Recent Comments
Prev 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 Next
Comments 42901 to 42950:
-
Sapient Fridge at 06:49 AM on 19 August 2013Putting an End to the Myth that Renewable Energy is too Expensive
In reply to Mark Harrigon I would like to ask where you are getting your figures from?
The figures from the EIA Levelized cost estimates don't seem to indicate that all renewables are anywhere near the multiples more expensive than fossil fuels as you suggest. For example hydro, geothermal and onshore wind all come out cheaper than coal when all factors, including transmission, are taken into account.
Some renewables are more expensive than fossil fuels, but it is not true across the board as you seemed to assert. And some costs are dropping rapidly e.g. for solar PV.
-
Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
DSL - Catastrophic? Don't forget monsters erupting from Arctic ice (along with mad scientists and frozen cavemen), cats and dogs living together in sin, and the horrors of the loss of our morning coffee:
...the most favourable outcome is a c. 65% reduction in the number of pre-existing bioclimatically suitable localities, and at worst an almost 100% reduction, by 2080... Arabica coffee is confimed as a climate sensitive species...
I would certainly consider that catastrophic, your opinion may vary. But don't talk to me until after my first cup!
Personal opinion - the catastrophe for most of those in denial are the loss of the "infinite growth" and "anyone can win" scenarios that are fundamental ideological touchposts for so many (they live in their parents basement, so to speak, but they could do so so much!). They just seem to be fundamentally disturbed by the ideas of limits, the idea that unlimited expansion is not possible in a finite world. And egged on by those whose income is related to not having accounting for social carbon costs, or to avoiding regulation, etc.
-
william5331 at 06:26 AM on 19 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #33B
On Carbon tax, any party that proposed Tax and Dividend a la James Hansen would have a huge advantage in the coming elections. Which voter could resist getting a monthly dividend from "The Man". This must be causing all sorts of angst amongst senators and congressmen. Do we go for re-election or do we support our fossil fuel lobyists. It's like the prince in Shrek trying to decide which princess to pursue.
-
Bob Lacatena at 04:53 AM on 19 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
Mark,
if warming turns out to not be severe.
and
...should warming turn out to be less severe than feared.
These "possiblities" are not on the table, not even remotely. There is absolutely zero chance that the consequences of warming will not be severe if we reach 450 ppm, and at the moment it appears virtually certain that we will not only reach but blow right past 450 ppm. I put 575 ppm at the bare minimum where we will stop, and then only after many national economies are simply crushed by the impacts, and so stop emitting by default.
Anyone who is saying "gee, this isn't so bad now" is kidding themselves. Climate change takes time, a lot of time, but after you've jumped out the window it's too late to start worrying about what happens at the end of the fall.
-
Bob Lacatena at 04:47 AM on 19 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
Catastrophic? Is that what the C stands for?
I always thought they meant Confused About Global Warming.
[You learn something new every day.]
-
DSL at 04:13 AM on 19 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
JH, I think SkS should start a compendium of all the definitions for "C" ("catastrophic") in the oft-used "CAGW."
Oceans boiling away. All life dead. All humans dead. Humans reduced to "caveman" status. 300 meter sea level rise. 40 Cat5 hurricanes per year. Multiple monster tornado outbreaks annually. And all of this should already have happened or else the theory of AGW is falsified and/or benign.
-
John Hartz at 01:26 AM on 19 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
@ BillyJoe #7:
What is your working definition of "severe AGW"?
-
BillyJoe at 23:21 PM on 18 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
Correct me if I'm wrong but the 97% figure applies only to scientists who believe that anthropogenic warming is happening,not that it will be severe.
-
michael sweet at 22:44 PM on 18 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
Mark,
I noticed that you provide exactly zero references to suppport you Gish Gallop against renewable energy. Here is a SkS link that discusses your myths. Gish gallopers like you never mention that natural gas plants also operate at 30-40% of capacity. If you stick around and provide support for your assertions (in the unlikely case that you can find support), I will link more articles that show renewable energy is cheaper than fossil fuels.
Moderator Response:[DB] Thank you for modeling good thread discussion habits.
-
david.hamilton at 22:16 PM on 18 August 2013Arctic sea ice extent was lower in the past
Good information, thank you. There is nice irony in an argument put forward by a "sceptic" in reality providing evidence for AGW. I have a question of fine detail - not because I want to criticise, but to fine tune my understanding. The OP mentions changes in the Earth's "orbital" motion: is it really the orbital motion that's operating here, or is it the Earth's rotational motion? I can envisage the Earth's precession around its rotational axis as having exactly the effect discussed, and that font of all knowledge, Wikipedia, tells me that the period of Earth's precession is around 26,000 years, which seems to fit in with the argument.
-
Mark Harrigan at 18:10 PM on 18 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
Unfortunately there is a gap in Andrew's logic that those who wish to avoid action can shoot huge holes in.
While I agree action should be taken one canot ignore the COSTS of taking action. These are not insignificant. The switch away from fossil fuels has a significant economic cost associated with it and is not a "no regrets" policy if warming turns out to not be severe.
Although it's a complex issue confounded by how the current economics of fossil fuels are determined (for example failing to account to the true health costs even without climate change) the fact is that overbuild required for renewables is not insignificant - estimates vary from as much as 2x to 5x nameplate capacity. And frequently such costs estimates fail to account for additional transmission costs (typically 50% or more of the real costs of grid based power).
And before anyone quotes BZE at me you need to address their heroic assumptions about reductions in consumption AND the fact that they largely ignore the ovebuild and transmission cost question.
For action to be logical today on the basis that the science is clear that there is a non-negligible risk of severe warming with potentially large negative consequences you have to address the issue that the costs of taking action (replacing fossil fuels as an energy source) do not outweigh the benefits should warming turn out to be less severe than feared.
Moderator Response:[DB] As Michael Sweet notes, your comment more properly belongs on the Putting an End to the Myth that Renewable Energy is too Expensive thread. Please take this discussion there.
-
william5331 at 07:30 AM on 18 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
If you don't accept that the climate is changing or that we are causing it or if we are causing it, it will only be good for us then forget Climate Change.
http://mtkass.blogspot.co.nz/2010/10/forget-climate-change.html
-
michael sweet at 00:52 AM on 18 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #33B
This article documents changes in apple taste and firmness caused by AGW in Japan. Apples don't taste as good and are less firm. At the start of the article they reference about 20 other articles documenting changes in fruit and food production worldwide. They say that changes in care of plants and cultivars grown make it difficult to document these changes in many areas (if cultivation practices have changed it is difficult to separate changes from AGW and changes from cultivation practices). In their orchard they have the same trees and care for them the same way.
-
ShaneGreenup at 22:54 PM on 17 August 2013Global warming games - playing the man not the ball
Hi John,
I have added most of the relevant posts to rbutr now, but can you submit your original presentation as a rebuttal to any instances of Monktons original talk which you can find online? Or at least let me know where they are, and I will submit them.
Thanks.
http://rbutr.com/rbutr/WebsiteServlet?requestType=showLinksByFromPage&fromPageId=140127
-
Paul D at 22:24 PM on 17 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
Regarding plane crashes etc.
Really the issue is survivability. If you happen to be on a plane that does crash the probability of surviving is far less than say that of being in a train crash.
eg. if you compare the worse case scenarios of different types of transport. Some are better than others.
It boils down to whether imagination wins over statistics.
If you imagine yourself in a crash, your better off in a train.
If you check the math, it probably doesn't matter much (although I haven't checked!). -
saileshrao at 11:52 AM on 17 August 2013Toward Improved Discussions of Methane & Climate
Have we been looking at Climate Sensitivity all wrong? We've been focused on global temperature sensitivity to CO2 doubling, but shouldn't we have been focusing on global temperature sensitivity to input radiative forcing? Atmospheric methane increases occurred in the ice-core data in tandem with temperature increases with just a 0.5W/m2 increase in input radiative forcing due to the Milankovitch cycle. The resulting feedback exacerbated the rise in temperature to around 5degC. Why should the planet's store of methane now NOT react when humanity has created a 3W/m2 increase in input radiative forcing (minus the aerosol component) by burning fossil fuels and deforesting the planet?
I don't understand this "what me worry" attitude among prominent climate scientists on the methane issue. Is it subconsciously linked to their consumption of beef? -
davidnewell at 09:59 AM on 17 August 2013A grand solar minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming
Although the informaion has received a fair amount of criticism because of source,
and even though I don't believe it either:
there is another innaccuracy, perhaps arising from pedantry, which I will eruct:
quote:"We're fortunate that the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface is very stable" endquote.
I would say that the author should report back on the accuracy of this statement the next time we're hit dead center by a solar flare.
Oh wait, he won't ba able to, as much of the electrical distribution system, and much of the electronics connected to it,
will be fried.
===============
I would agree that the cycle of the sun's output will have no significant net effect on our CO2 scenario
-
davidnewell at 04:52 AM on 17 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
KR, whatever Skeptical Science decides is appropriate is fine with me.
In point of fact, I am loathe to look at "geoengineering" wiith anything but a seriously "jaundiced eye", as in general they (the techniques) smack of just more wild-eyed demonstration of the human intellect's capacity to dick around with things we really have a poor understanding of: trying to use a hammer to adjust a wristwatch.
That being said, "this" technique takes a natural process (mineralization of CO2) and enhances it, in a natural way. (Spraying water in the air, duh!)
"This" technique, if shown to be harmful in any way whatsoever, can be discontinued, modulated,
: and if shown to be valuable, enhanced, expanded, etc..
============
It is an unfortunate fact that the "intellect / ego" has ignorantly gotten us into this mess,
but unlike what the flower children might want, which is to return to teepees and hunter-gathering, (which by the way might be OK in the long run, I've no opinion on the matter..)
what WE have to do is employ the SAME imagination and intellect, but in a different way, to reduce the ramifications of the die we've already cast.
"What do we do to make life prosper????" on this planet, whose wholeness is sometimes called "Gaia" by some: (although it does expose onto some abuse in these parts. )..THAT's the question we each should be continuously tryiung to answer and act on. .
So how do we decrease circulating CO2?
This methodology, utilizing the weathering products of granite, to both sequester CO2 and increase water vapor in the air, appears to be the best, most innocuous, route suggested, to the best of my knowledge of specific geoengineering suggestions, such as the others in your response. .
All speculative, but if there's a better speculation out there, let's hear it!
Thank you.
-
StBarnabas at 03:55 AM on 17 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
@mike roddy
agreed. To me this is a good statement of the obvious and we should all do our bit to lower our carbon footprint. I found www.navitron.org.uk/forum/ a good place for me in the UK for advice and help to do our bit.
I dispair of the USA. It was such a fantastic country when I lived there in the late '70s whilst doing my PhD at the Harvard Smithsonian Observatory. It seems however to have lost its way. Al Gore's book "The Future" is quite interesting in its analysis of the current disfunctionality of the US. For me its deeply saddening that a country I held in the highest regard seems to have become more part of the problem rather than the solution in a number of areas in particular CC
StB
-
catman306 at 03:16 AM on 17 August 2013A vicious cycle: Could droughts and storms make climate change worse?
Too bad there isn't a satellite or some such device that measures the Earth's total biomass from week to week and year to year. It would probably show a negative correlation with the Earth's average surface temperature. As the temperature rises, the total biomass dimminishes.
-
Leland Palmer at 01:34 AM on 17 August 2013Toward Improved Discussions of Methane & Climate
We should not forget that our future course of action- whether to massively switch to renewable energy sources or continue on our fossil fuel trajectory- is an economic problem as well as a scientiic problem.
The methane in the methane hydrates is worth hundreds of billions, perhaps trillions of dollars.
The methane in the methane hydrates could also arguably kill the biosphere.
A scientific paper which mentions the economic factors associated with the methane hydrate problem is linked to below:
Gas hydrates: entrance to a methane age or climate threat?
Methane hydrates, ice-like compounds in which methane is held in crystalline cages formed by water molecules, are widespread in areas of permafrost such as the Arctic and in sediments on the continental margins. They are a potentially vast fossil fuel energy source but, at the same time, could be destabilized by changing pressure–temperature conditions due to climate change, potentially leading to strong positive carbon–climate feedbacks. To enhance our understanding of both the vulnerability of and the opportunity provided by methane hydrates, it is necessary (i) to conduct basic research that improves the highly uncertain estimates of hydrate occurrences and their response to changing environmental conditions, and (ii) to integrate the agendas of energy security and climate change which can provide an opportunity for methane hydrates—in particular if combined with carbon capture and storage—to be used as a ‘bridge fuel’ between carbon-intensive fossil energies and zero-emission energies. Taken one step further, exploitation of dissociating methane hydrates could even mitigate against escape of methane to the atmosphere. Despite these opportunities, so far, methane hydrates have been largely absent from energy and climate discussions, including global hydrocarbon assessments and the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
Intense localized methane plumes could perhaps be captured, burned using (for example) oxyfuel combustion to generate electricity, and the resulting CO2 deep injected into fractured basalt sediments, I think. The resulting electricity could be transmitted to shore using submarine electrical cables- a new but farily well developed technology. This would be carbon neutral remediation of the captured methane, if it works.
On the other hand, trying to capture the methane would be like trying to catch soup in a net, in my opinion. Vast quantities of methane would go into the oceans, contributing to ocean acidification, leading to probable widespread anoxic areas, and perhaps even a dead arctic ocean- one incapable of oxidizing much of the methane released into it by the hydrates, according to modeling by the DOE/LBNL/LANL modeling done by the IMPACTS (Investigation of the Magnitudes and Probabilities of Abrupt Climate TransitionS (IMPACTS)) group. Check out their publications link:
Investigation of the Magnitudes and Probabilities of Abrupt Climate TransitionS (IMPACTS) Project
As an inhabitant of the Earth, I don't think that a "methane age" of abundant energy is worth the risk of low level or greater runaway destabilization of the climate system.
Fossil fuel corporation executives and major stockholders of fossil fuel corporations may disagree.
In such an environment, there is the potential for enormous profits to skew the scientific debate.
-
mike roddy at 00:32 AM on 17 August 2013Andrew Dessler on Why It's Stupid not to Act on Climate Change
This is an excellent summary, but overlooks our problem: Here in the US, money trumps all when key decisions are made. As long as the oil and gas companies are raking in such vast amounts of cash- and sprinkling it around to politicians and media companies- we will continue to bake.
-
DSL at 23:00 PM on 16 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
Thank you, Philippe. I knew there was a name for that lightless spot in my memory.
-
Philippe Chantreau at 14:09 PM on 16 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
"Neither has, IIRC, any president of the US. "
Andrew Jackson is known to have killed opponents in duels.
-
scaddenp at 08:49 AM on 16 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
I would note that ajkuiper has not responded to requests to support some sloganeering here. I hope he/she is more ready to engage with some actual science in this discussion.
-
DSL at 05:44 AM on 16 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
Deep, AJ, deep. Poverty's never killed anyone either. Neither has, IIRC, any president of the US.
The drop in ASI can change global weather patterns (hard to avoid doing that), and the resulting changes have undoubtedly led to specific deaths that wouldn't have occurred otherwise. Perhaps you should be more specific, AJ. Are you actually suggesting that changes to general circulation have no impacts on human life?
-
ajkuiper55 at 05:20 AM on 16 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
davidnewell - (-SNIP-)
Moderator Response:[DB] Repetitive sloganeering snipped.
-
MA Rodger at 04:56 AM on 16 August 2013How much will sea levels rise in the 21st Century?
jja @35.
Concerning radiative forcing and energy imbalance. The difference is actually rather great. For instance Hansen et al 2012 the discussion of energy imbalance and net forcing leading to their conclusion "Measured Earth energy imbalance, +0.58 W/m2 during 2005-2010, implies that the aerosol forcing is about -1.6 W/m2" and thus a net forcing of +1.4 W/m^2.The crucial point is that radiative forcing is a change over a period (say 1750 to date) and is a theoretical quantity while energy imbalance applies to a particular point in time and is an actual physical phenomenon.
Its a bit like a kid kicking a ball along a road. The forcing, the kid's kicks, can be expressed as increases in speed imparted into the ball by his boot and can be added up over a period of time when he kicks the ball many times. This 'forcing' will always increase adding up with each kick (unless the kid kicks it backwards). The ball will usually be slowing due to air resistance etc and on its own will come to a halt in the gutter. But until that point it will have a speed along the road which in this analogy would represent the energy imbalance. (The distance along the road would perhaps represent temperature.)
The definition of "forcing" given by the IPCC is given here. The altitude it is attributed to (ie the tropopause) is less important than the concept that it is "with surface and tropospheric temperatures and state held fixed at the unperturbed values" (in the analogy, not accounting for the slowing of the ball due to air resistance etc). -
MA Rodger at 04:40 AM on 16 August 2013How much will sea levels rise in the 21st Century?
Agnostic @34.
Indeed. Small increases in global temperature will result in very large SLR. And yes, the cause will be due to melting of land ice from Greenland & Antarctica. So the question is - how "rapid" or how slowly will that melt occur? Or how big will be the "heat" flows in that melting process?
The total global energy imbalance gives a value for the energy entering the global climate system. Polar amplification may suggest that a disproportionate amount of that energy is arriving at the poles but (1) That is not entirely the same as energy available for melting land ice (although it will be in part), and further (2) The vast majority of the global energy imbalance ends up heating oceans and thus not into melting ice. This suggests that the energy available to melt Greenland & Antarctica can only be a minority of the global energy imbalance. And small energy fluxes has to mean small melts and small resulting SLR.
I have yet to see anyone describing how an energy flux can be created large enough to melt enough ice for anything like a 5m SLR by 2100. The literature still shows findings that project sub-1m SLR although they are usually not entirely reassuring in these findings. The Ice2Sea project, for instance, tells us that with a 3.5ºC global temperature increase (A1B emissions), the total SLR contribution from land ice will be 350mm to 368mm by 2100 (so a 700mm total SLR) but but do not rule out higher SLR (5% chance of +840mm SLR from ice) saying "even the state-of-the-art models do not simulate all the processes and feedbacks that might be significant." Perhaps more reassuring is Pfeffer et al 2008 who find that 2100 SLR greater than 2m is "physically untenable."
Myself, I see it that however large the 2100 SLR proves to be, it is less the problem in itself. Rather the rate of SLR by 2100 will set the SLR for the following century when SLR greater than 2m probably will no longer be "physically untenable." And if global temperatures remain high SLR will continue at that rate for many more centuries to come. -
DSL at 04:24 AM on 16 August 2013A grand solar minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming
John, dating the LIA is anything but simple. The Maunder may have been responsible for the worst of the LIA, but the Wolf and Spörer mins preceded it. There is also the volcanic factor to account for. This article addresses the skeptic claim that a new Maunder would cancel global warming. The article does not attempt to explain the LIA.
-
Composer99 at 02:11 AM on 16 August 2013A vicious cycle: Could droughts and storms make climate change worse?
OK the pictures are showing up properly now.
-
Composer99 at 22:52 PM on 15 August 2013A vicious cycle: Could droughts and storms make climate change worse?
Don't know if anyone else has the same problem, but the pictures are coming up as broken links when I view this post.
-
John Chapman at 22:06 PM on 15 August 2013A grand solar minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming
If the LIA started 500 years ago, then that precedes the start of the Maunder minimum by about 150 years. So where's the evdience that a grand solar minimum triggers colder climate?
-
michael sweet at 20:36 PM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
Terranova,
Since the Milankovich forcing has been cooling for the past 5,000 years, what has warmed besides human interventions? Your claim of "contributing" not "causing" is splitting hairs. Humans have changed the climate for 8,000 years. The question is how much. You are being inaccurate with your pedantic hair splitting. Stop complaining that others have a minor issue until you no longer have the same problem, or worse.
-
chriskoz at 16:22 PM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
Terranova@17,19
Can you explain in non-inflamatory terms (so that your post is not snipped) the point you're trying to make?
Your emphasis about CO2 being "not determinative" to glacial cycles does not add anything new to the discussion and your focus on "manmade CO2 emissions" does not mean anything in this context. We already know that CO2 was the feedback rather than causality of pleistocene glacial cycles. And it's also obvious to us that manmade CO2 emissions have overriden the glacial cycles, because said emissions are 100 times faster. So to me, there is no logical value nor point in your post.
Your question about the "Where Are We At Today" section wherabouts can only be answered by Dana. But to me, the section is truthful and valuable, irrespective where it came from: it explains to the possibly unfamiliar reader the context and rate of current climate changes in relation to the changes the original study focussed on.
-
Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
davidnewell - Sites vary, but on SkS most visitors follow the Recent Comments page, leading directly to conversations in progress.
I would opine (personal opinion) that weathering and the long term natural carbon cycle are quite distinct from geoengineering, whether that involves granite chips or artificial aerosols or orbital mirrors or iron seeding of oceans, etc. And that discussions of natural checks and balances are a very different topic from modifying nature for our goals.
-
Terranova at 12:56 PM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
Michael Sweet @ 18
There is a difference between contributing and causing. Read your link again. There is nothing there that implies that humans are the main cause of climate change over the party centuries or millenia. Furthermore, the query about the statement being a part of the referenced paper is still not answered.
-
michael sweet at 12:03 PM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
Terranova:
There is substantial evidence that Humans have been causing climate change for 8,000 years. Primarily due to farming and deforrestation. The last that I recall, scientists were coming to a consensus that this explaination was the best way to model the recent climate changes. The rate of human caused climate change has substantially increased in the last 150 years. Your cries of "inaccuracy" would be a lot more convincing if you did your homework. Please read up on the past 4-8 millenia and retract your comment above.
-
Terranova at 11:36 AM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
From what's available on the nature website: "This fast retreat is governed mainly by rapid ablation due to the lowered surface elevation resulting from delayed isostatic rebound14, 15, 16, which is the lithosphere–asthenosphere response. Carbon dioxide is involved, but is not determinative, in the evolution of the 100,000-year glacial cycles." Emphasis mine.
From the article above: "Of course, on top of these epic natural cycles manmade carbon emissions are having an effect on the climate. Over short timescales (geologically speaking) of centuries and millennia, greenhouse gas emissions from human activities are the main cause of climate change." (-snip-).
I asked, but did not get a reply ( -snip-), about the final section of this post "Where Are We At Today". It appears to be an add-on from the article author and not part of the paper referenced.
If in fact it is not part of the paper represented in the post, then we are back to the "inaccurate" topic. If it is part of the paper, then I would like to see it and I will retract my statement.
Moderator Response:[DB] Argument from personal incredulity snipped. Inflammatory snipped.
-
Tom Curtis at 07:24 AM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
IanC @14, yes. I realized essentially the same point last night just before going to sleep. The key point is that given the rate at which heat propogates by conduction, the current warming will not yet have impacted basal ice except by means of surface melt water carrying warmth to the base of the ice sheet (where it is able to do so) or at the edges of the ice sheet.
-
martin3818 at 07:13 AM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
I think Freya Roberts post fails to mention that the most important feedback according to the research paper is geological - the delayed isostatic rebound. This keeps the ice elevation low and therefore ice loss remains high while the ice sheet retreats. It is this delay which is responsible for the 100 kyear cycle. Other feed backs, dust feedback, oceanfeedback are less important.
The 100 kyear cycle can be reproduced in models even if CO2 levels are kept constant, although CO2 does influence the size of the ice sheet. If the rebound is instantaneous the 100 kyear cycle is no longer dominant.
-
StBarnabas at 05:01 AM on 15 August 2013A grand solar minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming
Chaps agreed a bit disappointing regarding the Irish Times, when I lived in Ireland it was easily the best paper - in the UK the Guardian is my paper of choice. I know Ian Elliott, or at least knew him when I was an undergraduate in Physics at UCD (1970ies). He was vwry good at public engagement. I can't really comment on him professionally as after becoming a graduate student in astronomy our paths never crossed.
StB
-
shoyemore at 04:05 AM on 15 August 2013A grand solar minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming
cynicus,
Correct, and what is disquieting is that the newspaper in question if far from being the usual Murdoch lowest-common-denominator or Daily Mail rag. Like the Economist and the New York Times, even the quality publications are inconsistent. I suspect the Environment correspondent and the Science correspondent of the Irish Times do not seem eye-to-eye.
-
IanC at 03:29 AM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
Tom @ 13,
It is true that geothermal heat is trivial at the ice-air interface, but not so at the ice-land interface. I think 'surface' here is meant to be the surface of the lithosphere and not the surface of the ice; with this interpretation the abstract is correct.
-
Tom Curtis at 02:33 AM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
p4gs @11, I would also be interested in such an article.
Just from looking at the abstract, it is a very interesting paper. Evidently, the weight of continental ice sheets causes a thining of the crust under the ice sheet, allowing enhanced geothermal heat flow. The effect can be seen in the upper right of the diagram below, shown with increased detail in the inset. As can be seen, heat flow reaches a minimum (green colours) during interglacials, and a maximum during glacials when the ice is thickest. As an aside, that suggests a very significant melt back of the greenland ice sheet during interglacials, to relieve the burden of ice mass and allow thickening of the lithosphere beneath the Greenland Ice Sheet.

WUWT appears to want to beat this up into a major factor, claiming:
"The Greenland ice sheet is melting from below, caused by a high heat flow from the mantle into the lithosphere."
They assert his despite their cutaway view of the Greenland Ice Sheet showing no temperatures above freezing. However, the diagram below should put paid to any such denier fantasies. The range of geothermal heat flux shown is from 0.043 to 0.061 W/m^2. That compares to a global average of 0.087 W/m^2, and is relatively small even for continental plates as can be seen below: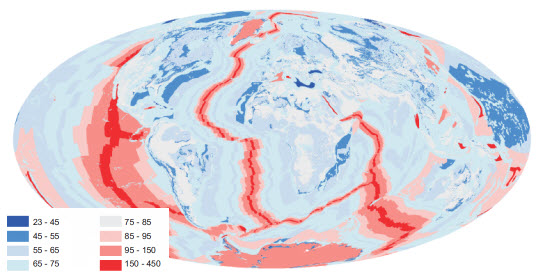
(Units are mW/m^2)
The peak rate, is therefore less than a 10th of the TOA energy imbalance caused by AGW, and the change in heat flow between glacial and interglacial is about a sixth of that again.
I must admit that having actually seen the figure shown, I am surprised that the abstract states:
"At the Earth’s surface, heat fluxes from the interior1 are generally insignificant compared with those from the Sun and atmosphere2, except in areas permanently blanketed by ice."
It would have been rather more accurate to state:
"At the Earth’s surface, heat fluxes from the interior1 are generally insignificant compared with those from the Sun and atmosphere2, except including in areas permanently blanketed by ice."
-
What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
p4gs - Looks like references to this paper are already showing up on the denial sites, in the apparent hopes of yet another claim that "it's not us".
Those claims would only make sense if there had been recent changes in the heat from the lithosphere - long standing heat patterns would be part of pre-Industrial conditions as well, and not causes of recent melt acceleration. Not to mention that observed changes in GHGs already account for the Greenland changes we've seen, and such "not us" claims would have to somehow explain those away...
-
BaerbelW at 02:18 AM on 15 August 2013Where SkS-Material gets used - Coursera's Climate Literacy Course
Just now received the Coursera email that the 2nd iteration of Climate Literacy will start on September 30, 2013!
-
p4gs at 01:22 AM on 15 August 2013What makes ice sheets grow and shrink?
I want Skeptical Science to do an article on this newly published research:
http://www.nature.com/ngeo/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/ngeo1898.html
Moderator Response:[JH] See: Greenland Ice Is Melting -- Even from Below: Heat Flow from the Mantle Contributes to the Ice Melt, ScienceDaily, Aug 11, 2013.
-
Tom Curtis at 00:50 AM on 15 August 2013A grand solar minimum would barely make a dent in human-caused global warming
chriskoz @2, you calculated the equilibrium climate response, wheras Dana calculated the transient climate response. The difference is in the factor of 0.67 Dana introduces for that purpose. Absent that, his value would have been 0.45 (or 0.48 with a less aggressive rounding).
One twist on this is that radiative forcing is calculated at the tropopause rather than the top of the thermosphere. Most UV radiation is absorbed above the tropopause, and the UV component of sunlight will varies in greater proportion with changing TSI. The effect is that with reduced TSI, relatively more of TSI will reach the surface than currently does. The solar forcing will still reduce, but not as much as the reduction in TSI so that the cooling will be even less than calculated.
Conversely, for the same reason, it requires a greater than 1.55% increase in TSI to generate a 3.7 W/m^2 increase in solar forcing.
Finally, it is possible that some such mechanism as that proposed by Svensmark would result in a greater reduction in temperature than simple calculations from TSI would suggest. His theory as it stands has been pretty much ruled out. Clouds form with great facility even in the absense of cosmic rays, and therefore cosmic rays are not the dominant force governing climate over the history of the Earth. However, cosmic rays may facilitate the generation of additional cloud nucleation particles thereby decreasing the average droplet size in clouds and hence increasing cloud albedo. This may amplify the direct TSI forcing by as much a factor of 2. Of course, there is as yet no solid evidence that this is the case. It just cannot be ruled out either.
-
Chris8616 at 23:15 PM on 14 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #33A
New discovered Mesospheric Polar Clouds possible indicator of Global Warming Link
Save the Earth Link
Prev 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























