Recent Comments
Prev 2243 2244 2245 2246 2247 2248 2249 2250 2251 2252 2253 2254 2255 2256 2257 2258 Next
Comments 112501 to 112550:
-
miekol at 19:28 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
Sorry I didn't realize mariner sea levels are different to science sea levels. -
Rob Painting at 19:06 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
BP, I don't know where you live, but down here in the Southern Hemisphere, citing Bob Carter doesn't bolster credibility, quite the reverse. -
Paul D at 18:28 PM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
re: the label 'less heat escaping to space'. Would it be more accurate to say that the 'heat is delayed from escaping to space'? As was pointed out by others, even if you add more GHGs eventually an equilibrium is reached and just as much heat as before escapes! The only alternative is that the missing energy is emitted at a different frequency which balances the in/out equation, or is that what is implied? If you consider extra insulation of a home, you have to reduce the energy input to maintain the same temperature as you had before, because the insulation causes a delay. If you turn off the heating then eventually the energy will escape. The time between turning off the heating and the house temperature reaching the same temperature as outside is the delay. The more insulation the longer that delay or 'gradient'. Sorry about the analogy! -
Berényi Péter at 16:24 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
#24 doug_bostrom at 15:03 PM on 31 August, 2010 By the way, did you notice that 3mm/year is right in the ballpark for global sea level change observations? Of course, if you express the same number as 0.0003 meters it sounds terribly small 0.0003 meter is 0.3 mm. It is a well established fact the average rate of sea level rise along the Australian coast is of this order of magnitude and no, it is not in the ballpark. If recent global estimate of ~3 mm/year is correct, the entire Australian continent should be rising at an alarming rate. BTW, I have not used New York (as a single tide gauge) for computing rate of sea level change but for assessing acceleration. That's a different game and in tectonically stable locations accuracy depends more on the length of record than on anything else. Modern acceleration term in isostatic rebound is minuscule. -
johnd at 16:20 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
doug_bostrom at 15:39 PM, I was referring to your inflating of the figure quoted in the article by a figure of 10. Is the article wrong, or did you unconsciously inflate it because you thought that it had to fit the ballpark figure you had in your mind. Is this a case where failing to focus on tiny portions of data might lead to false conclusions? By the way, the article is most relevant to the discussion, as it mentions, the small slow changes due to climate change is what initiated the work described. -
Tom Dayton at 15:46 PM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
No, johnd, random sampling is not alone the only good way to eliminate bias. Randomization always should be used, but only to attempt to reduce leftover biases that cannot or might not be reduced by systematic approaches. The decision of when to attempt to make systematic adjustments is informed by the confidence in identifying systematic sources of bias, and by the difficulty and expense of preventing or systematically compensating for them. Examples of excellent candidates for systematic adjustment are the movement of a temperature station, and its daily measurements being switched from morning to afternoon. This is all basic science and statistics. -
Doug Bostrom at 15:39 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
Good question, JohnD. I didn't get the relevance either. Perhaps Miekol can explain. -
archiesteel at 15:32 PM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
factfinder and mscavazz, I suggest you review the Comments Policy as your post are inflammatory in one case and off-topic in the other. -
johnd at 15:29 PM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
Jeff Freymueller at 13:17 PM, it really goes back to the principles devised to facilitate the acquiring of unbiased representative samples for any form of laboratory analysis. The degree of accuracy of the final result is determined by the refinement of the process of randomly taking samples rather than any concern about what variations might be in any individual sample. -
johnd at 15:13 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
doug_bostrom at 15:03 PM, 3mm/year may be right in the ballpark, but what is the relevance? -
Doug Bostrom at 15:03 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
Try to be a little more serious, or little less desperate to create an impression, Miekol. You're citing a web page concerning tidal predictions for mariners, thereby making yourself sound needlessly silly. By the way, did you notice that 3mm/year is right in the ballpark for global sea level change observations? Of course, if you express the same number as 0.0003 meters it sounds terribly small, certainly true when our concern is safe navigation of ships today, tomorrow, next year. That's actually not the point here. Perhaps you should read more carefully above, where it is suggested that focusing on tiny portions of available data leads to false conclusions. -
miekol at 14:33 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
The following is taken from a government report:- "Because the sea level rise is very low, averaging 0.0003 metres per annum for the Australian continent (Mitchell, 2002), the 15 to 19 years of readings available from Queensland tidal stations is not sufficient to calculate a reasonable estimate of sea level change. Accordingly an adjustment of 0.0003 metres per annum is made to the mean sea level within the tidal reference frame. The allowance is been calculated from the central date of the observation period at each station to the central date of the tidal datum epoch (31 December 2001)." http://www.icsm.gov.au/SP9/links/msq_tidalreferenceframe.html -
Rob Painting at 13:28 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
HR @18 - That Wenzel & Schroter fail to capture the acceleration in global sea level reflecting the rapid warming in the early to mid 20th century suggests some problems with their gap filling methods. If anything their technique seems to smooth out the entire record. This is what I mean: The early to mid century global sea level acceleration is evident in Church & White 2006
The early to mid century global sea level acceleration is evident in Church & White 2006
 And Jevrejeva 2006:
And Jevrejeva 2006:
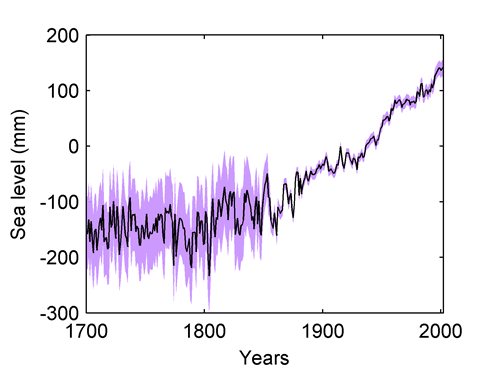 And also is seen in Vermeer & Rahmstorf 2009 (modeling global sea level to global temperature)
And also is seen in Vermeer & Rahmstorf 2009 (modeling global sea level to global temperature)
 I'd expect some aspect of that rapid rise in temperature to show up in the global sea level, via thermal expansion, but there's no trace of it in Wenzel & Schroter, the whole period seems smoothed out.
I'd expect some aspect of that rapid rise in temperature to show up in the global sea level, via thermal expansion, but there's no trace of it in Wenzel & Schroter, the whole period seems smoothed out.
-
scaddenp at 13:18 PM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
Johnd - The rate at which water vapour enters the atmosphere is surely dependent on the surface temperature - dependent on the radiation from both the sun AND from the atmosphere (ie the GHG effect). -
Jeff Freymueller at 13:17 PM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
#1 johnd, your question was pretty nearly answered several months ago, for example by Zeke Hausfather, and several others. I don't recall anyone having taken randomized sets of stations with sufficient global coverage, but unadjusted or adjusted matters very little, nor do several selection criteria for stations that people have proposed. So I suspect you are right, because the adjustments and any station biases are simply smaller than the warming signal. -
Phila at 13:14 PM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
Would it make sense to add something about the meaning of "anomaly" to this entry? That seems to be a sticking point for a lot of amateurs, and "skeptics" are very good at exploiting the confusion that arises. -
Rob Painting at 12:41 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
BP, I don't expect one tide gauge is going to reveal anything useful about global sea level trends, given the trends vary from region to region, but I do note that your 3rd figure (global sea level) matches well to ENSO events. -
Doug Bostrom at 12:23 PM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
I suspect adjustments have something to do with our fascination for units of measurement, JohnD. You could certainly confirm you hypothesis about a constantly morphing collection of instruments with a bit of work; folks like Hausfather et al have beaten a nice, flat path for the rest of us to follow. -
Doug Bostrom at 12:03 PM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
A single tide gauge, Peter? Surely you can do better. The isostatic and tectonic situation around New York is not simple so attempting to use a single gauge proves little. ( Vertical crustal movements along the East Coast, North America, from historic and late Holocene sea level data ) Shortcuts to conclusions via tide gauges are probably not available, a lot of work has to be done for inferences about rates of change. It's the same deal with satellites. We rely on a very intricate and fanatical effort for establishing the validity of measurements. See for instance this item on using GRACE and Argo measurements to further establish confidence in Jason data: Closing the sea level rise budget with altimetry, Argo, and GRACE. As you can see, from that paper there does in fact appear to be a slowdown in sea level rise ~2004-2008, rendering your concerns slightly less concerning as well as emphasizing the point in the article above that picking short periods from long datasets is usually unproductive. I could in turn ask, what do we see after 2008? Maybe a resumption of a higher rate, maybe not. Use a longer straightedge. -
Jim Meador at 11:30 AM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
All of the adjustments are described here. -
Jim Meador at 11:28 AM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
The United States Historical Climatology Network (USHCN) is the older of two surface temperature measuring networks in the US, and it is valuable because it is a continuous record stretching back more than 100 years. Over the years changes do occur at each station, and the adjustments are meant to make current readings compare meaningfully to the older measurements. For instance the stations are moved, or the instrument is changed, or the time of day that the measurement is taken changes. All of the adjustments are described here... http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/climate/research/ushcn/ushcn.html#QUAL Note also that this study pertains to the US HCN surface record only, and does not cover the entire globe. -
Chemware at 11:05 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
Suggested correction to point (3): (We know this because the two types of carbon have different chemical properties.) Err, no. They have the same chemical properties. They have different physical properties, specifically different 13C : 12C ratios. -
Berényi Péter at 11:03 AM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
Posted by doug_bostrom at 10:26 AM, Monday, 30 August, 2010 observed sea level rise is already above IPCC projections and strongly hints at acceleration No, there is no acceleration. Sea level rise is fairly linear. Let's have a look at the New York tide gauge, for example: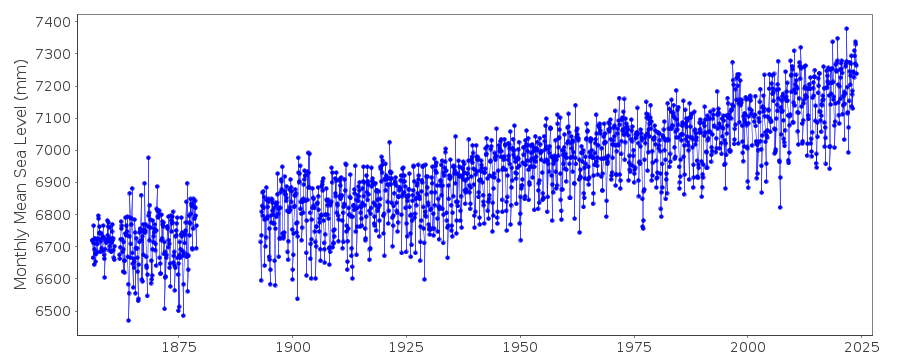 Acceleration can be computed by fitting a least square quadratic form to data. Acceleration is twice the coefficient of the quadratic term.
For New York it is 0.001 mm/year2 since 1900. That is, sea level rise got faster by 0.1 mm/year in a century, which is equal to zero for all practical purposes.
Of course it is possible the southern tip of Manhattan is accelerating upward at the same rate sea level rise is supposed to accelerate. However, it is extremely unlikely.
There is no substantial tectonic activity in the region, the island is a huge granite rock stable enough to carry the weight of the city and vertical movement due to post-glacial rebound, if anything, is decelerating as time goes by (New York is close to the neutral line where no vertical movement occurred after the Laurentide ice sheet melted away).
Acceleration can be computed by fitting a least square quadratic form to data. Acceleration is twice the coefficient of the quadratic term.
For New York it is 0.001 mm/year2 since 1900. That is, sea level rise got faster by 0.1 mm/year in a century, which is equal to zero for all practical purposes.
Of course it is possible the southern tip of Manhattan is accelerating upward at the same rate sea level rise is supposed to accelerate. However, it is extremely unlikely.
There is no substantial tectonic activity in the region, the island is a huge granite rock stable enough to carry the weight of the city and vertical movement due to post-glacial rebound, if anything, is decelerating as time goes by (New York is close to the neutral line where no vertical movement occurred after the Laurentide ice sheet melted away).
 As for more recent times, global sea level is measured by satellites.
As for more recent times, global sea level is measured by satellites.
 The trend line looks impressive, but if we draw a separate trend line for the TOPEX and Jason eras, a considerable deceleration is seen. On top of that, there is a hint of a 4 mm offset error between data from the two satellites (at the beginning of 2002). If it is taken into account, the trend is decreased for the full period.
The trend line looks impressive, but if we draw a separate trend line for the TOPEX and Jason eras, a considerable deceleration is seen. On top of that, there is a hint of a 4 mm offset error between data from the two satellites (at the beginning of 2002). If it is taken into account, the trend is decreased for the full period.
 BTW, I can believe acceleration values derived from satellite measurements, but absolute rate of sea level change also depends on the selection of the reference point set. As acceleration of vertical land movement is much smaller on these timescales than linear rates, it is easier to have a reference set with zero average acceleration than one with zero rate of change.
BTW, I can believe acceleration values derived from satellite measurements, but absolute rate of sea level change also depends on the selection of the reference point set. As acceleration of vertical land movement is much smaller on these timescales than linear rates, it is easier to have a reference set with zero average acceleration than one with zero rate of change.
-
johnd at 10:59 AM on 31 August 2010The surprising result when you compare bad weather stations to good stations
That raises the question as to why adjustments are necessary to individual records. By rights a random selection of sufficient stations that represents consistent global coverage, that is constantly changed should provide a consistent global record of temperatures over time irrespective of which individual stations are in each selected mix. -
HumanityRules at 10:33 AM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise: the broader picture
15.Peter Hogarth Thanks for those papers. I'm glad you point out the caveats in the Wenzel paper. Personally I have no problem with scientists describing the limitations of their work. In fact it's sound scientific practise. The opposite leads to wild exaggerated claims. I guess the caveat surrounding the uncertainty in early data is true for all SLR reconstructions, even those that use a larger number of gauges. With regard to the two papers. Both show SLR records from 1992-2010(ish). Both records look linear, ignoring the inter-annual variability. I'm just trying to imagine how this acceleration is working and how it fits into the real world. We have a 100 year record which shows a 1.6mm/yr rise and an 18 year record which shows a rate ~double (3.4) that suggesting something extraordinary is happening but at the same time that acceleration doesn't show up in the past 18 years. This would have to suggest that the acceleration occured prior to 1992 and for the last 18 years things have returned to a steady increase (albeit at a higher rate). This fits with neither the supposed acceleration in OHC and land ice melt over that time period. Can you just describe the nature of the acceleration? -
Doug Bostrom at 10:30 AM on 31 August 2010Can humans affect global climate?
Uh-oh. Dr. S. Fred Singer in his own words, in the PBS interview that is the source of Smitty's quotation. I'd heard of this guy but now I understand why he's notorious. The interview is worth an entire article in its own right. A sample of internal consistency and accuracy: "But since 1979, our best measurements show that the climate has been cooling just slightly. Certainly, it has not been warming." Followed later by: "Since aerosols are mostly emitted in the northern hemisphere, where industrial activities are rampant, we would expect the northern hemisphere to be warming less quickly than the southern hemisphere. In fact, we would expect the northern hemisphere to be cooling. But the data show the opposite. Both the surface data and the satellite data agree that, in the last 20 years, the northern hemisphere has warmed more quickly than the southern hemisphere." Completely incoherent but Singer ironically goes on to say this is very embarrassing to the "modelists." -
Riduna at 10:25 AM on 31 August 2010Ocean acidification threatens entire marine food chains
actually thoughtful @ 13 So only 5% of the global population depend on fish as their only or primary source of protein. This is at odds with views expressed by James et al (2010) and the FAO which claim that over16% are dependent seafood. Peter Hogarth @ 36 Thank you (I think) for a comment which alas reinforces my view that the future is indeed bleak and unlikely to improve given our voracious fishing industry driven by the need for profitability rather than sustainability. -
Unrecovered at 10:10 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
KR. Yes certainly, when you referring to the transient state. I guess my point is that, I don't think we have direct measured evidence of this imbalance. The current estimated imbalance (models) of 0.9 Wm-2 at the TOA is beyond our current capabilities to measure from satellite. What we have, and I think what you are referring to, is evidence is that the emission spectrum at the TOA has changed in the way we would expect it to from increases in various green house gases. That's useful information but doesn't quite amount to evidence that: "less heat escapes to space". Of course I haven't made a better suggestion yet. -
johnd at 09:46 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
KR at 05:16 AM, there is no philosophizing necessary, the H2O spectra moves from high absorption to high emissivity then to high absorption within a range that provides a window of opportunity for conditions conducive to the existence of life, that range being due to the unique properties of H2O. CO2 might be able to alter to some degree the factors that drive the closing of the emission window on one side, but that doesn't change the fact the properties of H2O alone would have closed that same window, all be it after a greater loss of heat from the system than what CO2 would close that same window of emissivity. -
Doug Bostrom at 09:40 AM on 31 August 2010Can humans affect global climate?
Which board, Smitty? The answer helps determine whether it's worth devoting any effort to an attempt. Meanwhile, it might help to put Singer's quote into context. -
johnd at 09:28 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
KR at 05:06 AM, the change of state that allows water vapour to enter the atmosphere is due entirely to conditions that occur at the immediate surface of the earth where the reservoir of H2O resides in either it's liquid or solid state. The process extracts heat from the surface which is then carried into the atmosphere being liberated through various levels until finally all is exhausted at the highest levels at which clouds form. The rate at which water vapour enters the atmosphere is therefore dependent primarily on the amount of solar radiation and water that is available at the immediate earths surface, and the rate at which the change of state takes place to enable the hydrological cycle to complete is dependent on being able to liberate heat into an environment where there is a ongoing process of nett heat loss out of the system. -
Smitty at 08:56 AM on 31 August 2010Can humans affect global climate?
I should have prefaced the previous comment. I am currently debating a number of people (who are probably smarter than I am) on a message board and I was asked to respond to Dr. Singer's claim. I have searched for an answer and have come up empty. I truly don't know the answer and any help would be appreciated. Thanks, Smitty -
johnd at 08:48 AM on 31 August 2010Human CO2: Peddling Myths About The Carbon Cycle
muoncounter at 13:33 PM, the peak to trough variation in the annual cycle is far greater in some places, as high as 50ppm as shown in Mechanisms for synoptic variations of atmospheric CO2 in North America, South America and Europe so there is far greater capacity to sequester CO2 than is fully realised. If the growing seasons extend then perhaps more of that capacity will be utilised. As virtually all enrichment trials indicate, plant growth under present conditions is far from optimum, low CO2 levels being the factor being focused on, with CO2 enrichment being a long established practice in many commercial intensive plant production systems. -
The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
Unrecovered - Actually, it's not the same amount of energy escaping. Reducing the emission spectra at a particular temperature directly reduces the amount of energy radiated at that temperature. The difference is the radiative forcing induced by changing amounts of greenhouse gases, accumulating energy here on Earth until the temperature rises, the emission spectra scales up accordingly, and the summed energy escaping matches the energy coming in - equilibrium. The various feedbacks and energy accumulation take a bit of time - even if we were to stop changing CO2 levels right now warming would still continue for decades, until that sum energy emitted matches the amount coming in. -
Unrecovered at 07:46 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
The amount of energy escaping is the same. Not sure if emissivity helps much here. -
dsleaton at 07:39 AM on 31 August 2010Climate Models: Learning From History Rather Than Repeating It
Fortunately, Pete, I saw your post of Droz (or druz, as Le Guin might call him) before it disappeared. Droz had the amazing logical faculty to promote the idea that unless a model perfectly predicts what it sets out to predict, it should be tossed out. Pete, look yourself in the mirror and ask yourself if you truly believe that. Every day you bet your life on imperfect modeling that you yourself perform. When you ride your bike to work, you know that the possibility exists that a car could swerve into the bike lane and kill you. Yet you make an educated guess that the likelihood is fairly low (yet people still die in bike lanes). Now, when people gather together and develop a rigorous public and peer-reviewed methodology that produces climate models, you reject them as useless because they do not perfectly predict the future. When all variables and rules are completely known, as in certain programming situations, then models can be created that perfectly predict the future. What about the climate suggests to you that such perfection is possible for climate forecasting? Or perhaps it is that you have a climate model that is capable of perfection? Your position, however, seems to consistently be that trying to model climate is totally pointless and a waste of taxpayer dollars. If that's not what you believe, then shut up already about it and try to help improve the modeling! -
Smitty at 07:27 AM on 31 August 2010Can humans affect global climate?
Is Dr. Singer's statement true? If not, how can it be refuted? " There is no dispute at all about the fact that even if punctiliously observed, (the Kyoto Protocol) would have an imperceptible effect on future temperatures -- one-twentieth of a degree by 2050. " Dr. S. Fred Singer, atmospheric physicist Professor Emeritus of Environmental Sciences at the University of Virginia, and former director of the US Weather Satellite Service; in a Sept. 10, 2001 Letter to Editor, Wall Street Journal -
The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
Unrecovered - Yes, "At equilibrium, the amount of heat escaping to space has to be the same has what is coming in". However, when increasing GHG's change the emissivity spectra, reducing the amount of radiation emitted at a particular temperature, the equilibrium temperature for equal energy is higher - things get hotter. Perhaps the statement should be "Less energy escaping to space at any given temperature [due to reduced emissivity]"? A bit wordy, but I think correct? -
Paul D at 07:17 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
factfinder: "For all this "empirical -circumstantial evidence" there is still no experimental data and test that prove that the "greenhouse gas effect " exists." Well Roy Spencer is happy with it: http://www.drroyspencer.com/2009/12/what-if-there-was-no-greenhouse-effect/ So why aren't you? It's based on fundamental science used as a basis of thermal imaging, in chemistry and other areas of engineering and science. eg. infrared spectrography, quantum physics. Some teenagers do an experiment: http://www.nvcc.edu/home/cbentley/geoblog/2009/05/greenhouse-effect-experiment.html However such experiments don't demonstrate the lapse rate. -
Unrecovered at 07:10 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
I find the "less heat escaping to space" label in the figure to be rather confusing and it could potentially be used to discredit the effort. I looked at it and cringed a bit until I saw that this label refers to the spectral signature of the TOA emission. At equilibrium, the amount of heat escaping to space has to be the same has what is coming in. If you are talking about the current imbalance due to lagging ocean warming, then I think you have to tell a different story. Maybe the label should be "emission fingerprint" but that might be too complicated still. -
Doug Bostrom at 07:02 AM on 31 August 2010Arctic sea ice... take 2
Argus dance around your words all you like but their meaning was fairly clear. You doubt what's reported, or perhaps more specifically you want to create an impression of doubt. "Dark water absorbs more of this energy than white ice." Sure, but how much energy are we talking about here? You go on to specify various parameters affecting absorption of solar energy in sea water at high latitudes. You "wonder" while projecting a rhetorical stance: Those who lament the absence of ice in the Arctic seem to forget (or pretend to forget) that the amount of solar energy per area unit that actually passes into the Arctic ocean through the surface, is at most a few percent (my guess) of what passes into tropic oceans. So how important is this effect? Duly answered. Nobody has forgotten the parameters you mention, but apparently you're not really interested in improved understanding, your mission or preferred perspective seems more about doubt. So in your next comment you focus on your earlier question about the difference in radiative properties of ice versus water: I have no answer, but I would like to see the subject discussed. Maybe the increased radiation during the darker hours, compensates for the absorption of energy when the sun is up? It sounds, to me, like an important negative feedback. You could have a stab at that question yourself, you could provide a constructive comment here with your result, but you appear to prefer leaving the question hanging in the air, conveying doubt. I'm done playing the game with you but here are clues to your answer: ice conducts heat about 4 times better than water, water and ice are similarly good radiators with water being a little better than ice with more emissivity particularly at longer wavelengths. Don't forget to extend your experiment into the atmosphere so as to get a net effect. -
mscavazz at 06:32 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
doug_bostrom, what brazen omission are you talking about ? -
Argus at 06:28 AM on 31 August 2010Arctic sea ice... take 2
doug_bostrom, First, I think you ought to be more careful with how you quote people. Where did I say "I doubt it"? The answer is nowhere. You made it up, just as you invented the N+ iterations. And what is so "boringly repetitious"? I have never before raised these matters about arctic ice. Instead of answering at least one of my questions yourself, you claim that I am implying that "the people studying this" are naive. I have read through the report you recommended, and I cannot find that they adressed the function of heat radiation from a dark ocean anywhere at all. The only things they talked about were ice albedo and solar heat input. But where there is input there is also output, and it is obvious that a warm black body radiates a lot more than an icy white cold body. So most of my thoughts from #29 remain unanswered. -
citizenschallenge at 06:14 AM on 31 August 2010Sea level rise is exaggerated
20 Andrew Hobbs at 21:06 PM on 13 June, 2010 Thank you for your post. Especially in light of no one else elaborating on the statement made in "The Skeptical Argument," and that I've been trying to find something on that charge for a little while: ~ ~ ~ "Scientists from Flinders University, Adelaide, certainly DID NOT abandon the project. " "In 2003 the University decided to cease the operations of the National Tidal Facility Australia (NTFA). ... The operation was transferred to the Commonwealth Government effective from 1 January 2004." "It is possible to access their latest results on the Australian Bureau of Meteorology website at the web page for the South Pacific Sea Level and Climate Monitoring Project. " "These results support the general rate of global sea level rise noted elsewhere." ~ ~ ~ Beyond that, earlier a comment was made: "... my comments have been deemed inappropriate by a rather draconian comments policy." Well, I for one, found this back and forth discussion another wonderful (and educational) example of how science should be discussed. Too bad such a sight can't be found in the AGW Hoax blogosphere. My point is that I'm sure it is the "draconian comments policy" that makes such discussion possible so thank you John for sticking to your guns. -
Doug Bostrom at 06:05 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
Wow, quote-miners going to work on the IPCC review w/pick and shovel. Amazingly brazen omission in pursuit of impressionism, mscavazz. How fortunate that the IPCC does not follow such degenerate techniques. Those looking for context might start w/the complete executive summary: Climate Change Assessments Review of the Processes and Procedures of the IPCC Meanwhile, notice that mscavazz' plucked cherry was from WGII. Notice from the topic heading here, this thread is about scientific evidence of climate change itself, not the subject of WGII. Find an appropriate thread mscavazz. Try plugging "IPCC" into the search box at upper left, pick an appropriate thread, go there w/further comments on the InterAcademy Review. -
Climate Models: Learning From History Rather Than Repeating It
Pete Ridley - I'm not terribly surprised that your post got deleted; I believe John Cook and the moderators prefer links to giant quotes, rather than cut-n-paste. Sadly, your post (and your ongoing attitude regarding models as in your posts here, and here) reflects one of the major characteristics of denialism: #4, Impossible expectations and standards of proof. If you include your references to John O'Sullivan and others, as you did discussing satellite temperature records, you are also using tactic #2, Fake Experts. Demanding absolute accuracy, absolute proof, 100%+ certainty - these are all tactics that have repeatedly been used to deny evidence and scientific consensus. I clearly recall these very same tactics used to argue that second hand smoking was not proven harmful, and that CFC's weren't shown to damage the ozone layer. In fact, my brother used to be one of the public apologists/deniers for a major tobacco company, trying to argue against the 'second-hand smoke' issue on his companies behalf. He frequently used the "Not absolutely proven" certainty argument - and he knew quite well he was making s**t up. He referred me to the book "Thank You For Smoking", and stated "This is my job - I am this man." I just cannot take the absolutist argument seriously. We're well past the 95% certainty level for anthropogenic global warming, with a 3 deg. C +/- ~1 warming for a doubling of CO2. Insistence on absolute proof, on climate models that absolutely reproduce temps in the presence of noise - these are just calls to do nothing, and have no scientific basis. The models do a decent job, which has been statistically shown, and ignoring predictions from them is just foolish. -
mscavazz at 05:50 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
breaking new InterAcademy Council - Review of the Processes and Procedures of the IPCC Quote: "authors reported high confidence in some statements for which there is little evidence. Furthermore, by making vague statements that were difficult to refute, authors were able to attach “high confidence” to the statements. The Working Group II Summary for Policy Makers contains many such statements that are not supported sufficiently in the literature, not put into perspective, or not expressed clearly." -
michael sweet at 05:48 AM on 31 August 2010Why we can trust the surface temperature record
Johnd, If people noticed that you had no winter that is a predicted sign of global warming. You claimed that the seasons were not shifting in post 12. Now we agree that the seasons have shifted so much that people are noticing it. Thats what scientists call "Climate Change". There is more water in the hydrological cycle because of increased temperature of the atmosphere and ocean. Increased temperature is caused by increased CO2. This was forcast decades ago. Water responds to temperature change. Water does not force temperature to change. Yes, it is complicated, but the base of the pyramid of climate change is CO2 forcing in the atmosphere. -
Doug Bostrom at 05:35 AM on 31 August 2010The empirical evidence that humans are causing global warming
KR there is a place here suitable for cloud discussions but it does seem as though a specific "Clouds will save us" topic would be a good thing. Comes up time and again. The albedo effect. Related to this I'm interested in current efforts to reprocess old Nimbus tapes to extend ice trends farther back. Follow that link and you can see the stunning results available via reprocessing. The same methods ought to work w/longitudinal cloud cover as well, something that's not well quantified now. -
Pete Ridley at 05:28 AM on 31 August 2010Climate Models: Learning From History Rather Than Repeating It
I tried to post this yesterday but it has disappeared so I try again. You should be interested in the alternative opinion of “physicist, computer Programmer, environmental activist, financial expert” John Droz presented in his January article “Climategate: The Perils of Global Warming Models” (Note 1). This requires no embellishment from me as it reflects my own opinion perfectly. QUOTE:Moderator Response: Use your own words, please.
Prev 2243 2244 2245 2246 2247 2248 2249 2250 2251 2252 2253 2254 2255 2256 2257 2258 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























