 Arguments
Arguments
 Software
Software
 Resources
Comments
Resources
Comments
 The Consensus Project
The Consensus Project
 Translations
Translations
 About
Support
About
Support


Latest Posts
- Sea otters are California’s climate heroes
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #06
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #6 2026
- The future of NCAR remains highly uncertain
- Fact brief - Can solar projects improve biodiversity?
- How the polar vortex and warm ocean intensified a major US winter storm
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #05
- Help needed to get translations prepared for our website relaunch!
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #5 2026
- Climate Variability Emerges as Both Risk and Opportunity for the Global Energy Transition
- Fact brief - Are solar projects hurting farmers and rural communities?
- Winter 2025-26 (finally) hits the U.S. with a vengeance
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #04
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #4 2026
- WMO confirms 2025 was one of warmest years on record
- Fact brief - Do solar panels release more emissions than burning fossil fuels?
- Keep it in the ground?
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #03
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #3 2026
- Climate Adam - Will 2026 Be The Hottest Year Ever Recorded?
- Fact brief - Does clearing trees for solar panels release more CO2 than the solar panels would prevent?
- Where things stand on climate change in 2026
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #02
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #2 2026
- UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
- Six climate stories that inspired us in 2025
- How to steer EVs towards the road of ‘mass adoption’
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #01
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #1 2026
- 2025 in review - busy in the boiler room
Archived Rebuttal
This is the archived Intermediate rebuttal to the climate myth "Satellite record is more reliable than thermometers". Click here to view the latest rebuttal.
What the science says...
|
Satellites don't measure temperatures, and their uncertainty is five times as large as that in the global surface temperature record. |
Satellites don't measure temperature. When people refer to the satellite temperature record, they're referring to microwave sounding unit (MSU) instruments on satellites. As Andrew Dessler describes in the video below by Peter Sinclair, MSUs measure voltages on detectors, which themselves are detecting microwave signals emitted by oxygen molecules in the Earth's atmosphere. To translate these voltages and microwave detections into estimates of the temperature of various layers of the Earth's atmosphere requires a model.
Satellite Temperature Record Challenges
Converting those MSU microwave detections into a reliable long-term atmospheric temperature record is a challenging proposition, made all the more difficult by a number of confounding factors. For example, the satellites have a limited life span. The overall satellite MSU record is comprised of numerous satellites, and each has a different calibration, orbit, etc. that must be accounted for. During that life span, the satellites also experience friction, which causes their orbits to drift. If not correctly taken into account, these factors can create a bias in the estimated temperature record.
Another issue is that the MSU detections can be influenced by factors besides just temperature-influenced oxygen microwave signals, for example, cloud liquid water. Weng et al. (2014) found that the MSU channel (Channel 3) that focuses on the lowest level of the atmosphere (the lower troposphere) is most influenced by the presence of cloud liquid water. Weng et al. suggest,
the global mean temperature in the low and middle troposphere has a larger warming rate (about 20–30% higher) when the cloud-affected radiances are removed from AMSU-A data.
Roy Spencer who, with John Christy, runs the University of Alabama at Huntsville (UAH) satellite temperature dataset disagrees, believing that the cloud-caused bias is insignificant. The magnitude of this bias in the satellite data remains an unresolved question.
Another issue related to changes in the satellites' orbits is called 'diurnal drift'. The satellites are in 'Sun Synchronous orbits' and are meant to stay aligned with the Sun so that they always cross the equator at the same time. If they don’t, then the normal daily temperature cycles below will start to add a false bias to the data. The UAH team tries to get around this bias by attempting to use these satellites during periods when the diurnal drift is small, while other groups (RSS and NOAA) apply a correction based on the diurnal drift in a global climate model. Po-Chedley et al. (2015) argue that the UAH method creates a cool bias in their dataset.
There are still further challenges, for example the fact that the increased greenhouse effect cools the stratosphere, which is the layer of the atmosphere above the troposphere. If microwave measurements from the stratosphere bleed into estimates of tropospheric temperatures, that can also cause a cool bias in the trend. The figure below shows all the processing required to get from voltage measurements on an MSU sensor to an estimate of the temperature in the atmosphere.
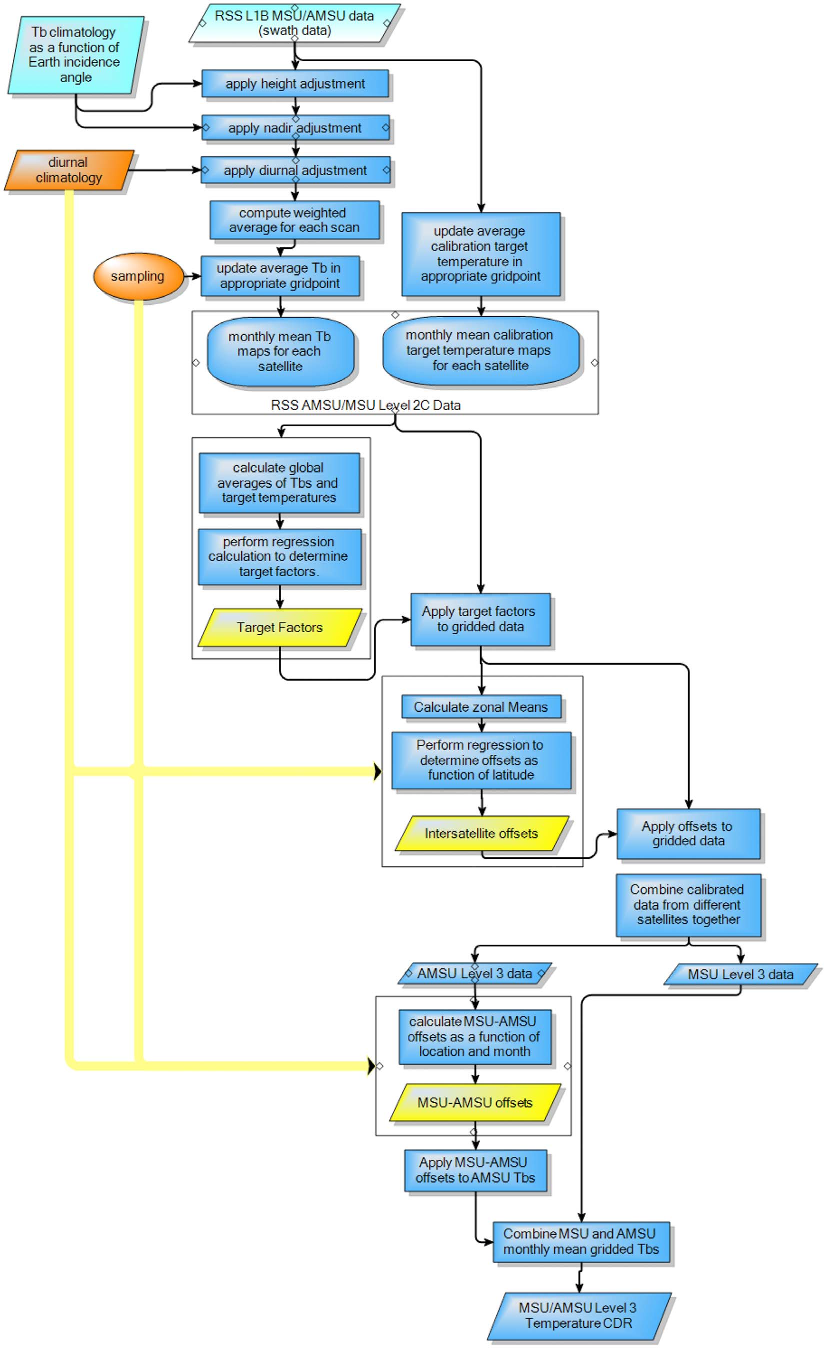
Flowchart of the processing algorithm for the RSS satellite data, from Mears et al. (2011)
As a result, the uncertainty in the satellite data is five times larger than that in the surface temperature record, which is based on direct measurements by thermometers.
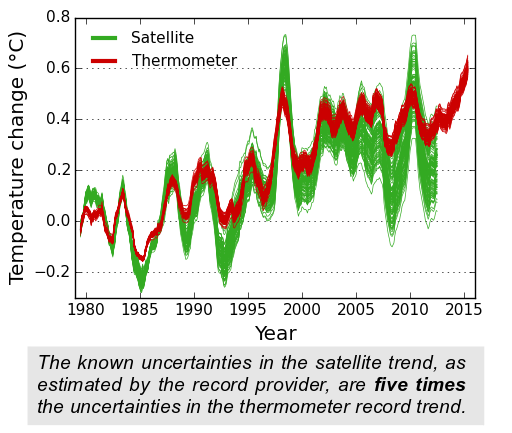
Spread in the satellite and surface temperature ensembles over time. Each line shows one possible temperature reconstruction from the ensemble (12 month moving average). All of the series have been aligned to a zero baseline for the 10 year period 1979-1988, so that the increasing spread after that period gives an indication of the variability in the trend. Created by Kevin Cowtan.
d
Updated on 2016-01-14 by dana1981.
THE ESCALATOR

(free to republish)
























































