Arguments
Arguments
 Software
Software
 Resources
Comments
Resources
Comments
 The Consensus Project
The Consensus Project
 Translations
Translations
 About
Support
About
Support


Latest Posts
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #6 2026
- The future of NCAR remains highly uncertain
- Fact brief - Can solar projects improve biodiversity?
- How the polar vortex and warm ocean intensified a major US winter storm
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #05
- Help needed to get translations prepared for our website relaunch!
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #5 2026
- Climate Variability Emerges as Both Risk and Opportunity for the Global Energy Transition
- Fact brief - Are solar projects hurting farmers and rural communities?
- Winter 2025-26 (finally) hits the U.S. with a vengeance
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #04
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #4 2026
- WMO confirms 2025 was one of warmest years on record
- Fact brief - Do solar panels release more emissions than burning fossil fuels?
- Keep it in the ground?
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #03
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #3 2026
- Climate Adam - Will 2026 Be The Hottest Year Ever Recorded?
- Fact brief - Does clearing trees for solar panels release more CO2 than the solar panels would prevent?
- Where things stand on climate change in 2026
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #02
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #2 2026
- UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
- Six climate stories that inspired us in 2025
- How to steer EVs towards the road of ‘mass adoption’
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #01
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #1 2026
- 2025 in review - busy in the boiler room
- Direct Air Capture
- IEA: Declining coal demand in China set to outweigh Trump’s pro-coal policies
Archived Rebuttal
This is the archived Intermediate rebuttal to the climate myth "Animal agriculture and eating meat are the biggest causes of global warming". Click here to view the latest rebuttal.
What the science says...
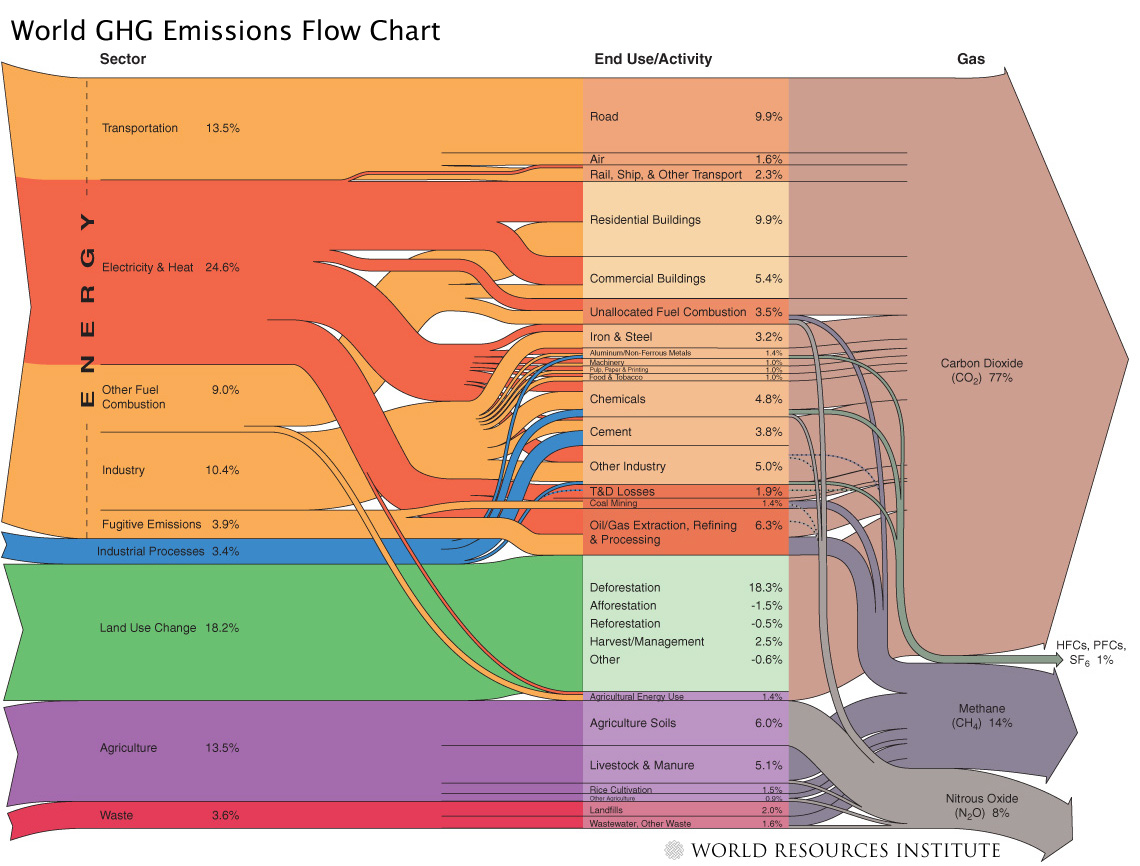
The burning of fossil fuels for energy and animal agriculture are two of the biggest contributors to global warming, along with deforestation. Globally, fossil fuel-based energy is responsible for about 60% of human greenhouse gas emissions, with deforestation at about 18%, and animal agriculture between 14% and 18% (estimates from the World Resources Institute, UN Food and Agriculture Organization, and Pitesky et al. 2009).
Global human greenhouse gas emissions flowchart, from the World Resources Institute.
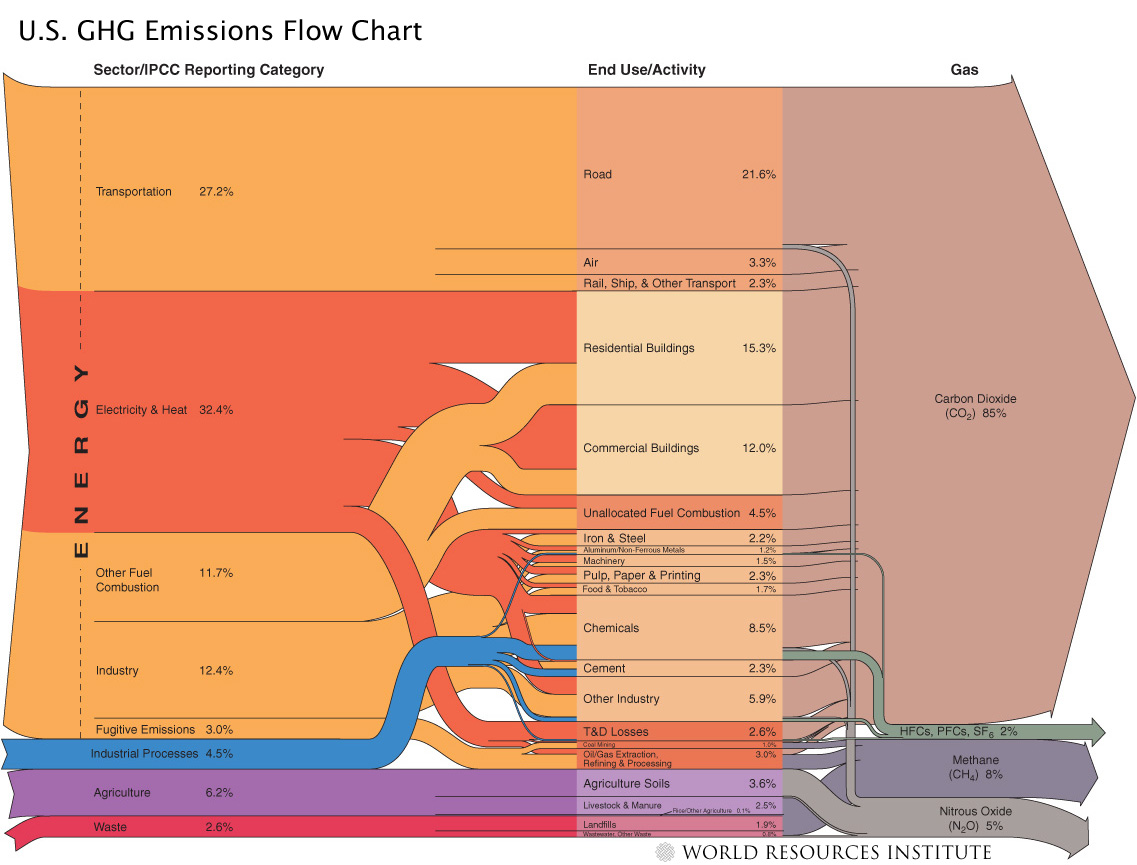
So, animal agriculture and meat consumption are significant contributors to global warming, but far less so than fossil fuel combustion. Moreover, fossil fuels are an even bigger contributor to the problem in developed countries, which use more energy and have increased livestock production efficiency (Pitesky et al. 2009). For example, in the United States, fossil fuel-based energy is responsible for about 80% of total greenhouse gas emissions as compared to about 6% from animal agriculture (estimates from the World Resources Institute and Pitesky et al. 2009).
US human greenhouse gas emissions flowchart, from the World Resources Institute.
How does animal agriculture cause global warming?
On of the main ways in which the livestock sector contributes to global warming is through deforestation caused by expansion of pasture land and arable land used to grow feedcrops. Overall, animal agriculture is responsible for about 9% of human-caused carbon dioxide emissions globally (UN FAO).
Animal agriculture is also a significant source of other greenhouse gases. For example, ruminant animals like cattle produce methane, which is a greenhouse gas about 20 times more potent than carbon dioxide. The livestock sector is responsible for about 37% of human-caused methane emissions, and about 65% of human nitrous oxide emissions (mainly from manure), globally (UN FAO).
Updated on 2015-11-26 by dana1981.
THE ESCALATOR

(free to republish)