My Research with Steve
Posted on 19 May 2015 by Guest Author
This is a re-post from ClimateSight
Almost four years ago I took a job as a summer student of Dr. Steve Easterbrook, in the software engineering lab of the University of Toronto. This was my first time taking part in research, but also my first time living away from home and my first time using a Unix terminal (both of which are challenging, but immensely rewarding, life skills).
While working with Steve I discovered that climate model output is really pretty (an opinion which hasn’t changed in the four years since) and that climate models are really hard to install (that hasn’t changed either).
At Steve’s suggestion I got a hold of the code for various climate models and started to pick it apart. By the end of the summer I had created a series of standardised diagrams showing the software architecture of each model.
These diagrams proved to be really useful communication tools: we presented our work at AGU the following December, and at NCAR about a year after that, to very positive feedback. Many climate modellers we met at these conferences were pleased to have a software diagram of the model they used (which is very useful to show during presentations), but they were generally more interested in the diagrams for other models, to see how other research groups used different software structures to solve the same problems. “I had no idea they did it like that,” was a remark I heard more than a few times.
Between my undergrad and PhD, I went back to Toronto for a month where I analysed the model code more rigorously. We made a new set of diagrams which was more accurate: the code was sorted into components based on dependency structure, and the area of each component in a given diagram was exactly proportional to the line count of its source code.
Here is the diagram we made for the GFDL-ESM2M model, which is developed at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory in Princeton:
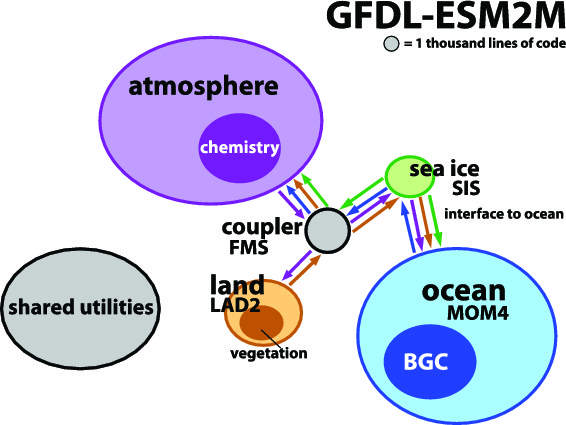
Figure 2 of Alexander et al., 2015
We wrote this all up into a paper, submitted it to GMD, and after several months and several rounds of revision it was published just yesterday! The paper is open access, and can be downloaded for free here. It’s my first paper as lead author which is pretty exciting.
I could go on about all the interesting things we discovered while comparing the diagrams, but that’s all in the paper. Instead I wanted to talk about what’s not in the paper: the story of the long and winding journey we took to get there, from my first day as a nervous summer student in Toronto to the final publication yesterday. These are the stories you don’t read about in scientific papers, which out of necessity detail the methodology as if the authors knew exactly where they were going and got there using the shortest possible path. Science doesn’t often work like that. Science is about messing around and exploring and getting a bit lost and eventually figuring it out and feeling like a superhero when you do. And then writing it up as if it was easy.
I also wanted to express my gratitude to Steve, who has been an amazing source of support, advice, conversations, book recommendations, introductions to scientists, and career advice. I’m so happy that I got to be your student. See you before long on one continent or another!































 Arguments
Arguments






























LOL - I think a LOT of scientists in just about any field of publication can relate to this!! Congrats on the first 'first author' article!
I remember when your monicker first popped up by way of climate blogs linking to yours. Great to have seen intermittent snapshots from there to here. Congratulations on your first lead authorship, and good on ya for contributing to the sum of knowledge!