 Arguments
Arguments
 Software
Software
 Resources
Comments
Resources
Comments
 The Consensus Project
The Consensus Project
 Translations
Translations
 About
Support
About
Support


Latest Posts
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #6 2026
- The future of NCAR remains highly uncertain
- Fact brief - Can solar projects improve biodiversity?
- How the polar vortex and warm ocean intensified a major US winter storm
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #05
- Help needed to get translations prepared for our website relaunch!
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #5 2026
- Climate Variability Emerges as Both Risk and Opportunity for the Global Energy Transition
- Fact brief - Are solar projects hurting farmers and rural communities?
- Winter 2025-26 (finally) hits the U.S. with a vengeance
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #04
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #4 2026
- WMO confirms 2025 was one of warmest years on record
- Fact brief - Do solar panels release more emissions than burning fossil fuels?
- Keep it in the ground?
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #03
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #3 2026
- Climate Adam - Will 2026 Be The Hottest Year Ever Recorded?
- Fact brief - Does clearing trees for solar panels release more CO2 than the solar panels would prevent?
- Where things stand on climate change in 2026
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #02
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #2 2026
- UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
- Six climate stories that inspired us in 2025
- How to steer EVs towards the road of ‘mass adoption’
- 2026 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #01
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #1 2026
- 2025 in review - busy in the boiler room
- Direct Air Capture
- IEA: Declining coal demand in China set to outweigh Trump’s pro-coal policies
Archived Rebuttal
This is the archived Intermediate rebuttal to the climate myth "Wildfires are not caused by global warming". Click here to view the latest rebuttal.
What the science says...
|
Global warming worsens wildfires by drying vegetation and soil, creating more fuel for fires to spread further and faster. In some areas like southeastern Australia and California, altered atmospheric patterns may also be creating stronger a |
The clearest connection between global warming and worsening wildfires is by increasing evapotranspiration and the vapor-pressure deficit. In simple terms. vegetation and soil dry out, creating more fuel for fires to expand further and faster. This is particularly a problem in Mediterranean climates that are prone to drought, like in California and Australia.
For example, California's record-breaking wildfire season in 2018 came at the culmination of the state's five hottest years on record (2014–2018) and a record-breaking drought (2012–2017). Australia's record-breaking bushfire season of 2019–2020 followed the continent's two hottest and driest years on record, and expanded during a record-breaking heatwave that included an average country-wide high temperature of 41.9°C (107.4°F) on 18 December 2019.
Though many factors contribute to wildfires, the reason the Australian wildfires are so much worse this year than other recent years is the combination of record drought and record heat. #AustraliaFires
— Robert Rohde (@RARohde) January 4, 2020
History of national-average temperature and precipitation since 1910. pic.twitter.com/aHh3kDFIZ7
Because of the long-term warming trend, the Fourth National Climate Assessment Report concluded,
“Climate change has led to an increase in the area burned by wildfire in the western United States.Analyses estimate that the area burned by wildfire from 1984 to 2015 was twice what would have burned had climate change not occurred. Furthermore, the area burned from 1916 to 2003 was more closely related to climate factors than to fire suppression, local fire management, or other non-climate factors.
Climate change has driven the wildfire increase, particularly by drying forests and making them more susceptible to burning.”
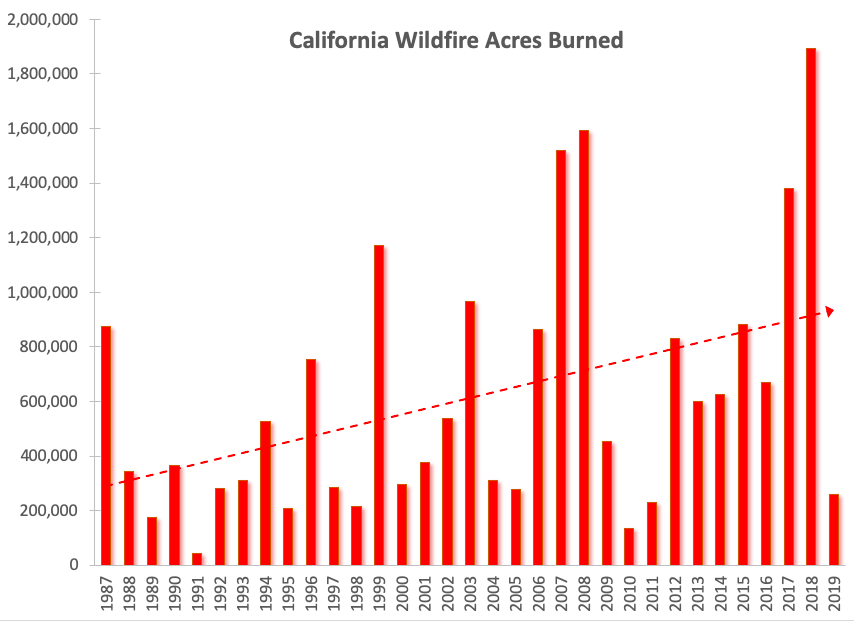
Acres burned by wildfires in California 1987–2019, with the linear trend shown. Data from Cal Fire.
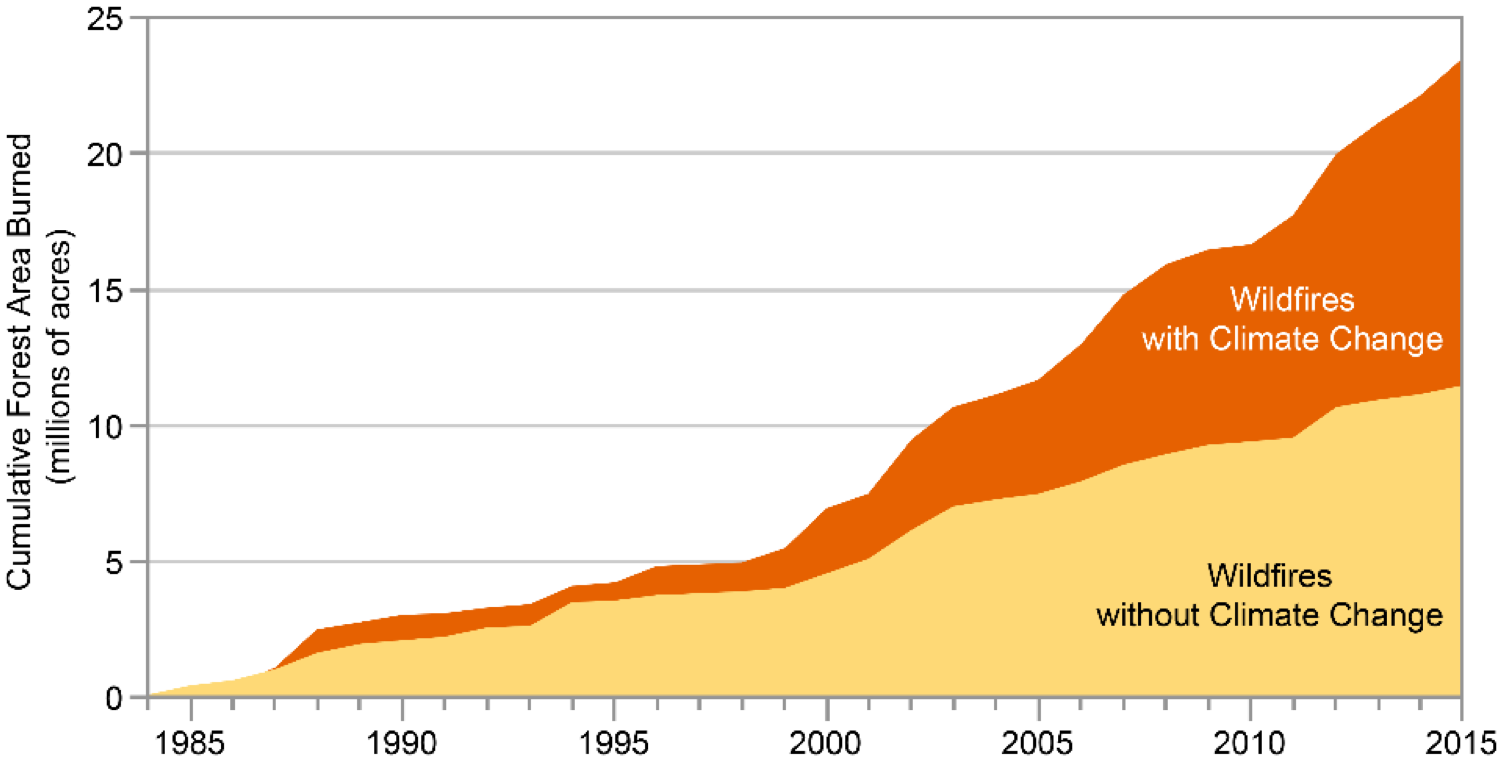
Cumulative forest area burned in the western United States 1984–2015, and attribution to human-caused climate change. Source: Fourth National Climate Assessment.
A second, though more scientifically uncertain connection between climate and worsening wildfires involves changing atmospheric circulation patterns.
Updated on 0000-00-00 by dana1981.
THE ESCALATOR

(free to republish)
























































