A severe winter storm that brought crippling freezing rain, sleet and snow to a large part of the U.S. in late January 2026 left a mess in states from New Mexico to New England. Hundreds of thousands of people lost power across the South as ice pulled down tree branches and power lines, more than a foot of snow fell in parts of the Midwest and Northeast, and many states faced bitter cold that was expected to linger for days.
The sudden blast may have come as a shock to many Americans after a mostly mild start to winter, but that warmth may have partly contributed to the ferocity of the storm.
As atmospheric and climate scientists, we conduct research that aims to improve understanding of extreme weather, including what makes it more or less likely to occur and how climate change might or might not play a role.
To understand what Americans are experiencing with this winter blast, we need to look more than 20 miles above the surface of Earth, to the stratospheric polar vortex.
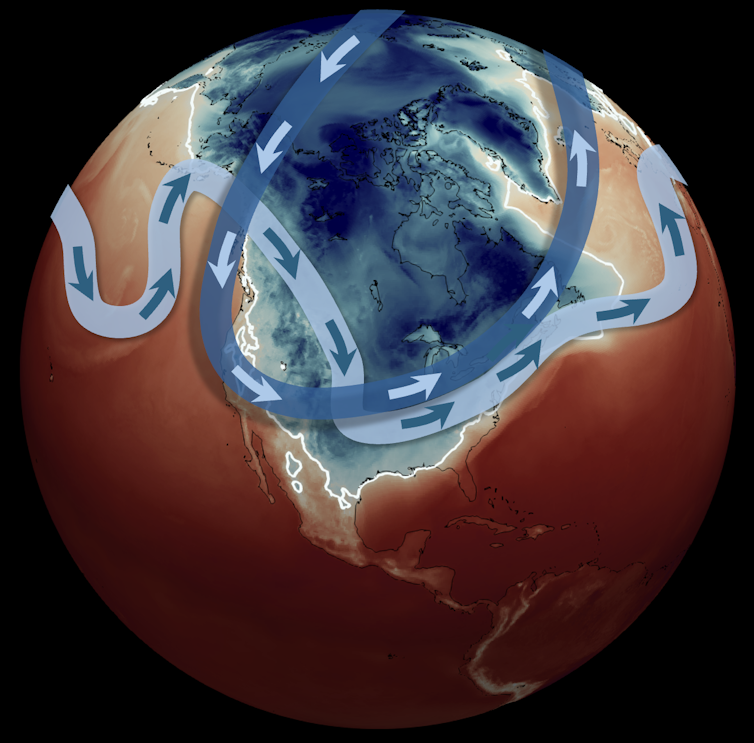 On the morning of Jan. 26, 2026, the freezing line, shown in white, reached far into Texas. The light band with arrows indicates the jet stream, and the dark band indicates the stratospheric polar vortex. The jet stream is shown at about 3.5 miles above the surface, a typical height for tracking storm systems. The polar vortex is approximately 20 miles above the surface. Mathew Barlow, CC BY
On the morning of Jan. 26, 2026, the freezing line, shown in white, reached far into Texas. The light band with arrows indicates the jet stream, and the dark band indicates the stratospheric polar vortex. The jet stream is shown at about 3.5 miles above the surface, a typical height for tracking storm systems. The polar vortex is approximately 20 miles above the surface. Mathew Barlow, CC BY
What creates a severe winter storm like this?
Multiple weather factors have to come together to produce such a large and severe storm.
Winter storms typically develop where there are sharp temperature contrasts near the surface and a southward dip in the jet stream, the narrow band of fast-moving air that steers weather systems. If there is a substantial source of moisture, the storms can produce heavy rain or snow.
In late January, a strong Arctic air mass from the north was creating the temperature contrast with warmer air from the south. Multiple disturbances within the jet stream were acting together to create favorable conditions for precipitation, and the storm system was able to pull moisture from the very warm Gulf of Mexico.
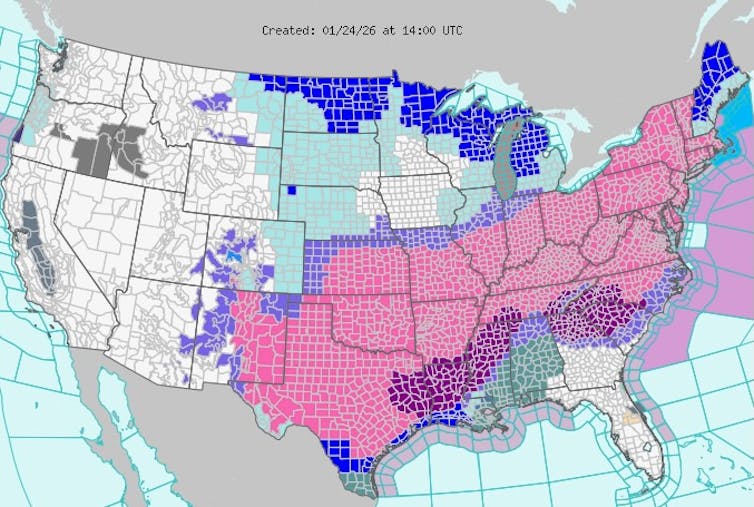 The National Weather Service issued severe storm warnings (pink) on Jan. 24, 2026, for a large swath of the U.S. that could see sleet and heavy snow over the following days, along with ice storm warnings (dark purple) in several states and extreme cold warnings (dark blue). National Weather Service
The National Weather Service issued severe storm warnings (pink) on Jan. 24, 2026, for a large swath of the U.S. that could see sleet and heavy snow over the following days, along with ice storm warnings (dark purple) in several states and extreme cold warnings (dark blue). National Weather Service
Where does the polar vortex come in?
The fastest winds of the jet stream occur just below the top of the troposphere, which is the lowest level of the atmosphere and ends about seven miles above Earth’s surface. Weather systems are capped at the top of the troposphere, because the atmosphere above it becomes very stable.
The stratosphere is the next layer up, from about seven miles to about 30 miles. While the stratosphere extends high above weather systems, it can still interact with them through atmospheric waves that move up and down in the atmosphere. These waves are similar to the waves in the jet stream that cause it to dip southward, but they move vertically instead of horizontally.
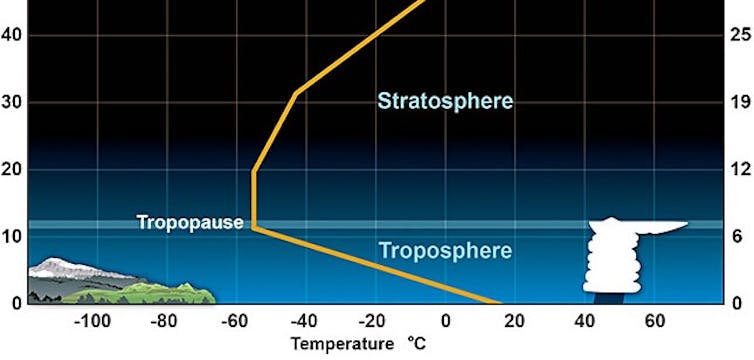 A chart shows how temperatures in the lower layers of the atmosphere change between the troposphere and stratosphere. Miles are on the right, kilometers on the left. NOAA
A chart shows how temperatures in the lower layers of the atmosphere change between the troposphere and stratosphere. Miles are on the right, kilometers on the left. NOAA
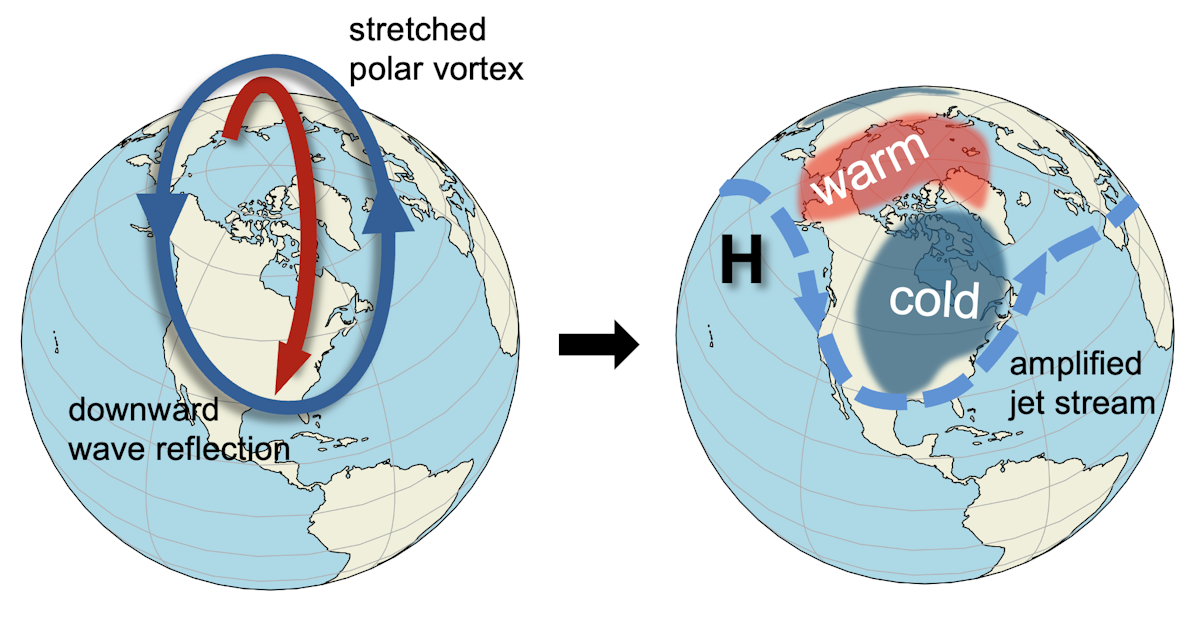
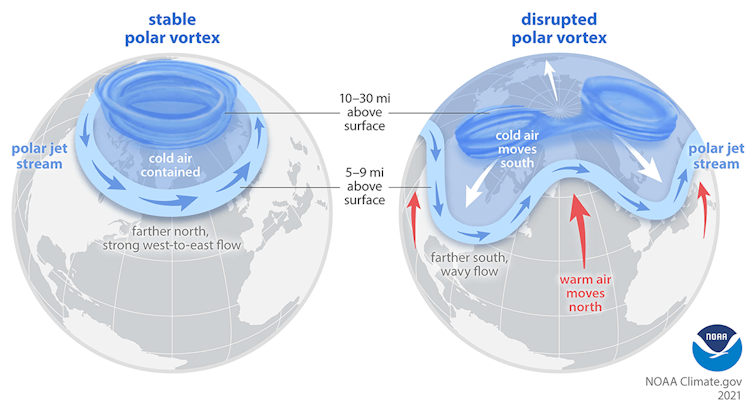
You’ve probably heard the term “polar vortex” used when an area of cold Arctic air moves far enough southward to influence the United States. That term describes air circulating around the pole, but it can refer to two different circulations, one in the troposphere and one in the stratosphere.
The Northern Hemisphere stratospheric polar vortex is a belt of fast-moving air circulating around the North Pole. It is like a second jet stream, high above the one you may be familiar with from weather graphics, and usually less wavy and closer to the pole.
Sometimes the stratospheric polar vortex can stretch southward over the United States. When that happens, it creates ideal conditions for the up-and-down movement of waves that connect the stratosphere with severe winter weather at the surface.































 Arguments
Arguments






























Comments