Recent Comments
Prev 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 Next
Comments 41701 to 41750:
-
Mel at 07:58 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Nature Climate Change recently published a paper entitled ‘Overestimated global warming over the past 20 years’ by Fyfe, Gillett and Zwiers. The paper compares CMIP5 results with observations and the general conclusion is pretty much summed up in the title. Could SkS please comment on these findings in relation to the discussion here.
I suspect this paper will be used to challenge the utility of climate models in general.
-
Kevin C at 07:54 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Anyone played contract bridge?
So as declarer, I look at my hand and dummy and see that whether we make the contract or not depends on a finess, which depends on the card split in the opponent's hands. And on the basis of the statistics of the split I calculate that I've got an 80% chance of making the contract.
We play it out, and go down on a bad split. Was my calculation wrong? No, it was exactly right. I just got the 20% split. If we were to play the hand 100 times with all the known cards in the same places and the rest distributed randomly, we'd make the contract around 80 times.
Someone else will have to reframe that for poker or blackjack players.
So, climate.
Thought experiment: Imagine a system with a linear component which is varying slowly, and a large chaotic signal overlayed on the top. We can model the physics of the system. But when we run the real system the result we get will contain the linear component, plus a random realisation of the chaos. If we run the real system many times, we can average out the chaotic component and just see the linear part. But if we can only run the system once, we're stuck with that one run.
Suppose we have a perfect model. We run it once, and it also produces the linear response with the chaotic signal on top. We can run it lots of times and average, and we'll see just the linear signal. But that doesn't look like the real run, because the real run has the chaotic part too.
But neither do any of the individual runs of the perfect model look like the real run, because the chaotic component is different.
So even with a perfect model, we can't reproduce the real run either with an individual model run or with an ensemble of model runs. And yet that's with a perfect model, a model which is right.
That's exactly the problem we're facing here. Because weather (or more generally the internal variability) is chaotic.
-
engineer8516 at 07:48 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
@ Mammal_E
You're dealing with probability which is dependent on the sample size and a sample size of 1 is insufficient. However, if your math dictates that you should get a 10 of clubs 5% of the time but you do the experiment and draw 10 of clubs 20 times in a row off the bat, a probability that amounts to 0.05^20 = 9 * 10^-25 %...then it's probably time to revisit your model. But the key here is that the model is still ultimately judged by nature, which is how it's supposed to be.
It seems you disagree with my statement "if a model disagrees with nature then there is something wrong with the model." Let me ask you this, if a particle is discovered that can travel faster than the speed of light, is Relativity Theory wrong?
-
Mammal_E at 07:11 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
@Rob Honeycutt -- you interpret my comments correctly. I'll see if I can gin up something that is brief and clear. I see this issue a lot with people misinterpreting population simulations, e.g., projecting the fate of endangered species.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 07:03 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Also, if I'm interpreting your comments correctly, you're saying what I was saying (albeit more precisely than me) about climate modeling being a boundary conditions problem. I'm equating boundary conditions to your statements about prediction intervals.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 07:00 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
I agree with Tom. Mammal_E, you're providing great insight into what are pretty common misinterpretations of what climate modeling is about.
-
Tom Dayton at 06:42 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Mammal_E, I think it would be great for you to write a post expanding your explanation of prediction interval versus confidence interval, if it includes some graphs.
-
Mammal_E at 06:28 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
engineer --
"if a model disagrees with nature then there is something wrong with the model."
Let's say I have a model that simulates the outcome of process of drawing cards from a shuffled deck. I run the model once, and it generates a 3 of diamonds. I have an actual shuffled deck, and draw a 10 of clubs. The model and reality disagree. Is that sufficient information to conclude that something is wrong with the model?
-
Mammal_E at 06:24 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
franklefkin --
@19: Who specified that it had to be 90%?
@26: I think there may some confusion in terminology here. The range containing 95% of model realizations (from the 2.5th percentile to the 97.5th percentile, not -- as you might be thinking -- from the 0th to 95th percentile) corresponds to what is properly called a 95% prediction interval, not a confidence interval. Confidence intervals reflect uncertainty in estimated parameters (e.g., population mean), whereas prediction intervals denote uncertainty in individual observations (e.g., a single sample from the population). Since the behavior of the Earth system only happens once in reality, it should be compared with a model's (or group of related models) prediction interval.
The big difference is that a confidence interval always shrinks with more higher sample sizes (e.g., the estimate of the mean becomes less uncertain), but the prediction interval does not (although the interval boundaries do become more precise with higher sample sizes). Running more model runs will tighten up the confidence interval around the ensemble mean, but will not generally tighten up the prediction interval.If intervals are based on decent sample sizes, a very large fraction of observations will fall outside the confidence interval (for the mean) but within the prediction interval (for observations).
-
engineer8516 at 06:13 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
"Please dial the tone back a bit and try to see the value in the contents of the posts to which you are replying, rather than merely trying to refute them."
I think I'm being misunderstood. My comment was just directed at the statement, "This is why climate modelers don't make predictions; they make projections, which say in scenario 'x', the climate will change in 'y' fashion." I was commenting on a statement that looked like it was arguing differences in the definition of words as a way to gloss over inaccuracies in a model's predictions. I don't want to get into a philosophical discussion, but if a model disagrees with nature then there is something wrong with the model. And that applies to any model.
-
franklefkin at 05:35 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
DSL @21,
The link you have is to a REAL Climate graph that shows 95% of model runs. It is not a 5 - 95% confidence graph. There is a difference.
-
engineer8516 at 05:29 AM on 2 October 2013Models are unreliable
@ Scaddenp,
Of course, but I thought climate sensitivity can be considered constant for small changes in temp. ∆T = k * 5.35*ln (C/C0), where k is climate sensitivity. I graphed 5.35*ln(C/C0) and it looks approximately linear in the range for C: (275 ppm, 550 ppm) and C0=275ppm. Is climate sensitivity not supposed to be considered constant even for small changes in temp?Thanks.
-
Mammal_E at 05:19 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Engineer -- The models of probability allow us to accurately calculate the chances of a blackjack player winning given a certain dealt hand and dealer card showing, given a particular playing strategy. Averaged over many random hands, this gives the long-run payoff of that strategy, as well as upper and lower bounds on what the player can expect to experience over a given number of hands. However, the models cannot predict WHICH cards will be dealt nor whether the player will win any given hand. Does that mean that the models are wrong or inaccurate, or unfalsifiable? No! It's just that shuffling the deck produces randomness that no model can possibly predict, and predicting what specific cards will be dealt is not the purpose of the model in the first place. Players that employ strategies that such models identify as having the highest payoff will, in the long run, do better than players using other strategies, even though they may will experience runs of losses and other players may will experience runs of wins.
A chaotic natural oscillation such as ENSO acts like a shuffling mechanism, preventing short-term prediction of particular years' conditions (without advance knowledge of ENSO behavior, volcanic eruptions, etc.), but allowing projections about the long-term trend as well as conditional predictions (e.g., if 2014 has a strong El Nino influence, mean surface temp is predicted to be higher than otherwise, given no volcanic eruption). The truly impressive accuracy of recent model hindcasts that are constrained to reproduce past ENSO behavior (which are analogous to predicting the winner of blackjack hands after you know the dealt and showing cards) point to the conditional accuracy of the models and lend confidence to their skill, despite their inability to predict short term randomness.
-
DSL at 05:06 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Engineer, a prediction is understood to be a single best estimate. Climate models don't produce single predictions. You can average all model runs and get the ensemble mean, but the line will not be representative of the science. The variables involved have high-likelihood ranges based on existing research. The result is a projected outcome range, not a single line of prediction. A single line of prediction would be absurd given the complexity of the system.
-
Dikran Marsupial at 05:01 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Engineer, you are missing the point "IF X, then Y", notice the "IF". That is the difference between a prediction and a projection, the accuracy of the Y is contingent on the accuracy of the scenario X. Please dial the tone back a bit and try to see the value in the contents of the posts to which you are replying, rather than merely trying to refute them. Projections fit Poppers prescription for what is and what isn't science perfectly well (please let's not get into a discussion of philosophy of science, we have all been there done that, and oddly enough the scientists that make the projections are quite familiar with it).
-
engineer8516 at 04:54 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
"This is why climate modelers don't make predictions; they make projections, which say in scenario 'x', the climate will change in 'y' fashion."
Wait what? It doesn't matter what you call it, predictions or projections. The fact is that scientific models are supposed to accurately predict natural phenomenon: as you stated given x, the outcome will be y. Besides, if a model doesn't make predictions then it's not scientific because it's not falsifiable.
-
DSL at 04:40 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Frank, I'll re-post the link I included in the last post: link (hint: click on it). CMIP3, GISS (better coverage), 95%.
-
IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
franklefkin - I would suggest you look at the draft report itself, where Figure 1.4 is clearly labeled:
For the AR4 results are presented as single model runs of the CMIP3 ensemble for the historical period from 1950 to 2000 (light grey lines) and for three scenarios (A2, A1B and B1) from 2001 to 2035. (emphasis added)
-
franklefkin at 04:13 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
DSL,
Its a 90% confidence range, and it depends on the data source for the observations.
separate question, CMIP3or5?
-
DSL at 03:26 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Franklefkin: "The message is, no they haven't done better than I think!"
Frank, is observed GMST still within the 95% confidence range of the CMIP3 ensemble? Yes or no?
-
John Hartz at 03:16 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Memo to deniers:
Your attempts to argue that the accuracy of GCMs undermines the entire body of scientific evidence about climate change is a "Dog that won't hunt!"
-
Albatross at 03:01 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Franklefkin @14,
Don't believe everything that you think.
-
Albatross at 02:59 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
As expected the fake skeptics are now trying to undermine the models by suggesting that they are a cornerstone of climate science (they recycle this myth frequently). Climate science and theoretical models of how much warming will result from a doubling of CO2 (an arbitrary value, because we will far exceed a doubling of CO2 if fake skeptics get their way) have existed long before the first comuter climate models.
The obvious caveat is, of course, that no model is perfect. Yet models are valuable tools for not only objectively quantifying future climate states, but also for learning more about the workings of our climate system.
The figure below is from the fifth assessment (AR5) report (Fig. TS.9a). As a similar figure above shown by Dana (also from AR5) the models so an uncanny job of simulating the variability of the climate system, but only when one includes anthropogenic forcings in addition to natural forcings.
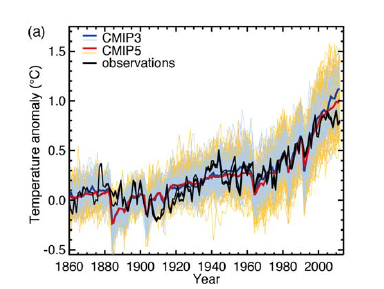
The other mistake that fake skeptics make is that they insist on comparing temperature trends (or sea-ice trends or ocean heat content trends) over periods of time that are way too short to have any statistical significance or meaning. They do this in a desperate attempt to undermine the models' credibility. However, it is well established that one of the areas that climate models are not good at is replicating the marked interannual variability because of ENSO, aerosols etc, or short-term variability (~<10 years). So they are making a straw man argument.
To illustrate, the Figure below (Box TS.3, Fig.1 from AR5) shows that between 1984 and 1998 the models as a whole were running to cool. In contrast, between 1998 and 2012 the models as a whole have been running too warm. But when one considers a longer period of time (say 1951 though 2012) or even 1979 through 2012 (as one should do), the models do a remarkably good job when compared with observations. The goal here is the long term outlook on a centennial scale.
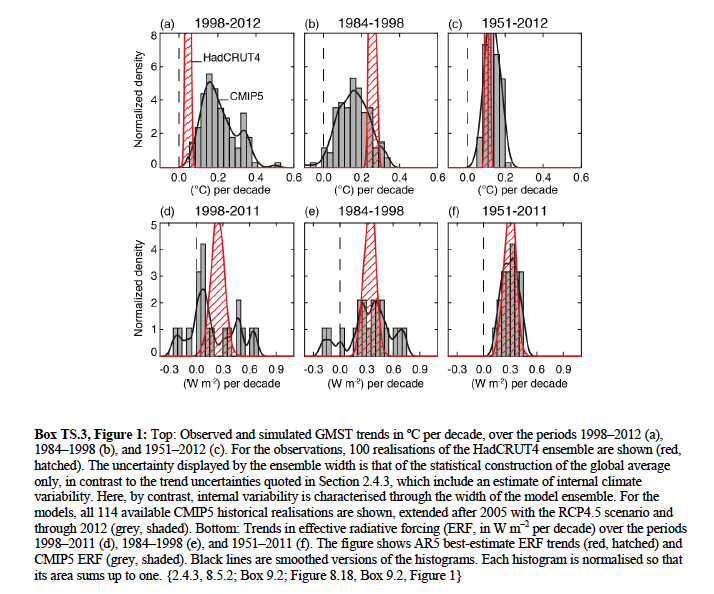
That clearly indicates that the models are much better than fake skeptics would try and trick people into believeing.
-
franklefkin at 02:56 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
DSL,
So what message are you fishing for?
The article is titled "
IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
"
The message is, no they haven't done better than I think!
-
Rob Honeycutt at 02:56 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
What I keep asking people who castigate the models is if they're expecting surface temps to follow the model mean. If so, then they're missing something very fundamental about climate modeling.
Models are never going to be able to predict short term surface temperature trends. That's just a fact. You have to get it into your head that climate modeling is a "boundary conditions problem." It's not about predicting the short term trend. Climate modeling is about estimating the boundaries we expect surface temps to fall for given forcing scenarios.
-
DSL at 02:40 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
franklefkin, we can play with short-term trends all day long. What's the trend for 1974-2008? 0.192C per decade, just about where it's expected. The trend from 2008 to present is flat. So what? There are at least three similar periods between 1974 and 2008. Didn't matter much for the overall trend, did it?
It seems like you're digging for approval for a specific message rather than trying to get a better understanding of the science. A period of flatness in the surface trend means what, exactly? Global warming has stopped? Not in the slightest. Global energy storage continues as projected.
So what message are you fishing for? General circulation models suck at projecting short-term GMST trends? Duh. General circulation models suck at projecting long-term GMST trend? Show me. Given everywhere the long-term trend could have reasonably gone (setting aside physics), CMIP3/5 modeling has done a remarkable job of confirming the strength of human-induced warming.
What do you think will happen when the next El Nino pops? We just had the warmest ENSO-neutral June on record. August was close. September, if the dailies are any indication, is going to set a record for ENSO-netural conditions. Ocean heat content has put the pedal to the metal in the last six months. PDO is also negative and has been since 2008. Solar, despite climbing toward the cycle peak, is also weak and has been for the last six years.
Yah, natural variation is putting a damper on things. No reason to rejoice, though. And certainly no basis for claiming that "global warming has stopped" or even paused. Surface warming has been weak since 2008.
-
franklefkin at 01:39 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Tom C & Dana1981,
So, right now surface temps are lower than predicted a few years ago. So if we compare in another 15 years, predictions from say 2003, you are saying that those predictions should be lowered because actual temps are lower now. <-snip-> The predictions are what they are. Consider what was said in the AR4:
"
Since IPCC’s fi rst report in 1990, assessed projections
have suggested global average temperature increases
between about 0.15°C and 0.3°C per decade for 1990 to
2005. This can now be compared with observed values
of about 0.2°C per decade, strengthening confi dence in
near-term projections. {1.2, 3.2}
"
(from AR4 SPM pg 12)
In the Article above, DANA1981 quotes a fiqure of
"within the range of model projections of about 0.10 to 0.35°C per decade. As the IPCC notes,"
The AR4 report clearly states that the lower end is 0.15 per decade. Regardless of where the baseline occurs, observations are at the very lower limit of predictions.
The report goes on to state "
Best-estimate projections from models indicate
that decadal average warming over each inhabited
continent by 2030 is insensitive to the choice among
SRES scenarios and is very likely to be at least twice
as large as the corresponding model-estimated natural
variability during the 20th century"
(also from pg 12)
So unless natural variability has suddenly spiked, natural variability cannot be the reason for the models' over estimate of warming.
Moderator Response:[RH] Dial it down just a little.
-
dana1981 at 00:38 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Andrew @8 - I addressed the Christy/Spencer TMT graph here (see Stage 2).
-
dana1981 at 00:34 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Bob @3 - McIntyre adds nothing of value whatsoever. His post is basically "I don't understand why the data shifted up." Ever heard of proper baselining? Just goes to show that Tamino is 10 times the statistician McIntyre is, as Tamino figured this out 10 months ago. Also, if you're confused about the proper baselining, then compare the trends! It's easy for a graph to be visually misleading, but the trends don't lie. I literally see nothing of value in McIntyre's post.
franklefkin @4 - as I noted, the fact that climate models don't accurately predict ocean cycles in the short-term is not particularly relevant. We're not especially concerned about climate change in 2020, we're concerned about climate change in 2050 and beyond.
-
Andrew Mclaren at 00:20 AM on 2 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
I'm seeing a lot of contrarians using the old Spencer/Christy "hunt for the fugitive TMT hot spot" cherry-picked graph comparing 20N to 20S latitude band satellite/balloon readings to the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP5) ensemble. This is then implied to challenge the global extents of the models... as stated in the following article:
http://opinion.financialpost.com/2013/09/27/nota-bene-climate-models-vs-actual-climate/
Spencer's original is at his site:
http://www.drroyspencer.com/wp-content/uploads/CMIP5-73-models-vs-obs-20N-20S-MT-5-yr-means1.png
Of course all this conveniently does away with the amplified warming at higher latitudes which all global models must account for. I was initially skeptical about the integrity Spencer's original since it indicates the (dotted line) Mean calculation "Mean USA" which I'd assumed meant data that had nothing to do with equatorial latitudes, but I guess having looked at another citation at Watts' site that was supposed to indicate "US based research". Still, a nasty cherry pick considering how it is being used for exaggerated claims of "none of the models work".
I recognize the TMT hot spot as something of a red herring, as it really seems to be more of a potentially amplified heat capacity at altitude, than uniformly warmed atmospheric layer. It's not the subject of this thread per se, but certain bloggers etc. do seem to be milking this hunt-for the-nonexistent-'signature' for all its worth (which is not a lot) and more.
Thanks for presenting more accurate information here. I'd like to see the missattribution of Spencer's work in the contrarian media, better shown up for what it is.
-
IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
fretslider - Astounding. You make claims of data distortion by linking to a figure that has in fact been airbrushed and reworked to remove critical data.
Even with the incorrect 1990 baselining, the draft figure 1.4 (seen here) includes a light grey region that shows the range of model variations and the uncertainties in temperature measurements, the expected range around model means due to natural variation. Observations are well within those bounds. McIntyre's reworked figure that you point to above lacks the range of model variations, showing only the range of model ensemble means - see denial tactic #2 in the opening post.
That reworked McIntyre figure (along with other 'skeptics' like Patrick Michaels in Forbes, who edited the figure captioning and falsely claimed: "The very large grey zone is irrelevant to the forecasts that were made") is a clear distortion. I would go so far as to say it is a demonstrable lie about the science on McIntyre's part. Don't be fooled.
-
John Hartz at 22:54 PM on 1 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
@fretslider: Your comment was deleted because it is sloganneing. Please read the SkS Comment Policy and adhere it.
-
Tom Curtis at 22:24 PM on 1 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
franklefkin @4, of course it shows a bias. It shows a massive bias that results from a carefully selected start point for observations at one of the largest El Nino's on record. You fail to show that their is any additional bias beyond that in the cherry picked start point, something you need to do before concluding that the models show a bias.
-
franklefkin at 21:57 PM on 1 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Bottom line however, the models have not done an adequate job, which even the IPCC admits:
Box 9.2: Climate Models and the Hiatus in Global-Mean Surface Warming of the Past 15 Years
The observed global-mean surface temperature (GMST) has shown a much smaller increasing linear trend over the past 15 years than over the past 30 to 60 years (Section 2.4.3, Figure 2.20, Table 2.7; Figure 9.8; Box 9.2 Box 9.2 Figure 1a,c). Depending on the observational data set, the GMST trend over 1998–2012 is estimated to be around one-third to one-half of the trend over 1951–2012 (Section 2.4.3, Table 2.7; Box 9.2 Figure 1a,c). For example, in HadCRUT4 the trend is 0.04 ºC per decade over 1998–2012, compared to 0.11 ºC per decade over 1951–2012. The reduction in observed GMST trend is most marked in Northern- Hemisphere winter (Section 2.4.3, (Cohen et al., 2012)). Even with this “hiatus” in GMST trend, the decade of the 2000s has been the warmest in the instrumental record of GMST (Section 2.4.3, Figure 2.19).
Nevertheless, the occurrence of the hiatus in GMST trend during the past 15 years raises the two related questions of what has caused it and whether climate models are able to reproduce it. Figure 9.8 demonstrates that 15-year-long hiatus periods are common in both the observed and CMIP5 historical GMST time series (see also Section 2.4.3, Figure 2.20; (Easterling and Wehner, 2009), (Liebmann et al., 2010)). However, an analysis of the full suite of CMIP5 historical simulations (augmented for the period 2006–2012 by RCP4.5 simulations, Section 9.3.2) reveals that 111 out of 114 realisations show a GMST trend over 1998–2012 that is higher than the entire HadCRUT4 trend ensemble (Box 9.2 Figure 1a; CMIP5 ensemble-mean trend is 0.21 ºC per decade).
Being on the high side 114 out of 117 times is indicative of a bias.
Moderator Response:[DB] It is customary to provide a link to the source when quoting.
-
Bob9499 at 21:45 PM on 1 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Dana, you should really take a look at this.
http://climateaudit.org/2013/09/30/ipcc-disappears-the-discrepancy/
-
skywatcher at 19:46 PM on 1 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
Excellent article Dana. It seems so many people fall into the trap of thinking that the temperatures should doggedly trail the inexorable rise of the multi-model mean, failing to realise that every individual model run rises and falls around that line.
I can't see if you link to it above (very probably you do), but for readers I might highlight Foster and Rahmstorf 2011 which elegantly showed what happens when you remove exogenous factors - you end up with the underlying warming signal, still continuing unabated through the past decade. The Kosaka paper you discussed recently shows how including some of that variability leads to an excellent modelling of surface temperatures including the recent surface temp 'slowdown'. And yet deniers still claim the change in surface temperatures is unexpected or represents a model 'failure'...
Keep up the superb work!
-
Matt Fitzpatrick at 17:11 PM on 1 October 2013IPCC model global warming projections have done much better than you think
I've also been seeing a little bit of a #4) Curve fitting exercises purporting to have better predictive power than IPCC model forecasts based solely on short-term hindcasts with arbitrary parameters. Not many stoop that low to make the IPCC's models look bad, but some do.
-
scaddenp at 16:32 PM on 1 October 2013Models are unreliable
Engineer, the issue is estimating climate sensitivity is non-linear feedbacks. Decreasing ice and increasing methane emissions would be two examples. Models attempt to build these influences in whereas linear extrapolation does not.
-
engineer8516 at 15:51 PM on 1 October 2013Models are unreliable
"Climate trends are weather, averaged out over time - usually 30 years. Trends are important because they eliminate - or "smooth out" - single events that may be extreme, but quite rare."
So if we look at the past 30 years we should get the climate trend. According to skepticalscience's trend calculator from 1983 to 2013 the earth's temp has increased by 0.17 C per decade (GISTEMP moving average 12 months). Since CO2 has risen at about a linear rate since 1980 (according to: http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/), is it reasonable to predict a best guess rise of 1.7C from decades (1990 - 2000) to (2090 - 2100)? This would point to the low scenario from IPCC 2007, which has a best guess of 1.8C.
-
John Hartz at 07:56 AM on 1 October 2013Understanding the pre-IPCC Anti-Climate Science Misinformation Blitz
@rockytom #49:
As long as the fossil fuel industry exists, Deniersville will exist.
-
rockytom at 06:05 AM on 1 October 2013Understanding the pre-IPCC Anti-Climate Science Misinformation Blitz
I guess the deniers couldn't find any emails to steal! They do become more strident as their numbers decline.
-
John Cook at 03:24 AM on 1 October 2013Public talk explaining our consensus paper & answering critics
The Monckton quote comes from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xZSPOawk698 - around the 2:30 minute mark.
-
Smith at 03:05 AM on 1 October 2013Public talk explaining our consensus paper & answering critics
Can you please give the provenance of the Monckton quote?
-
AndersM at 18:23 PM on 30 September 201316 ^ more years of global warming
The video in the post is "private". A mistake?
-
Jim Hunt at 18:17 PM on 30 September 2013Latest myth from the Mail on Sunday on Arctic ice
The Mail on Sunday's "retraction" yesterday didn't amount to the proverbial hill of beans, so here's our latest report deconstructing the recent "Shock news!" about "And now it’s global COOLING!":
http://GreatWhiteCon.info/2013/09/santas-secret-summer-swim/
-
TonyW at 17:41 PM on 30 September 2013Why is the IPCC AR5 so much more confident in human-caused global warming?
I'm not sure about the usefulness of the RPCs as they all seem to assume economic growth continuing to the end of the century. That seems like an awfully large assumption given resource depletion and environmental deterioration (not to mention debt levels). However, I suppose the people they are targetting all make the same assumption so maybe it's useful as a way of engaging the unengagable. -
scaddenp at 12:47 PM on 30 September 2013Models are unreliable
Further to Zwiers. Any good scientist is a skeptic - a real one. Fake skeptics are only skeptical about things they disagree with and will swallow any kind of junk uncritically if it supports their notions.
-
scaddenp at 12:43 PM on 30 September 2013Models are unreliable
tcflood "wouldn't the effect be to remove the ENSO effects thereby insuring some departures of observation from the models when real ENSOs would occur? "
Essentially true. See for instance the graph here. Forcing ENSO in model to match what happens is somewhat like Kosaka and Xie did. See discussion here.
Comment from Mike at RC on Zwiers.
"[Response: Francis is a top-rate scientist of the highest integrity. I strongly suspect that he has been misquoted and mischaracterized quite a bit lately. -mike]
-
Taiko at 11:07 AM on 30 September 2013Secretary of State Kerry and Senator Boxer Remark on the IPCC Report
It's been interesting to see some of the reader comments on sites like the UK Guardian and PBS Newshour. The climate denier trolls seem to be out in full force. But none of them appears to have actually read the Summary Report for Policymakers. As an American I am embarrassed that someone as ignorant about science as Lamar Smith chairs the House Committee on Science, Space and Technology.
-
tcflood at 09:36 AM on 30 September 2013Models are unreliable
@jsmith. Thanks for the response. I read somewhere that many of the GCMs actually do produce ENSO episodes but that the timing of their appearance (as in nature) is chaotic. If modeling results are reported as an average of many models, wouldn't the effect be to remove the ENSO effects thereby insuring some departures of observation from the models when real ENSOs would occur? So, hypothetically, if there were some way to trigger an episode at the same time in all the models, the match between models and observation might be much improved. I don't pose this as a realistic modeling strategy, but rather as an accurate and effective counterargument to this common cavil in the denier echo chamber?
Also, the denier rant that called my attention to the above-cited paper said Zwiers is a vice chair of the IPCC. I infer from your comment that he is nonetheless a skeptic. The paper certainly reads like he is.
Prev 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























