Recent Comments
Prev 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 Next
Comments 30201 to 30250:
-
Stephen Baines at 07:27 AM on 2 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
JohnD at 311
Two points. First I don't think the post you're responding to was suggesting that you did not understand the first law of thermodynamics. In fact, it was presuming that you did understand it. The point was that what confidence modelers have comes from the application of relatively simple laws of physics, albeit impliemented in a complex context. What looks like religiosity to you many stem from the confidence in those laws.
Second, until we understand what you are specifically talking about with respect to poor predictions, it's hard to discuss you concerns. For the most part models have done pretty well, especially when the inputs actually reflect reality. They certainly do well enough to discern a human influence on climate vs a natural one. Projections forward are very much dependent on basically random events like volcanoes and El nino and by the actions of humans, which may be influenced by the models.
If you gave us some specifics people could respond more constructively.
-
Tom Curtis at 07:22 AM on 2 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Watchdog @37, I note that you have posted a version of the Loehle 2007 temperature reconstruction. That is disappointing, not least because Loehle 2007 was found to have several errors, some of which at least were acknowledged by Loehle himself in Loehle and McCulloch (2008). Given that correction, there is no excuse for continuing to use Loehle 2007. Here for comparison is the Loehle 08 reconstruction alongside the BEST LOTI:

Even using Loehle 08 is dubious, however. He used just 18 proxies, nearly all of which are from the Northern Hemisphere, and a majority of which (10) are from the North Atlantic and immediate surrounds. As his method was to take a simple mean, this is equivalent to assuming that the North Atlantic and immediate surrounds occupies 55.6% of the Earth's Surface, with China (22.2%), the Pacific Warm Pool and South Africa (11.1% each) making up the remainder.
The decision to use so distorted a geographical representation of proxies was not justified by lack of data, with long ice cores known to exist for Antarctica, the Andes and the Tibetan plateau; and long coral sequences verly likely existing for the Great Barrier Reef. It was, however, a convenient decision given Loehle's known preferences as the North Atlantic shows the greatest temperature variability over time relative to other regions; and the strongest effect of the MWP. That is, not only was the data selection biased, it was also tendentious.
These fact entirely undercut your argument. The long term trends you point to are as much an artifact of limited and biased data selection as of actual global temperatures. Potentially more so. Even so, as can be seen even on your graph, the twentieth century warming has endured longer than any period of equivalent slope to the trend, or equivalently, has shown a stronger trend than any period of equivalent duration. Ergo it is not just another natural trend. Further, as it is a predicted trend, on the basis of the theory that predicted it, it is likely to continue.
-
Tom Curtis at 05:39 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
sgbotsford @10, taking your lake analogy, a high wind tide on one side of the lake would result in a low wind tide (reduced apparent level) on the other side of the lake as volume overall would be unchanged. If you had three or four water level gauges spaced around the lake, you would be able to detect this effect and remove it from any measure of total lake level.
By analogy, you can do the same with the world's oceans. Admitedly the oceans are large enough that such effects might result in a temporary rise in sea level at the center of the ocean, but tide gauges are found on islands as well as on continental shores. Therefore such an effect is unlikely to not be detected. Of course, such measurements will not be perfect, and there will be a small amount of noise resulting. The noise, however, is likely to be unbiased (ie, to not create spurious long term trends) and short term so that it will not effect overall measurements.
Further, with regard regular tides, tidal measurements are made for high and low tide so that the effect is easilly removed. Tide gauges can also easilly remove the effect of waves by a variety of means, ie, by buffering the water so as to reduce wave motion where measured, or by continuous measurement with the effect of the waves being removed as with tides.
However, as CBDunkerson points out above, the measurements above are satellite measurements so that they have near universal coverage of the oceans. Therefore they do not miss the total effects of "wind tides" with rises from one being compensated by falls in the other. They can eliminate the effect of tides by calculation (as the effect causing the tides is well known, and easilly calculated for the ocean surface, if not for all shorelines) and waves will be averaged out at the resolution of the radar used for altimetry.
-
Tom Curtis at 05:23 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
ranyl @7:
1) It is estimated that a 0.66 meter sea level will cover 26 thousand square kilometers of land. In contrast, the oceans have an area of 361 million square kilometers. Ergo, a 0.66 meter rise in sea level would require an expansion in volume of 238.3 x 10^12 cubic meters if the shore line was vertical such that no extra land was covered, and an additional 8.6 x 10^9 cubic meters to cover the land. That is, it would require an additional 0.004% volume to allow for the sloping shore line. So, while the effect you describe is real, it is also negligible.
2) The melting of floating ice actually raises sea level slightly due to the different densities of saline water (as found in the sea) and fresh water (as found in ice). Grounded ice, which by definition is not floating, and hence has more volume than an equivalent area of barely floating ice must raise sea level rise even more. Ergo when grounded ice is undercut be melting, that melting provides sufficient water to fill the cavity, and then some.
3) When ice shelves break up, the ice does not melt instantaneously. Rather, it hangs around as ice bergs, some of which can survive several years. Further, the volume of ice in any given ice shelf is not larger relative to the total mass loss from Antarctica or Greenland. So, while the break up of a large ice shelf may slightly accelerate sea level rise, it is unlikely to do so appreciably.
-
Tristan at 05:22 AM on 2 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
John @311
You neglected to answer my question.
There are large confidence intervals for many of the projected future scenarios. Those confidence intervals aren't hidden. Fortunately, climate science isn't confined within any single paper or projection. The current state of climate science represents a consilience of evidence from thousands of papers. Most climate scientists aren't saying 'exactly x will happen by year y', they are saying 'these are the range of things that are likely to happen, given current trends and models based on physical constraints, and it is smart money to acknowledge these likelihoods'.
-
Tristan at 05:14 AM on 2 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Watchdog @30
Taken alone, anything could be considered a 'poor measure of global climate'. Because the global climate includes the totality of litho-, hydro-,cryo-,atmo- and bio- spheres. That's why climate science looks at multiple lines of evidence within each domain, in order to examine what is happening.Sea Ice predictions/projections are not merely extrapolations of trends - that is what is known as a naive model. If that's your comprehension of what climate science is, you've been woefully misinformed.
-
JohnD11920 at 04:56 AM on 2 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
It's childish and unnecessarily insulting to suggest I don't understand concepts of conservation laws. Perhaps poor reading comprehension by some lead to that conclusion. I’m not sure. But I never suggested the concept was wrong or I didn’t make sense to my weak and feeble mind. And the thought that I don’t understand that a complex system is difficult to predict or understand instrumentation errors and sensitivities is ridiculous because that is my point…
I do indeed believe that it has to be a fact that CO2 has many negative effects (and really I thought I made that obvious and even stated that to begin with). Like I said however, what is disturbing to me is the religious-type fervor on the subject in particular the condescension (such as insulting people’s intelligence over expressing a caution when trusting a model that cannot be validated except over time) and lack of good predictability (using early 2000s as a reference for myself). I only posted because the pretentious attitudes and condescension are disgusting. I did not suggest it is not a problem. But it is important to remember that there has to be a large band of confidence by any model with so many factors.
Perhaps a major issue is only the poor predictions are making it to the media, but all I have seen in the past is the extreme scenarios that has not panned out. I’m not going to devote large amounts of time to researching this because it’s better for me to devote my time to my own industry, but I am skeptical of the level of confidence many have in the problem’s *rate* not its existence and the fervor around predictions. I’m not even saying that it’s overstated… I’m just saying there cannot be an enormous level of confidence in the rate in which the effects of the added heat occur. If someone posts again that I don’t understand the concept of a closed system or the 1st law, then I will be disappointed. The questions I raise are about the confidence in rates not the mechanism.
Moderator Response:[JH] You make numerous assertions in the above, some personal and some about the science. The tone of you personal assertions is argumentative and this argumentative tone should not be repeated in you future posts. Your assertions about the science are undocumented. If they are merely your personal opinion, they have little value in this venue.
-
Watchdog at 04:42 AM on 2 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
PhillippeChantreau@32
My placing "quotes" around my comment "relatively stable" is intended by me to convey the somewhat indistinct objective character of various "time period" terms, such as: "short", "long", "insufficient".
2014 evidences the Coldest Arctic Summer during our most recent 10yr time period. 2014 exhibited almost 2 million km2 more sea ice (area) during its Summer than had the Warmest Summer (2012) within that same 10 yr time period.
In post 20, I was referring to Total (Land & Sea) Antarctic Ice Mass as ad being a part of my suggestion that -> All Global Ice Volume Data (e.g., graphed against time) should be used for determining the affects of Global Ice upon Global Climate - rather than using only averaged Arctic sea ice fluctuations.
Phillippe@28 - You asked: "how many years of data are necessary to establish a statistically significant trend.", and I responded, "when it comes to me examining any Climate Change, the longer time periods to examine, the better."
IMO The key (unqualified) term above is "trend".
How far into the future can a 30yr Global Temp trend be extrapolated?
Is 30 yrs of temp data sufficient to establish historical Global Cooling and Warming periods which occur in cycles of 100's of years?
I exhibit this following graph (revised 2007) representing 2000 yrs of Global Temperatures constructed from 30yr temperature periods
In spite of any potential more-recent proposed reconstructions this graph still clearly evidences numerous longer-than-30yr periods of significant warming and cooling trends which cannot be realized from any singular 30yr trend.
http://jennifermarohasy.com/2007/11/2000-years-of-global-temperatures/ -
ryland at 04:22 AM on 2 April 2015Ipso proves impotent at curbing the Mail's climate misinformation
CBDunkerson. Why not just show smoke stacks belching out smoke? That gives a double whammy of CO2 plus very visible atmospheric pollution?
-
billthefrog at 04:09 AM on 2 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
@witsend
Is it possible that you are reading something into this article that was neither stated or intended? When a paper talks about California being "in the midst of its worst drought in over 1,200 years", that doesn't necessarily mean things were worse just over 1,200 years ago. (Or that 2,000 year old trees must therefore have lived through worse times.)
Over the 2013/14 winter, the UK experienced the exact opposite of the Golden/Brown State, and we had record levels of precipitation. However, the amount of misinterpretation surrounding the reporting of this event was simply jaw-dropping. How much was deliberate, and how much was accidental, is open to conjecture.
The longest running temperature & precipitation dataset from a fixed location anywhere in the UK, is that from the Radcliffe Meteorological Station at Oxford University. Although not completely continuous, this, nonetheless, has data stretching back to 1767.
Apart from some newspapers (and individuals) not appreciating the difference between a national record, and a merely local record, many people appeared confused by the phrase "wettest since 1767". In many quarters, this was immediately taken to mean that 1766 must, perforce, have been wetter still.
Some of the blame must be laid at the door of jounalists who are either too lazy, or too incompetent, to address any ambiguity. However, the onus is also on the reader not to extrapolate beyond what was said.
On the other hand, if it was specifically spelled out somewhere that things were worse 1,000 or 1,200 years ago, and I simply failed to notice that, then it looks like I need to arrange a visit to the optician. (And that, of course, would also mean that it was mea culpa time yet again.)
cheers bill f
-
PhilippeChantreau at 03:57 AM on 2 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Watchdog, you still don't get it. Statistical significance is not a matter of opinion. It is calculated by mathematical methods. Given a specific time series, one can determine what is the minimum sample size to establish statistical significance. 10 years is not enough. Arctic temperatures have increased so much that saying this was the coldest summer in 10 years or the most ice in 10 years is like saying this is the coldest that a sauna room has been in the past 30 minutes. It is of no value at best, dishonest at worst. By the same token, referencing a paper that points out regional changes in ice mass balance and trumpeting that it shows overall positive ice mass balance when the conclusion of the paper says opposite is called what exactly? You do not comment on that either, I note.
The graph from Marohasy's web site comes from Spencer and has numerous known issues. Marohasy is not a reliable source for anything, as is demonstrated by her history. If you want to talk about the science, reference science publications, not blog posts. You are also totally silent on the sea ice volume studies mentioned earlier. How can you possibly expect to be taken seriously? Do you realize how weak your argumentation is? Reminds me of a certain sketch in which it is argued that the parrot is just resting...
-
billthefrog at 03:15 AM on 2 April 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #13
D218O ?
Why stop there? We could have Tritium instead, and the liquid could be methanol. (As the half life for Tritium's Beta decay is about 12.3 years, it shouldn't melt the ice too quickly.)
This does, however, add a whole new dimension to the term "getting blind drunk".
cheers bill f (completely teetotal, except when not)
-
Watchdog at 03:10 AM on 2 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
PhillippeChantreau@32
My placing "quotes" around my comment "relatively stable" is intended by me to convey the somewhat indistinct objective character of various "time period" terms, such as: "short", "long", "insufficient".
2014 evidences the Coldest Arctic Summer during our most recent 10yr time period. 2014 exhibited almost 2 million km2 more sea ice (area) during its Summer than had the Warmest Summer (2012) within that same 10 yr time period.
In post 20, I was referring to Total (Land & Sea) Antarctic Ice Mass as ad being a part of my suggestion that -> All Global Ice Volume Data (e.g., graphed against time) should be used for determining the affects of Global Ice upon Global Climate - rather than using only averaged Arctic sea ice fluctuations.
Phillippe@28 - You asked: "how many years of data are necessary to establish a statistically significant trend.", and I responded, "when it comes to me examining any Climate Change, the longer time periods to examine, the better."
IMO The key (unqualified) term above is "trend".
How far into the future can a 30yr Global Temp trend be extrapolated?
Is 30 yrs of temp data sufficient to establish historical Global Cooling and Warming periods which occur in cycles of 100's of years?
I exhibit this following graph (revised 2007) representing 2000 yrs of Global Temperatures constructed from 30yr temperature periods
In spite of any potential more-recent proposed reconstructions this graph still clearly evidences numerous longer-than-30yr periods of significant warming and cooling trends which cannot be realized from any singular 30yr trend.
http://jennifermarohasy.com/2007/11/2000-years-of-global-temperatures/Moderator Response:[JH] You have now fallen through the thin ice of sloganeering. Any future posts by you along the lines of the above will be summarily deleted.
-
CBDunkerson at 02:29 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
sgbotsford, the answer to all your questions is found in the caption for the first image in the article above, "...as measured by satellite altimetry".
-
PhilippeChantreau at 01:25 AM on 2 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
John D, skepticism is a good thing indeed, when it is sincere. Refusing to acknowledge an entire body of evidence because one dislikes what it implies is not skepticism. Believing ideas that are not supported by evidence because they are more appealing or conform to one's preferred ideology is not skepticism. Stating that, in essence, one's ignorance is just as good as a bunch of other poeple's expertise is not skepticism. Choosing to trust an isolated fruitcake or a charlatan vs a large number of experts with converging results is not skepticism. The last time that I know of that a skeptic went about it with sincerity, the result was the BEST study. That's sincere.
You make claims of "blind faith" and inaccurate predictions that beg for further development. The thread mentioned higher would be the place to go for that.
-
sgbotsford at 01:19 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Education please: How do you measure sea level to the accuracy needed to determine a rise?
You are measuring something that:
- has a wave hitting shore several times a minute with a magnitude of a few inches to many feet.
- Tides that have a daily and a monthly cycle of several feet.
- Have storm surges, and smaller disturbances that push water toward/away from shore, on a scale of individual fronts, as well as longer established winds such as the trades and the westerlies.
- Strong cyclonic storms create a pile of water away from the shore. Anti-cyclones a hole in the water.
As a younger pup I used to do canoe expeditions that would finish on Lake Winnipeg. That lake, much smaller than an ocean was subject to 'wind tides'. Water level in the south basin could rise 2-3 feet with a strong northwesterly, common after a major storm passed.
The short term effects I can see being smoothed out by locating your guage in a tube of porous material such as gravel or sand. This has enough drag to smooth out the waves. But how do you deal with the long term cycles?
Assuming that you get one instrument readings ironed out, how do you merge the readings for a world, given that the guages are not well distributed over the world's coast lines, and there is a lot of ocean that isn't handy to a coast line?
This would be a good education piece.
-
bozzza at 00:31 AM on 2 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
Cool,.. but did they look healthy? More to the point: did they look like the healthiest gum-trees you've ever seen?
-
bozzza at 00:27 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
If we are looking at a linear increase since the 1990s that means the economic rise of China hasn't been reflected in the graph and presumably we all still have this to look forward to.
-
bozzza at 00:19 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Regarding paragraph three: I'd be assuming this factor is close to negligible! (Never thought about it but so nice point.)
-
bozzza at 00:12 AM on 2 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
@ 307, how can an engineer not understand tolerance value for instrumentation?
-
bozzza at 00:10 AM on 2 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
John D, being a skeptic is one thing but lying is another.
-
ranyl at 00:04 AM on 2 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Sea level rise is interesting.
It looks like an almost linear rate of increase however the rate has accelerated since the 1990's.
Also not sure if accounted for or what influence this has, however seeing the sea as a wide flat rimmed basin, as the level goes up doesn't the surface area covered by the sea go up also, and therefore doesn't the volume expansion needed just to miantian the same rate of sea level rise have to be accelerating?
And when melting the underneath of an underwater grounded icesheet (e.g. Pine Island), presuming the above sea level proportion is still effectively supported, won't sea levels fall slightly as the ice in the melted hollow below sea level is replaced by water due to ice's larger volume? Sure this is a tiny effect, although large parts of Greenland and Antarctic do have below sea level and seabed grounded icesheets.
And considering those underwater ground icesheets further, if the above sea level icesheet that is supported below by a column of ice that reaches to the seabed (i.e. the icesheet above sea level is not floating and therefore not displacing sea water at the moment), suddenly became unstable due the melting by the warm bottom water undermining the below sea water level ice's supporting structure to the point of failure, such that the now unsupported part of the ice sheet would effectively suddenly falling into the sea, could relatively rapid jumps in sea level occur? Presuming the above sea level ice sheet would falls slowly and gracefully into the sea.
Sort of like undermining castles walls, do the above sea level parts of the below sea level icesheets have the potential to basically fall into the sea as there bases become more and more undermined??
Could that be a sudden event?
Suppose depnends on how fast and extensive the undermining is?
-
John Hartz at 22:48 PM on 1 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Directly related to the current mild temperature of the Western Pacific Ocean...
Category 5 Super Typhoon Maysak is packing sustained winds of at least 160 miles per hour as it takes aim at the tiny island of Yap in the Caroline Islands on Tuesday. The typhoon is the third of the year so far, which sets a record for the most typhoons so early in the Western Pacific typhoon season, according to meteorologist Jeff Masters of Weather Underground.
The storm is rarer still when looking only at the record of typhoons that reached an intensity of Category 3 or stronger before April 1. Such typhoons are known as major typhoons.
Super Typhoon Maysak marks the first time two major typhoons have occurred in the Western Pacific before April (the other was Typhoon Higos). The storm is even rivaling the strongest storms on record for so early in the year, which were Super Typhoon Ophelia in 1958 and Super Typhoon Mitag, which occurred in March 2002. The typical Western Pacific typhoon season runs from April through October.
Category 5 Super Typhoon Maysak sets record in Western Pacific by Andrew Freedman, Mashable, Mar 31, 2015
-
CBDunkerson at 22:23 PM on 1 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
JohnD wrote, "I have never seen an accurate prediction of global temperatures over any appreciable period of time."
This can only be true if you haven't looked very hard or are definining 'accurate' and/or 'appreciable' in ways that I would consider unreasonable. I mean, look at the list of top climate myths at the upper left part of this page. Number six is 'Models are unreliable'.
Climate models can not predict volcanic eruptions or fluctuations in various cycles (e.g. ~11 year solar cycle, ~30 year PDO, et cetera)... which is why they do multiple runs assuming different variations for these factors. Observed warming has consistently been within the range shown by those scenarios, and when you plug in a scenario matching the actual unpredicted variations you get results matching the actual observations. If that isn't 'accurate' then you're using the word in a way which reverses its most common meaning.
-
Stephen Baines at 22:23 PM on 1 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Yes, Maybe I jumped the gun on NOAA's official call of a full fledged El Nino episode as it seems a fait accompli. The fact that different organizations differ indicates how weak the El Nino conditions are.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 21:17 PM on 1 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
"if you want to see a good Gum(tree) don't look for it in Australia."
Reminds me of a strange travel experience. Driving through southern Portugal when suddenly all we could smell was Australia - Gum-Trees everywhere.
-
bozzza at 20:59 PM on 1 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
This reminds me of a saying they have here in Australia: if you want to see a good Gum(tree) don't look for it in Australia.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 14:02 PM on 1 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Stephen Baines @1
Based on the NOAA method of 5 consecutive 3 month averages of the Nino 3.4 region being 0.5 C or more above the baseline value the soom to b published JFM value is likely to establish that an El Nino event is occuring and it started in the SON 2014 set of months.
However, the latest Australian Meteorological ENSO wrap up (issued March 31), does not yet consider the conditions to have reached El Nino status.
So based on NOAA methods for indicating El Nino the warm event has been with us for a while, but the Australians do not think El Nino conditions have even started, it is only near to occuring.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 12:39 PM on 1 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
JohnD
The key question isn't about a lack of predictbility. It is about what is reasonable to be able expect of prediction. If models are achieving the degree of predictability that one would expect of them given the nature of the problem being studied, then they are doing pretty well.
As an engineer, do you regard the acceptance of the basic Conservation Laws - Energy, Mass, Momentum etc - as 'blind faith'? Because that is what climate is; the application of the basic laws of physics. At its very simplest, Climate is an application of the 1st Law of Thermodynamics.
If we maintain the energy flow into a system while restricting energy flow out of that system, is expecting that the total energy within the system will increase, and thus tmperatures increase 'blind faith'? Is the 1st Law 'blind faith'?
-
Tristan at 11:28 AM on 1 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
Hi JohnD
Care to provide an example of blind faith in modelling within climate science?
-
JohnD11920 at 11:14 AM on 1 April 2015It hasn't warmed since 1998
Let me just say I am not skeptical of the fact the globe is warming so don’t think my comment is guided by that bias, but I do see a lack of predictability that I know is being worked on.
I too am an engineer. I’m not going to discuss in depth the notion that mechanical engineers have an unusual variation in skill. I assume the belief held by bozzza is that all scientists are equally brilliant and some of them haven’t barely gotten by in school? Futile point to say the least. There are poor scientists and poor engineers. Not realizing that is disappointing. I am not surprised how several people comment on the profession like it is subordinate. Many engineers view scientists the same way, but it is seen as a study that is ignorant of application, blind beyond their own work/views, completely void of practical understanding, and contributes nothing directly to the world. I’m kidding mostly – so relax.
But my point is that after decades of engineering research and enormous amounts of time working for/in/with teams of many different disciplines and backgrounds both scientific and engineering, the thing I have found to be a problem across the board is the lack of understanding most people have of their own inabilities. I have seen people work on something for 10 years and think they understand every facet of the topic because they explained why something has happened in the past, but couldn’t predict a thing. But the truth is their models were terrible and without a practical view they would never understood that and improve.
I have never seen an accurate prediction of global temperatures over any appreciable period of time. We should be very grateful for skepticism. Without it we would be worshiping the sun and sacrificing each other. Skepticism drives improvement. Blind faith in modeling is a very serious problem and outside academia (or at least in industry where the risk of error is critical as it should be for global warming) this is well understood.
-
witsend at 10:45 AM on 1 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
Think about this - the current drought is compared to drought 1000 years ago by looking at tree rings. Obviously, some trees lived through the drought then, because there are trees 2,000 years old and more in California. So, devastating as this worsening climate change heat and drought will become, it isn't anything SO FAR trees couldn't survive before. The question should be, why did they ALL start dying prematurely several years ago - why is the entire state brown? Live oaks, Monterey Cypress, all sorts of conifers, every species in, say, the Santa Cruz Arboretum, even those that are extremely drought resistent imported from Australia have been dying prematurely for several years - why is there an unstoppable epidemic of beetles? http://www.latimes.com/science/la-sci-beetle-trees-20140530-story.html#page=1
Could it be that the foresters are missing a huge piece of the puzzle??
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sn1Xy_j48k0
Why are Europeans and the Chinese so much more willing to examine the underlying cause? https://royalsociety.org/~/media/Royal_Society_Content/policy/publications/2008/7925.pdf
http://www.scmp.com/lifestyle/technology/article/1749736/nitrogen-emissions-smog-threatens-massacre-worlds-forests
-
michael sweet at 10:23 AM on 1 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Wili,
The GRACE satellite can measure where the water is coming from. We will undoubtedly hear in 6-18 months where that is. If more water moves around during this El Nino cycle (as is likely) it may get complicated. Until then we all get to cherish our pet theories. (I am interested in your idea also).
-
michael sweet at 10:18 AM on 1 April 2015Heat from the Earth’s interior does not control climate
Maark,
The concluding aragraph of your reference reads:
"Regardless of the eventual connections to be established between the solid Earth and climate, Dickey said the solid Earth's impacts on climate are still dwarfed by the much larger effects of human-produced greenhouse gases. "The solid Earth plays a role, but the ultimate solution to addressing climate change remains in our hands," she concluded."
My emphasis. The scientists involved think the correlation they found is interesting but Humans cause AGW.
-
Tom Curtis at 10:14 AM on 1 April 2015Heat from the Earth’s interior does not control climate
I should add to my comment @28 that the NASA scientists involved are arguing for a correlation between temperature as adjusted to remove anthropogenic influences, and the Length Of Day (LOD). They are not arguing, as Maark does, that this effect is brougth about by fluctuations in geothermal heat. Ergo only my third point is directly relevant to their actual theory.
-
Tom Curtis at 09:38 AM on 1 April 2015Heat from the Earth’s interior does not control climate
Maark @27, that hypothesis faces several major obstacles. First is the claim that it accounts for plus or minus 0.2 C in the Earths Global Mean Surface Temperature (GMST). In terms of power, that requires fluctuations of 0.8 W/m^2, or approximately 9 times the average energy flow from the Earth's interior. That is implausible on the positive side, but absurd on the negative side (where it would require the energy to be flowing into the interior rather than out of it).
Second, such a large change in energy flow would be evident in borehole temperature reconstructions, but is not:
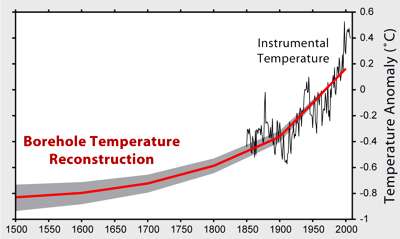
Third, and on their own evidence, the theory fails to match observations prior to 1900:
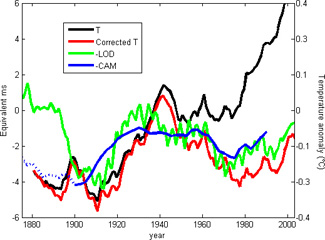
So, at best they show an emperical fit over one cycle length, but a complete mismatch prior to that one cycle. That is hardly compelling evidence.
-
Watchdog at 09:22 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
John Hartz@33, Interesting reading.
-
John Hartz at 06:11 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Recommended supplemental reading:
Global Warming Hole by James Hansen, Mar 31, 2015
-
Maaark at 06:07 AM on 1 April 2015Heat from the Earth’s interior does not control climate
The hypothesis of earth core heat affecting sea temperature and atmosphere should be taken more seriously. NASA takes it seriously enough to research it. Here is a link to their 2011 study which shows significant correlation but inconclusive in the end. Maybe the variable to consider is not overall increased heat but movement of the heat source which changes exposure to different areas.
http://climate.nasa.gov/news/489/
-
wili at 05:03 AM on 1 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
From the description under the first figure: "...may signal the drying out of the major continental basins in the tropics."
Is this really the only likely explanation? Don't we expect an acceleration in slr at some point from increasing losses from GIS and WAIS among others? Haven't we been hearing more about further evidence of destabilization of both? How would we know if increase loss from these source are or are not part of the cause of the recent increase in the rate of slr? -
GFW at 05:02 AM on 1 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
One suggestion that would greatly improve the ability of that scatter plot to convey information: Color code the dots along a spectrum from the earliest year to the latest year. That way it's obvious at a glance if there is an overall trend. -
jja at 03:50 AM on 1 April 2015Global warming and drought are turning the Golden State brown
one planet @4
The temperature effects that the earth is experiencing today is at the emissions levels from 2005. This is without considering the substantial dimming and albedo effects of short-lived anthropogeic aerosols. If you include those factors the earth system response may well be operating at forcing values consistent with 1994 levels, when Russia had its emissions slowdown.
It is extremely unlikely that, in the face of rapid 'catch-up' of recent emisisons increases and the reduction of chinese aerosols due to economic cycles and pollution mitigation efforts, that the Summer Arctic Sea ice will last the next 10 years.
This will produce a significant northern push of the Hadley Cell and exacerbate the perpetual drought that the U.S. southwest has experienced these last 15 years.
For more info see: http://www.latimes.com/science/sciencenow/la-sci-sn-climate-drought-california-20150223-story.htmlModerator Response:[JH] Link activated.
-
Stephen Baines at 02:05 AM on 1 April 2015Sea Level Rise is Spiking Sharply
Technically speaking, we are in an El Nino now, albeit a very weak one. So it may not come down top whether an El Nino develops, but whether this one persists and intensifies.
Interestingly almost all of the statistical models reviewed by NOAA are predicting a shift to neutral conditions, whereas most of the more mechanistic models are predicting a strengthening of the El Nino.
-
PhilippeChantreau at 01:06 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Watchdog, the statement with which I have a problem has been clearly established. You made it in post# 9 above. You exact words were: "Arctic Climate is relatively stable from 2005 to today." Such a statement is not a matter of opinion. It can be made only if supported by data. By the same token, how many years are necessary to establish a significant trend with that data is not a matter of opinion either. That's why I'm asking. You say the longer the better, so 10 years seems to not meet your own preference.
In post #20 you made a bold statement with an exclamation point: "Antarctica's Land Ice Mass is Growing!" It is impossible to honestly not construe that this means the whole of Antarctica's land based ice mass.
You supported that statement with Memin et al, 2014. Two other contributors above quoted the conclusion section of the paper, which I re-quote here:"Comparing our mass-balance budget with that from King et al. (2012) for AIS regions not covered by Envisat, we obtained that the AIS lost −47±35 Gt/yr in good agreement with recent published results and validating our methodology." I do not see how one can use this paper to make the bold statement you made in post #20, while there is a weight of evidence pointing to negative mass balance for the whole continent. You diverted attention from that fact by pointing at regional changes, as there are unfortunately no squirrels to point toward in Antarctica.
The NASA article in which you quoted the uncertainty about land based ice mass balance is dated from 1999. How much research has since been published on the subject?
You said in post # 20 that one should consider the overall, two-hemispheres ice volume. It is not entirely clear whether this applied to sea ice or land based ice. Ice volume is not the best metric for land based ice sheets, whose mass is usually the object of study and gives a much better idea of the true quantity present. So I assume that you meant sea ice volume. Unlike land ice, sea ice does not undergo compression over the years, but its thickness greatly affects the true quantity present, so volume really is the best metric, you were right on that.
DSL cited 3 papers that are sea ice volume studies, showing that the Arctic loss is about an order of magnitude greater. That's a factor of 1000, not exactly benign. You responded by a comparison of sea ice area numbers, in contradiction with your own claim earlier that ice volume should be considered.
I'll make the mother of all understatements by saying I'm not impressed.
-
DSL at 00:27 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
My final comment should have read as follows:
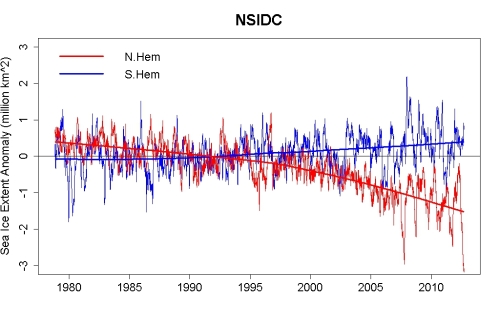
As you can see, the positive winter trend over the satellite period (35 years) in the Antarctic is half of what the negative winter trend is in the Arctic. The Antarctic summer trend, also positive, is 8x less than the negative Arctic summer trend.
-
KR at 00:24 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Watchdog - Total Antarctic mass balance is negative, declining, and all the evidence points to that loss accelerating. The Memin paper you've referenced is discussing snow and ice height, not mass balance (only one side of the equation), and certainly is not in contradiction to other estimates of mass loss. It's very very certain that Arctic, Antarctic, and Greenland ice sheets are diminishing, despite your misinterpretation of htat paper.
You've presented some factoids (somewhat smaller than a fact, due to lack of context) regarding Antarctic ice. What your numbers neglect is seasonal variation - when looking at longer term climate change you need to look at trends in anomalies, in change. For example, here's some data charted (and discussed by) Tamino:
[Seasonal cycle removed - Source]
As is quite clear, the increase in the Antarctic is considerably less than the decrease in the Arctic.
Over on RealClimate there's a very good discussion of Antarctic sea ice, it's effect on climate, and the very different causes of ice changes there as compared to the Arctic. I would suggest you read it. The take-home point is that while counter-intuitive, those changes are themselves due to climate change.
-
DSL at 00:23 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Shorter Watchdog:
Ice mass is increasing in some places and decreasing in other places. I'm not willing to do the math, and I'm going to ignore comprehensive analyses such as Shepherd et al. 2012.Your comparison of sea ice area is irrelevant or a red herring with regards to your earlier comments about volume--which I addressed. Area is not volume.
Antarctic sea ice increases by about 13 million km2 each SH winter (not 16 m km2). You'll note from the same link that it decreases by about the same amount each SH summer. The area anomalies within the last few years have almost cancelled out, but, again, over the last 35 years, the Arctic has lost much more area than the Antarctic has gained.
The greatest Antarctic winter maximum area for the satellite period (up through 2013 — I haven't updated my data) is 16.232 km2 (2007). The lowest max in the period is 14.604 million km2 (1986). The linear trend for the period is +19,926 km2 per year. The difference between the two is 1.628 million km2.The greatest summer minimum in area is 2.473 million km2 (2003). The lowest summer minimum is 1.296 million km2 (1993). The difference between the two is 1.177 million km2. The linear trend for the period is +8965 km2.
The greatest Arctic winter maximum area for the satellite period (up through 2014) is 15.01 million km2. The lowest max in the period is 13.04 million km2. The linear trend for the period is -38,213 km2. The difference between the two is 1.97 million km2.
The greatest summer minimum in area is 5.59 million km2. The lowest summer minimum is 2.28 million km2. The difference between the two is 3.31 million km2. The linear trend for the period is -70,309 km2.
As you can see, winter gain over the satellite period (35 years) in the Antarctic is half of what winter loss is in the Arctic. Antarctic summer gain is 8x less than Arctic summer loss.
-
PhilippeChantreau at 00:13 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Watchdog, you are not answering any of my 2 questions. You made the assertion that Arctic climate was stable over the past 10 years. I'm asking you on what time series you are basing this claim and, for the time series considered, how many years of data are necessary to establish a statistically significant trend.
-
Stephan at 00:11 AM on 1 April 2015Scientists link Arctic warming to intense summer heatwaves in the northern hemisphere
Re. 20, Watchdog: That seems to be a very selective reading of "Snow- and ice-height change in Antarctica from satellite gravimetry and altimetry data". From the conclusion of the paper: "Comparing our mass-balance budget with that from King et al. (2012) for AIS regions not covered by Envisat, we obtained that the AIS lost −47±35 Gt/yr in good agreement with recent published results and validating our methodology."
So while there are some areas where snow accumulation is contributing to ice mass, overall the balance is significantly negative.
-
witsend at 00:01 AM on 1 April 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
A well-known effect of pollution exposure on plants is increased insect activity. Vegetation loses natural immunity as it becomes weakened from repairing the damage from absorbing ozone and it also is caustic, eating away at protective way coating on leaves, opening the way to biotic attacks. Apparently, this occurred during the PETM extinction: http://www.pnas.org/content/105/6/1960.short
Prev 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 Next































 Arguments
Arguments