Recent Comments
Prev 2219 2220 2221 2222 2223 2224 2225 2226 2227 2228 2229 2230 2231 2232 2233 2234 Next
Comments 111301 to 111350:
-
archiesteel at 06:10 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
@Baz: "The term "acidification" is bizarre." It's not, really. The oceans' pH has lowered at unnaturaly high rates, hence they are "acidifying" according to a very well-understood metric. "I never claimed to be rational!" Well, science is a rational enterprise. You don't have to be rational all the time (I know I'm not), but when discussing something so important developing a rational argument is paramount. "Five MORE years has done nothing to change that, but hey, if warming picks up again significantly then I'll change sides." Warming has picked up significantly since 2006, and even more so since 2008 (if you like looking at short time spans). "I think the trouble (from looking out of my tent) is that too many of you 'think' you know what will happen to the temperature in 20-30 years time. You do not!" As Paul Daniel said above, no one does know, however we can map out some degree of probability. If there is even a one in ten chance of a catastrophic outcome (I believe it's much more than than), then it makes sense to try and mitigate it, especially since the best way to mitigate it is to transition away from fossil fuels, something we should be already doing for *other* reasons. -
johnd at 06:04 AM on 14 September 2010Climate change: Water vapor makes for a wet argument
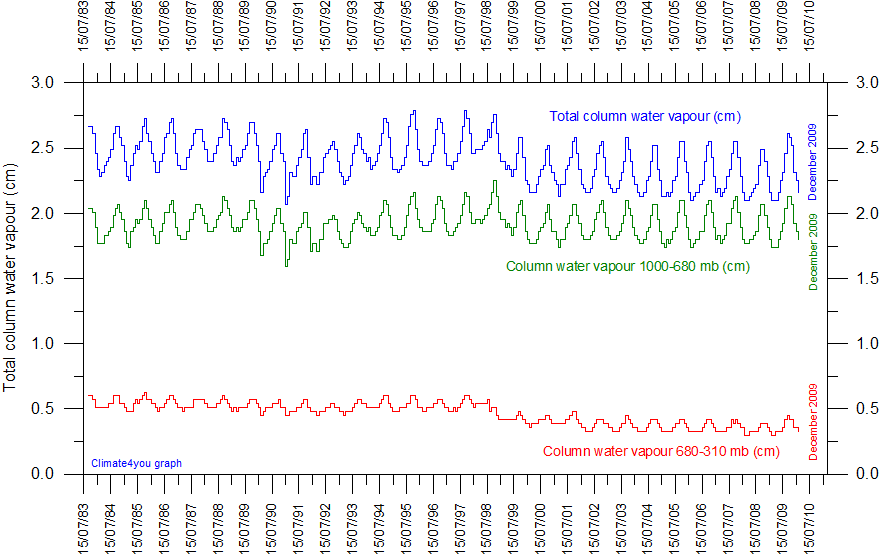
scaddenp at 07:52 AM and KR at 23:09 PM. With regards to the question "how fast would temperatures have dropped if there was NOT back radiation", that really is not what we are seeking to understand. What I would like to understand is why with soil temperatures radiating warmth from below, and air temperatures measured at about 1.2m above ground level supposedly providing back radiation, why then do the minimum temperatures AT ground level fall so low. We know that normally temperatures quickly fall as distance from the surface increases, but as these terrestrial minimum temperatures indicate, whatever warmth contained in the air just 1.2 m above the ground is not enough to stop even more warmth being lost at ground level. Whilst focusing on this difference of minimum temperatures over a short 1.2m distance, we should also consider what differences we would find between the maximum temperatures recorded by a thermometer in the shaded enclosure and an exposed thermometer at ground level, especially when considering just what factor direct solar radiation has on evaporation as against back radiation. Whilst stations such as Alice Springs may measure back radiation, the network of stations that BOM use from across all of Australia to collect data for agricultural use are exactly the appropriate ones to use in a thread regarding water vapour, in that determining the conditions that drive evaporation is perhaps the most important part of understanding why the water vapour in the atmosphere varies as it does. What is there to tell us that conditions in the atmosphere drive the evaporation instead of evaporation driving conditions in the atmosphere? It is of little use to measure back radiation unless this can then be measured in how it manifests itself as heat arriving and being absorbed at the surface, and whilst the BOM data only gives the nett result without breaking it down as to individual inputs that determine the nett result, those nett results expose an situation that is inconsistent with what input back radiation is supposed to have. With regards to clouds, firstly I don't think the climate has ever been stable, a quick look at any cycle over any time frame indicates short term cycles within longer term cycles within even longer cycles. However I have seen some information from NASA that concludes that overall, clouds have a nett cooling effect, rather than a warming effect on the earth. -
Albatross at 06:00 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
radar30331, Google "global warming has halted". -
Paul Daniel Ash at 05:48 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
No, I can't give you an "internally-consistent thesis" because I don't know... too many of you 'think' you know what will happen to the temperature in 20-30 years time. I don't know of anyone who seriously thinks they know the future. Most everyone has some expectation of what they think it may be. You say right in that same comment that "I was a 'warmist' in 1999, and thought that the warming would continue... By 2005 I figured that I may have my theory about warming wrong... if warming picks up again significantly then I'll change sides." So you have your own theories about what will happen. The only difference is that climate scientists' are systematic and evidence-based, and yours seem to be WAGs rooted in a rather selective reading of the available data. It's an OK place to start, but for someone who claims that you're "not here to argue, but to learn," you're doing an awful lot of argument by assertion. -
michael sweet at 05:45 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
Humanity Rules: Here is the temperature map for J-F-M from the NCDC:While Siberia has large cold areas, the USA is not that cold. Canada is hot and evens out Siberia. The majority of the world is hot or warm. The temperature anomaly was 0.66C, the fourth highest on record. Fourth highest out of 130. For me that is a hot period. It just happened that the cool areas were the USA and Europe. By contrast, this summer has been RECORD heat in many areas.
-
A detailed look at climate sensitivity
Berényi - In regards to water vapor feedback, you should look at Dessler and Sherwood (2009) (as referred by Chris Colose), where they discuss gridded averaging of complex behavior, and how it appears to work just fine in modeling. At it's core, they state that "The large-scale wind and temperature fields that mainly control the humidity are explicitly calculated from the basic fluid equations, unlike small-scale processes that must be represented by crude parameterizations.", as the water vapor involved in the feedback is primarily in the upper tropical troposphere, above the majority of clouds. -
ClimateWatcher at 05:38 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
"Finally, ClimateWatcher is simply wrong on almost everything he said. I'd urge him to review the Dessler and Sherwood (2009) paper, or the observations of upper air moistening (e.g., see some of Brian Soden's work)." --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- I have read Dessler and Sherwood. Was there a particular passage that you found relevant? I am taken by the upper air decrease in both absolute humidity: and relative humidity:
and relative humidity:
 as outlined by Paltridge, Arking, and Pook:
http://www.springerlink.com/content/m2054qq6126802g8/fulltext.pdf
Particularly in the tropics, the region that Dessler and Sherwood assess to control water vapor feedback.
This appears to be consistent with the ICCSP data as well:
as outlined by Paltridge, Arking, and Pook:
http://www.springerlink.com/content/m2054qq6126802g8/fulltext.pdf
Particularly in the tropics, the region that Dessler and Sherwood assess to control water vapor feedback.
This appears to be consistent with the ICCSP data as well:
-
Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
Gah - the link I put in my last post for the Comments Policy was poorly formed; my apologies. -
Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
ClimateWatcher - minor point for readability, you should look at the Comments Policy for the instructions on posting large images, under "IMPORTANT: The image must be no wider than 450 pixels". The extremely large images you posted tend to break the site layout. Moderator - can these be reframed with the appropriate HTML to bring their size back down? -
Chris Colose at 05:10 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
Thanks, this is a nice addition to the internet posts on feedbacks I would urge readers to be cautioned of a few subtleties in the post by neal which was not made explicit, and could lead to some confusion for first-time readers. For one thing, he was not explicitly talking about the radiative-based feedbacks (e.g., water vapor increase, albedo change in a warmer world) but rather carbon-cycle feedbacks (such as more CO2 ==> warming ==> more CO2) which involves complex interplay between the bio geochemistry of the ocean-land system. The notion of a converging series that can stabilize the system is valid in either case, but the carbon-based feedbacks are not that well understood and usually they become irrelevant if you choose to define a sensitivity metric in terms of a doubling of CO2 (as is commonly done). When we're talking about whether feedbacks are "positive" or "negative" in the context of global warming, we are *usually* talking about the radiative balance of the planet being further modified by the temperature change caused by some forcing (the most relevant forcing being CO2 in the modern day). This is also semantical to some extent, because the most dominant stabilizer of planetary temperature change is the Planck blackbody radiation law, which simply means hot stuff emits more radiation. This is not classically called a 'feedback' however, and so the notion that feedbacks are "positive" is a bit artificial given the lingo in the field. Rather, positive feedbacks should be thought of as modifying the Planck response, essentially smoothing out a plot of the outgoing longwave radiation vs temperature. I have been recently collaborating with Rasmus at RealClimate to put up a post about feedbacks, which hopefully will provide some clarity into this topic, including the runaway greenhouse. I'm hoping that can be available soon. The answer to the question about the runaway greenhouse effect is that CO2 is not a big part in that process. I'm not entirely sure Hansen understood this, but I've also not followed his public statements closely to know what caveats he might have made or what distortions other people may have spun on it. In fact, the runaway greenhouse process occurs when the solar radiation exceeds something known as the Simpson-Kombayashi-Ingersoll limit, and the runaway threshold is almost exclusively determined by the absorbed incoming solar radiation and a planet's gravity. The SKI limit is basically a 'maximum outgoing longwave radiation' threshold that occurs when water vapor can become a dominant constituent in the atmosphere (on Earth or Venus, it doesn't need to be water vapor though in general). Finally, ClimateWatcher is simply wrong on almost everything he said. I'd urge him to review the Dessler and Sherwood (2009) paper, or the observations of upper air moistening (e.g., see some of Brian Soden's work). -
Josie at 05:02 AM on 14 September 2010Positive feedback means runaway warming
In fairness, this is not just something that skeptics fail to understand, many environmentalists don't get it either. The media (in the UK anyway) really got addicted to talking about 'runaway climate change'. I am not sure where it came from because I've hardly ever seen the term used in the science. I am aware that a lot of climate scientists are very uncomfortable about the use of this phrase. But there are different ideas bound up in it- if there is a low probability of carbon cycle feedbacks doing something extreme and becoming very nasty even if not becoming self-perpetuating, then is that 'runaway'? How much does something have to run away before it is 'runaway'? -
jyyh at 04:48 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
though chlorophyll using organisms have been found quite high in the atmosphere (in storm whipped marine clouds), no one has proven they could live and proliferate there in the extreme heat, discussed in this thread, thus eventually decreasing the IR absorbance. in any case the temperature on the current ocean sea level would have to be higher than 100 since there are many mountainous areas which could become hot pools of photosynthetic bacteria. But, unlivable (meaning in case too hot) conditions for humans are quite possible in the tropics by human means AFAIK. -
ClimateWatcher at 04:46 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
"ClimateWatcher, CO2 has increased from ~280 ppm to 390 ppm... about 40% of one 'doubling'. Temperatures have increased just over 0.8 C... about 73% of 1.1 C. Do you still think 1.1 C total warming for a doubling of CO2 is the most likely outcome?" ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Somewhere around that. The century trends since the MSU era began look like: RSS MT 0.9K/century UAH MT 0.5K/century RSS LT 1.6K/century UAH LT 1.3K/century CRU 1.6K/century GISS 1.6K/century CRU SST 1.3K/century That yields a mean of 1.3K/century. Fairly consistent. Your look at long term variations is a worthy notion, but do recall: 1. There is not a good yearly, or even decadal correlation of GHG forcings and temperature trends. 2. Gasses other than CO2 (CH4, NO2, CFCs) accounted for a large but now declining portion of GHG forcing during the 70s and 80s:
 3. In fact, from 1910 through 1945, the CRU
land/ocean index rose at a rate (1.7K/century) that
is greater than the current rate (1.6K/century), even though GHGs were increasing at a rate of about one third of the recent rate.
If one assumes that recent warming is due to GHGs,
then something else must have contributed to
the 1910-1945 warming to keep the scaling consistent.
This period is certainly consistent with an increase in insolation:
3. In fact, from 1910 through 1945, the CRU
land/ocean index rose at a rate (1.7K/century) that
is greater than the current rate (1.6K/century), even though GHGs were increasing at a rate of about one third of the recent rate.
If one assumes that recent warming is due to GHGs,
then something else must have contributed to
the 1910-1945 warming to keep the scaling consistent.
This period is certainly consistent with an increase in insolation:
 So too, of course, is a period of centuries long
high temperatures commencing in the latter half of the twentieth century.
From the CRU data set, the recent warming is not
at a record rate, though it has taken us to higher
absolute temperature levels.
By the way, the IPCC says the
"Best estimate for a 'low scenario' is 1.8 °C"
They describe the 'low scenario' as the 'most optimistic'.
When was the last time you heard the warming is
taking place at a rate better than the 'most optimistic'?
So too, of course, is a period of centuries long
high temperatures commencing in the latter half of the twentieth century.
From the CRU data set, the recent warming is not
at a record rate, though it has taken us to higher
absolute temperature levels.
By the way, the IPCC says the
"Best estimate for a 'low scenario' is 1.8 °C"
They describe the 'low scenario' as the 'most optimistic'.
When was the last time you heard the warming is
taking place at a rate better than the 'most optimistic'?
-
The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
actually thoughtfull, I didn't "ignore" those metrics, but when all is said and done it is the thermometer we must look to. As for ocean "acidification", sorry but I hate that term. If I add a tiny, tiny piece of sugar to a glass of sea water, I haven't "sweetened" it, I've made it a tiny, tiny bit less bitter. The term "acidification" is bizarre. No, I can't give you an "internally-consistent thesis" because I don't know. That's what makes me different from a lot of you, and from a lot of sceptics. I don't profess to know whether we'll suffer from positive feedbacks, or whether the climate system will 'equate'. I think the trouble (from looking out of my tent) is that too many of you 'think' you know what will happen to the temperature in 20-30 years time. You do not! VeryTallGuy. No, in a word, I'm not here to argue, but to learn. Sorry, but I don't get as much time as some of you obviously do. Family and work commitments are too much. Albatross, I didn't gravitate towards HadCRUt, I'm English, so it's natural for me to use a UK organisation. However, that said, I don't think GISS is valid as it uses Arctic data where no recording stations exist, relying on proxies from 1,000 miles away. That ain't good science! When I actually asked Phil Jones which I should rely on (yes, I did) he said HadCRUt - well, he would, wouldn't he? JMurphy: Re, HadCRUt, last 10 years: 0.40 0.46 0.47 0.44 0.48 0.42 0.40 0.32 0.44 0.49? (2010) Archiesteel - I never claimed to be rational! Ann, 5 years. I was a 'warmist' in 1999, and thought that the warming would continue. Admittedly, I have to confess I didn't know about El Ninos then(!). By 2005 I figured that I may have my theory about warming wrong. Five MORE years has done nothing to change that, but hey, if warming picks up again significantly then I'll change sides. No one has ever accused me of not being flakey! But it's interesting to note that a few scientists have come out with cooling predictions for 20-30 years based on PDO/AMO. So all, I think we can safely say 15-20 years then, yes? -
radar30331 at 04:20 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
SS regulars, Seems like you're being a bit pedantic here. Somebody at R/C, was it Rasmus? titled this plateau "a pause". Pielke Sr. says 'has halted since 2004' or to that effect. Only time will tell whether the R/C line - that it is a "pause" is correct or not. However Pielke is right no matter what, that in 2008 (or 2009 or 2010) "This means that global warming halted on this time period." This shouldn't be controversial, he is not saying AGW is finished. The POV / idea that it's only a pause will be proven right or wrong. Pielke is accurate, even if you don't care for his wording or lack of caveats. Considering the ocean temp lags the energy imbalance, it's fascinating that it has leveled off even temporarily at a time when warming is supposed to be accelerating. (Yes, noisy signal & sensor limitations understood). -
CBDunkerson at 03:41 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
ClimateWatcher, CO2 has increased from ~280 ppm to 390 ppm... about 40% of one 'doubling'. Temperatures have increased just over 0.8 C... about 73% of 1.1 C. Do you still think 1.1 C total warming for a doubling of CO2 is the most likely outcome? -
ClimateWatcher at 03:17 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
The biggest problem with the IPCC predictions is this. The sensitivity for a CO2 doubling is somewhere around 1.1C. The IPCC suggests that is the lowest possible 21st century trend ( not too far from the observed thirty year trends from multiple temperature records - land, ocean, lower and middle trop from satellites ). So the IPCC indicates that net zero feedback is the LOWEST possible outcome. Since there are known negative and positive feedbacks, I would suggest that a balance of feedbacks for a net zero feedback would be the MOST LIKELY outcome, not the lowest possible as the IPCC suggests. That would mean the MOST LIKELY outcome a response somewhere about the 1.1C per century. The problems with claiming the water vapor feedback (which is modeled to be by far the greatest positive feedback, even exceeding the original forcing from GHGs) are: 1. the actual observations (sonde data and ICCSP) indicate a negative feedback due to drier air aloft over lower level more humid air ( there, of course difficulties in measuring humidity, even greater than the difficulties measuring temperature, but that's what the data indicate). -and- 2. the models do not well accommodate the dynamics of moisture distribution. ( were the upper troposphere to become more humid, it would lead to increases cooling of the upper troposphere: which in turn leads to subsidence,
which also leads to greater loss to space of IR)
The global area of subsidence greatly dominates the global area of rising
air ( convection takes place mostly at the ITCZ and
along frontal boundaries, subsidence, largely caused by IR cooling aloft covers a much larger area even though the mass of air exchanged should balance. ):
which in turn leads to subsidence,
which also leads to greater loss to space of IR)
The global area of subsidence greatly dominates the global area of rising
air ( convection takes place mostly at the ITCZ and
along frontal boundaries, subsidence, largely caused by IR cooling aloft covers a much larger area even though the mass of air exchanged should balance. ):
 Finally, lots of papers demonstrate a seasonal temperature humidity correlation.
But it's important to realize that a large
contribution to this is dynamic ( dynamic migration of the ITCZ, subsidence and cold(dry) air mass migration in the winter hemisphere, etc. ).
Observations do support some moistening of
the surface, but since drier air over more humid air
actually increases the IR cooling rate, it may well be that the water vapor feedback is actually negative.
Response: I'd really appreciate it if for future reference, you could add width=450 to your larger images so they don't break the website format. Thanks.
Finally, lots of papers demonstrate a seasonal temperature humidity correlation.
But it's important to realize that a large
contribution to this is dynamic ( dynamic migration of the ITCZ, subsidence and cold(dry) air mass migration in the winter hemisphere, etc. ).
Observations do support some moistening of
the surface, but since drier air over more humid air
actually increases the IR cooling rate, it may well be that the water vapor feedback is actually negative.
Response: I'd really appreciate it if for future reference, you could add width=450 to your larger images so they don't break the website format. Thanks. -
Albatross at 03:04 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
Huh? Pielke made that statement on February 15, 2008...7:00 am This is the timeline for the paper by Willis et al. which he is citing: Received 22 August 2007; revised 24 January 2008; accepted 22 February 2008; published 14 June 2008. Pielke wrote on this before it was accepted, but he cites it as being "in press". -
Albatross at 02:59 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
Thanks J Murphy @199:) -
John Hartz at 02:46 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
@Graham Although I agree with what you said in the Moderator's Response" posted on #173, if I or another individual were to post something similar, it would be deleted because it would be deemed to be "poitical." Are Moderator's exempt from the Comments Policy of this website? -
robert way at 02:43 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
Arkadiusz Semczyszak, It does look interesting...especially to see the change in the climate regime since the 1970s. Thank you for pointing this out. It clearly shows the dominance of natural forcings such as the AMO (which fits this almost perfectly) prior to 1970 and the dominance of the anthropogenic signal post 1970 with the consistent warming. -
robert way at 02:41 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
KR All you're seeing in the pre-1970s graph is essentially the changes due to the AMO.... -
JMurphy at 02:41 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
Just in case gpwayne is otherwise occupied at the moment, the quote seems to be from here : The above paragraph reinforces a conclusion reached on Climate Science that global warming, at least as diagnosed by tropospheric and upper ocean heat content (see), has not been occurring since 2004. It is impossible to know if this lack of warming will continue, but these observations are inconsistent with the predictions of the long-term global climate predictions, such as reported in the 2007 IPCC report. Don't know how that fits in with this, from the following year : There has been no statistically significant warming of the upper ocean since 2003. -
Albatross at 02:37 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
Dr Pielke, Exactly which Figure from Willis et al. (2005)did you adapt in your opinion piece (which you link us to above) and how? And it seems that in said opinion piece that you do in fact concede that four years is a short period of analysis, yet here you have been reticent to acknowledge that. You say in your opinion piece: "Although four years is a relatively short period of analysis...." (from pg. 54). Some clarification is necessary. -
Albatross at 02:24 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
From von Shuckmann et al. (2009, JGR-Oceans), rate of change of 0-2000 m heating storage +0.77 W m-2 between 2003 and 2008. Hansen et al. (2005) reported a planetary heating rate of +0.85 W m-2. Von Shuckmann et al. can be found at: http://www.agu.org/journals/ABS/2009/2008JC005237.shtml Von Shuckmann et al. (2009) state that: "Global mean heat content and steric height changes are clearly associated with a positive trend during the 6 years of measurements." Hadley and PMEL show a slight increase in 0-700 m OHC after 2004. Now OHC for 0-700 m from Josh Willis show otherwise, while global SLR data show no slowdown. So much uncertainty. Yet some insist on publicly making unequivocal (and misleading) statements that global warming has halted after 2004, such statements are like fodder for the "skeptics" and those in denial about AGW. Scientists have a responsibility to clearly report the facts, which includes stating caveats and uncertainties in the data and analysis. -
actually thoughtful at 02:21 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Baz Skepticsim does not equal "I doubt." Nothing you have posted indicates you have earned the title of skepticism - approaching the world with a "let's see the facts" attitude. Instead you express your (personal, unfounded in facts) doubt selectively, and yet you are gullible in regards to anti-science (not being harsh - AGW IS the science of climate) claims. Thus you buy into "no warming since (pick a recent year)" but refuse to seriously consider trends over 15-20 years. You ignore sea level data, but are a fan of ARGO based OHC numbers. You ignore satellite data, temperature data, ice volume data, sea acidification data and the slam-dunk - night time warming data. Help me out - can you put your position into a internally-consistent theory or thesis? It is 2010 and I claim that "I doubt" is no longer a valid counter to the science of our climate (aka AGW). -
CBDunkerson at 02:11 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Eric #102, I responded to your comments on polar bear hunting here. Basically, I think the data shows this to be a red herring. -
Albatross at 02:06 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
Hi HR, Thanks, yes I got lucky there with my back-of-the-envelope estimate for the trend. Yes, they are fused, you can compare their data online using an interactive plotting too. What is interesting is that the ERA-40 seems to have been slightly warmer than the newer ERA-interim, which is anything would have reduced the warming trend. I cannot speak to how they spliced the data together, you would have to chat to them about that. -
CBDunkerson at 02:01 AM on 14 September 2010Polar bear numbers are increasing
Eric, actually they use "removal" and "harvest"... if you really think that is "obfuscation" then I'd say you place entirely too much weight on semantics. In any case, the claim that hunting is the most significant problem are simply insupportable from the data. Even setting aside the fact hunting quotas can be (and ARE) adjusted as their impact is determined and thus have no long term significance... the majority of population decline is attributed to sea ice loss. For example, the large Davis strait sub-population has an estimate of sustainable kills per year of 66 bears... and 60 bears average actually taken over the past 5 years. Yet the population is in decline, because sea ice conditions have deteriorated. Ditto for the Southern Beaufort sea and Western Hudson Bay groups. Likewise Southern Hudson Bay is currently stable, but the bears have begun to lose body mass due to loss of sea ice (just as observed in other areas prior to population declines) and thus are projected to decline in the future. Over hunting is a temporary problem correctable by adjusting quotas (which is done all the time) and which is only impacting a small percentage of bears. Sea ice loss is a long term problem with no known solution that is threatening several of the largest sub-populations with being wiped out entirely. -
HumanityRules at 02:00 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
17.Albatross The graphs in this article are actually data from ERA-40 and ERA-Interim fused together. Which seems strange? You can get the data for each of those from the link in #17. The trend for ERA-Interim (1989-2010) is 0.168 C/decade. Good guess! -
VeryTallGuy at 01:59 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Baz, I'd second Riccardo and Ann above, but also, as I did the work for you I'd appreciate more than just a "that's fair enough" response. Could you let us know whether you agree with the analysis, and if not, why not, providing your own working. Fair enough ? -
dana1981 at 01:59 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
Nice job Neal! All levels are excellent. -
Albatross at 01:58 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
GPWayne, When (and where) exactly in 2008 did Pielke Snr say this? "Global warming, as diagnosed by upper ocean heat content has not been occurring since 2004” Thanks. -
Albatross at 01:57 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
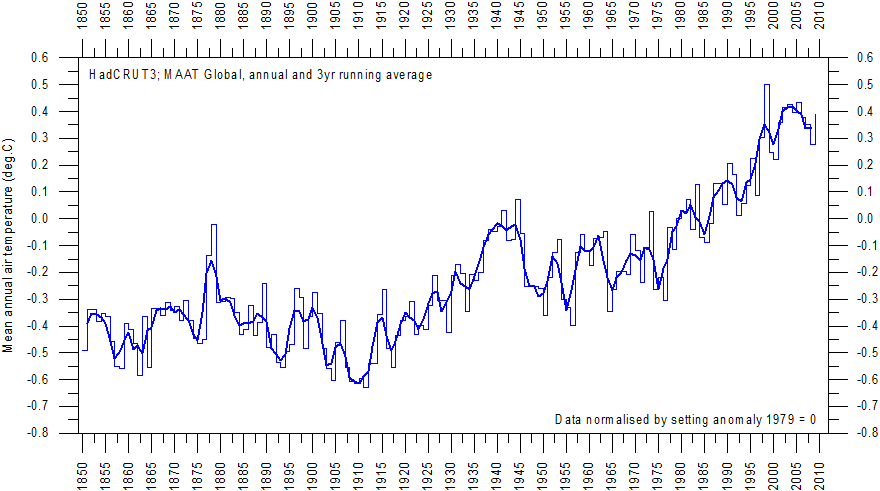
Baz @98, I too will warm you of the pitfalls about drawing conclusions based on short windows. Oh, and the there is another contradiction made by "skeptics", I thought the CRU data was "corrupted" after (faulty) claims where made after the stolen emails were posted. But now skeptics seem to gravitate towards HadCRUT because it shows the least/slowest warming of all the global SAT products (mostly b/c it excludes the Arctic where we know rapid long-term warming is taking place). Hansen has written on the global SAT and he says, with good reason, that using a running average of SATs is a better way to depict the global SATs (it effectively reduces the noise). Baz, have a look at the NASA GISS graph below and tell me that you think global warming has stopped: Also, consider reading this
If time is an issue just look at Fig. 21.
Also, consider reading this
If time is an issue just look at Fig. 21.
-
HumanityRules at 01:55 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
11.michael sweet You can investigate the ERA-Interim reanalysis using this tool. http://climexp.knmi.nl/selectfield_rea.cgi?someone@somewhere It shows for NH winter (DJF) that, as you say, NH mid-latitudes (30N-60N) were below normal. But actually quite cold, -0.4oC below average. SH mid-latitudes were fairly ordinary, +0.1oC. The two polar regions and the tropics were hot at +0.4oC to +0.6oC above average. -
Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
In a first for Skeptical Science, Neal actually wrote all 3 levels of this rebuttal in one fell swoop. Nice work, Neal. Congratulations on being the first one to accomplish this! It will be interesting to see how different people are able to make use of the basic, intermediate, and advanced versions. -
archiesteel at 01:27 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
@Eric: sorry, I didn't realize the Norwegian group was studying polar bear populations in Canada as well. However, it's clear you are biased in your interpretation that overhunting is the primary reason for population decline - for example, the article you linked to does not say that, even though the quota was 105, 200 bears had been killed. You seemed to have pulled that number out of nowhere. Ask those indigenous communities if the warming should be cause to worry, and you'll get a clear positive answer. One of the very reasons they want to shoot polar bears is that the latter are going further inland every year, increasing the number of human-bear interactions (which almost inevitably end up with the bear being shot). -
Albatross at 01:20 AM on 14 September 2010European reanalysis of temperature confirms record warmth in 2010
Yvan @15, Look at the second graph-- that is for the globe (a true global temperature, unlike the SAT data and even the MSU data). A clear warming pattern is evident. This is an estimate from looking at the graph, but for the period 1970-2010 the mean rate of warming I get is about 0.17 C/decade. Pity that ECMWF don't provide the mean rate of warming and/or actual numbers (then again, I have not undertaken a thorough search). TOP @14, ECMWF also have plot of Td (dew-point temperatures) available on their web-site, requires a little digging though. -
JMurphy at 01:18 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Baz : "Because when warming didn't continue at the same pace (around 2005) I began to question if I was right about my beliefe in warming." What pace ? Since when ? What belief ? Didn't you accept the facts, then ? You just believed ? What figures do you remember from that time, which made you doubt ? Baz : "As I have said on here, I don't deny the facts - the physics of GHGs, but what I do deny is that we 'know' what the overall result will be (pos/neg feedbacks)." We don't 'know' anything about the future, in fact, but scientists can make projections and suppositions based on scientific work. What, among all that scientific output, leads you to believe that the "overall result" will be better than the consensus states ? Baz : "AGAIN(!) I'm not sceptical of warming thus far. I'm sceptical that warming will continue - that there will be a postive feedback from contuing with our release of CO2 etc." For what reason are you sceptical ? Why do you think that warming has stopped or will stop, or that the feedbacks will be of little consequence in total ? Baz : "The HadCRUt global series shows remarkable stability over the past 10 years despite an ever-increasing CO2 release. So five years ago I questioned if my belief was correct." I can't see that stability, myself : what with all the peaks and troughs showing between the beginning of 2000 and the most recent figure (shown here). It also shows a positive trend, although small (data here). I find it even stranger that you had such doubts, when you compare the 10 year trend up to 2005 - when you say you had your doubts. Still lots of peaks and troughs but the trend is much more positive. So, what exactly made you doubt the evidence ? As for your question, I would give it between 20 and 30 years before being able to even determine any sort of significant flat or downward trend because we have had those in the past, as has already been noted, and we would have to understand why it was happening before throwing away any theories. It would also be nice to have a replacement theory... -
archiesteel at 01:14 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
@Baz Five years is not a sufficiently long period to claim warming has stopped, especially since it's clear 2010 will be one of the warmest years on record. Fifteen years is barely enough to produce a statistically-significant thread with the amount of noise produced by natural cycles, but is *is* enough. As VeryTallGuy said, a 20-year period is a good start, assuming we cannot ascribe it to some specific phenomenon. It still doesn't change the fact that you didn't act in a rational manner by "losing your faith" over a five-year period. -
archiesteel at 01:08 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
@Eric: "in laymen forums I always ask the same question: what is the catastrophe?" So, for you the catastrophe has to take place first before we try to mitigate it? I'm sorry, but that is not a rational position. We are already seeing the dire effects of AGW in the oceans, we are already suffering the effects of increased extreme weather. You're basically taking a gamble with the future. "So far I can safely say there is no catastrophe" Tell that to Pakistanis and people in Moscow. As for polar bears, here in Canada they are being forced southward, so much so that they have (in at least one case) started mating with brown bears. Declining numbers here are *not* due to hunting, because polar bear hunt is severely restricted. It seems to me you like to cherry-pick evidence that supports your agenda. That's hardly what a real scientist is supposed to do, but it's entirely consistent with the kind of disinformation spread by contrarians. Your excessive caution in dealing with this threat might be justified if we didn't need to transition away from fossil fuels for *other* reasons, but the fact is that we do. It makes no sense to argue against such a transition, even if you're skeptical of the science. What other reasons would one have to argue in favor of keeping fossil fuels, a finite resource that is the cause for conflict and inequality? -
michael sweet at 00:50 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
A runaway greenhouse is one where the final temperature causes the ocean to boil away. At that point there is no way for a return to a lower temperature. Venus has a runaway greenhouse, so we know it is possible. Even there the temperature stabalizes at a high temperature. Dr. Hanson studied Venus and he feels that it could be a problem on earth if enough CO2 is emitted. The consensus is that it is unlikely to happen. Even without a runaway greenhouse it can get too hot for most of us. -
Paul Daniel Ash at 00:48 AM on 14 September 2010The contradictory nature of global warming skepticism
Mosh @67: Pieces are slected [sic] because they are new, unusual, puzzling, contradictory. What you want is for somebody else, some authority, to settle the controversy. Anthony is happy to let his readers try. blood sport This is pretty much the issue I have with most of the soi-disant "citizen scientist movement." What is taking place at WUWT, at its best, is argument. Sophistry, if you will. That's all well and good, but it's not science. Pretty much every post and every comment there is suffused with the attitude "these scientists have no idea what they're talking about, I can understand this stuff much better than they." And perhaps some - even many - of those commenters could make a contribution, if they set aside 38 Ways to Win an Argument, got a science education, found a lab, and published. Instead it's just LOLs and WTFs. Nobody wants "some authority to settle the controversy." The controversy should be settled by good science, competently and transparently done. Not 'blood sport.' -
John Hartz at 00:43 AM on 14 September 2010Pielke Sr and scientific equivocation: don't beat around the bush, Roger
@ Dr. Pielke: In your most recent post (#194), you conclude by directing everyone to a website to learn more about global warming. The website that you direct us to seems to be the official website of the “Pielke Research Group.” Unlike most websites of this nature, your website does not contain a “Who we are” webpage. What is the Pielke Research Group? -
RSVP at 00:37 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
The Ville #9 You beat me to it. I was going to comment the exact same thing, however, one could also question what is meant by "runaway". Doesnt the transitional state imply some degree of runaway? -
Paul D at 00:12 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
Maybe the title needs to be changed. Something like 'Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming' And in the article, have something like 'although positive feedback can result in runaway..., it doesn't necessarily result in runaway..., here's why...'Response: I'm having a deja vu from this morning. Tonight when I tweeted this blog post, I inserted a (necessarily) into the tweet. Again, thought briefly about updating the blog heading, decided against it (mainly due to laziness). I hope all the authors (who are doing a fantastic job writing all these rebuttals) aren't getting too fed up with me creating all the distractions from their articles :-( -
beam me up scotty at 00:10 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
Needed to read more carefully. Sorry -
Paul D at 00:07 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
What about the release of methane? -
John Cook at 00:04 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
Let me speak for Neal and explain that this article is meant to address the sentiment often expressed in comments here on Skeptical Science: if our climate has net positive feedback, why haven't we experienced runaway warming? So this rebuttal establishes one very simple point - you can have net positive feedback without experiencing runaway warming. So the rebuttal is not saying runaway warming is impossible. Given a strong enough positive feedback or a strong enough warming, it may be possible. But that's not the point of this rebuttal. -
MrAce at 00:02 AM on 14 September 2010Why positive feedback doesn't necessarily lead to runaway warming
If the limit is above 100C, we will end up like Venus, because we will cook the oceans.
Prev 2219 2220 2221 2222 2223 2224 2225 2226 2227 2228 2229 2230 2231 2232 2233 2234 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























