Recent Comments
Prev 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 Next
Comments 31801 to 31850:
-
Daniel Bailey at 06:30 AM on 24 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
The Greenland cited data is only indicative of regional trends over the period you indicate. You need to support your contentions with a global reconstruction.
-
Watchdog at 06:22 AM on 24 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
ranyl, My "1000 yr Global Cooling period during the last glaciation period",
is also supported by Greenland Ice Core Data.The following graph is based upon GreenLand Ice Core Data.
NOTE: Multiple significant cyclical Cooling & Warming Temperature periods from Today on back to 17kya, including extreme Cooling & Warming Climate Change from 10kya on back which occurred during the last glaciation.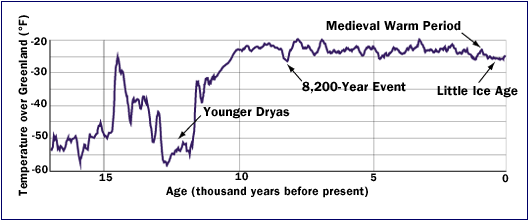
My focus has obviously been upon obvious negative effects of extreme Global Cooling upon the Biota, of which one known cause is the Atmospheric Blockage of Solar Radiation due to e.g, Volcanic Emissions.
ranyl - Can CO2 - which is said to be the cause of Global Warming - also be the cause of Global Cooling? -
uncletimrob at 05:51 AM on 24 March 2015New measurements confirm extra heating from our carbon dioxide
Thank you. One of my interests is amateur radio and I've been working with a fellow ham on IR cloudbounce communication. This is a nice lok at IR from another perspective. A very interesting article.
-
jja at 05:16 AM on 24 March 2015New measurements confirm extra heating from our carbon dioxide
Interestingly, this quote from the abstract:
This (CO2 component warming) is approximately ten per cent of the trend in downwelling longwave radiation5, 6, 7And that the overall increase in the rates of warming being experienced by the planet (also called the Top of Atmosphere energy inbalance, or TOA) is growing at a much more rapid rate. This is especially true when one considers that the emissions of Chinese aerosols during this same period increased by over 400%
-
howardlee at 04:33 AM on 24 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
I found this statement in the introduction of the just-released textbook: "Volcanism and Global Environmental Change" edited by Schmidt, Fristad and Elkins-Tanton: "The composition of some past volcanically-released gases are frighteningly evocative of anthropogenic emissions..." (my emphasis).
-
howardlee at 04:22 AM on 24 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
ginckgo @1Methanosarcina may possibly have played a role in the P-T extinction but I'm skeptical of the Rothman et al theory for the following reasons:
It is a one-off explanation, whereas LIPs have a criminal record – they are a serial killer with a consistent “MO”: greenhouse gas release, warming, rising sea levels, ocean acidification and anoxia.
Rothman et al use a 82-million-years-wide time window for the horizontal gene transfer that enabled the runaway methanogenesis. Even if we overlook the often elastic nature of molecular clocks, and that their clock is not calibrated to fossils, that’s a time window extending from the lower Permian to the lowest Jurassic. For the mutation to have happened exactly coincident with the Siberian Traps eruptions is just too fortuitous to be probable. The authors explain the coincidence by citing nickel fertilization by the Siberian Traps eruptions – but that would place the mutation, even more fortuitously, as having occurred between the Emeishan and Siberian LIPs, or else we should have had the Guadeloupian Mass Extinction.
-
New measurements confirm extra heating from our carbon dioxide
Yep. The denialati were yelping about this paper last month (archived link). With the usual nonsense references to Salby, volcanos, "it's the sun", 2nd law of thermodynamics, etc...
-
PhilippeChantreau at 01:47 AM on 24 March 2015New measurements confirm extra heating from our carbon dioxide
Now prepare for the onslaught of flat-earthing pseudo physics that some will undoubtedly launch following these results...
-
wili at 00:56 AM on 24 March 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #12B
And...Cruz is now running for president.
-
DSL at 00:31 AM on 24 March 2015DMI show cooling Arctic
bozzza, a little more argument would be helpful.
-
ranyl at 23:35 PM on 23 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
Well Watchdog I refer to Howardlee article and references within for CO2 mechanisms and James Mason articles. (http://www.skepticalscience.com/pollution-part-2.html)
However not sure why you feel it necessary to point out CO2 is colourless, so is sarin!
And the publishers pointing out CO2 role are very aware of the effects of eruptions and bolides (although the previaling opinion now is that the global climate effects are more like 5-20years not the 1000 years as you suggest.
e.g. http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn23458-supervolcano-eruptions-may-not-be-so-deadly-after-all.html#.VRAVi2ezWdI
Therefore as I have no problems with accepting all the effects from a volcanic eruption of bollide impact cause major issues, just no mass extinctions, unless a CO2 impulse part of the picture.
Again what is about CO2 the makes you feel it is not involved as a pivotal player?
There must be something for all the scientific evidence and expert opinion is, that a large CO2 impulse can easily cause major prolonged global ecosystem disturbance that can reach the scale of a mass extinction, yet you don't, therefore just wondering how come that is?
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 20:22 PM on 23 March 2015Antarctica is gaining ice
bozzza
That might have been a fair possibility a week ago. Now a late rise in extent would look less likely. That said, a record low maximum extent doesn't tell us what the minimum in September will look like. 2012 was the record minimum, but it certainly wasn't an unusually low maximum. It all depends on the weather up there over the next 6 months.
Regions to watch:
- The Kara and Laptev Seas. They seem to have been stubbonly refusing to thicken over this winter so might melt out quickly.
- The central Arctic Basin above the Barentz and Kara. Much of the ice there seems to be quite broken up - more easily moved around, splashed with water etc.
- The Beaufort Sea. Currently a lot of the older, thicker ice is there (and the Canadian Archepelago). If the weather applies a blow torch to that, while it may not contribute much to what happens to Extent and Area, it could have a big impact on what happens to Volume.
If you haven't discovered it already, Neven's Arctic Sea Ice Blog is a treasure house:
- The Arctic Sea Ice Graphics page give you links to loads of different resources, webcams, long term data sets etc. If a Polar Bear is going to get it's picture taken by a drifting ice buoy, somone at Neven's blog will probably spot it.
- His Forum has a lot of true Arctic Nerds (in the very best sense of the word) who can dissect data you may not have even heard of. One regular (Wipneus) produces his own area/extent calculations by combining the best of the raw data feeds from multiple satellites. A regular here at SkS, Jim Hunt, can wax lyrical about what the thermocouple tree below a buoy can tell us about the mixing of waters below the ice - when he isn't tearing David Rose at the Mail in England a 'new one'.
-
uncletimrob at 20:12 PM on 23 March 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #12B
re: Ted Cruz goes full Orwell. Well who voted him in? He's not a scientist but feels capable to mock those who are and deny science because he either is to thick to understand it, or frankly doesn't care because he has a political agenda ( keep voting for me ). "You get what you pay for" pollitically is "you get who you vote for". Until these morons are voted out we will continue to reap the benefits of their limited intellect or ability to reconcile ther beliefs with REAL science.
-
bozzza at 16:35 PM on 23 March 2015DMI show cooling Arctic
I think figure 1 gives the deniers some ammunition to work with.
-
bozzza at 15:57 PM on 23 March 2015We didn't have global warming during the Industrial Revolution
I like the graph: it has mutiple inflection points that may serve us all well as a time guide. For instance I might like to reflect on the Keeling Curve in comparison to it, for example--> it is my opinion that the rise of China hasn't been reflected in the Keeling Curve yet though I am willing to be corrected.
-
Tom Curtis at 15:49 PM on 23 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
angela @22:
"I speak for the genral public..."
Really? Who appointed you to that position? And can we see the documentation showing that you have been appointed to "speak for the general public". Personally I only ever speak for myself. That is probably because I am flabberghasted at the arrogance shown by people who claim to speak for the "the general public" (or whoever else they want to drag in to give their questions unwarrented authority).
Moderator Response:[TD] I believe Angela is a bot, so I've deleted her/its comments. Angela is quite welcome to prove me wrong by posting a comment having more substance.
-
bozzza at 15:42 PM on 23 March 2015Climatology versus Pseudoscience book tests whose predictions have been right
@10, regarding contributors that work for government departments these people go from working in the field and contributing data to the desk jobs of organising the reports and analysis and finally perhaps rise to the rank of giving them to ministers. It can take 30 years to get to these latter stages of which none are more important than the other.
-
bozzza at 15:08 PM on 23 March 2015Antarctica is gaining ice
The year 2010-2011 for the Arctic, (from here) , shows a late peak... not to mention a very flat projection towards said late peak. The following year, 2011-2012, didn't seem to suffer in terms of ice extent!!
From this may I be permitted to guess that we perhaps haven't seen the maximum ice extent for 2014-2015 yet??
-
denisaf at 13:02 PM on 23 March 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #12B
A major point missing in the discussion of water usage is the existing commitmnet to use water in the operation of many aspects of infrastructre operation and maintenence. For example, thermal power stations use vast quntities of cooling water. Decisions about using water more effectively are constrained by these commitments.
-
John Mason at 12:33 PM on 23 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
Bill - sort of spot-on! Certain elements may through their similar properties substitute directly for Zr in zircon. U, Th and Hf are examples. However, lead is not one of these elements. Its non-radiogenic "primordial" isotope, Pb 204, does not occur in zircons. Any Pb that is present within a zircon crystal is therefore a product of radioactive decay - isotopes like Pb 207 and 208 - and that's why these tiny crystals are proving such excellent geochronometers.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 11:04 AM on 23 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
Chriskoz
In addition to JM's comment, we need to remember the roughly logarithmc nature of the CO2 forcing. John has described a rise from aeound 2000 ppm up to around 8000 ppm - 2 doublings. A comparble change for us is a rise from 280 to 1120 ppm. So we only need to cause a rise of 840 ppm to produce a comparable forcing to a roughly 5000-6000 ppm change back then - around 6 or 7 times different.
So the ratio you use of 27,000 to 1,000 should actually be looked at as more like 4-5,000 to 1,000. Obviously if we can restrict emissions to 1000 GTonnes then we will hopefully be OK. But emissions of several 1,000 GTonnes are certainly achievable if we don't achieve restrictions. So an impact that is at least a significant proportion of the impact of the end-Permian certainly seems plausible if we don't act.
Even an end-Permian-lite would still be disastrous for a human population for 10 billion or so people.Of course this relativity only applies to the radiative forcing aspect. The ratio of severity for ocean acidification will be diffferent.
-
Watchdog at 04:38 AM on 23 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
ranyl @53 - You asked me: "Watchdog, as howardlee's research is extensive and the evidence convinving, what is it about CO2 being the primary murder weapon that makes you feel that this possibility is in error?"
Great Question
All published science research connected with the K/T extinction have also been "extensive with convincing evidences". And as howardlee notes, "The case is probably not closed".
Currently, the answer to the overall question is akin to a jig-saw puzzle; all of whose pieces have neither been clearly identified as yet; nor, therefore, can presently be assembled into a finalized overall picture.
•
Frontnotes concerning the deleterious effects of asteroidal impacts and volcanic particulate and aerosol emissions upon biotic life..
V. Rough Quantification of Chicxulub's Effects upon North America:
Chicxulub's energy is equivalent to 100,000,000 - 1MT HBombs
One 1MT HBomb creates a crater 0.2 miles in diameter and 0.04 miles deep.
It's energy converts to: shockblast, thermal, seismic waves and ejecta debris
Within a circle 3.4 miles in diameter c.98% of life is killed.
Serious damage extends out to a circle c. 10 miles in diameter.
Moderate damage occurs out to a circle c. 20 miles in diameter.
•
Chicxulub's energy of c.10^8 1MT HBombs - created a crater variously estimated to be c. 100 miles in diameter and c. 12 miles in depth.
Its arrival angle is estimated to be 20° to 30° from the horizontal with a general directional heading toward the remainder of North America.
“These asymmetric signatures suggest a trajectory for the Chicxulub bolide from the southeast to the northwest at a 20°–30° angle from the horizontal. As a result, biotic extinctions may have been most severe and catastrophic in the Northern Hemisphere.” [url]http://geology.geoscienceworld.org/content/24/11/963.abstract[/url]
•
Asteroidal Craters and Antipodal Locations:
In addition to Chicxulub (not necessarily connected with Deccan Traps), evidences exist for 2 or more major asteroidal impacts occurring c. 65MYA.
1. Antipodal location of the Deccan Traps is at the Eastern Pacific, whose seafloor evidences a major asteroidal impact.
2. A proposed crater location - 2.5 times the diameter of Chicxulub - lies East and South of Mumbai, India
[url]http://www.dinodatabase.com/dinothry.asp[/url]
[url]https://gsa.confex.com/gsa/2003AM/finalprogram/abstract_58126.htm[/img]
Comparative Volcanic Eruption Effects upon Global Temperature
On June 15, 1991, Mt. Pinatubo erupted, spewing Ash Dust, Smoke and 30 Million Tons of Sulphur Dioxide into the stratosphere. It's ash and aerosols plume was 250 miles wide, reaching an altitude of 34km.
The SO2 formed into sulphuric acid which depleted the Ozone Layer.
From 1991 to 1993, average global temps declined by 0.5°C.
In 1992 the USA experienced its coldest summer in 77 yrs.
A combination of ash particulates, smoke, and aerosol droplets of H2SO4 (see: noted historical “darkening of the skies” events) into the stratosphere lowers Solar Radiation arriving to Earth, thus, historical Lowering of Global Temperatures and ensuing widespread impact upon the biota.
Size Comparison of Historical Ejecta Events
Volume of Ejecta of 1991AD Pinatubo has been estimated at 2 cubic miles
Ejecta from 1883AD Krakatoa was Twice that of Pinatubo.
1815AD Tambora was 10 times larger than Krakatoa.
10,000BCE Toba Ejecta was 2,800 cubic km: 100X larger than Tambora, and coincided with the onset of the last glaciation period. .. Greenland Ice Core data evidences a 1000-year lowering of Temps in Toba's aftermath.
Chicxulub's Crater Volume is c. 28,000 km3 (c.10 times Toba's)
The volume of the basalt lava of Deccan Flats is c. 512,000 km3,
which is 500,000 times as large as that from Mt. St. Helen’s 1km3.
Add in possibilities of theorized additional large asteroidal impacts of 65MYA?
CONCLUSION
Historically and Evidentially, Massive Asteroidal and Massive Volcanic Events can not be deemed as mere “suspects". Taken fully and solely by themselves, the Effects of these Events which are dulely noted above - when taken alone by themselves - are of sufficient intensities to be causal to massive extinctions of life forms.
•••
ranyl — What is it about the colorless gas CO2 that leads you to think that CO2 is the prime suspect in the deaths of dinosaurs?Moderator Response:[JH] Yopu are now skating on the thin ice of excessive repitition which is prohibited by the SkS Comments Policy.
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can be rescinded if the posting individual treats adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
Theorist at 04:20 AM on 23 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
Tom Curtis @60
I agree with your last statement but just to clarify your last statement:
The study makes the point that 50% of the living microplankton disappeared AT THE ONSET of Phase 2 of the Deccan eruptions. Each Phase has four lava mega-flows. Within Phase 2 the magnitude of the four mega-flows increases substantially with time. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that the Deccan Traps volcanism was not responsible for the extinction.
-
michael sweet at 23:55 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Ryland,
I frequently ask posters here to provide evidence (preferably peer reviewed) to support their positions. Since Chris had no data, only his claim of personal authority, I asked for evidence of that.
If other posters want to be taken seriously they have to provide evidence to support their positions. That is the scientific method. Everyone is required to provide citations to support their position if asked (better posters like Tom provide evidence when they make the claim). All claims are evaluated based on the supporting evidence, not on the authority of the poster. I have an MS in chemistry. If I make a chemical based claim I am still required to provide citations if asked, even if the other poster has no chemical experience.
Kevin Cowtan is a reknowned world authority on temperature records who posts at this site. If questioned by skeptics who have no qualifications (which happens frequently), he provides citations to support his positions. I do not ask Dr. Cowtan for citations because I know his reputation and am comfortable that he can support his claims. Likewise mpelto is an occasional poster on this site who is a world authority on glaciers. If questioned by novices he provides citations to support his positions.
I am sorry, I meant Andrew Montford the well known denier.
-
billthefrog at 23:37 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
John,
I think I have a vague grasp of how zircon dating works, but it wouldn't surprise me if I've got the wrong end of the stick. Is this how it goes?...
When the zircon - nominally ZrSiO4 - is initially formed, other silicates, such as USi04 and ThSiO4, can be present in minute quantities. The decay paths of Uranium and Thorium will result in a variety of Lead isotopes ending up being present in a modern-day sample.
However, there is a bit I'm really shaky on, as I don't know the differing chemistry of the Actinoids and the Transition metals. I think any Lead originally present when the Zircon is formed does not get incorporated into the structure of the crystal lattice. Ergo, any Lead present in the modern sample is there as a daughter product formed post-crystallisation.
The relative abundances of the Lead isotopes, can therefore be used as a dating mechanism.
How much of that have I misunderstood?
cheers bill f
-
ryland at 23:03 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Michael Sweet @18 Thank you for answering my question. With regard to your question "What evidence do you have that Chris really has a geology degree?" etc. The answer is none. But then, I don't have evidence of the background of many of those who comment here and equally those who comment here have no evidence of my background. Is it a pre-requisite to provide details? Not sure who Montfort is. Anyway, thanks again for your courtesy.
-
michael sweet at 22:07 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Ryland,
Chris's entire argument was that he is an expert and we should believe him because he is so smart. He provides no data or citations of research to support his wild claims. Vroomie was making a personal comment and not a claim of fact. The other commentors were citing peer reviewed papers to support their claims. Since Chris is making an argument from authority I wondered what his authority is. Here Chris is an unknown internet poster with no credentials. When he was asked for his experience, he has declined to provide any support for his claims that he is an authority. It appears he does not feel that he is qualified as an authority when he is asked.
By contrast, John Mason has posted many times here about geological subjects and has a reputation for being informed. He cites peer reviewed data to support his claims, not his personal authority as Chris did. He provides citations to the original research to suport his claims. I can check them if I doubt John. When there was a question of qualifications he provided evidence that he is qualified, although a simple search of this site would provide background about him.
What evidence do you have that Chris really has a geology degree and is not just a troll who falsely claimed that he knew about geology? What evidence do you have that Chris's specialty in Geology is related to the OP? Why should I accept Chris' argument from authority?
"Skeptics" rely on the unsupported authority of false experts like Monfort and Watts. At SkS we have scientific discussions and people are required to support their claims. I am not impressed with Tom Curtis college degrees (the only qualification Chris claims). His long, detailed posts with multiple cites of recent research are difficult to argue with. Tom has authority here because he makes strong, scientificly based arguments.
-
John Mason at 21:29 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Thanks Bill - it was a .htm suffix instead of the correct .html one. Fixed!
-
billthefrog at 20:59 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
@ John Mason (or moderator)
Speaking as a genuine non-geologist... ;)
I'd just like to add my thanks for a well-written and informative piece, but I'd like to point out that the embedded link to Part 2 appers to be broken.
Please see para 4, beginning...
"For those readers already familiar with LIPs, you may want to skip this and go straight to Part Two"
cheers bill f
-
ryland at 20:44 PM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Michael Sweet @9 Why have you singled out Chris to provide information about his professional background but do not ask other geologists, for example vroomie @1, to provide similar information?
-
Tom Curtis at 07:36 AM on 22 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
Theorist @59 says:
"As stated in the research paper ... is the following quote, which describes the foram extinctions:
"After studying microplankton remains in sediment from below, between and above the second-phase lava flows, the researchers observed that the number of living species dropped 50 percent at the onset of eruptions."
Clearly, if this statement is accurate then neither the volcanic eruptions nor the bolide impact could have caused these extinctions. They occurred much too early for the negative environmental effects (specifically sulfur dioxide emissions and carbon dioxide) to have had an effect on forams."
Below is the chart to which Theorist earlier refers. It's caption reads:
"In the past several years, improved dating technology has allowed geologists to identify three distinct phases of Deccan volcanism. The first and weakest began roughly 67.5 million years ago. The second and largest phase accounted for 80 percent of the total volcanism and produced the largest lava flows in Earth's history (represented by vertical black bars). Princeton researchers found that this activity wiped out nearly 100 percent of planktonic foraminifera and ultimately initiated the Cretaceous-Tertiary mass-extinction event. They further reported that a less severe third eruption phase occurred roughly 300,000 years after the mass extinction and kept the Earth nearly uninhabitable for another half-million years. (Image courtesy of Gerta Keller)"
(My emphasis)

As can be seen from the emphasized statement, the geologists interpretation of their own work directly contradicts the claim Theorist bases on that work. That is, where Theorist concludes from this data that the volcanism of the second phase Deccan traps could not have caused the K/T mass extinction, the geologists interpret the same evidence as the smoking gun showing that it did.
-
John Mason at 05:31 AM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
Indeed, Wili - there are many examples. If you back into a lamp-post at 15mph you get a depressing garage bill to fix the damage: if you go head-on into one at 50mph the chances of survival are minimal. What "A" and "B" are does not matter a jot: it's the speed of change. A 6C warmer world would in fact be quite nice for a number of reasons if it took us a few million years to arrive at that point, but doing it over a few centuries would, as we say here in Wales, knacker us up badly!
-
Theorist at 04:08 AM on 22 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
The author of this article concludes that the Chicxulub impact was not the cause of the mass extinction. I agree. The author then concludes that the Deccan Traps must therefore be the cause.
I disagree.
Gerta Keller, who has studied the Deccan Traps extensively produced a chart displaying the three main Phases of eruptions of the Deccan Traps, which can be found at the following link:
http://www.princeton.edu/main/news/archive/S32/14/62G75/
The chart in the paper cited above is proof that neither the bolide impact nor the Deccan volcanism was the cause of the foram extinction:
PHASE 1 starting about 67.5 Mya and produced about 8% of the lava.
PHASE 2 starting about 65.3 Mya and produced about 80% of the lava.
PHASE 3 starting about 64.7 Mya and produced about 12% of the lava.
Each of the three Phases are sub-divided into 4 megaflows of lava.
As stated in the research paper and supporting the GTME is the following quote, which describes the foram extinctions:
"After studying microplankton remains in sediment from below, between and above the second-phase lava flows, the researchers observed that the number of living species dropped 50 percent at the onset of eruptions."Clearly, if this statement is accurate then neither the volcanic eruptions nor the bolide impact could have caused these extinctions. They occurred much too early for the negative environmental effects (specifically sulfur dioxide emissions and carbon dioxide) to have had an effect on forams.
The paper also states:
"The species count plunged by another 50 percent after the first of what would be four lava mega-flows."
This refers to PHASE 2.This indicates that about 75% of the forams became extinct by the end of the first megaflow within PHASE 2. And, by the end of the fourth megaflow the extinction was complete, which is when the bolide impact occurred.
If neither the bolide impact nor the Deccan volcanism caused the extinctions then what did?
Moderator Response:[PS] "the author then concludes that the Deccan Traps must therefore be the cause." Actually he puts forward an alternative scientifically plausible explanation. If you wanted to discuss "GTME", then you need peer-reviewed paper supporting the physical plausibility.
This article was published on this site because it has some relevance to possibilities inherent in rapid climate change. No further offtopic discussion of wild alternatives will be tolerated. Find another forum.
-
Timothy Chase at 02:32 AM on 22 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
The article you reference is open access:
Bond, David PG, and Paul B. Wignall. "Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions: an update." Geological Society of America Special Papers 505 (2014): SPE505-02.
http://specialpapers.gsapubs.org/content/505/29It is part of a special collection:
Keller, Gerta, and Andrew C. Kerr. Volcanism, Impacts, and Mass Extinctions: Causes and Effects. Vol. 505. Geological Society of America, 2014.
http://specialpapers.gsapubs.org/online-first/505... which has a total of 24 articles, three others being open access:
Font, Eric, et al. "Atmospheric halogen and acid rains during the main phase of Deccan eruptions: Magnetic and mineral evidence." Geological Society of America Special Papers 505 (2014): SPE505-18.
Self, S., A. Schmidt, and T. A. Mather. "Emplacement characteristics, time scales, and volcanic gas release rates of continental flood basalt eruptions on Earth." Geological Society of America Special Papers 505 (2014): SPE505-16.
Miller, Steve. "The public impact of impacts: How the media play in the mass extinction debates." Geological Society of America Special Papers 505 (2014): 439-455.
-
wili at 22:26 PM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
Good points, JM. If you take a small piece of metal and move it at a snail's pace toward someone's head, they are not likely to feel threatened by it in the least.
Take the same small piece of metal and shoot it out of a gun at the same person's head and they are instantly dead.
The only difference between the two scenarios is rate of change.
-
John Mason at 21:53 PM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
Chris - IMO it is not the totality of the change but the rate of change from A to B that is so dangerous. Consider:on a repeated basis over the past 2.55 million years there have been transitions between glaciated and non-glaciated states, yet the rate of them has been sufficiently slow that no major mass-extinctions have resulted, despite the utterly transformative nature of such changes. If they took place over 500 years the outcome would likely be disastrous. The similarity between AGW and LIPs, and where they differ from Milankovitch-type fluctuations, is that the rate of change is much faster.
-
chriskoz at 21:29 PM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
The outgased amount - 100,000GtCO2 (or my preferene 27,000GtC) is so enormous that it dwarfs any imaginable scale of AGW. The 2 degree warming target allows for 1000GtC only; we are just half way through it. Burning all available fosil fuels would release no more than 5000GtC, some 5-6 times less. Humanity is unable to match the scale of Siberian LIP excursion by burning FF no matter how hard it tries.
I agree will your math showing the rate of C release in AGW is comparable to that of siberian LIP, but those two events differ so much in magnitude that comparing their impacts seems almost incorrect. How can you justify such comparison? Is the difference in starting conditions (lower starting background CO2, brighter sun, polar ice caps) enough to justify the opinion that ongoing AGW event, bound to be at least 5-6 times smaller than said LIP event, can have the same consequences?
IMO, you should not ignore such difference in magnitude and simplify the equasion to the rate of C release only. To give an extreme example: the release of say 30MtC in one day (current rate AGW event) only and nothing more would be totally inconsequential and ignorable among natural variations. However, the same rate sustained for 100y results in AGW. The same rate sustained over 10,000y as in Siberian LIP results in more than AGW.
-
Tom Curtis at 12:37 PM on 21 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
Theorist @56, conservation of angular momentum only becomes relevant if the continents generates a significant mass anomaly. As seen above, they do not now and your assumption that they did in the era of Pangaea is entirely evidence free. I am not going to discuss this further. There is no point discussing pseudo-science with pseudo-scientists, and on the pseudo-science scale, yours is right up their with young earth creationism. Right down to the false, unevidenced claims that scientists do not have explanations for phenomenon which are well explained (or for which there are several scientific explanations between which evidence is insufficient to decide).
Moderator Response:[PS] Further discussion on these lines will be deemed offtopic and deleted.
-
Watchdog at 12:24 PM on 21 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
ranyl -
I'm placing the question of a chicxulub -> deccan traps connection, and Sulphur Trioxide and other gasses - including CO2 - on the side burner - for the sake of maintaining attention upon both events being self-evident causal factors of widespread catastrophic extinction of life.
What is it about their unquestionably individual catastrophic affects upon extinctions of life over millions of square miles of Earth, along with both of their acknowledged causings of known periods of inhospitable Global Freezing - that leads you to feel that they were not - at least - a very large part of the extinction of Dinosaurs?
I don't mind discussing CO2 and other Gasses, but not at the expense of what I perceive to be a possible glossing over the effects of: A) Chicxulub (and theorized additional meteroric impacts). B) Deccan Flats as well as both of the their accompanying C) - Global Freezing — - as if "CO2" somehow minimizes or supplants A, B & C. -
One Planet Only Forever at 09:08 AM on 21 March 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #11
In addition to the 12 months ending in Feb 2015 being the warmest 12 months in the GISTEMP data set, the 6 months ending in Feb 2015 are also the warmest 6 months in the data set. The average for any other number of months more than 6 in the record also has the set ending in Feb 2015 as the warmest. And:
- The warmest 5 and 4 month sets were the ones ending in May 2010.
- The warmest 2 and 3 month sets were the ones ending in April 2010.
- And the warmest month was Jan 2007.
And the warm values ending in Feb 2015 have not been bumped by a significant El Nino event like the 2010 and 2007 values were bumped by.
-
Theorist at 09:02 AM on 21 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
@Andy Skuce .54 and Tom Curtis .55
As I stated in a prior posting, current gravity anomalies found around the globe are due to variations in crust/upper mantle densities, usually from compression by ice. These are minor and not related to core movement.
There is much evidence to support the GTME. If you viewed the Youtube video referenced earlier, you understand the basic concept:
When the continents, coalesced into larger masses, e.g., Pangea, and especially when that consolidated mass moved latitudinally, the law of conservation of angular momentum comes into play in the same way that it does when a spinning skater moves their outstretched arms close to the body or away from the body. In the case of the skater, their rotational velocity must change. For the Earth, when the coalesced mass moves latitudindally, the distance to the Earth’s axis changes in a comparable manner. Therefore, either the Earth’s rotational velocity changes or something else compensates to conserve angular momentum. GTME posits a movement of the core elements to compensate because there is no rotational change known. The movement of the core elements creates a gravitational gradient around the Earth.
Based on the above, some of the results are:
1. Terrestrial and marine life exhibited a much wider range in physical size than is possible today when the core elements moved away from Earth-centricity.
2. When the core elements moved rapidly toward Earth-centricity, surface gravity increased, flood basalt volcanism began and a massive drop in sea level occurred. The latitudinal movement is supported by a scientific study mentioned in the video which illustrates the latitudinal movement of Pangea over the last 300my.
3.When (2) above happens, methane is disassociated from the sea bottom because of the drop in sea level coupled with the (still) relatively low surface gravity. The volcanism further increases the disassociation because it raises the ocean temperature. In fact, the experts claim that the carbon isotope excursion at the P-T boundary was too large to be accounted for by the Siberian Traps alone.
4. At the Cretaceous-Triassic boundary, marsupials in N.America were almost completely wiped out in contrast to other small mammals.
http://phenomena.nationalgeographic.com/2014/12/24/the-opossums-tale/
This can be explained by a rapid increase in surface gravity. If you have an alternate explanation, I would be interested.
5. The reduction in size and complexity of the forams at the Cretaceous-Triassic transition can be explained by an increase in surface gravity, not only by a change in ocean chemistry. Smaller, less dense forams would be more buoyant and more likely survive if surface gravity increased.
Moderator Response:[PS] This discussion is now far offtopic and as far as I can see well away from the realms of peer-reviewed science. If proponents wish to continue this, then please find another forum. Further on-topic discussion can continue provided any assertion is first backed by peer-reviewed literature.
-
Tom Curtis at 08:43 AM on 21 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
Andy Skuce @54, agreed. If the GTME held any water (pun intended), there would be a consistent difference in the gravitational field such that continental areas has a stronger field than oceanic areas. That turns out not to be the case:

The strongest gravitational field, as it turns out, is not just (vaguely) near the North Pole, but along the mid oceanic ridge in the North Atlantic where active volcanism brings magma to the surface, with the second strongest being in the Indonesian archipelago.
Nor should this be a surprise. Continental crust floats on the asthenosphere, ie, the semi solid magma beneath the surface. Ergo it has a lower density and is, overall gravitationally neutral. Ergo the basic premise of GTME is false. We need not bother to follow through to its (sometimes very bizarre) conclusions to know the theory fails.
-
Andy Skuce at 06:16 AM on 21 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
I urge everyone here not to take the "Gravity Theory of Mass Extinctions" or GTME seriously at all. It is physically impossible and is completely unsupported by any peer-reviewed research.
If you are curious to know more read this, but please bear in mind that it is bunk.
There are indeed small gravity variations on the present Earth, due principally to the planet's rotation and changes in altitude of the surface. This means that the lowest gravity on Earth is to be found at the summit of Huarascan in Peru and the lowest near the North Pole. These differences are approximately 0.7%.
In other words, an average man weighing 80 kg, standing at the North Pole, would be about 600 grams heavier than the same guy perched on top of a peak in the Andes. If the chap at the pole emptied his bladder, they would then be about the same weight.
-
howardlee at 06:05 AM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
L. Hamilton @ 2 - I made a point of attending as many of the sessions concerning plumes vs no plumes as I could. The geochemistry of plume-related magmas does argue for a base-mantle source and the fact that plumes have been imaged down to the D'' layer seems a clincher to me. Plus if you have residue of subducted slabs sinking down to the teepest mantle (as a number of studies have imaged) you must, as even Don Anderson agreed, have a compensating mass movement upwards. Agreed, plumes may not be universally accepted, but they are increasingly the consensus and about as accepted today as Plate Tectonics was in the mid 1970s.
Did you catch Barbara Romanowicz's AGU presentation "Of Mantle Plumes, Their Existence, and Their Nature: Insights from Whole Mantle SEM-Based Seismic Waveform Tomography"? Some clear imagery of ~400km wide plumes extending from the CMB there.
-
howardlee at 05:47 AM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Interesting related paper just came to my attention today in Geology by Lindstrom et al, concering the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP) associated with the end-Triassic Mass extinction. They say:
"magmatic intrusions into sedimentary strata during early stages of CAMP formation caused emission of gases (SO2, halocarbons, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) that may have played a major part in the biotic crisis"
-
howardlee at 05:41 AM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
Chris Geo - I have just received a copy of "Volcanism and Global Environmental Change" by Schmidt, Fristad, and Elkins-Tanton (Cambridge University Press). As a genuine geologist you will find this interesting - and it goes into further detail about the topics John Mason has written about, with chapters from 53 eminent scientists including a number of genuine geologists.
You may also enjoy Geological Society of America Special Paper 505, by a bunch more geologists, which you will find entirely consistent with this post.
I have spent the last few years following the research on LIPs and global climate change and I also connsider myself a genuine geologist. Many of us geologists were educated some time ago with the idea that LIPs were slow-burn phenomena, but the latest high-resolution dating shows us they were far more rapid than thought. Lake all scientists we must follow the data, even if they overturn old ideas.
-
ranyl at 04:53 AM on 21 March 2015So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
"Sediments drilled from within the Chicxulub crater itself tell a remarkably similar story to that at Boltysh. Once thought to be the settlings from the immediate aftermath of the impact and tsunami, they have since been shown to include a regular marine limestone containing the distinct late-Cretaceous CF1 fossils - so the crater must have been formed before the end-Cretaceous mass extinction! Corroborating that, rocks from Texas and Mexico show that the impact fallout (in the form of the oldest layer of impact spherules) predates the mass extinction by more than 100,000 years"
100,000years seems a long while really to be premature by.
"Deccan eruptions - for the Cretaceous global warming, ocean acidification, and extinction in the marine realm: guilty! For the terrestrial extinction including the dinosaurs: also guilty – but some may still claim reasonable doubt.
Chicxulub impact – for the Cretaceous global warming, ocean acidification, and extinction in the marine realm: not guilty! For the terrestrial extinction and doing-in the dinos: not guilty - It has an alibi, and there’s insufficient evidence of its ability to kill on a global scale to prosecute. After 30 years it’s time to let this one go. It has done its time."
Well drawn conclusions.
And if the bullet did start the eruption, still the CO2 heating and acidificatiom that are the murder weapons found present at the scene of the crime, rather than a historical impact which clearly caused major issues just not the extinction of the dinosaurs.
Given the evidence as well as that from other mass extinctions it seems a sudden release of CO2 can change climatic zones and transforms oceans rapidly enough for the global ecosystem to essentially reset itself to the new conditions, that is why there is always a boom after the bust; sometines after such a huge event it goes bbust, boom, bust, boom until it resettles in a more stable state again.
Watchdog,
As howardlee's research is extensive and the evidence convinving,
What is it about CO2 being the primary murder weapon that makes you feel that this possibility is in error?
-
One Planet Only Forever at 04:47 AM on 21 March 2015Fossil fuels are way more expensive than you think
alby,
I agree with your clarification about what can be continued, but would further clarify that since this planet is expected to be habitable for several hundred million more years, any activity that can be continued for 100 years or even 1000 years is essentially pointless, unless the benefit created from that short burst of unsustainable activity will continue to be a benefit for everyone for a few hundred million years.
-
John Mason at 03:34 AM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 1)
I can certainly state a BSc, M.Phil, time spent in the minerals industry, a number of papers and involvement in more than one book. Plus a penchant for - if I am going to write about a topic - obtaining the latest peer-reviewed research. So come on Chris, whoever you are. Speak up!
-
John Mason at 03:31 AM on 21 March 2015The cause of the greatest mass-extinctions of all? Pollution (Part 2)
Indeed - BGS have been using them for years - but portable zircon-dating units are still Star Trek! A lot of legwork is involved to do this type of dating.
Prev 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























