Recent Comments
Prev 2197 2198 2199 2200 2201 2202 2203 2204 2205 2206 2207 2208 2209 2210 2211 2212 Next
Comments 110201 to 110250:
-
Nichol at 19:42 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
Would it be reasonable to compare the IPCC process with the way Wikipedia tries to collate knowledge in general, trying to have a neutral point of view, and not contributing original findings, but to refer to information published elsewhere. Only the IPCC work is not done by random volunteers, but by actual experts in the field. And the requirements for the referenced literature are much more serious. And the editing process is more strictly defined and negotiated. -
CBDunkerson at 19:25 PM on 25 September 2010A detailed look at Hansen's 1988 projections
angusmac #117: "The point that I am trying to make and that you, and some others, are ignoring is that the real world is not following Scenario B. This is a case of right emissions in - wrong (too high) temperatures out." Actually, 'scenario B' emissions were slightly higher than actual emissions have been... and the temperature divergence is of such short duration (5 years) as to be meaningless. This should be obvious from the fact that there are divergences that great between the scenario B temperature line and actual temperatures in the years BEFORE the paper was published. -
angusmac at 19:19 PM on 25 September 2010A detailed look at Hansen's 1988 projections
#102 archiesteel. Scenario B is also incorrect – it uses the right emissions but over-predicts current temperatures. #105 Dana, you don't need to explain. I already understand the theory (hypothesis?) of AGW. The point that I am trying to make and that you, and some others, are ignoring is that the real world is not following Scenario B. This is a case of right emissions in - wrong (too high) temperatures out. My Figure 2 clearly shows that Scenario C is tracking the real world temperatures much better than Scenario B. This is a case of wrong emissions in - right answer out What is required is a model that gives real world emissions in - real world temperatures out. I have not seen one yet, probably because this would mean revising radiative forcings and/or temperature sensitivity downwards from currently accepted norms. Your statement that, "There is simply no chance that Scenario C will continue close to reality because it does not reflect real-world emissions or radiative forcings" is extremely brave. I prefer Jim Hansen's stance to wait until 2015 to differentiate between the outcomes of Scenarios B and C. This would enable us to assess whether or not current assumptions are correct. If Scenario C still gives correct predictions then the assumed radiative forcings and/or climate sensitivity would need to be revised downwards. -
CBDunkerson at 19:11 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
PS: I should have also mentioned ice core CO2 records... direct readings of CO2 levels in air bubbles. Which ALSO verified Callendar's results and made Beck's analysis obviously false before he even published it. -
CBDunkerson at 19:09 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Yes, three years ago Beck picked a fight with a dead man... and lost. Apparently this nonsense is coming back up again because Beck died this week. In brief, decades ago Guy Stewart Callendar took atmospheric CO2 readings by various people all over the world (see the list of name at the bottom of Beck's chart) and analyzed them in an effort to determine if there was any trend in CO2 levels. He found that alot of the readings showed a steadily increasing trend line, but there were also alot of outliers... all on the high side and all downwind of major industrial centers. He therefor reasoned that these high readings were being caused by recent emissions that had not yet mixed through the atmosphere and excluded them. Beck, forty years after Callendar's death, called this 'scientific fraud' and insisted that the only proper way to do a scientific study is to include ALL of the data... even that which is clearly erroneous. His results, based on including readings from right outside coal plants (which were, of course, one of the places such readings were taken) yielded the graph above... further skewed by the fact that there were very few readings available for the early part of the chart and almost all of them were from industrial regions. Of course Beck's paper was provably nonsense the day it came out. Multiple stations around the world have long since validated Callendar's results and satellite analysis has also confirmed it in recent years. There is no greater proof of the deficiency of the 'skeptic' position than their insistence on holding fast to pure fiction. -
Rob Painting at 18:12 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Cruzn @ 39 - is that by that German school teacher?. -
The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Yet again I have to post a reply that clarifies what I said! I find this very tiresome. I think that WUWT is a very good website, not scientific like this one, or Tamino's, or Climate Audit. As you see if you look there now (as I just have) WUWT run non-climate pieces very often like the present Google-Earth meteor crater, and solar storms. If you read back you'll see that I was berated for going there! I find this behaviour very odd, to say the very least. I certainly wasn't rude (I never am) and there's a huge case of kettle/pot there! On the subject of Open mInd, no the 'typo' wasn't fixed while I was there, but I never went back to find out. I couldn't even hope to find it now. Archie, you've achieved what you wanted. I'm leaving this forum as I cannot devote my precious time to construct meaningless posts like this that serve no purpose in AGW debate. As an ad hominem is just not me, I'm going to leave it there for you to think over. Thanks to everyone for being patient and clarifying points. If we don't get the peak in temp that the UK Met Office is predicting in 2014, or if we get falling OHC, then I'll pop back to get your opinions based on that. However, if temps rise, and OHC goes up, then you won't need me back here. I hope, not for personal reasons, that I'm right and you're wrong. Thanks to 'the moderator' for allowing me my posts. Cheers. -
cruzn246 at 17:14 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Anyone seen this?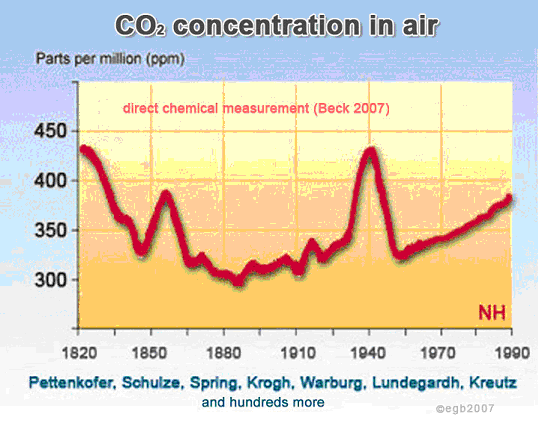
-
RSVP at 17:07 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
MattJ #1 "I do not agree with Dyson, and am I mystified and disappointed that he objects." As per your comment, his interview on YouTube may help. To see, just google his name, etc. I dont think he is saying global warming is not real as much that stratospheric cooling might be a bigger problem. Similarly, while he plays down the imperative to reduce fossil fuels (towards the end of the video), in his book, Disturbing the Universe, he pretty much writes that humanity missed its opportunity in the sixties to go nuclear due to unwarranted alarmism, such that he was more optimistic about the ability to build safer reactors. -
cruzn246 at 16:28 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Well Dunkerson, you think it is all us? I mean think about it. How can they claim that a change in temperature is completely or even mostly the responsibility of man when we are not even at the point when we truly know what makes our temperatures change and how much they change anyway. We have never been around at this point in a glacial period, so who are we to know what happens when it gets to this point? -
Phila at 16:17 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
#8 RSVP What I get out of this article. The IPCC is an impartial bureaucracy with a name that implies climate is changing. Sounds like what you get out of it is what you bring to it. -
Daniel Bailey at 15:09 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
Re: RSVP (8) Perhaps you should read more than just the title then. Or if you'd like a different place to start to learn about our changing of our climate, ask. "Fill your mind with the coppers of your pockets and your mind will fill your pockets with gold." The Yooper -
The Big Picture (2010 version)
Tariscio - I would love to read your comments, but find your translations difficult to follow. I would suggest including both your native language (Spanish?) in appropriate detail, and using Google translate to produce an additional English version. Many of us can read or at least puzzle out other languages. -
RSVP at 15:04 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
What I get out of this article. The IPCC is an impartial bureaucracy with a name that implies climate is changing. -
kdkd at 14:54 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
gallopingcamel #5 Presumably this is because that quote can be used in an ironic / self deprecating sense, or it can be used in an attempt to reject the entire field of statistics. This latter usage is destructive solipsistic nonsense. As someone who is reasonably experienced at using statistics, I can assure you that used appropriately statistics can be highly informative. Understanding how to do so is a fairly arduous task, and I have particularly enjoyed teaching undergraduate science some of the core skills for the appropriate use of statistics. -
Daniel Bailey at 14:53 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
Re: gallopingcamel (5)"On a couple of occasions when the subject has been Tamino and his ilk you have deleted my use of the quote attributed by Mark Twain to Benjamin Disraeli: "There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies and statistics." "
GC, your usage of "ilk" in conjunction with your quote should be in violation of the comment policy, as it is tantamount to an accusation of deception and/or dishonesty. The fact that you openly admit to doing this previously and having it deleted each time is troubling enough. It is hard enough to maintain one's own decorum & be a positive factor on this blog without comments like yours inviting a likewise response. I've already "really not helped" once tonight. And you're not helping me now. The Yooper -
Daniel Bailey at 14:25 PM on 25 September 2010How you can support Skeptical Science
Re: John Cook"So I'm just laying the offer on the table for anyone interested in proofreading any skeptic arguments to contact me."
I have experience in proofreading and quality control. If you still have a need of this service, let me know. The Yooper -
gallopingcamel at 14:15 PM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
John, On a couple of occasions when the subject has been Tamino and his ilk you have deleted my use of the quote attributed by Mark Twain to Benjamin Disraeli: "There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies and statistics." Now you are paraphrasing the quote to head this post but I do not object. You hit the right target! -
kdkd at 14:01 PM on 25 September 2010Urban Heat Islands: serious problem or holiday destination for skeptics?
Ned #58 Thanks for this. Any chance you can post the csv file of the raw data that you used up to a site like this one so that I can take the regression diagnostics a bit further. It looks like with a correlation coefficient of 0.23 uncorrected for autocorrelation while statistically significant, is of very little practical significance. BP's mistake has been to assume that his estimate of the slope is not an estimate but is the true value of the slope, and so therefore has not accounted for uncertainty in his estimate. This appears to be an excellent example of confirmation bias in action. -
Roger D at 12:30 PM on 25 September 2010Climate scientists respond to Monckton's misinformation
Thank you Rob re: @38. - that makes sense. Also - Thanks John C for the website -
Daniel Bailey at 12:15 PM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Re: Tarcisio José D'Avila (32,34) and Tom Dayton (33) If I understand Tarcisio José D'Avila correctly, he is postulating the existence of a broken "climate thermostat". Broken, because it is not correcting for the actions of man's fossil fuel CO2 emissions. An iteration of the Gaia hypothesis, I believe. He believes the science of anthropogenic warming is right, but that it only is warming because the thermostat itself is broken. Or something like that. If I've misunderstood, I apologize. The Yooper -
barry1487 at 12:13 PM on 25 September 2010There is no consensus
Well that awful Inhofe 400 is now over 420 as in the time it took for you to complain about the one that didn't sign 20 more "scientists" did
I'm 2 years late to the party, but for the record... Nobody signed Inhofe's list. It was created by garnering selected quotes and adding the person saying/writing them. A good number of the people on it actually endorse the IPCC general conclusions, and some have even written to ask to be taken off. Inhofe's 400+ is not a petition or a declaration, just a concoction of names and highly elided quotes. -
Roger A. Wehage at 11:44 AM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
You use IPCC without defining it. That is rude. It forces readers unfamiliar with the subject to go elsewhere for a definition. Always define an acronym when first introduced. -
kdkd at 11:37 AM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
"it is prudent to observe that the IPCC does no science or research at all" Nope this is incorrect. Collating the work of others, and subjecting it to analysis is an important part of the research process. Perhaps Graham means that "it is prudent to observe that the IPCC does no primary scientific research"? -
archiesteel at 11:34 AM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
@miekol: I don't get it. Aren't panel and committee synonyms? -
miekol at 11:30 AM on 25 September 2010The Phony War: Lies, Damn Lies and the IPCC
" it is prudent to observe that the IPCC does no science or research at all" Precisely, its a politcal committee, enough said. Except it should be called the ICCC. They couldn't even present their name right. Intergovernment Committeee for Climate Change -
johnd at 10:24 AM on 25 September 2010Does Climate Change Really Matter?
doug_bostrom at 10:04 AM, re "or something like that" Beautiful. That drives direct to the quintessence of the dilemma as it stands. -
Doug Bostrom at 10:04 AM on 25 September 2010Does Climate Change Really Matter?
Shorter johnd: More convection will manifest itself invisibly. Or something like that. -
johnd at 09:52 AM on 25 September 2010Does Climate Change Really Matter?
ianw01 at 23:42 PM, all weather events, extreme or otherwise, are driven by the same combination of a heat differentials and moisture, and they all unfold the same way. As the water vapour picked up rises, it gradually releases heat, condensing out forming different cloud types in sequence until finally the air becomes dry above where cirrus clouds are the last to form. The albedo effect dominates the low altitude clouds, so they then provide a nett cooling effect to the Earth's climate. However uncertainty remains about the high level cirrus clouds, which alone cover about 35% of the earths surface, but as this passage from a CLOUDSAT overview would indicate, linking extreme weather events with climate change is treading on uncertain ground as you noted. (http://cloudsat.atmos.colostate.edu/overview) "Because clouds have such a large impact on Earth’s radiation budget, even small changes in cloud abundance or distribution could alter the climate more than the anticipated changes in greenhouse gases, anthropogenic aerosols, or other factors associated with global change. Changes in climate that are caused by clouds may in turn give rise to changes in clouds due to climate: a cloud-climate feedback. These feedbacks may be positive (reinforcing the changes) or negative (tending to reduce the net change), depending on the processes involved. These considerations lead scientists to believe that the main uncertainties in climate model simulations are due to the difficulties in adequately representing clouds and their radiative properties." -
Tarcisio José D at 09:13 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Tom #33 I go wrait with may poor english escuseme... If the thermostat of the climate is brook or is out of range, the global warm has great potential of be antropogenic. And in this case the science is rigth. Only the target of resershing is bad. It's look to the fingeprint only. -
Tom Dayton at 08:20 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Tarcisio, please rephrase your comment. I don't understand your point. -
Tarcisio José D at 07:50 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Retification... Do you ever wonder, "Is the thermostat of nature" is not stuck? If it is stalled antropogenic actions has great potential to be the cause of all this damage. I do not believe that acts falcification of data. -
PeteM at 07:27 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
(I don't claim to be a specialist in this area but I do have a science degree ) When talking with friends and colleagues who don't have a science background I tend to use the following way of describing what a few degrees centigrade rise really means ... "The numbers one ,two , three and four don't sound much. Two centimeters seems a small number . However to understand a two degrees (c) rise in temperature think what you would say if I suggested you lift (by yourself) Mount Everest by two centimeters - it's only a small number so it should be easy . Now think about how much disruption must have occured to make a one degree centigrate rise to the temperature of the Earth .... and then project what the consequences could be of a two or three degree rise - a small number can mask gigantic changes.... This is the impact of fossil fuels on the green house effect " -
Stephen Baines at 07:21 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Dana, I think this is a great post. I'm forwarding it to my relatively climate naive sister so she has a good entry point to the amazing resources on this web site. One thing regarding falsification. (This particular line of argument from deniers drives me completely batty!) I would argue that it's more correct to say that ober 50 years AGW has been repeatedly subject to intense attempts at falsification by skeptical scientist and it has passed those tests repeatedly, so that now it would take a truly astonishing series of events/findings to shake the hard won belief in it that most now scientists have. The way it's put now is strictly true, but it sounds a little condescending for those not very aware of those physical principles you speak of (I presume this level of explanation is targeted at such people). It reads a bit like "us smart people thought this up using theories that you can't possibly understand, so don't question it." That plays perfectly into the whole anti-elitism meme that lurks beneathe this debate. It also somewhat undersells the great body of observational data that does not rely on those physical principles. Perhaps some way for people to understand how they depend on those physical principles in their every day lives would help bring it home too. -
archiesteel at 06:30 AM on 25 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
@Baz: what was the error? A typo? Did Tamino correct it? You're attacking the reputation of a well-respected scientist, and an expert in his field; the least you could do is provide evidence. Why don't you show others the same courtesy you expect for yourself? Earlier you were quite rude and ill-mannered by basically saying we were close-minded for criticizing WUWT's status as a scientifically legitimate web site. I have yet to hear you apologize for such a broad accusation... So, please, substantiate your allegations. What was the error, and did Tamino fix it? Thanks. -
Rob Honeycutt at 06:29 AM on 25 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Baz... Actually, archie is right. Both those guys will quickly delete comments with very basic level errors from either side of the fence. I've had comments deleted as well. I totally understand why they do. When people post basic erroneous material it leads to a long engagement that takes everyone off topic. Here at SkS you usually only get a warning and are redirected to the proper discussion thread. -
Daniel Bailey at 06:22 AM on 25 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Re: Baz (342)"Tamino did the same to me a year ago when I pointed out that he had made an error."
Couple of points to make here:1. Tamino is a professional time-series data analyst; he checks his work microscopically for errors before posting. The errors I've seen have been typo's only, and are acknowledged cordially when pointed out. About his data analysis skills...the man has probably forgotten more about statistical analysis than any 3 posters on Skeptical Science know. 2. How the message is constructed is often more important than the message itself. It's not what you say, but how you say it that is paramount. Diplomacy & tact may get you room for debate...
Hope that helps. Baz (345)"Daniel, what's your opinion on the theory of a falling PDO that may cause considerable Arctic recovery, and then later (with a falling AMO) the possibility of it being brought back to 'normal'? "
Not an area of expertise for me, but since you asked for an opinion: no evidence exists for either the PDO and/or AMO having any meaningful effect that possibly explains the warming seen to date (the warming introduced by the hand of man has now reached the point of perturbation of the system that natural cycles have been over-ridden). As such, they are immaterial. The summer of 2007 initiated such a catastrophic loss of multiyear ice (through ice advection) that a long term "recovery" of the ice became a fait accompli. That's when the "death spiral" began. The ice now remaining is on life support; the only question remaining is how little time left it has. The Yooper -
The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Archie. Usual stuff then! Thanks for your always-delightful comment. I did spot an error, and thought I was being kind by pointing it out. It wasn't on a scientific point, but a numerical one. -
The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Daniel, what's your opinion on the theory of a falling PDO that may cause considerable Arctic recovery, and then later (with a falling AMO) the possibility of it being brought back to 'normal'?Moderator Response: I betcha there is a more appropriate thread (maybe more than one!) for that question. Follow Ned's example. -
Daniel Bailey at 05:57 AM on 25 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Re: Baz (342) On this post by Neven, he lists the July Century Melts (individual days of 100,000+ km2 ice area lost):Century breaks in July: * 2005: 10 * 2006: 3 * 2007: 11 * 2008: 4 * 2009: 11 * 2010: 2
Note the alternating pattern of melts. If we get a decent Arctic Dipole formation in 2011, most of the remaining multi-year ice will be advected out the Fram. Basically, if we don't see some open water at the pole in 2011, we will in 2012. Maslowski's prediction, 2016 +-3 years, was based on older data (he said it was conservative). Note the quadratic line Tamino fit to the existing pattern of melt (and he was nearly dead-on for this year's melt). At some point, the summer insolation/Arctic Ocean albedo will will pass a critical threshold/tipping point and the majority of it will be lost in a summer... This doesn't mean NO summer ice; just that so much volume has been lost that the majority of what's left will be seasonal (winter ice) from that point forward. Some ice should linger just north of the Canadian Archipelago and Greenland for a few more years. By 2013 we'll have a better idea of when even winter ice will cease to exist... The Yooper -
archiesteel at 05:54 AM on 25 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
@Baz: I've had comments deleted at WUWT as well, what's your point? The science presented on Climateprogress and Tamino's is sound, contrary to the usual driverl at WUWT... (Exception made of the rare times where Anthony invites an actual scientist, who is then universally panned in the comments...) As for Tamino's, it's likely you didn't in fact spot an error (considering your unrepentant admissions of confirmation bias, non-rationality and basic misunderstanding of statistics. If Tamino removed your post, then he probably had a good reason to do so. Instead of whining, you should take the opportunity to learn where you got the science wrong and correct your position accordingly. -
The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Thanks Daniel. I'm afraid Joe Romm is running exactly as they say he does (at WUWT). First comment allowed, second never even made a show - just wiped straight off. Tried a third - same result. Censoring does nothing for debating the issues! Tamino did the same to me a year ago when I pointed out that he had made an error. Thanks anyway. -
Doug Bostrom at 04:40 AM on 25 September 2010Video update on Arctic sea ice in 2010
Extent appears to have declined near to the bottom of the early melt season ARCUS invited predictions.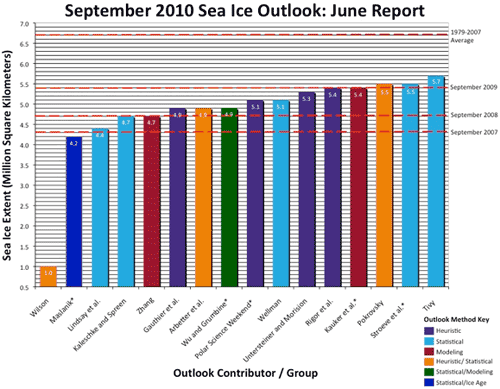
-
Philippe Chantreau at 03:21 AM on 25 September 2010Video update on Arctic sea ice in 2010
Cryosphere today is showing even more evidence of how warming has stopped and how sea ice is doing a spectacular recovery: Arctic sea ice area appears to have bottomed very close to 3 million sq. km, on par with 2008, pretty close to the all time low of 2007 and significantly lower than last year. Lowest sea ice anomaly so far this year was reached in June, when a strong Arctic dipole led to the fastest melt ever recorded at that period, a similar rate to that of August in the all time low 2007. That month in 2007 also had a strong dipole situation. This year's lowest anomaly may not have been reached yet, depending how fast the ice is going to form. Meanwhile, something funny is happening to Antarctic sea ice. After a strong positive anomaly early in the season, it is now showing over 700k sq. km below baseline, a rather unusual occurrence at the time when it should peak. If the data are correct, that brings the global sea ice around 2.5 million sq. km below the 1979-2008 average, close to 2007, on par with 2008, much lower than 2009. Some recovery. -
dana1981 at 02:37 AM on 25 September 2010A detailed look at Hansen's 1988 projections
angusmac, I'll try one more time to explain to you. The temperature change is based primarily on 2 factors, radiative forcing (which depends heavily on emissions scenarios) and climate sensitivity (which is a product of the climate model). Regarding the first factor, Scenario B has been quite close to reality. There is no point in comparing to Scenario C, which has not. It doesn't matter if the temps follow closer to C, because the real-world emissions do not. Since the real-world emissions and forcing have been close to B, we can then examine the second factor - climate sensitivity. As I showed in the article, we can then determine that the real-world sensitivity has been around 3.4°C for 2xCO2. Notice my use of the term "real-world". You're obsesing with Scenario C, which is a hypothetical world which does not match the real world. Both of the factors mentioned above are incorrect in Scenario C. One is too high and one is too low. The problem is that in Scenario C, the forcing flattens out, whereas that will not happen in reality. There is simply no chance that Scenario C will continue close to reality because it does not reflect real-world emissions or radiative forcings. -
dana1981 at 02:21 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
cruzn246 #7 - I suggest you actually click the links and learn something. There's a pretty darn big difference between scientific evidence and "pure speculation." bverheggen #9 - valid point, I may add a bit on aerosols. I wrote a rebuttal on the subject recently which I didn't link in this article. Dan Olner #11 - there's a difference between what it would take for AGW to be wrong (our understanding of physics would have to be wrong) and what it would take to disprove AGW. To disprove the theory, just demonstrate that the planet is not warming or climate is not changing as it predicts. I recommend you click the 'fingerprints' link in the article to see what I mean. Ken Lambert #24 - perhaps you're unfamiliar with Skeptical Science. The purpose of the site is to debunk false skeptic arguments with scientific evidence. paulm #25 - I'll consider rewording the conclusion a bit. -
Urban Heat Islands: serious problem or holiday destination for skeptics?
As a postscript, I'm happy to discuss this all further, but I'll be leaving town shortly for the weekend and may not be revisiting the site much if at all before Monday. -
Doug Bostrom at 02:06 AM on 25 September 2010The Big Picture (2010 version)
Following from PaulM's comment, this is a useful article: The Psychology of Global Warming (AMS, full text pdf) Leaving aside that little group tagged by Leiserowitz as the "dismissive," if we take heed of what we've learned of how people think, our communications actually can be made more effective, more robust in the face of industrial PR. -
A detailed look at Hansen's 1988 projections
RE: comments from myself, kdkd, and BP above: It's off-topic for this thread, but I've just posted a lengthy "reanalysis and commentary" over in the appropriate thread (Urban Heat Islands: serious problem or holiday destination for skeptics?). -
Urban Heat Islands: serious problem or holiday destination for skeptics?
Since BP's analysis on the first page of this thread has become the subject of discussion elsewhere, I thought I'd revisit it briefly. Recall that BP picked 270 GHCN stations, calculated their temperature trend over the decade 1990-2000, and then calculated their change in population density over the same period from GPWv3. He then created a model relating temperature trend to the number of doublings of population density. His claim was that the Y-intercept of this model showed that a hypothetical station located at a site with no change in population density would have a trend of +1.5C/century over that decade. For context, note that a bunch of different reconstructions using land stations only show an actual trend of +2.25C/century over the same time period. Thus, BP's results, if you grant all the various assumptions underlying his analysis and assume that his hand-picked stations were representative of all land stations, would suggest that UHI explained about 1/3 of the observed temperature increase over land and about 10-12% of the global increase. Commenter kdkd and others have questioned the statistical significance of that model. Since BP hasn't been able to explain that, I've tried to sort-of replicate it. Of course, without knowing what stations he used it's not possible to replicate his analysis exactly, and for a number of reasons (to be explained below) I don't think it's worth going through all the work of fully replicating it even if we did know what stations he used. Instead, I took the short-cut of just digitizing the points on the graph from his comment, and re-doing the regression analysis. Unfortunately, the graphic is noisy and it's not possible to identify all 270 points. I got 204 of them, but for the rest I'm just not confident in my ability to correctly identify them in the noise. Using those 204 points gives a model with an r2 of 0.075, meaning it explains very little of the variance within the data. (This is not surprising given the spread among the points in the graph). The estimate for the intercept is 1.4C/century, just a hair below BP's calculation of 1.5. The 95% confidence interval around this estimate is approximately 0C/century to 3.0C/century. In other words, UHI could explain all the observed warming over land, or at the opposite extreme it could be artificially cooling the data, actually reducing the land surface trend from its "true" value of 3.0C/century to the observed 2.25C/century. Of course, neither of those extremes seems likely. Given that the land is presumably warming faster than the ocean (heat capacity), UHI can't realistically explain most or all of the observed warming over land. Likewise, I don't think anyone seriously suggests that overall, globally, UHI would be negative. So my admittedly crude attempt to replicate BP's analysis suggests that his model is not very informative, since it fails to exclude what are almost certainly unrealistic values at both the high and low extremes. That's OK, it's still interesting (though probably not publishable....) As I've mentioned earlier in this thread and elsewhere, there are serious concerns/problems with BP's analysis that probably make it non-worthwhile to pursue it much further. First, the quality of the locational information in the GHCN metadata is known to be poor, and the spatial resolution of the GPW population density data is clearly insufficient to provide estimates of local population density at individual stations. Second, one decade is a very short time to be looking at trends in both temperature and population density. Third, we don't have any reason to believe that BP's hand-picked 270 stations are representative of the overall land surface, and in fact there are good indications that they are not (according to BP's original comment their mean trend differs substantially from the observed land surface trend based on various reconstructions). This is not to suggest that BP deliberately picked unrepresentative stations -- it's just difficult to get a representative sample without using somewhat sophisticated methods. It's worth noting that there's no a priori reason to expect that the real world would actually conform to this model, particularly when extrapolated to low population densities. On the contrary, it seems physically improbable. It's also worth noting that we have reliable and well-validated satellite measurements of sea surface temperature trends which show clear warming during this period. Given that there are good physical reasons to expect warming over the ocean to lag warming over land, the global SST trend would seem to limit how much land warming could be explained by UHI (if your claims for UHI would bring the land trend below the ocean trend, you've probably made a mistake somewhere). If you dealt with the first three objections, and found that the resulting model actually explained a large proportion of the variance in the observed data, it would definitely be worth pursuing this. What we have right now, though, is an analysis that is crippled by those three objections and only yields an r2 of around 0.075, and fails to rule out more or less impossible answers at both extremes. Bottom line, BP's analysis doesn't really do anything to support the claim that UHI explains as much as 10% to 12% of the observed global temperature increase. The true value is probably in the low single digits. Apologies for the length of this comment.
Prev 2197 2198 2199 2200 2201 2202 2203 2204 2205 2206 2207 2208 2209 2210 2211 2212 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























