Recent Comments
Prev 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 Next
Comments 6451 to 6500:
-
Philippe Chantreau at 11:07 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Ingrahammark7's: "Chart the incremental temperature insulation from different thicknesses of co2" is a little cryptic a question but it seems that the Iacono & Clough 95 paper would answer that, to an extent, I think (hard to tell, the language is a little puzzling). The Iacono & Clough graph is featured in post #381 of this thread by Tom Curtis.
This following statement, to me, is not making enough sense to try to answer: "You chart should be utterly absurd because you have to explain why the first few co2 cause the entire effect and once you get to hundreds or thousands of feet which exist a doubling does nothing."
-
Rob Honeycutt at 11:00 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
My question for Ingrahammark7 is, given that what is being explained here is science that's been well accepted for over a century, what makes you think that somehow the world's leading scientists don't understand something that, as you put it, would be obvious to a small child?
I find that to be a rather ridiculous position to put forth.
-
Bob Loblaw at 10:33 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
MAR:
Possibly, but Ingrahammark7's statement also resembles the kind of thing you'd hear from the group that think there is absolutely no greenhouse effect, no backradiation, violates the 2nd, law, etc., and pressure is the only factor.
Ingrahammark7's understanding of basic physics hasn't been very good so far.
-
Philippe Chantreau at 10:33 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
As DB said years ago, this is not quite like reinventing the wheel but rather reinventing the flat tire..
-
MA Rodger at 06:34 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Bob Loblaw @602,
I think the comment from Ingragammark7 @600 that "The temperature gradient in the atmosphere is determined by pressure." is not actually away with the faries as I see it as a less-than-precise description of the Lapse Rate being close to adiabatic, thus atmospheric pressure & temperature are strongly linked. It is the statement following that quote from #600 "The greenhouse effect would break this relationship and raise temperatures at lower altitudes where diminishing returns is less." that makes no sense to me.
-
Bob Loblaw at 06:21 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Oops. I dropped a factor of 1000 when I first made the image in comment #601. I have corrected the image.
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:59 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
In #600, Ingrahammark7 says "The temperature gradient in the atmosphere is determined by pressure."
Oh, my, you're in that group of alternate physics. I suspect there is no hope for you.
You may wish to continue alternative explanations of the atmospheric temperature gradient on this thread. Please actually read the post before you start commenting, though. I doubt you have any new arguments to make.
https://skepticalscience.com/postma-disproved-the-greenhouse-effect.htm
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:53 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Oh, my, Ingrahammark7. You certainly are persistent in your misunderstandings.
You said in #599: "This does not take any math, or diagrams, if insulation worked in a linear way then it would lead to absurd outcomes and everyone would already be dead."
Well, your diagram linked to in #596 must have taken some math, so let's see if we can reproduce it. (And remember that "linear" statement - we'll test it later on.) First, I wll establish some assumptions:
- We'll work with a wall that is 1000 m2 in area
- We'll assume that the wall material has a thermal conductivity of 1 W/mK
- We'll assume that we want to maintain a temperature difference (inside - outside) of 1C (or 1K, whichever you prefer).
What amount of heating is required to maintain that temperature difference for different wall thickness?
The equation we want is
(heat input/area) = (conductivity * temperature difference)/(wall thickness)
At 1m thickness, we need 1000W (or 1 W/m2 of wall area).
We can graph the heat required as a function of wall width and get this:
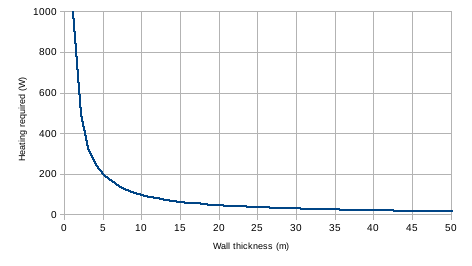
So, here we can see the "diminishing returns" that Ingrahammark7 thinks proves the CO2 effect is saturated.
Let's look at our wall thickness calculations slightly differently. As MA Rodger points out in #598, buildings have thermostats. In a building,we want to know how much heat it takes to maintain a certain temperature or amount of warming, as in the above diagram (and the one that Ingrahammark7 chose to display).
...but that is not what is happening in the earth-atmopshere system. We have a slightly different set of conditions:
- A constant rate of heating
- A temperature rise that varies depending on the "insulating effect"
How does our building behave in similar conditions? We will work with a matching set of assumptions:
- A wall that is 1000 m2 in area
- The wall material has a thermal conductivity of 1 W/mK
- ...but instead of a constant temperature difference controlled by a thermostat, we have a constant heat input of 1000W.
Now, our temperature difference needs to be calculated. We rearrange the above questions, and get:
temperature difference = (heat input/area) * ((wall thickness/conductivity)
What does our graph look like when we plot temperature difference against wall thickness?
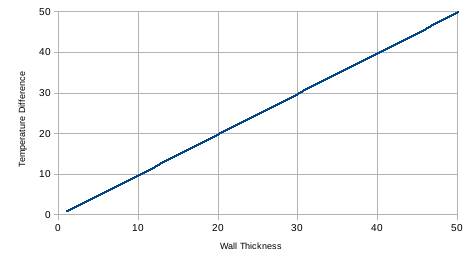
...and Ingrahammark7's "diminishing returns" go *poof*. The temperature difference is a linear function of wall thickness for constant heat input. It turns out that unless you turn the heat down, adding too many blankets will kill you. (And the linearity is obvious from the equation.)
So, Ingrahammark7's "obvious" argument is obviously wrong.
-
Ingrahammark7 at 03:57 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
"Also, the temperature gradient up through the atmosphere is not determined by CO2." In case you were expecting a response to this- that statement is unrelated to the discussion but it nonethless further refutes your point. The temperature gradient in the atmosphere is determined by pressure. The greenhouse effect would break this relationship and raise temperatures at lower altitudes where diminishing returns is less.
-
Ingrahammark7 at 02:42 AM on 25 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Eclectic, the second diagram is incoherent, if you think adding to a five mile blanket adds any insulation then then there is something wrong. This does not take any math, or diagrams, if insulation worked in a linear way then it would lead to absurd outcomes and everyone would already be dead.
"Add too many blankets and the occupant will die of hyperthermia" this is what I want you to see demonstrate in real life. You are not going to arbitrarily raise heat by adding blankets. Insulation only raises temperature a few degrees in the first few inches and after that is negligible.
Here is my request, since the graph I provide would just show the same as I already gave. Chart the incremental temperature insulation from different thicknesses of co2. Whether you call It insulation or something else is irrelevant. You chart should be utterly absurd because you have to explain why the first few co2 cause the entire effect and once you get to hundreds or thousands of feet which exist a doubling does nothing.
-
HK at 23:57 PM on 24 July 2021It's Urban Heat Island effect
Here's the rate of warming per century since 1960 at some Berkeley Earth reference points.
50 km north-west of New York City:
+ 2.86°C
North-western Maine:
+ 2.90°C
Close to Barrow in northern Alaska:
+ 4.79°C
170 km north-west of Yellowknife, northern Canada:
+ 4.60°C
Northern Finland:
+ 3.03°C
Franz Josef Land, north-east of Svalbard:
+ 5.63°C
Central Kazakhstan:
+ 2.55°C
Close to Yakutsk in eastern Siberia:
+ 4.15°CWhat happened to the urban heat island effect?
-
MA Rodger at 22:51 PM on 24 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Ingrahammark7 @595/596,
While it is correct that conductive insulation is dependent on the temperature gradient through the insulation and the less the gradient, the less the heat loss, the OP above makes clear the mechnism of CO2 insulation does not work in that manner. So only a badly taught "small child" would hold the views you suggest.
We are not taking blankets where an additional blanket will diminish the outward energy flow by stretching the distance between inside and outside temperatures and thus reducing the temperature gradient within the insulative blankets. The level of radiative energy flying about the atmosphere is not diminished by adding extra CO2. Also, the temperature gradient up through the atmosphere is not determined by CO2. The workings of the greenhouse effect is explained by the OP in its Basic/Intermediate/Advanced versions.
Mind, your logic about R-values and blankets is also in error. The logic of the R-value is used to assess the insulation of buildings. It is useful because buildings have thermostats. The planet Earth has no thermostat (other than CO2 levels). And there is no thermostat in a bed. Add too many blankets and the occupant will die of hyperthermia.
-
Eclectic at 22:46 PM on 24 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
Ingrahammark7 @ 595 / 596 :
You have missed the mark - by a mile.
What a pity you did not read the Original Post. And in particular, have a think about the second diagram there.
Ingraham . . . how can you educate yourself, if you don't read?
( Hint: the atmosphere is a gas, not a wool blanket. )
-
Ingrahammark7 at 19:14 PM on 24 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
-
Ingrahammark7 at 19:11 PM on 24 July 2021CO2 effect is saturated
The co2 saturation is obvious, it's the difference between wearing five feet of blankets and five miles. Insulation is proportional to 1/thickness^2 so obviously anything beyond the first few feet of the hundreds of meters of co2 in the air is irrelevant.
This is obvious to a small child so the global warming advocates are just not beleving what they are saying. -
prove we are smart at 10:21 AM on 24 July 2021As scientists have long predicted, warming is making heatwaves more deadly
Taken from Wiki: "Mass maintains a popular weblog in which he posts regular articles on meteorology, Pacific Northwest weather history, and the impacts of climate change[8] written for the general public. According to Mass, "Global warming is an extraordinarily serious issue, and scientists have a key role to play in communicating what is known and what is not about this critical issue.[9]"
Mass has stated publicly that he shares the scientific consensus that global warming is real and that human activity is a major cause of warming trend in the late 20th and 21st centuries.[10][11] He has been critical of the Paris Climate accord for not going far enough to address the negative impacts of climate change.[12]
However, Mass is frequently critical of and has expressed concern that when media and environmental organizations make exaggerated claims about the current impacts of climate change, or cite climate change as the cause of specific weather events. He is concerned about misinforming the public about a key societal issue, distracting public and governmental attention from more immediate environmental concerns, and stifling opportunities for effective bipartisan policy-making to slow climate change and mitigate its effects.[13][14][15][16]
His statements on the severity and progression of anthropogenic global warming have elicited condemnation from The Stranger[17] as well as members of activist environmental organizations[18] due to concerns that Mass's scientific approach to understanding and communicating the risks associated with global warming could result in public apathy or be used by climate change deniers to bolster their claims."
I think Professor Mass is just typical of climate scientists giving responses to their perceived inaccuracies in the increasing climate craziness reporting. What is different with this professor is he is more of a "personality". Possibly the second link from 2.Bob Loblaw at 22:18 PM on 21 July, 2021 disproves Mass' theory but the science though was beyond my understanding.
The back and forth exchange between scientists peer reviewing "science" is what keeps us up to date and reliably informed. The fact Climate Change deniers can cherry pick a "headline" will never change. I don't know whether to feel hopeful or nor when I read this either,
-
sfkeppler at 02:24 AM on 23 July 2021As scientists have long predicted, warming is making heatwaves more deadly
Scientists rarely question the fact of Climate Change. The question is why climate is changing, and the fellows of the carbon theory won the pot, contaminating every climate discussion with their "Bad Humanity" idea. And actually, all people solely think about CO2 and Greenhouse gas emission. No other idea has permission to be pronounced. Other opinions are judged as non-scientific and are demoralized. At the same time, people forget to think about the greenhouse effect of water, the most abundant substance on earth. It is the fact, that water cools the earth’s surface by evapotranspiration by making possible all living conditions in the biosphere. Even if carbon plays its role in global warming, the water’s cooling effect is much important for immediate corrective action, by massive reforestation in the tropics.
The tropics distribute their energy by convection of water-vapor and cool the hemispheres by precipitation and washing out of carbon dioxide. Therefore, we should intensify research on the global hydrological cycle and stop immediately all deforestation in the tropics. Especially the Mangroves should be preserved, as we perceive looking to Somalia and the consequences of its prehistorical extinction. We argue that even the expansion of the Sahara desert is a consequence of deforestation an the western shore of the Red Sea.Moderator Response:[DB] As constituted, your comment is a Gish Gallop of unrelated and uncogent claims. Please first read the Newcomers, Start Here page and then the History of Climate Science and the Big Picture pages before commenting further. If you still have concerns needing answers at that point, use the Search function in the Upper Left corner of any page here and place those concerns formatted as questions on the most appropriate page. Thanks!
-
michael sweet at 01:21 AM on 23 July 20212021 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #29
An article in the Guardian today talked about how people moved to the Pacific Northwest in the USA because it is cool and was perceived as a refuge from climate change. The recent heat wave scorched the area and people are changing their thinking. The article ended with this quote from a local resident:
"“To me, it is climate change in action. I don’t really want to move away but I don’t want to live here and cut short my life either [from breathing all the smoke]. That’s something we are struggling with. The question is, though – where would we go to?” my emphasis.
-
MA Rodger at 22:15 PM on 22 July 2021It's Urban Heat Island effect
blaisct @59,
You say:-
"When urban areas of the earth were small (less than 1%) the “heat island” effect was probably insignificant. Now that the urban area is over 3% of the earth’s surface an area correction is needed."
The area of urban development is (according to Gao & O’Neill (2020) 'Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways' ) still well below 1% of global area at 0.6 million sq km in 2000 or 0.12% and, while growing, will remain below 1% by 2100 even with the highest of projections which show a rise to 0.7%. The Fig 1 of that paper is pasted below.
This then suggests "the “heat island” effect is and will remain probably insignificant." and thus no "correction is needed."
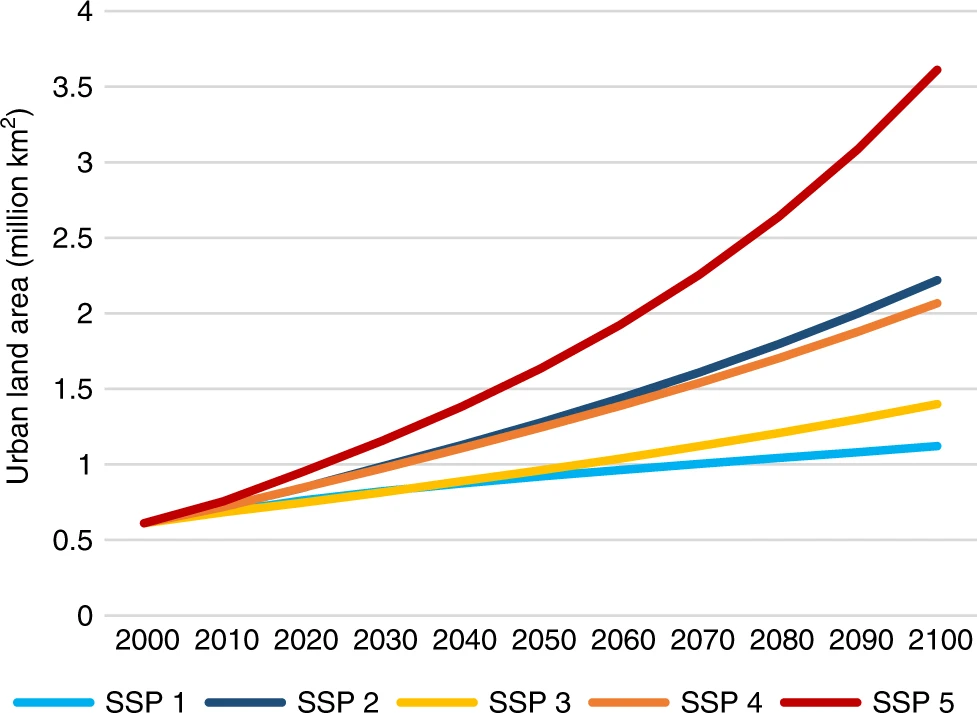
-
John Hartz at 05:02 AM on 22 July 2021As scientists have long predicted, warming is making heatwaves more deadly
Recommended supplementary reading:
Scientists are worried by how fast the climate crisis has amplified extreme weather by Angela Dewan, CNN, July 20, 2021
An exceprt from the article:
"Climate scientists have for decades warned that the climate crisis would lead to more extreme weather. They said it would be deadly and it would be more frequent. But many are expressing surprise that heat and rain records are being broken by such large margins.
Since the 1970s, scientists have predicted the extent to which the world would warm fairly accurately. What's harder for their models to predict — even as computers get more and more powerful — is how intense the impact will be."
A number of prominent climate scientists were interviewed for the article and are extensively quoted.
https://www.cnn.com/2021/07/20/world/climate-change-extreme-weather-speed-cmd-intl/index.html
-
blaisct at 02:23 AM on 22 July 2021It's Urban Heat Island effect
Should we be looking at the surface area of the earth these differences in trends represents? These graphs would better be related to climate change if they included some correction for urban area change. Over time this urban area may be increasing (and suburban area decreasing) thus the total heat into the atmosphere is also increasing proportional to that area change. I expect that including urban area increase due to population would show a significant increase in total heat going into the atmosphere over time vs the suburban areas. When urban areas of the earth were small (less than 1%) the “heat island” effect was probably insignificant. Now that the urban area is over 3% of the earth’s surface an area correction is needed. There may also be some differences in the albedo of cities due to construction practices and population density.
Moderator Response:[BL] Land use changes such as albedo are a regular part of the IPCC reporting. You can look through their reports to assess the effect of known changes.
You have posted a lot of speculation (maybe this, maybe that) without supporting evidence. In particular, what is the source of your claim that the urban area has changed by the amount you claim?
Meaningless speculation without supporiting information is not productive.
-
Bob Loblaw at 22:18 PM on 21 July 2021As scientists have long predicted, warming is making heatwaves more deadly
Although his blog post does not refer directly to Clifford Mass, Tamino (who has participated in the discussion of this at RealClimate, has posted an analysis of the heat wave:
https://tamino.wordpress.com/2021/07/16/northwest-heat-wave/
-
shoyemore at 17:01 PM on 21 July 2021As scientists have long predicted, warming is making heatwaves more deadly
This blogpost by Clifford Mass of UoW has already attracted a lot of adverse comment on Real Climate, and elsewhere.
https://cliffmass.blogspot.com/2021/07/was-global-warming-cause-of-great.html
Though more than one error has been pointed out e.g. Mass claiming no trend for increasing temperature records in the Pacific NW, when there clearly is a trend in the chart he shows, he has not modified the post in any way.
It is a dispiriting reminder that some scientists are still lending their credibility to climate change denial, whatever their intentions. I found mass being cited by the "uninformed" as an excuse for inaction.
A more detailed refutation of Mass' post may be in order.
Moderator Response:[BL] Link activated.
The web software here does not automatically create links. You can do this when posting a comment by selecting the "insert" tab, selecting the text you want to use for the link, and clicking on the icon that looks like a chain link. Add the URL in the dialog box. -
Jds at 04:50 AM on 21 July 2021The number of lives that clean energy could save, by U.S. state
Data graphs... Interesting... Fact sheets, do tell. Article by who? Really. Source links to a group that links it's source information back to itself.
C02 is not a poison until it reaches highly concentrated levels. Rarely happens.
.04% of our atmosphere is c02. .0016% of that .04% is manmade. Multiply the two figures together to get the % of the atmosphere which is manmade c02. That's .000064. If you added .000064% pink panther fiberglass to your outhouse your butt would still be cold in the winter.
Studies reveal!!! What studies? Oh, Yale. University. Must be smart kids there these days. Reading books. Looking at thermometers.
Been researching C02 detectors myself lately. Basic description for the most detailed I shall provide now.
Too housing contains filter mechanism. Bounces Electrons (little buggers) back and forth between electrode plates. Electrolytes (salt water? Potassium? Gatorade?) change c02 to o2 through oxidation (rust) and reduces (evaporates)... get ready far this... oxygen into water. O into H2O. Yup... water into wine as well I suppose. The electrodes are biochemically sensitive to these changes.
I'll have to look this convuluted one up again for further details. It didn't mention any silicone chips nor as usually typical the almighty laser.
Fancy thermometer at best. Get yours free shipping from Walmart for like $30.
You can't even find anyone who wants to admit being the inventor of these snake oil charms nor will you find any original patents. Yet hundreds of mostly fly by night companies sell them for prices up into the thousands.
Shows parts per million.
NASA has these million dollar detectors that shoot lasers from far above to hit the earth surface and I suppose eventually be picked up by some big Gatorade coated hunk of metal which detects out of each of the million parts that exist in the atmosphere... 400 are C02. Further calculations determine that we cased half of this.
Here is an interesting argument. It has been millions of years since the global temperature and C02 levels have been this high and man wasn't even around back then which proves man is the current cause!!! Most unintelligent argument to date. Who caused the high rates back then if we were not around? Wooly mammoth? Hairy hippos? It's like saying your daughter's boyfriend must not have worn a condom the last time they had sex because your great grandmother was pregnant at one time.
Please think before you make pointless arguments.
We humans if all in one spot on a globe shoulder to shoulder would not even be much of a pin point. Combine all of our biggest cities into one megalopolis... a small freckle on the on the face of ma Gaia.
Mother earth has made home for countless creatures... if we were to just add the ones we have yet to discover to the internet... google would overheat and break down from an overload. And yet we still search for even one or to life forms elsewhere.
Mother earth has survived subzero trips to the shore and hot lava baths. She is covered in worm poo and skunk diddle.
And you worry she will die from second hand smoke which has been circulating since the dawn of her birth.
Your numbers are baseless. Your charts disconnected. Your facts biased. Your proofs conjectured. Your projections assumed. Your own researched will lead you down rabbit holes that will have you as well ask questions to determine validity. Give it time and you find... fancy thermometers. People pointing lasers at silicone chips. Digital readings.
There are no valid reputable respectable people in the realm of all of our highest minds who can validate and properly explain the how function of your fancy thermometers. They just assume like you did that the producers knew what they were doing by way of high intelligence and education and not one in the line of them would ever attempt to decide or hoodwink. Nobody dares to question fancy thermometer for fear they will look unintelligent themselves.
And you can take my statements directly to any of our scientists. Then bring those kids to me. I would like to see their heads sink in sullen shame as we review all of the information available in the world about fancy thermometer... and here them admit to it's nonsense.
Nice charts. Splendid graphs.
Pretty fancy thermometers.
Now prove to me that our c02 without one shred of any doubt 100% caused the average number of tsunamis per year to go from 2 to 3.
Show me just one autopsy report stating cause of death was... air pollution.
Show me the beaches where brilliant scientists are dutifully lined up measuring constant instant by instant changing ocean depths and receding shorelines.
Show me that the number of facilities which extract atmospheric data from the air are evenly distributed across the world and not primarily clumped into rural areas. The ratio difference of such facilities between rural and non grows every year in favor of the rural. That in itself makes for apparant temperature anomalies.
Show me where climate summits, committees, activist gatherings and fancy thermometer operators ever saved or even improved the life of even one person. Common sense of a child would tell you if they spent one tenth of the time exploring ways to prepare ourselves for natural disasters that are unavoidable regardless of our activities (you do know such things exist?) they would save many lives. Just one tenth of your focus shifted toward a more fruitful activiy... it is not much to ask.
Show me empirical evidence and precision studies prove that a two degree raise in global temp makes an unstable earth when global temperates rise and fall many multiples of degrees higher and lower within seasons (Siberia holds 100° record differential), months, weeks, days, hours... any increment of time. Regionally two degree shifts happen within seconds... why can you not make a connection to calamity in these instances? Why do you refuse to admit 2° shifts over a century might be a small % normal. bet if I told the right activist that scientists predict an unpredicted ten degree shift in average global temperature within the hour... those activist would fall in panic, run out the back door with their fancy thermometers pass out from the frantic exhaustion of getting their ownselves heated over a common occurrence.
Show me the credentials of each and every root source of every last statistic you have blind faith in. I would like to know if fancy thermometer makers might not be pushing a few numbers. Bet your bank account some are.
Show me how C02 is killing anything currently. Start looking for actual single file individual case examples in the anals of all our history of even one person who passed out from too much carbon dioxide... I'll give you the rest of your life to produce such papers... good luck. Before you can do that I will prove c02 allows for more life to flourish.
Show me a year that has not had both record high and low temperatures. Of course we must remember readings are not evenly dispersed yet and the lasers attached to satellites are yet to be a cover all.
Show me again the ice age many of the scientists from the 70's were warning us about... where is it? Guess that concept was beginning to sell less copies so they had to change the format or big guv who has an interest in people who have a concern the main public is following will stop funding them... seriously I want you to reread that last statement a few times... let it sink in. Think about the implications and how very real they might we'll be.
Show me causation, not correlation. The person did not get a sun tan on a hot day because a coconut dropped on their head that day.
And really a bunch of the information I may come up with is questionable as well. Who knows what's right? They give us estimates, rounded figures, apple orange comparisons. Coming up with pictures of prehistoric creatures bases on fragments of a single jawbone... then tell us approximately how millions of years since jawbone beast roamed earth... somewhere within this multimillion year range... and the temperature at that time was... and their favorite food was... and they squatted when they pooed fluffy spinich like clumps. Really. They know these facts due to the data represented by their Walmart C02 detectors.
Suckers are not born every minute. They develop through passages of time by way of emotional stimulations. They are targeted. Their opinions are advocated, supported and fed so to break down their defenses. Once trust is gained... (after all, fancy thermometer man has my same concerns therefore his concerns are for me personally as well)... they strike.
And you buy... in full... pun intended (aren't most all?).
And I buy as well... in part.
I wish not to find you reGret the weather... the Thunder... the iceBerg. Us grown ups are patiently waiting for your heroes... your people of the year... fan favorites... to grow up yourselves and drop the hatred and blame. Please stop pointing to the minute spinach stains on the teeth of others when immense festering cavities are being ignored.
8% of human c02 production counted is through breathing. So you can't get us to net zero anyway unless you well... kill us. A % of our CO2 production which makes up part of the statistical reports you adhere to... are from farm animals... eating, pooing, breathing... existing. Us meat eaters are trying to be rid of them as well for your satisfaction but only so much can fit on the plate.
Getting to NetZero is impossible. Waste of time anyway.
Proving that the .00005% is the only factor in 2° rise in the last century is harder than proving the chickens furting in a tornado caused more property damage.
Please be useful.
Activism is well intentioned griping. Would you like reward for it? I don't ever think I found any activist of any cause who enriched our environment beyond a sprinkling... especially the griping or as as I like to call the negative activist. Even the great MLK who was a positive activist is predominantly known by his most endearing followers by just four words... "I had a dream" sad how the majority of the world only knows this much of the man. The four words can be attributed to anything. Further research will educate a follower his dream was basically that some day all races will get along... not to insult but many have said same message with less recognition. It was a world wide sprinkling recognized best because of his ability to sell the product of his speech with the decor of his character. Charisma was the salesman. Same for the young swedish girl with face twisting sputtering gripe furiously. If said in a calm sensible tone she would have been ignored. So I see the point of bringing out the personality to sell the product. A 90 yo business owner/salesman friend told me to be successful you must sell the sizzle not the steak...
I will not abide to that when it comes to you and this subject you invested in. Instead I simply ask you...
where's the beef?
Moderator Response:[RH] Excessive off-topic Gish Gallop.
-
MA Rodger at 10:29 AM on 20 July 2021The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
blaisct @14,
You say you are curious about recent NASA satellite data "finding increase heat loss to space." And you correctly add, the forcing due to increased GHGs will restrict "heat loss to space," this resulting in an energy imbalance and planetary warming.
I'm not entirely sure what it is you enquire about, but this NASA web page 'NASA Satellites See Upper Atmosphere Cooling and Contracting Due to Climate Change' does report a measured cooling of the mesosphere from which they inferred "more heat is lost to space" from the mesosphere.
Assuming this to be what prompts your enquiry:-
The mesosphere roughly lies between 60km and 90km above the surface, sitting above the stratosphere. Both these regions of the atmosphere sit above the mechanism which results in global warming. Both these high-up regions of the atmosphere are cooling as would be expected with CO2-induced global warming. CO2 is well-mixed up to about 50km and lower altitude increases will also impact levels above 50km.
The blanket analogy does not properly capture what is going on as an increase in a greenhouse gas like CO2 cools as well as warms due to mechanisms not present in blankets.
The atmosphere radiates to space (indeed radiates anywhere) only via greenhouse gases. The other atmospheric gases do not radiate at the relatively low atmospheric temperatures. If GHGs are added to a bit of atmosphere, there will be more molecules to radiate so radiation flying about. Also the amount of radiation depends on the gas temperature which increases collisions with GHGs and so stimulates more radation.
In the lower troposphere, the level of GHGs is high enough such that the radiation cannot travel far before it encounters another GHG molecule and is reabsorbed by the atmosphere. Down low, none of it gets to space. What is important for global warming is the altitude above which the GHG density becomes low enough to allow emissions to space. As the lower atmosphere becomes cooler with increased altitude and the level of radiation is dependent on temperature, the higher this altitude is, the cooler the atmosphere radiating to space is and the cooler t is the less radiation can reach space. And if you add GHGs, that altitude rises resulting in less space-bound radiation and thus a warming planet.
But go above that critical point above which radiation can reach space and an increase in GHGs means more radiation flying about and more of it being "lost to space." This is why the mesosphere with rising CO2 levels is expected to cool with global warming. (The stratosphereric cooling is a different story again.)
Hope that helps explain that NASA webpage statement "Scientists have long predicted this [mesosphere cooling] effect of human-driven climate change."
-
scaddenp at 07:28 AM on 20 July 2021The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
blaisct - first off, this is somewhat offtopic here, and urban heat island effect is entirely off topic. Try posting to thread skepticalscience.com/urban-heat-island-effect-intermediate.htmfor such discussions or moderators will remove you post.
As to increased heat loss to space - consider the blanket analogy. The blanket doesnt stop heat loss, but it slows it so person in the bed stays warm. Now, what do you expect to happen to measurement of heat loss through the blanket if you put two people in the bed (or the person has a fever?). More detail on the science can be found in the actual paper which I believe is this one. agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2021GL093047
As to whether this contradicts radiative theory, lets see what that paper have to say. Note that EEI is "Earth energy imbalance" - if energy out is less than energy in, then earth heats up.
"The excellent agreement between satellite and in situ trends in EEI obtained in this study demonstrates the benefits of having independent satellite TOA radiation observations and ocean heat content measurements for tracking changes in EEI. That both produce nearly identical results provides confidence that the trend toward an increased EEI reported here is robust, since it is unlikely to be due to artifacts in both observing systems." Ie expected result.
Note too also that IPCC doesnt have theories - it simply reports on the science consensus.
-
blaisct at 06:35 AM on 20 July 2021The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
Reading about resent NASA satellite data on finding increase heat loss to space makes me wonder how this increase in heat loss is consistent with the Radiative Forcing theory of the IPCC. My understanding of that theory is that as atmospheric CO2 increase it hold in more heat and makes the surface temperature hotter like a blanket effect while the heat loss to space remains the same. The NASA data does not seem to support the Radiative Forcing theory or I must not understand the Radiative Forcing theory. Where is the extra heat coming from?
Also reading about the “heat island” effect from big cities (up to 15’F difference between urban and suburban) makes me wonder could this be related to the NASA data on heat loss? Has population gotten big enough to have an impact on global warming? The “heat island” effect is caused by the much lower albedo (reported as 0.04, cloud free) of urban areas vs the earth as a whole (reported at 0.31). Using IPCC data one can calculate that an albedo change of only 0.15% (+1’C) is needed to account for all of the temperature change from 1880 until now. (that is a hard to detect 0.001%/year). While we are waiting on that detection level we can use related data to estimate man-made albedo change like population or atmospheric CO2.
The earth’s urban area is reported at 3.1% of the total area of the earth. The urban area back in 1880 (start of IPCC global warming data) is estimated at 0.7% (proportional to population) over 4X change. In 1880’s the “heat island” albedo effect was probably insignificant plus there was not many black parking lots or paved roads. The IPCC reports a 1’C rise in temperature since 1880. Using published information one can calculate the heat rise of the current 3.1% urban area at 4’C rise (since 1880) in earth temperate just from the urban area albedo change. (Using IPCC data of sun’s radiation to the earth at 1367w/m^2 and surface temperature rise correlation of 0.5 ‘C/w/m^2). The calculated 4’C rise is more heat than necessary to account for the 1’C observed this is probably due the reflective increase in clouds (water evaporation that eventually become clouds and reflects sun light) that would come with more heat from urban area. This overly simplified estimate of the man-made albedo effect suggests a more scientific version of albedo change should be included in any global warming model or theory. As the population of the earth gets bigger and urban areas grow this effect will get bigger. There are also other man-made albedo effects (destruction of rain forest, forest fires, melting of sea ice, and agricultural practices) which would be proportional to their % of the earth’s surface and their individual albedos.
The earth’s population should be a good indicator of urban area increase and thus man-made albedo change. Atmospheric CO2 is also corelated to population should also be a good indicator of urban area increase (albedo decrease). Are CO2 and albedo confounded in their correlation to global warming? Which force is bigger? The above calculation suggest albedo. NASA's ongoing map of the earth's cloud free albedo should be a big help in including albedo in global warming models, initial results seem to support the above.Moderator Response:[BL] Please learn to format your comments for readability.
Much of your comment is off-topic for this thread.
It does not look like you have improved your understanding of the physics of climate change since your last post here over two years ago.
In your first paragraph, you are correct in saying "I must not understand the Radiative Forcing theory." The fundamental aspect of greenhouse warming of the atmosphere is that adding CO2 reduces the IR loss to space and increases the blanket effect - until the system heats up to restore the balance. Once balance is restored, IR loss will equal solar absorbed - but that may be at different values due to albedo feedback effects.
For discussion of the urban heat island - how it works, how it relates to our measurements of temperature trends, please go to this thread. Hint: it's not just albedo effects.
https://skepticalscience.com/urban-heat-island-effect.htm
In order to avoid off-topic posts, please take the time to review the Comments Policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
Jds at 06:07 AM on 20 July 2021Human CO2 is a tiny % of CO2 emissions
1. More testing for temp & c02 happens in or close to rural areas. Common sense logic. I need no link to prove. Why would you?
2. Saying the ocean increase of 8 inches since 1800's? When was the last time you saw vast amounts of brilliant scientists up & down the coastlines with yardsticks or God help me dipsticks measuring the lines as the ocean ebbs and wanes a great amount of times more than eight inches many times within decades yrs mnths wks days hrs mins? Maybe the guys back in the 1800's were comparing satellite images to determine the beginning rises? I do not need a link to prove this is b.s. Nor should you.
3. C02 gauges determining 400 parts out of 1,000,000 are c02? Fancy thermometer you have there & that is all it is. Electrochemical sensors? Did they count the atoms? Did they feel them? Smell them? Sorry el ch sensors only are in c0 detectors. C0 is even lower ppm than c02. C02 detects by measurements of laser intensity. Fancy thermometer. & Considering C02 can only possibly take up .05 to 5% of a given area that would mean variant temp detect would need be within those ranges as well. & Typal it would take the area of 3 average adults to have required amount of oxygen atoms needed to bond with carbon for such a reading of 400 ppm? Fancy thermometer. And this junk measures the laser intensity (pressure on the silicone chip... yes that's all.) in order to assume raises in c02 due temp rises? Fancy. Like if you had a concealed area void of all carbon oxygen etc and you lit a match to it the inner temp would not raise because only c02 can raise a temp! I do not need a link to prove this as quakery nor should you.
4. Global warming causes tsunamis? Do they mean the consistent average of 2 a yr which has never shown an increase as far as I know to 3 is & has been caused by humans? I do not need a link. Suddenly I am hungry for sausage though. How about you?
5. If .04 % of atmosphere is c02 & of that .04 we contribute .0016 of it that means we are changing approximate .00005 of atmo. An alien bug shifted a cosmic wind storm with a furt... seriously it did! But .00005% of your outhouse wallscovered in pink panther fiberglass... your still gonna shiver during snowy winter outdoor poo runs. Suddenly I no longer feel like sausage. Do you?
6. 2 degrees!!!! Omgomgomg! Over 200 yrs! Imagine if that happened in a minute? It does. & Within an hour day week month season decade century Millennium four score seven years etc. I even heard it goes up & down by higher than 2° in those time increments! Could you imagine waking up one morning and it was like 10°!!! This is why Eskimos don't visit Africa... they would melt. Animals, especially humans cannot adapt to extreme 2°+ changes... impossible... especially if they happen over decades... trust me that's what common sense scientists say. I'm trying to make a segue with Abe right now but politics are not allowed here. Shoulda txt 5 score & 8 yrs. Nor should you... sorry just trying to stick to a format here.
7. It's been millions of yrs since the earth has been this hot or had this much c02 & man was not even in existence back then which proves man did it! So who did it? Wooly mammoths? Hairy hippos? It's like saying your great grandmother to the ten millionth power got pregnant which prove the guy dating your daughter will not where a condom. Yeah I know... poor link. Norse soot dew.
8. 8% of our c02 production is what we breathe out. Gw alarmists should put a bag over there heads to help us get to the 0% c02 in the air which is what they want so that all plant life can die followed by all other life but at least surfers will not wipe out when a hundred ft high wave crashes upon them. Annette Fettuccine. Ignore her doo.
9. Animals breathe too... little effers. Get over here fido. It's time I introduced you to Mr. Gallon size ziplock. I'll leave the pasta in there so you can have a last meal. Dogs don't know it's not seven degrees hotter for Kevin bacon... nor does he.
10. You would think that after all this blaming mankind for every catastrophic thing that happens in nature from the monsoons to the tidal waves to rats overrunning Portugal the one's hitting the near end panic buttons with all their summits & committees & conferences & picnic BBQs & gov funding & YouTube funny cat video empirical research would come up with a way to significantly bring the average gt down by at least half a degree of our controllable portion so we could have only one & one half the amount of disasters. Like one and one half of a Suzuki.
The moral of the story.
Spending time preparing for the unavoidable will save more lives than attempting to eliminate mankind's effects toward the consequences of a chaotic nature. Therefore gw are murderers by way of their ignorance. It is like they are watching a man beat child while attempting to prove a too many carbohydrates will make man beat child... now if we can just keep Frankie Avalon from the spaghetti we might save a child from abuse!
Moderator Response:[BL] Long, mostly off-topic Gish Gallop snipped.
To our usual commenters: please refrain from responding to this until we have had the time to check if this particular user is another sock puppet of a previously-banned user.
[BL] July 20 moderation update. Although this user does not appear to be a previously-banned user, the behavior so far violates several aspects of the comments policy - especially with respect to staying on topic.
All comments must be on topic. Comments are on topic if they draw attention to possible errors of fact or interpretation in the main article, or if they discuss the immediate implications of the facts discussed in the main article. However, general discussions of Global Warming not explicitly related to the details of the main article are always off topic.
Warning
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can and will be rescinded if the posting individual continues to treat adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Moderating this site is a tiresome chore, particularly when commentators repeatedly submit offensive or off-topic posts. We really appreciate people's cooperation in abiding by the Comments Policy, which is largely responsible for the quality of this site.
Finally, please understand that moderation policies are not open for discussion. If you find yourself incapable of abiding by these common set of rules that everyone else observes, then a change of venues is in the offing.Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
Bob Loblaw at 03:59 AM on 19 July 2021Analysts dissect historic Pacific Northwest ‘heat dome’
As usual, if you want it done right, ask Tamino. He has a new blog up on the recent NW US heat wave, and the very first graph illustrates the point I was making in comment #11.
https://tamino.wordpress.com/2021/07/16/northwest-heat-wave/
Bringing in the graph:
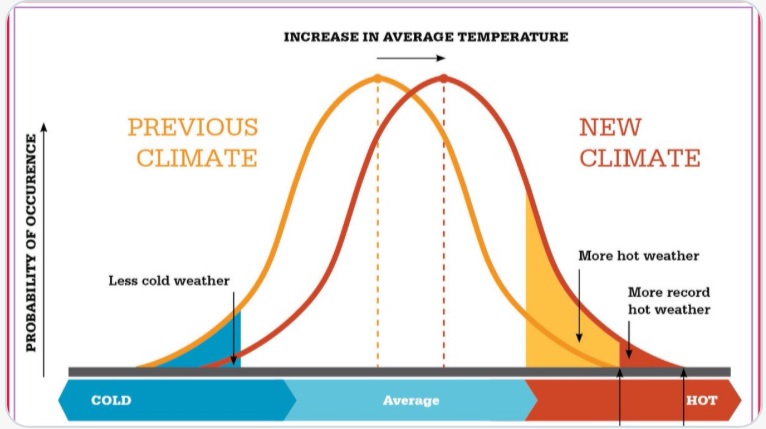
-
MA Rodger at 01:16 AM on 19 July 2021It's not bad
TVC15 @351,
To throw in my own ten pen'orth.
If anyone says “those disasters are here and now already,” it's a bit of an end to the discussion. I think your intended message is that the "disasters" are starting to happen. But as the analogy set out by Bob Loblaw @353 runs "if we can't stop the car before it hits the wall, slowing it down helps." So we are seeing disasters. We are in the process of hitting the wall. It is a very slow process. Things will get a lot worse before we come to a stop. But as we crash into the wall, it will help greatly if we take our foot off the accelerator and slam harder onto the brake.As for where we will end up, as Eclectic @352 says, the idea that humanity could drive itself to extinction through AGW is not on the cards.
If we fail to wean ourselves off FF where will we be? As michael sweet @354 suggests we are seemingly weaning ourselves off coal. That is significant. The +4ºC-and-higher 'outcomes' turn to +3ºC 'outcomes' (and higher) if we stop burning coal. I add the 'and higher' as +3ºC 'outcomes' also greatly increase the uncertainty relative to +2ºC 'outcomes'. Yet even +2ºC 'outcomes' will have bad consequences such as the melt-down of Greenland if we stay at +2ºC for too long. So we shouldn't lose the limit of +1.5ºC if we don't want 7m SLR in the next millennia or so.
And if we fail to buck up our game, still buried within the +3ºC (and higher) is the potential for our nation states to start tussling over real estate and resources and 'devil take the hindmost', thus the breakdown of the civilised world order. How bad a breakdown? There are 193 nation states in the world. So pick a number between 193 and zero.
In terms of climate, I don't think we have reached a point where we cannot with tomorrow's technologies reverse the climate forcings that is causing AGW. But that doesn't mean we reverse all the consequences. If we reverse the climate forcings there will already be irreversable events, certainly within the biosphere. There are thus many 'points of no return' we are creating but the idea of a 'runaway GH-effect' that would turn us into a carbon-copy of Venus; that is not going to happen.
-
michael sweet at 22:11 PM on 18 July 2021It's not bad
Eclectic:
We agree. At one time people complained that gas cars would never replace horses. Once electric cars are established and charging stations are built everywhere everyone will accept them. Then in the future people will wonder why we put up with the air pollution killing so many people for so long.
-
Eclectic at 09:50 AM on 18 July 2021It's not bad
Michael Sweet ~ LOL, in a Mustang maybe : but I wouldn't like to drive the average country road at 150mph in a pick-up truck. The Ford F150 is heavy, but has 4WD electric motors of total 420 horsepower (in lower spec.!!) Not too shabby. The battery has a 9 Kw outlet for portable power tools, or for powering your house during a blackout. Due late 2022, so not far away.
My point is, that many Americans will find this type of electric vehicle attractive. And this will shed a halo glow onto other "electric stuff" . . . and, I hope . . . soften some of the pro-fossil attitudes, and this will spill over into the more political arena.
-
michael sweet at 09:16 AM on 18 July 2021It's not bad
I have a friend who likes muscle cars and owns a high power Mustang. I saw an ad for an electric car that beat a bunch of muscle cars off the line in a drag race. I asked my friend and he said the electric car would beat his car for 1/8 of a mile (by a lot) but that after they got up to 100 mph his car had better acceleration and would win the 1/4 mile. I guess if you want to go 150 on the street (this friend does) you need a more powerfull electric car.
-
Eclectic at 06:20 AM on 18 July 2021It's not bad
Red Baron @394 ,
There's no hope for direct persuasion of the sort of denialist who comes out with the kind of "Models are All Wrong" argument that you mention. The deniosphere is full of that deliberate mental blindness.
But things are hopeful in other directions. Denialists are in some alarm about the current European Union moves to establish (more extensively) what is in effect a Carbon Tax on imports. This must cast a shadow into the future ~ a shadow influencing the investment choices of financiers & large corporations, and tilting their future decisions away from coal etc.
And in the USA, the new Biden Administration - however temporary it may be - must be having a chilling effect on the commercial advocates of future fossil-fuel developments.
Red Baron, your own interest in carbon-fixing (in the soil) does also add the possibility of lowering CO2, by a small but ultimately significant amount. We shall see !
And for the persuadable Middle Americans who like to drive "gas-guzzling pick-up trucks" , it seems the Ford F150 Lightning (due 2022) will have both the traditional looks & the carrying/hauling capabilities they fancy. An all-battery truck, with adequate range and muscular performance ~ quite a breath-taking acceleration, in fact. Forget the wimpy Prius and nerdy Tesla cars, because this "truck" will soften the gasoline addiction of even the average red-blooded right-winger.
-
RedBaron at 12:45 PM on 17 July 2021It's not bad
@393
Michael,
That's a very good point. I recently heard a denialist argument talking about how the models were wrong. The interesting thing about his argument was he used the "worst case do nothing" projection and then tried to claim, "See? The models were exagerated!"
Ironically the reason we are no longer on that old worst case scenario projection is because actions were taken! When the proper scenanio was selected and projected, the models proved to be almost uncannily accurate!
"it's not that bad." only because we are making the changes needed. Maybe not enough. But we are moving in that direction!
Potholer put out a great video about that 3 years ago! Projections still look bleak. We can do much more. But it is not as bad as it could have been.
-
michael sweet at 09:13 AM on 17 July 2021It's not bad
While I wish stronger actions were being taken now, it is way better than it was ten years ago. I remember thnking "how can we get people to build out wind and solar when they are 5 times more expensive than fossil fuels?" Now renewable energy is the cheapest so they are building out renewables in Texas!! No greenies behind those wind turbines and solar farms, they are building them because it is cheapest.
Carbon Brief reports many coal plants planned 5-10 years ago that were not built yet are being cancelled. That is not because they are worried about climate change, it is because renewables are cheaper.
I am worried about the future, but it looks way better to me than it did 10 years ago.
-
Bob Loblaw at 01:00 AM on 17 July 2021It's not bad
I'm sort of where Eclectic is, too.
There is an old saying: an optimist believes that we live in the best of all possible worlds; a pessimist fears that this is true.
Even if we can't stop the car before it hits the wall, slowing it down helps. And in the case of climate change, trying to stop at 1.5 or 2C but failing will still help us avoid 3 or 4 later on. And even if we fail to stop the bad consequences, knowing what they are going to be helps us prepare for them.
Anyone that thinks "it can't possibly get worse" is fooling themselves - there is always some creative genius out there who can find a way to make it worse.
-
Eclectic at 19:07 PM on 16 July 2021It's not bad
TVC15 @390 :-
Permit me some general waffle : my comment is that you should be half'n'half ~ half optimist, half pessimist. The global situation is going to get bad but not catastrophic. Yes, we are going to blow straight past the 1.5 degree mark in global surface temperature rise since pre-industrial. The rise already (over 170 years) is about 1.1 degrees, and this makes a mockery of any contrarian who opines that the CO2-doubling Climate Sensitivity is less than roughly 2.0 degrees (and seems most likely to be in the 2.5 to 3.0 degree range at equilibrium ~ which also fits with non-historic data e.g. the paleo data).
With extraordinarily good management, we might conceivably halt the rise by 2.0 degrees . . . but our political track record so far is poor.
It is not just the politics, but technological advances which are still required. Sure : cheaper solar & wind technologies are coming, but we really should have started seriously developing these at least 10 years before we actually did. (But the past cannot be changed.)
The 2050 date for "carbon neutral" will require more than the present-day solar & wind, even at half of today's prices. Energy storage is absolutely necessary ~ and I am looking to bulk storage of electrolytic hydrogen. Hydrogen to provide electricity via fuel cells (at small scale) or steam-driven turbines at large scale (possibly combined-cycle?).
The second leg to stand on, is a hugely-increased supply of liquid hydrocarbon [octane / kerosene / diesel types] produced from non-fossil feedstocks, by means of catalytic / enzymatic / fermentational technology. In brief, we need to produce these hydrocarbons at a scale little short of present-day fossil fuel consumption. For a great amount of our energy usage, these hydrocarbons are necessary ~ and I suspect it will take many decades after 2050 , before we could replace such hydrocarbon fuels.
Extinction of a very large slice of animal/plant species . . . is arguable. Extinction of the human race ~ certainly impossible. The casualty rate may be high in the future ~ but extinction, no way. Mass migration of "climate refugees" will increase as sea level rise and heat waves occur, and there will be major social disruption. "Interesting Times" , as the old Chinese saying goes.
-
TVC15 at 10:06 AM on 16 July 2021It's not bad
Hi Skeptical Science Team,
I am not trying to come across as a pessimist, in fact I am very jolly happy optimist. (it’s my nature).
However, looking around at all the attitudes that lack an understanding of how urgent our climate situation is, and the fact that not much has been done to ween the globe from fossil fuel burning, I can’t help but to think we are past the point of being able to curb the future disasters that are coming our way due to climate change. Those disasters are here and now already.
We are now living on a planet that is in the beginning stages of driving humans, as well as other animal species towards extinction. We’ve already caused extensive death and destruction. Over 50 percent of the world's coral reefs have died in the last 30 years and up to 90 percent may die within the next century. The rate of normal background extinction is hundreds, or even thousands of times higher than the natural baseline rate.
Also, since CO2 lingers around in the atmosphere for 1000’s of years and we are continuing to pump ~50 Billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents a year into the atmosphere, how on earth are we going to prevent the creation of a runaway greenhouse effect?
Am I alone in thinking we’ve reached a point of no return? -
Philippe Chantreau at 03:42 AM on 16 July 2021Exxon's Own Research Confirmed Fossil Fuels' Role in Global Warming Decades Ago
And an opinion piece from Newsweek resulting from the unintentional disclosure I linked above:
The underlying reality is unescapable and very simple: there is no long term future for humans on this planet that includes continued, industrial scale use of fossil fuels. Everyone knows it. The ones profiting from it just want to make sure they extract every last little penny before they are forced to change.
I don't say this lightly. I come from a culture that values speed and skill at handling machines powered by fossil fuels. When I was growing up, the coolest thing one could do was riding motorcycles, doing Rallye racing or flying airplanes. I am a pilot, flight instructor, love to fly and I still love to ride motorcycles. However, reality does not change according to our preferences, despite what some would have the crowds believe.
-
BaerbelW at 02:39 AM on 15 July 2021Additional Fact Briefs published on Repustar
MAR @3
One broken link always slips through, sorry about that. Thanks for the heads-up and link fixed now.
Hameiri @ 1
Did you follow the link in the first paragraph? It renders your comment rather moot, doesn't it?
-
Bob Loblaw at 02:05 AM on 15 July 2021Additional Fact Briefs published on Repustar
Until the link MAR mentions is fixed in the blog post, you can follow this one:
It looks like the orignal has an echo. It looks like the orignal has an echo.
-
MA Rodger at 00:40 AM on 15 July 2021Additional Fact Briefs published on Repustar
The link to Do natural climate cycles disprove that modern global warming is caused by humans? ... read more needs editing.
-
Eclectic at 22:47 PM on 14 July 2021Additional Fact Briefs published on Repustar
Hameiri @1 ,
LOL. If you wish to be scientific, you should falsify the fact checker.
I will be interested to see if you can come up with anything!
-
Hameiri at 22:20 PM on 14 July 2021Additional Fact Briefs published on Repustar
A fact checker that always finds you right? Very scientific ❗ How long did it take to find this firm❓
-
TVC15 at 14:50 PM on 14 July 2021Climate's changed before
Many thanks to Eclectic, Bob Loblaw, MA Rodger and Daniel Bailey.
I gain so much from each of you every time I post denier claims.
Thank you all for your time and efforts to help educate us!
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:57 AM on 14 July 2021The cool, lush Pacific Northwest roasts in Death Valley-like temperatures
Just a little more trivia on the Lytton weather station during this record-setting heat and fire event noted in comments above.
Communications were lost early in the morning (UTC) on July 1, but the system ran on battery power until July 2 at 03 UTC.
Power was restored shortly before July 6, 00 UTC. The system transmitted data from July 1 at that time, and has been operational ever since.
-
Daniel Bailey at 01:05 AM on 14 July 2021Climate's changed before
IIRC, the Last Glacial Maximum saw a greater buildup of land-based ice than in previous glacial phases. By the time maximum warming in the Holocene had been achieved and a natural cooling initiated, a great deal of ice remained in Greenland and Antarctica that had already been lost by that same point in previous interglacials.
Given time to reach equilibrium with the modern forcing, global sea levels will eventually surpass any levels achieved in previous interglacials spanning the previous 800,000 years+, and likely far longer than that.
From Dutton 2015, Figure 5:
-
knaugle at 01:04 AM on 14 July 2021Study: Extreme weather may not lead to increased support for climate action
I think it relevant that Dr. Katherine Hayhoe of Texas Tech recently noted that while 70% of people in the USA believe global warming is real, only 43% think it will affect them in THEIR lifetimes. So more than half of us here still think that dealing with global warming is someone else's problem, one for another generation. That kind of inertia is difficult to overcome.
Meanwhile, I still think most people fear nuclear power far more than global warming.
-
MA Rodger at 00:21 AM on 14 July 2021Climate's changed before
TVC15 @873,
Your denialist is actually making four bold statements that are patently nonsense with the rather pathetic request that you "Tell us why this Inter-Glacial Period should be different.""Ice sheets and glaciers always melt during Inter-Glacial Periods." The melting actually happens in the run-up to the "Inter-Glacial Periods" which is what makes them "Inter-Glacial Periods" so in one respect this is entirely straw man territory. If the bold assertion is that glaciers and ice sheets shrink as they do today throughout an inter-glacial, that is false as sea levels of past millennia demonstrate.
"Sea levels are normally 4 meters to 14 meters higher than they are now during Inter-Glacial Periods." This is not supported by the evidence that
suggests only two or three of the eight had higher sea levels. (The graphic is from here but originates from this web engine.)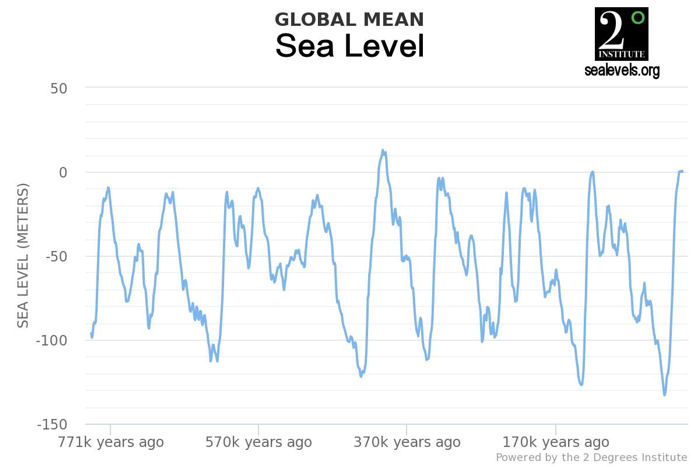
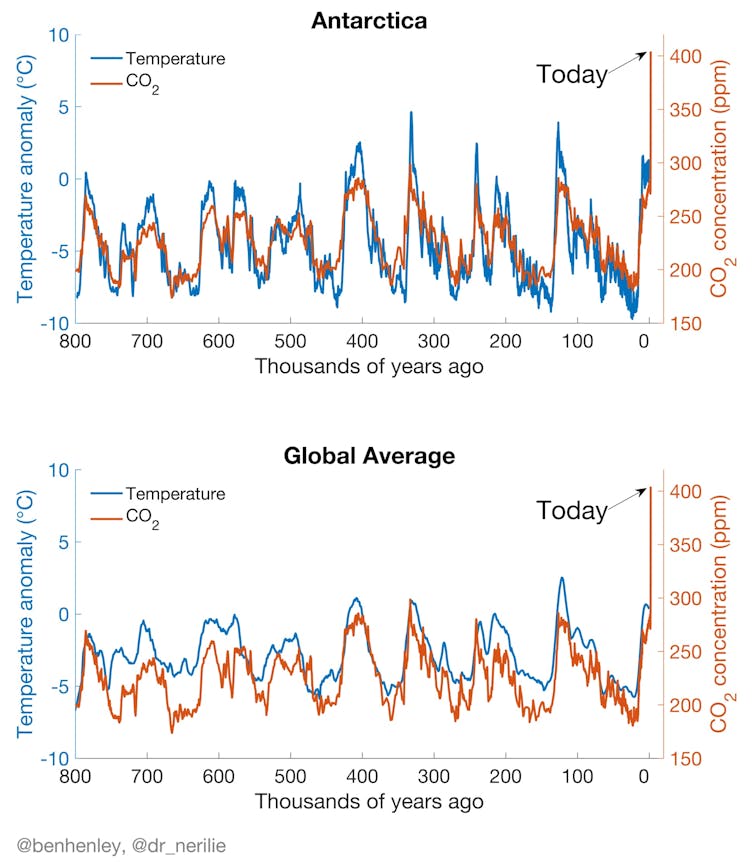
"Global temperatures in the other 8 previous Inter-Glacial Periods were at least 7°F warmer than present." Again not supported by the evidence. A google search provides many graphical representations of 800,000y temperatures and globally the present interglacial has been warmer than all but three of them (although AGW may be on course to change that ranking).
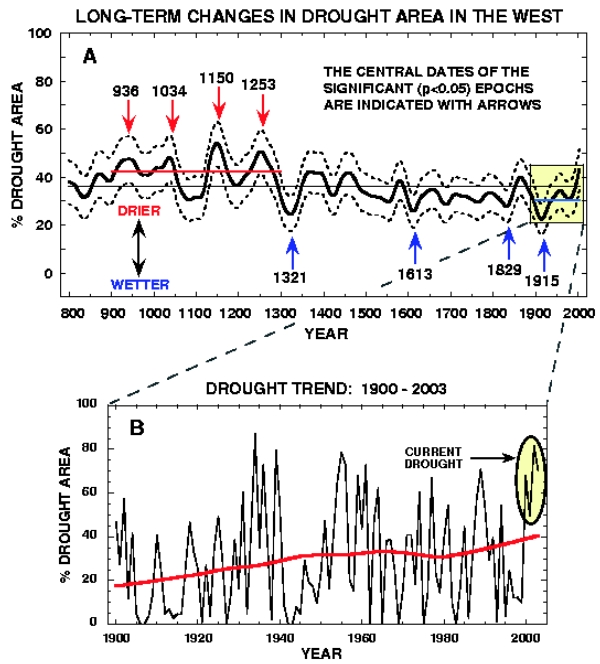
"The West always undergoes a drought during Inter-Glacial Periods." This is a more specialist assertion. That there has been "a drought" in "the West" through the Holocene is potentially correct. It isn't a place with massive rainfall. But more accurately there are periods of drought and periods when the rain is heavier. What we see to make sense of that is a bit of a Hockey Stick situation with drought conditions becoming more wide-spread. The graphic comes from here an account which does address the question "Will anthropogenic climate change cause the West to get drier or wetter?"
Prev 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























