have lots of air conditioners, each causing their own increase in CO2 emissions during periods of elevated temperature. If the conditioners are already working, which they often are keeping things unnaturally cool, then they just work harder. That kicks into touch many of those studies, hint we don't all live in cities and those in the sticks are likely to suffer power failures, thus air-conditioner failure, more rapidly and more often. As for that third down the list seeing as to who was involved in that then large pinches of salt should be used when perusing it. But don't panic, increased sweating releases more salt. I am curious as to why you picked that one and not this one mentioned here ? Whatever here is the other side of the coin and be sure to check out 'Related articles...' at the foot of. -
les at 00:52 AM on 25 April 2012Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
I agree with KR and Uncle Ben - Excellent insights there, Tom Curtis. I'm a little bemused by Uncle Ben's reaction. Many of us here have used and taught something by way of data analysis and statistics - and anyone who has done tends to be very cautions of 'seeing' signals; and so use tools (analysis, simulations etc.) to ensure some objectivity results... this is a great illustration of the point. What does worry me, where Mitt Romney to get elected - this seems to be the perfect 'science' for an etch-a-sketch president... -
Chip Knappenberger at 00:49 AM on 25 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
dana1981, Interesting arguments, but not really where the rubber meets the road. Perhaps you could review some papers that actually looked at observed trends in heat-related mortality in the face of global warming. Here are a few to get you started: Barnett, A.G., 2007. Temperature and cardiovascular deaths in the U.S. Elderly: Changes over time. Epidemiology, 18, 369-372. Carson, C., S. Hajat, B. Armstrong, and P. Wilkinson, 2006. Declining vulnerability to temperature-related mortality in London over the 20th century. American Journal of Epidemiology, 164, 77–84. Davis, R.E., P.C. Knappenberger, P.J. Michaels, and W.M. Novicoff, 2003. Changing heat-related mortality in the United States. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111, 1712–1718. Donaldson G.C., W.R. Keatinge, S. Nayha, 2003. Changes in summer temperature and heat-related mortality since 1971 in North Carolina, South Finland, and Southeast England. Environ Res 2003;91:1–7. Kalkstein, L.S., S. Greene, D.W. Mills, and J. Samenow, 2010. An evaluation of the progress in reducing heat-related human mortality in mjor U.S. cities. Natural Hazards, doi:10.1007/s11069-010-9552-3 Kyselý, J., and E. Plavocá, 2012. Declining impacts of hot spells on mortality in the Czech Republic, 1986-2009: adaptation to climate change? Climatic Change, doi:10.1007/s10584-011-0358-4 Matzarakis, A., S. Muthers, and E. Koch, 2011. Human biometeorological evaluation of heat-related mortality in Vienna, Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 105, 1-10. If you look through these papers, you'll not only see evidence for declining sensitivity (through adaptation) to extreme heat, but also that these adaptations can and do occur rather quickly. -Chip -
Yvan Dutil at 00:24 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
#4 @Flakmeister The estimated impact of the Maunder minimum is larger from what is expected elsewhere in the scientific litterature. http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2010/2010GL042710.shtml http://www.leif.org/EOS/2011JD017013.pdf http://www.eiscat.rl.ac.uk/Members/mike/publications/pdfs/Sun_Climate_final.pdf -
Ari Jokimäki at 00:23 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
I'll add that when I add these papers during the week, I check if full texts are available for them, but I won't do that again just before this post is published. Therefore there's a good possibility that a new full text search is successful, when this post has been published. -
Ari Jokimäki at 00:18 AM on 25 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Thanks for the comments. For these new papers Google Scholar has not been the best place to look for full texts. Normal Google search has returned better results for them. However, I haven't tried Google scholar much in this context for a long time so it's possible that the situation has improved. -
Flakmeister at 23:55 PM on 24 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Came across this http://hinode.nao.ac.jp/news/120419PressRelease/index_e.shtml I seen commentary to the effec that this might presage a new Dalton-like minimum.... Any insights out there? -
DSL at 23:51 PM on 24 April 2012Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Uncle Ben, when you first began to post, I thought you were attempting to breathe life into the uncertainty monster. I see that's not the case, but I would suggest taking a closer look at Roy's apparent apotheosis. After all, the book and the arguments used in it have long since been taken apart both in the blogosphere (here at SkS and Barry Bickmore's lovingly titled "Just Put the Model Down, Roy") and in publication (e.g., Murphy & Forster 2010), and general (and generally eye-opening) critiques of Roy's work are all over the place. To his credit, Roy has responded to some of the criticisms, yet he has ignored others. When defenders of Spencer say things like "the first part is clear, something Spencer might have written," it just makes the hair on the back of my neck stand up. It sometimes seems to me that Roy, rather than being the usual type of politically-driven obfuscator, is on a personal quest with his climate science, a quest in search of the "perfect language" or the GUT, that simple equation that makes sense out of everything in the anthrocentric universe. Questers seek to confirm that the universe is constructed in such a way that humans (particularly individual humans) are perfectly (providentially?) suited to "figure it out." As I've probably walked over the edge of the Cliff of Moderation in a number of ways, I'll shut up now. One more thing: Tom, that was good stuff. I can explain many complex things, but as I came back to the thread yesterday, I tried to figure out a comprehensible way to explain what was intuitively obvious, and I just couldn't do it. -
Uncle Ben at 23:27 PM on 24 April 2012Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Tom 64 Thank you, Tom, for a most interesting exercise. I disagree with your bold print statement. The slope I saw in the plot I responded to is infinite, corresponding to sensitivity zero. And in the real data, it appears to me that conditions are not nearly as noisy as you think. But let us agree to disagree. Thank you for sticking to the science instead of the man. That does you credit. -
Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Tom Curtis - Thank you, a wonderful illustration of finding what you're looking for, despite a lack of support in the data. And a good overview of what Spencer has attempted to do with these papers. -
CBDunkerson at 22:49 PM on 24 April 2012A prelude to the Arctic melting season
Cryosat-2 has released more results. Also a BBC story here. Some of the significant findings; Total arctic ice volume calculated by Cryosat is consistent with PIOMAS results. About 14,500 km^3 for March 2011. This confirms that the sharp drop in ice volume shown by PIOMAS over the past few years was not an error in the model. Average ice thickness was just 1.5 meters in October 2010. Rising to about 2.4 meters by March 2011. This is significant because in the past 'first year ice' was frequently about 3 meters thick. Now only 2+ year old ice is that thick. There was virtually no 5 meter thick ice remaining in October 2010, but over the winter scattered tiny pockets formed by March 2011. -
Daniel Bailey at 22:46 PM on 24 April 2012Global Surface Warming Since 1995
Then there's this latest research by John Nielsen-Gammon, here GISTemp global temperatures, with trends for El Niño, neutral, and La Niña years computed separately. Pinatubo years are excluded
Yup, still warming
(latest CRU data included, for the nay-sayers)
GISTemp global temperatures, with trends for El Niño, neutral, and La Niña years computed separately. Pinatubo years are excluded
Yup, still warming
(latest CRU data included, for the nay-sayers)
-
Daniel Bailey at 21:54 PM on 24 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
One can always search via Google Scholar. When that fails (as it did in this case), a fruitful next step is to search the publication pages of the various authors. For example, a search for author Tor Eldevik yielded this publications page, which then yielded a link to this PDF: Quantifying the influence of Atlantic heat on Barents Sea ice variability and retreat Arthun et al 2012 If all else fails, write to one of the authors. You'd be surprised how helpful they can be. -
Don9000 at 21:30 PM on 24 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Ari, A good week's haul. While a number of the entries caught my interest, the article on the Atlantification of the Arctic looks particularly interesting. I just wish more of the journals that publish these articles could figure out a way to make them available for free or at a much lower cost on-line so access could be wider and easier than it is. Far too often, I see an interesting article on your weekly lists, click through to the firewall and see the asking price--typically on the order of $25.00, and think 'I should get over to the local university and make a photocopy for a couple bucks,' and then don't even do that because it does not fit into my schedule, or I discover the journal is not available at the local uni. -
Tom Curtis at 20:15 PM on 24 April 2012Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Uncle Ben @62, thankyou. Now it is time for me to place my cards on the table. All graphs I have presented on this thread (except for the satellite channel graph) have come from Spencer and Braswell, 2010. They have been figure 8d @31, figure 3a @57, and @39, figure 7d, presented below without modification: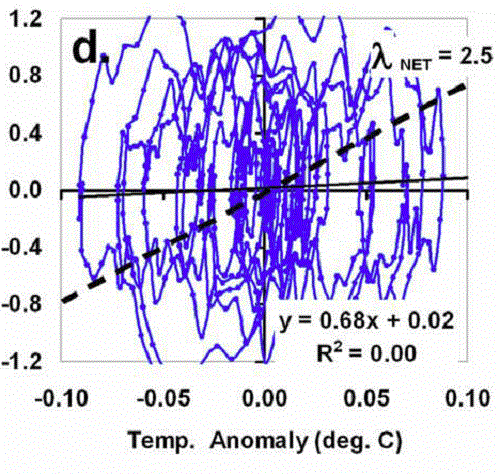 Figure 7d is the time connected phase space plot of dH/dt against t (as all three are), but of a model run where the net radiative feedback parameter (lambda) is 2.5, but the forcing is a low pass filtered series of random numbers.
Neither Spencer (knowing what it is), nor you (not knowing) seem prepared to face the implications for his theory. Spencer practices creative avoidance, calling the pattern a "looping or spiral pattern". That is a poor description, however. The pattern clearly lacks the long nearly straight lines horizontally to match the vertical lines I drew attention to that you would expect in a looping or spiral pattern. You draw attention to the slight curvature of those lines, but the curvature is no greater than the lines you (and certainly Spencer) are prepared to call straight when they appear in figure 8d:
Figure 7d is the time connected phase space plot of dH/dt against t (as all three are), but of a model run where the net radiative feedback parameter (lambda) is 2.5, but the forcing is a low pass filtered series of random numbers.
Neither Spencer (knowing what it is), nor you (not knowing) seem prepared to face the implications for his theory. Spencer practices creative avoidance, calling the pattern a "looping or spiral pattern". That is a poor description, however. The pattern clearly lacks the long nearly straight lines horizontally to match the vertical lines I drew attention to that you would expect in a looping or spiral pattern. You draw attention to the slight curvature of those lines, but the curvature is no greater than the lines you (and certainly Spencer) are prepared to call straight when they appear in figure 8d:
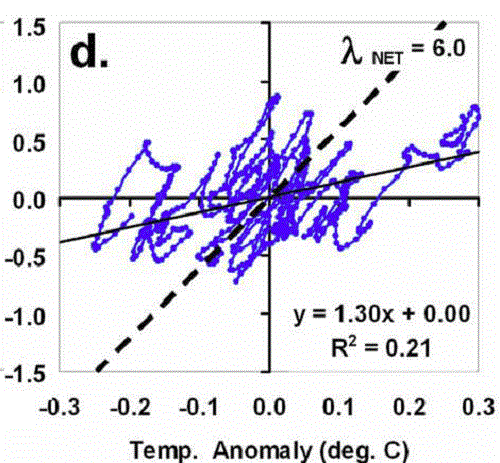 In fact, what distinguishes this figures from the ones you are used two are two simple facts:
1) The random fluctuations in forcing are large relative to the feedback parameter; and
2) There is no overall trend in temperature with time, so that unlike in figure 8d, the pattern keeps tracing out in the same space rather than progressively moving to the right.
In fact, in figure 8d the only two thing which were changed in the model from fig 7 to fig 8 were the significant increase in size of the feedback factor relative to the size of the random forcings (countering 1), and the addition of a steady time independent forcing which induced a positive temperature trend with time (countering 2).
The key point here, however, is that the vertical nearly straight lines in figure 7d are directly analogous with the diagonal "striations" in figure 8d (and 3a). As such, according to your theory and Spencer's their slope should give the feedback parameter. Clearly it does not. In other words, at the very minimum, the claim that the slope of the diagonal striations give the feedback parameter does not hold true when random influences are large relative to the feedback parameter. In other words, in noisy conditions such as obtain in the real world, Spencer's analysis does not hold.
And suggestions that it is just a mathematical fact that the slope gives the feedback factor are just empty bluster.
In fact, what distinguishes this figures from the ones you are used two are two simple facts:
1) The random fluctuations in forcing are large relative to the feedback parameter; and
2) There is no overall trend in temperature with time, so that unlike in figure 8d, the pattern keeps tracing out in the same space rather than progressively moving to the right.
In fact, in figure 8d the only two thing which were changed in the model from fig 7 to fig 8 were the significant increase in size of the feedback factor relative to the size of the random forcings (countering 1), and the addition of a steady time independent forcing which induced a positive temperature trend with time (countering 2).
The key point here, however, is that the vertical nearly straight lines in figure 7d are directly analogous with the diagonal "striations" in figure 8d (and 3a). As such, according to your theory and Spencer's their slope should give the feedback parameter. Clearly it does not. In other words, at the very minimum, the claim that the slope of the diagonal striations give the feedback parameter does not hold true when random influences are large relative to the feedback parameter. In other words, in noisy conditions such as obtain in the real world, Spencer's analysis does not hold.
And suggestions that it is just a mathematical fact that the slope gives the feedback factor are just empty bluster.
-
shoyemore at 19:01 PM on 24 April 2012New research from last week 16/2012
Never mind about being funny and witty, Ari. Your posts are a must-read and I always look forward to them, especially the Classic of the Week. -
KeefeandAmanda at 18:24 PM on 24 April 2012Global Warming Causing Heat Fatalities
People need to fully understand what Huber in that National Academy of Sciences paper was talking about. The point is that this is not about thermometer temperatures, but essentially heat indexes, a combination of thermometer temperatures and relative humidity. Heat indexes high enough to kill most everyone do not require thermometer temperatures higher than what we already see regularly. This is important because this is about more and more water vapor in the air as the planet gets hotter and hotter. There is 4% more water vapor in the air now than just 40 years ago. The wet-bulb limit Huber talks about below is 35 degrees C or 95 degrees F, which according to him is a 170-196 degrees F heat index. This limit would cause death for most any human within hours, and this would include probably most any modern bird or mammal that lives on the surface. This limit, according to the online heat index calculator below, can be achieved with a thermometer temperature of only 105 degrees F with 75% relative humidity. But many if not most people would still not survive a heat index range at lower levels than this. This calculator below shows a thermometer temperature of 100 degrees F with 75% relative humidity gives a heat index of 150 degrees F, still enough to kill pretty quickly probably a high percentage of people or modern birds and mammals that live on the surface. Note: Air conditioners would not save us, certainly not the outside animals in question. All it would take is a single power failure at the wrong time. At the National Weather Service Hydrometeorological Prediction Center, I encourage everyone to play around with entered data for this online heat index calculator: "Meteorological Conversions and Calculations Heat Index Calculator" http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/html/heatindex.shtml I like what Huber himself said. Here are some quotes of his: "The Health Effects of Hotter Days and Nights" http://www.gaia-movement-usa.org/?q=node/46 Quote: ""Most people are more familiar with the heat index, or the feels-like temperature they see on the weather report. The wet-bulb temperatures we are talking about would have a feels-like, or heat-index, temperature of between 170 to 196 degrees Fahrenheit," Huber said. "Researchers find future temperatures could exceed livable limits" http://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/research/2010/100504HuberLimits.html Quote: ""The wet-bulb limit is basically the point at which one would overheat even if they were naked in the shade, soaking wet and standing in front of a large fan," Sherwood said. "Although we are very unlikely to reach such temperatures this century, they could happen in the next."" -
Uncle Ben at 16:53 PM on 24 April 2012Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Rom 60 Sorry. Should be Tom 60. It's late here. -
Uncle Ben at 16:49 PM on 24 April 2012Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Rom 60 I answered before, Tom, that is a strange plot. The lines are curved and vertical, and they are the majority of the segments. Without any more information about the circumstances under which the data were taken, I can only repeat that some single process is dominatig, and is characterized by hardly any sensitivity at all to any forcing by the independent variable dH/dt. The bowing out of the nearly vertical lines into slight curvature represents perhaps a forcing which is reversed by some negative feedback to keep the temperature more narrowly confined to a range than it would without it. But the dH/dt seems to affect dT very weakly. Something else must be going on. Will you provide more information? -
Roy Spencer finds negative feedback
Uncle Ben - "After the storm of protest by those who wanted to do something different, he did publish results for all the models." Can you point to where this was published? I am unaware of any peer-reviewed response by Spencer to the Dessler and Trenberth papers. I am, on the other hand, aware of Wolfgang Wagner, Editor in Chief of Remote Sensing, resigning over the poor peer review, and unwarranted publicity and misstatements by the authors, of that Spencer paper. Please, if you have any pointers to a peer-reviewed Spencer response, I would love to see it! -
TOP at 14:29 PM on 24 April 2012Weird Winter - March Madness
2009 had a somewhat similar temperature pattern in March and April, but March was just to the high side of normal and April was near the low side of normal. In 2007 the pattern was a bit later, but April got real cold. Wrecked my pears. Blocked systems and a warm and then cold spell this time of year is common. Just not to the extreme as this year. As I recall there was the opposite pattern occurring in eastern Europe all the way down to Tripoli, Libya with unusual cold and snow a short time before Summer in March.
Prev 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























