Recent Comments
Prev 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 Next
Comments 12301 to 12350:
-
michael sweet at 10:37 AM on 7 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
Sunspot:
Here at Skeptical Science we try to focus on what data is known. The scientific consensus is generally accepted as what is known. Sometimes there is no consensus on a topic and it is interesting to review the various proposals.
In any discussion we support our arguments with data that comes from the scientific literature. BBC documentaries are sometimes helpful but are not considered authoritative. If you say what you think based on something you read on the internet that is hearsay and not acceptable. You might want to read the comments policy.
The rule that you have to provide evidence to support your claims keeps the discussion within limits. Sites that allow anyone to say whatever they think devolve into arguments we do not like.
Your claims have been made before. They are at the extreme of scientific views. We all hope that they are incorrect. If you want to discuss them someone might engage you if you have a less hostile attitude.
A word to the wise: the fastest way to get banned is to suggest you should be banned. Any complaints about moderation will cause you problems. If you provide evidence to support your worries people will engage with you.
-
Sunspot at 08:33 AM on 7 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
I have no idea how anything I have said can be interpereted as supporting an intentional program of combatting Global Warming by using a Global Dimming strategy. I don't support such efforts.
There is evidence for a rapid rise in temps in the few days after 911 when the planes in the US were grounded. Here's the BBC Horizon video from 2005: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c0BMyT4RCzY&t=41s There is a lot of other information on Global Dimming, some from sources that people here might actually trust. At any rate, you'll be hearing more about it - I just saw it in a MSM article the other day...
"If the particulate is due to human actions that are unsustainable and harmful, then the global dimming is unsustainable and harmful." Well, in this case, the "cloud" actually does reflect solar energy back into space. Just like any cloud, right?? This has a cooling effect. I have certainly noticed that it is generally cooler on a cloudy day. Brown pollution clouds certainly act the same way, and I don't think that's conjecture. So, a bad and immoral (I guess) action by humans actually has a beneficial effect. Maybe everything isn't so black-and-white after all...
While we're talking (before you ban me) - the Methane video being promoted here ignored the real issue as to a SUDDEN release of large quantities of methane. The video discussed permafrost discharges from the land, which of course really can't come out suddenly due to the nature of the situation. However, the video didn't even mention the vast amount of methane stored in the sediments of the Arctic Ocean, which certainly can be released suddenly in large quantities. Clathrates are very unstable, and a warm pulse of salty water just might trigger something. MIGHT! Please don't accuse me of thinking that I know what is going to happen, BECAUSE I DON'T. And I'm sorry if these concepts don't fit neatly in the Skeptical Science philosophy that the warming will be linear, we can fix it with enough windmills and solar panels, and we will go on living our middle-class lives with just a little tweaking. And bad things might happen in 100 or 200 years. I suppose it's comforting to think this, but for a site that pretends to be all about science, you have to ignore a lot of science to come to that rosy conclusion.
So you can ban me before or after publishing this comment. I'm sure I once again violated all sorts of rules and regulations and guidelines or whatever. Forgive me for using plain English.
-
nigelj at 08:22 AM on 7 April 20192019 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #14
Like another character named Don, US President Donald Trump is tilting at windmills. The president disparaged wind farms this week while spinning his arm like a turbine and making an unpleasant whirring sound. TRUMP: "If you have a windmill anywhere near your house, congratulations. Your house just went down 75 per cent of value."And they say the noise causes cancer." - remarks at Republican fundraising dinner Tuesday.
The facts. The sound from wind farms has not been proved to cause cancer. Trump has had it out for wind power since turbines were proposed off the coast of Scotland within sight of his golf resort near Aberdeen.
(America by electing this guy you make yourselves look incredibly stupid, just in case you don't know by now)
-
nigelj at 07:50 AM on 7 April 20192019 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #14
We are indeed "gobbling up the earth's resources at an unsustainable rate" and its pretty darned serious, but I feel solutions need to also be realistic as well. Expecting people to reduce use of their use of cars by "90% this decade" and other drastic changes in consumption are not realistic to me. 25% might be a more realistic goal. Public transport is desirable, but cities are spread out and its hard making it work for everyone.
While land based lithium reserves are limited, there are billions of tons dissolved in sea water (along with most other metals) and numerous other battery technologies under development not reliant on lithium here.
More realistic solutions to looming resource scarcity problems would include this generation of people aiming for zero rates of population and economic growth, recyling, and wasting less, although poor countries have to be allowed economic growth.
-
william5331 at 06:25 AM on 7 April 2019Why results from the next generation of climate models matter
I wonder if the new models take aerosols into consideration. Have we done enough research for them to be realistically included.
-
nigelj at 06:02 AM on 7 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
"If we actually succeeded in eliminating the "Asian brown cloud", the increased solar energy reaching the surface of the planet would lead to a very rapid increase of the global average temperature of up to .5 degrees C, within a few days to maybe a week."
0.5 degrees c is conjecture with no evidence, but even if it was correct use of all coal fired power won't stop simultaneously, so temperatures could not possibly rise 0.5 degrees in a week. In fact any gobal dimming would be gradual spread over years. It's just another in built problem created by burning fossil fuels.
-
TVC15 at 05:58 AM on 7 April 2019CO2 lags temperature
Hi,
I am dealing with a denier who constantly puts up graphs that he's created from the EPICA Ice Core Data.
This denier makes the following cliams.
No correlation, and EPICA Ice Core data proves it:

Temperature increases CO2 levels, but CO2 levels do not increase temperature.

I made my own graph of the EPICA Ice Core data and it appears that this denier is only taking a very small era of time from the EPICA ice core data.
Here is my graph of the data and the yellow highlighted section appears to be erea of time this dener is zooming in on.
Moderator Response:[DB] Please limit image widths to under 500 pixels.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 02:15 AM on 7 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
Regarding 'global dimming from particulate' as a potential way to 'address the climate vulnerability' problem.
If the particulate is due to human actions that are unsustainable and harmful, then the global dimming is unsustainable and harmful. At some future date the unsustainable harmful human action has to be stopped. It would be morally unacceptable for more harmful CO2 impacts to be created because 'human induced global dimming is claimed to be helpful'. There is more harm from the burning than the excess CO2 that stays in the atmosphere.
Therefore, the people wanting to promote global dimming must be required to prove conclusively that no harmful consequence will occur as a result of the 'added human impact on the global climate system' or the diversion of human brilliance from the need to reduce the harms of fossil fuel burning. That means proving that maximum effort to curtail fossil fuel burning will still happen if global dimming is considered.
Another way to state the moral requirement is that global dimming would be done only if it is almost certain to create no harmful impacts and be done in addition to aggressive reduction of the harms done by fossil fuel burning.
The current generation is clearly morally challenged by the growing need to minimize the harm done to the future generations. The development of unsustainable and harmful pursuits of profit has been morally corrupting societies and the development of their economies for a very long time. For many decades the ability of societies to develop sustainable improvements for the future generations have been overwhelmed by the burden of having to try to minimize the developed and developing harm done to future generations by popular and profitable attitudes and actions. Economies are loaded with harmful activities. Correcting them without reducing perceptions of prosperity and opportunity is virtually impossible. And the required decline of perceptions of prosperity and opportunity for the increases each year of 'continued progress in unsustainable and harmful directions'.
Regarding climate change, the identified moral requirement is to limit of impact to 1.5 C warming, with impacts to the level of 2.0 C reluctantly identified as an absolute upper limit of impact.
Regrading global dimming, the temperature limits must be understood to be met without any additional help from human induced global dimming. And the global dimming actions must also be proven to have virtually no risk of causing any harm to people in any region of the planet. Global dimming promoters may be able to met that standard of proof to be able to morally justify consideration and pursuit of such an action. But discussing human induced global dimming without clearly correcting for the morally corrupted reality of currently developed socioeconomic-political environments is likely to result in more harm being done.
-
Daniel Bailey at 21:50 PM on 6 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
So you don't actually have any evidence to support your assertion, got it.
Let's then return to the topic of this post.
-
Sunspot at 18:54 PM on 6 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
There are many sources of information on Global Dimming from the internet. There is a 2005 BBC Horizons documentary. Some of it may be speculation unsupported by peer-reviewed journalism. How about if I had said "could" instead of "would"?
I am interested in all facets of Global Warming and the Climate Change it is creating. I don't know what is going to happen. I am convinced big things are likely to happen soon. Websites like this that are so restrictive of the subjects that are allowed for discussion that it just seem unscientific to me. Global Dimming is a real thing. So is the potential for massive methane releases from the Arctic, and elsewhere. Deal with reality or reality will deal with you.
-
Cedders at 18:15 PM on 6 April 2019Major PAGES 2k Network Paper Confirms the Hockey Stick
Broken link. The Carbon Brief article has moved here.
-
TVC15 at 16:35 PM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
MA Rodger @708
Thank you for the clarifications!
scaddenp @ 706,707
Ops sorry to step off topic but I appreciate the insights. I read some interesting information about Eddenhofer on Desmog.
-
MA Rodger at 14:23 PM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
TVC15 @701,
The sun illuminated the disc of the Earth with an intensity measured by TSI. The disc has an area of πr^2. But this energy is spread out, not over a disc but over a globe with area 4πr^2. So TSI requires dividing by 4 to give the average solar climatic impact.
TVC15 @702,
The denialist is quoted @695 saying "Is man made CO2 not 5% of atmospheric CO2?" With 410ppm CO2 in the atmosphere, 5% would be 20ppm. But since pre-industrial times CO2 has rise from 280ppm, a rise of 130ppm. If mankind is responsible for only 20ppm of this, where did the other 110ppm come from? Perhaps the denialist is believing that this extra 110ppm is down to the shape-shifting lizards, or perhaps all the unicorns he sees inhabiting the world.
-
scaddenp at 12:11 PM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
I would also say this is totally off-topic. PLease put your comments in an appropriate thread.
-
scaddenp at 12:11 PM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
This is more motivated reasoning. Well obviously there is science behind it - the whole IPCC WG1 is nothing but science. However, solving it is political and economic and the argument he is trying is that there is a nefarious plot by scientists who want everyone including themselves to suffer massive economic damage for no good reason except... But people which view the world through ideological glasses seem to believe this.
There is also the IPCC WG3 on ... solutions. In there you can see the published opinion from the many that have studied the issue instead of the opinions (misrepresented at that) of carefully chosen few. I wonder how well Ottmar Eddenhofer feels his views were represented by the Global Warming Policy Foundation.
-
Daniel Bailey at 09:57 AM on 6 April 20192019 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #13
To any interested, NASA could use your support in the ongoing Webby Award voting. If you are OK with voting, vote your heart and your conscience.
I didn't vote in many categories because I lacked the background to make the needed decisions and/or the time to differentiate between the nominees, but I did what I could, where I could. NASA is currently in 2nd place in this category.
23rd ANNUAL WEBBY AWARDS
PEOPLE'S VOICE
You decide the best of the InternetVoting is open until Thursday, April 18th
-
TVC15 at 08:45 AM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
@703 David Kirtley thank you so much. Odd that did not come up when I searched for Ordovician-Silurian.
-
TVC15 at 08:43 AM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
I need your help again guys! I posted this statement: In July 2007, a survey of hurricanes in the North Atlantic over the past century noted an increase in the number of observed...
A denier who many on the sidelines thinks is brilliant and who I suspect is being paid to spout what he spouts responded with this.
"The operand is "observed."
You have the technology to observe both tornadoes and hurricanes that you were never able to observe in the past.
And that's the recent past, outside of the last 50 years.
There's no science behind "climate change." It's all political and socio-economic-based:
German economist and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) official Ottmar Eddenhofer, explained prior to the Cancun conference in an interview with the Global Warming Policy Foundation (Potter 2010): First of all, developed countries have basically expropriated the atmosphere of the world community. But one must say clearly that we redistribute de facto the world's wealth by climate policy. Obviously, the owners of coal and oil will not be enthusiastic about this. One has to free oneself from the illusion that international climate policy is environmental policy. This has almost nothing to do with environmental policy anymore, with problems such as deforestation or the ozone hole...Basically it's a big mistake to discuss climate policy separately from the major themes of globalization.
In a paper prepared for the Cancun conference Professor Kevin Anderson, Director of the Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research, said the only way to reduce global emissions enough, while allowing the poor nations to continue to grow, is to halt economic growth in the rich world over the next twenty years.He called for World War II-type rationing of electricity in order to force people to conserve (Gray 2010)
Source: http://www.usu.edu/ipe/wp-content/up...Climate-Policy"
-
David Kirtley at 07:23 AM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
TVC15 @700. Re. CO2 levels in the distant past, see this rebuttal: Do high levels of CO2 in the past contradict the warming effect of CO2?
-
nigelj at 06:30 AM on 6 April 2019Why results from the next generation of climate models matter
Something related. First successful model simulation of the past 3 million years of climate change discussed here. "Our results imply a strong sensitivity of the Earth system to relatively small variations in atmospheric CO2....The climate sensitivity of the model is around 3°C global warming for a doubling of CO2 concentration, which is at the center of the range of current best estimates of climate sensitivity that range between 1.5 and 4.5°C."
-
TVC15 at 06:08 AM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
Hi MA Rodgers,
Why would the denialist consider that just 5% of atmospheric CO2 is down to anthropogenic causes? That would be just 20ppm. Where did the other 110ppm come from? That's 860Gt of CO2 so the source should be quite evident.
I'm a bit confused. What do you mean by where did the other 110ppm come from?
-
TVC15 at 05:59 AM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
@ 699 MA Rodger,
What is a discal projection?
-
TVC15 at 05:32 AM on 6 April 2019Climate's changed before
@ 699 MA Rodger,
Indeed it's been a huge up-hill struggle in my attempts to find a way around deniers.
I appreciate all the new insights I'm gaining from this site. I am so thankful this site exits!
Here is another poor fool making these claims and trying to tell me I'm wrong for stating that analysis of past climates shows that greenhouse gasses, principally CO2, have controlled most ancient climate changes.
"Proof that CO2 does not drive climate change is to be found during the Ordovician-Silurian and the Jurassic-Cretaceous periods (approx 450 and 150 million years ago, respectively) when CO2 levels were greater than 4,000 ppm and about 2,000 ppm, respectively. If the IPCC AGW/ACC theory is correct, there should have been runaway greenhouse gas-induced global warming during those periods but instead there was glaciation.
Current CO2 level is slightly more than 400 ppm. Compare at will."
I'm not sure how to respond as I came up with nothing when I search for Ordovician-Silurian on this site.
Thank you for the great responses!
-
sauerj at 05:17 AM on 6 April 2019Why results from the next generation of climate models matter
Interesting article! ... The ECS from my simple, 1-box "Temp vs CO2" modeling is 3.24 C with a 1st-order time constant of 14.6 yrs. Data from 1958 to Feb-2019. I don't know how to do the statistical math to determine the various uncertainty ranges. Could someone give me a link that will teach me how to do that for a model correlation like this? Thanks!
The math I'm using is: Temp(@yr n) = a/Ln(2) x Ln(Cn/Cb) x [1-exp(-1/k)] + Temp(@yr n-1) x exp(-1/k) ... where, a=ECS; Cn=CO2 for yr n; Cb=CO2 for the baseline yr; k=time constant; Temp(@yr n-1) is temp at previous year of Temp(@yr n). ... Note: I am using a macro to find the best-fit a & k constants. It does this by incrementing one of the constants up & down (in tighter and tighter incremental steps), and then, at every incremental step, it uses solver to find the least squares best fit for the other constant, until the incremental steps get very small. I get the same results either way, no matter which constant increments, and which constant is found by solver.
This Excel model file is located HERE [file name = TempRise vs CO2-Rise_Rev2(2019-02).xlsm]
-
stonefly at 04:02 AM on 6 April 2019Milankovitch Cycles
I see also that at aphelion it is ocean rather than land mass receiving insolation.
-
Daniel Bailey at 03:30 AM on 6 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
Sunspot, I'm going to assume that's conjecture on your part, unless by some remote chance you can cite a credible source that supports that assertion?
-
Sunspot at 02:34 AM on 6 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
Reducing CO2 in the atmosphere would be a good thing of course. But reducing the particles in the atmosphere would lead to very rapid warming by reducing the reflectivity of the atmosphere, aka "Global Dimming". If we actually succeeded in eliminating the "Asian brown cloud", the increased solar energy reaching the surface of the planet would lead to a very rapid increase of the global average temperature of up to .5 degrees C, within a few days to maybe a week.
-
stonefly at 02:33 AM on 6 April 2019Milankovitch Cycles
Yes, thank you, Bob.
Then I will assume that the reason precession does not treat the northern and southern hemisphere equally is because of distance.
The sun's rays strike the planet at the same degrees north latitude at perihelion as they strike at south latitude at aphelion, six months later. So it's not the angle of the sun's rays that is affected by precession, it's the distance.
Is that correct? -
stonefly at 00:02 AM on 6 April 2019Milankovitch Cycles
Yes, thank you, Bob.
Then I will assume that the reason precession does not treat the northern and southern hemisphere equally is because of distance.
The sun's rays strike the planet at the same degrees north latitude at perihelion as they strike at south latitude at aphelion, six months later. So it's not the angle of the sun's rays that is affected by precession, it's the distance.
Is that correct?
-
MA Rodger at 19:43 PM on 5 April 2019Climate's changed before
TVC15 @695,
Correcting someone who refuses to be corrected is a bit of an up-hill struggle. I'm sure we have been over his (2) before (although @652 it was 4%). Why would the denialist consider that just 5% of atmospheric CO2 is down to anthropogenic causes? That would be just 20ppm. Where did the other 110ppm come from? That's 860Gt of CO2 so the source should be quite evident.
And his (7), the poor fool appears to be confusing the average length-of-stay of an individual CO2 molecule in the atmosphere with the length-of-stay of an increased CO2 concentration. On the latter, the 'half-life' is perhaps 100 years but there is a long tail in that the last fifth will remain in the atmosphere for many thousands of years. After just three years, an injection of CO2 into the atmosphere would have reduced by less than 5%. (When we consider this, we talk of the Atmospheric Fraction, the amount CO2 rises each year relative to the anthropogenic emissions. The Af is roughly 45% but implying 55% has been sequestrated into oceans/biosphere. But the 55% is actually the sum of all those tiny percentage reductions for all the years since human emissions began as a percentage of just one year's emissions.)
And back upthread @683, you quote presumably the same denialist source insisting that "the fact that we are in a 50-75 year solar minimum cooling phase". I did a quick 11-year averaging of TSI data which stretches back to 1976. The weak Sunspot Cycle has resulted in TSI dropping by 0.25Wm^-2 which needs converting from a discal projection to a global value and adjusted for albedo, yielding 0.04Wm^-2. That is about the same as one year of AGW so if there is a full Maunder Minimum on the way, its impact is yet to show up in the TSI data.
-
TVC15 at 13:51 PM on 5 April 2019Climate's changed before
@696 scaddenp @697 Eclectic
You guys are great! I see most of his silly Gish Gallops can be addressed from the Myth Section here on Skeptical Science.
Thank you both so much for all the wonderful information you provide me with in order to debunk these deniers. I have learned so much from you all and I am honored to be able to interact with people who know what they're talking about!
-
Eclectic at 13:33 PM on 5 April 2019Climate's changed before
TVC15 , welcome to the world of crazy Gish Gallops. Don't bother to reply on every point ~ just select a few, e.g. :-
1. On your skin, a very thin smear of suncream chemicals causes a major reduction in sunburn. A big change, from a very small dose.
13. Thermometer readings vary slightly from year to year, but the Earth is still warming because excess heat is still coming in (through the excess Greenhouse effect) and the oceans are still building up heat since they absorb around 93% of the excess incoming heat ~ that's why the world's ice is continuing to melt. No cooling and no pause in melting!
14. If it does ever happen to come, a prolonged solar minimum (just like the Maunder Minimum) will cause a cooling of about 0.3 degreesC [ about 0.5 degreesF ]. Since the world's warming is continuing at approx 0.15 degreesC per decade, that means it will take only 20 years of Greehouse warming to cancel the effect of the solar minimum (if it comes at all). And then the warming will just continue to get worse. Nope, there's no hope to be gotten from a grand solar minimum.
15. In the distant past, when CO2 was much higher, the sun's radiation level was significantly LOWER. (Over the long term, our sun gets 1% hotter per every 150 million years approx.). If you want to see oceans boil, come back in a few bilion years' time!
22. All else being the same, more CO2 is helpful to most plants ~ but in the real world, more CO2 leads to more droughts, more floods, and hotter & more prolonged heat waves : so plants suffer damage and produce less crop-yield. Not good for humans.
TVC15 , tell 'im to go away and educate himself and not spout the rubbish he's been giving us.
-
scaddenp at 13:14 PM on 5 April 2019Climate's changed before
Since it looks to me like all the above are readily answerable and mostly from our myths section, I would assume that your denier has not the slightest interest in the correct answer and very much doubt they would take the time to read it anyway. Aside from the strawmen like "what happened to time without snow" -sure sign someone has never opened IPCC report.
I'd repeat, you cant reason someone out of something they werent reasoned into. If this is an online public argument, then post links to the answers here (we can help if you cant find them), so observers can see he is an idiot, but be assured that reply wont change the mind of someone who's position is based on identity. If it is someone you know, then I would recommend Katherine Hayhoe TED talk for more effective way to talk, but I suspect you are way past point where person is capable of hearing anything you say.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 12:20 PM on 5 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
nigelj,
I should have been clearer. My concern about pointing out the benefits of reduced particulate is that morally corrupted leaders could try to claim that reduction of particulate is a moral justification to continue burning 'clean coal'.
Reducing excess CO2 is the main ethical objective. As you said, reduced particulate is a side-benefit.
-
TVC15 at 12:16 PM on 5 April 2019Climate's changed before
This is the craziest Gish Gallop I've ever seen. Yes it's one of the deniers I deal with.
Please refute the facts, instead of simply launching emotional diatribes.
1. Is CO2 not .04% of atmospheric gases?
2. Is man made CO2 not 5% of atmospheric CO2?
3. Does water vapor not absorb IR energy over bandwidths 30X that of CO2?
4. Is water vapor not .4-1% of atmospheric gases?
5. Can one accurately compare over time temperature measurements estimated or measured by four different methods?
6. Why don't the "temperature plots vs time" show the error bars for the methods used for temp measurement? (comparing "proxy temps" to digital, satellite proxies, and mercury thermometer measurements should immediately disqualify any scientific comparison).
7. Why did temps not fall in the Great Depression when CO2 production fell 60%? (atmospheric CO2 has a half life of 3 years, not the very long periods suggested)
8. Why did temps fall in ww2? Was the Battle of the Bulge and Stalingrad fought in tropical climates?
9. How can the 1930s be the hottest decade on record when the AGW crowd says temps have continually increased since then?
10. Why has Miami and New York not flooded?
11. Why has there not been worldwide droughts?
12. What happened to the "times without snow"? Tell that to everyone in the US this year.
13. Why are temps falling?
14. Are we not at the beginning of a prolonged solar minimum, similar to the Mauder minimum?
15. Why did the earth not end and temps reach the boiling point of water when CO2 levels were 10X what they are now?
16. What is the contribution of solar activity and sun spots to temps?
17. What is the contribution of the orbit of the earth around the sun?
18. What is the contribution of volcanic activity?
19 If the "warming" models from 20 years ago are wrong, why are they correct now?
20 How did they measure multiple temp points at remote areas of the ocean and polar regions 200 years ago?
21. Have all the locations of temps measured over time been consistent geographic points? (Of course not- there has not been one consistent data point until the last twenty years).
22. Why were temps warmer during the Roman Empire when CO2 levels were half what they are today?
CO2 provides all the carbon that is the building blocks for ALL ORGANIC LIFE on this planet. Every carbon atom in your body that makes up all of the carbon compounds in your body were once CO2. It is not surprising that the death cult of AGW would seek to reduce or eliminate a molecule equally important as water or oxygen for life on earth.
The "optimal" CO2 for plant growth is 900-1100 ppm. We need a lot MORE CO2, not less. Due to higher CO2 levels, plant life has increased over the last 30 years, providing a greening of the planet and higher crop production. Do you want to reduce plant life and cause famines?
-
Bob Loblaw at 11:06 AM on 5 April 2019Milankovitch Cycles
stonefly:
Precession means that the orbit maintains the same eccentricity (eilliptical vs. circular), and the earth maintains the same tilt, but the timing during the year of closest/furthest parts of the orbits changes. RIght now, earth comes closest to the sun in January (NH winter, SH summer), and is furtherest away in July. (NH summer, SH winter).
If the opposite were true, - the earth and sun were closest in July, and furthest away in January - we would expect NH summers to be a bit warmer, NH winters to be a bit cooler, SH summers to be a bit cooler, and SH winters to be a bit warmer. So the NH would see greater seasonality, and the SH would see less.
The diagramns above show the same orbit/earth-sun reletaionship and change the labels for Dec/Mar/Jun/Sep. This may be a little hard to follow. Look at the single diagram in the upper left of figure 4, I reproduce it here:
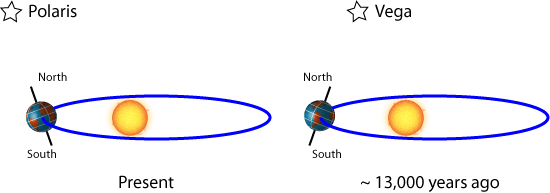
Look a tthe left half only, and think "what would happen if the sun were offset to the right of centre, instead of the left of centre?"
The diagrams in the article keep a different fixed reference, so in the right half the sun and orbit are in the same position but the earth is titled differently. The other diagrams in the change where in the diagram the months are labelled. This is correct in terms of the fixed background positions of the stars, but makes it harder to see that from another viewpoint it is just a matter of which end of the ellipse the sun is located at.
Does that help?
-
stonefly at 08:41 AM on 5 April 2019Milankovitch Cycles
"It is important to note that under the precessional cycle, the change in solar radiation striking the Earth is opposite in each hemisphere, unlike the case of obliquity where a higher tilt will mean more intense radiation at both poles as the planet revolves around the sun (although, obviously at the local summer summer for both poles, and thus at different points in the orbit)."
I've been trying to understand precession. I cannot envision the precession cycle. I cannot understand why the above quoted passage holds true.
When I envision precession, I imaging the precession adding to obliquity, therefore insolating both hemishpheres equally.
Can somebody help me understand precession?Moderator Response:[PS] Edited for clarity at posters request
-
nigelj at 06:58 AM on 5 April 2019Why results from the next generation of climate models matter
Regarding the article. The evidence does indeed point at a climate sensitivity of 3 degrees and its good the new models are helping refine this. The problem is this spread of climate sensitivity numbers is still quite large and 3 degrees is still not hugely certain. Politicians will look at this spread of numbers and be bewlidered and uncertain: and they hate that. It's really important that climate senstivity is pinned down so you can say you are 95% sure it's a certain number.
Regarding Direct air capture. I agree with OPOF. I think this probably has a place and enough potential to draw down some limited atmospheric CO2, but its going to have big problems doing more than this. These machines are still expensive and use a lot of specialist materials that are not in infinite supply.You will also have to find places to store the carbon, which will also require a lot of transport, and you will need unprecedented global cooperation.
While something is obviously possible, sucking all the carbon from the air obviously looks like it would require tens of thousands of machines, perhaps millions, and would strain the planets resources and economy beyond the limit. I think the use of massive levels of direct air capture to suck all the excess CO2 out of the air is lord of the rings fantasy stuff. So using this technology as an excuse to go on burning fossil fuels looks delusional. There is a difference between well reasoned evidence based technological optimism and pure wishful thinking.
-
SirCharles at 06:01 AM on 5 April 2019Asteroid to hit Earth in August 2046 - Emergency IPCC UN panel formed
Last time CO2 levels were this high, there were trees at the South Pole
-
nigelj at 06:00 AM on 5 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
OPOF @13, no you might be misunderstanding me. I'm not promoting clean coal, which is an idea that doesn't really work very well. I'm just saying we should all do more to emphasise the side benefits of transitioning to renewable energy. The media could do far more in this respect.
For example stopping using fossil fuels has obvious health benefits through less particulate emissions and nitrous oxides. Renewable energy has a range of advantages as well as the climate advantage. We need to emphasise these things because people respond well when they see they will be better off. Psychology 101.
By all means promote the moral duty aspect as well, because that is central to the issue. I do the same on various websites, (you do it here so no need for me to repeat what you say). However it won't be sufficient alone, and it's hard, slow work shifting peoples moral positions. It also has to be promoted in a way that connects with people positively because people can get a bit defensive about moral judgements.
I agree CO2 scrubbing by direct air capture must not be used as an excuse to go on burning fossil fuels. It may have its place to reduce some atmospheric CO2 but not all. It's important for people to realise it's costly, and is untested at scale. To directly capture all or most of the CO2 from the air will require tens of thousands of scrubbers (someone calculated this I cant remember the exact figure) and the planet probably doesn't have have the reserves of specialist metals required for this. While its ok to be optimistic about technology to a point, faith in future generations finding a way to scrub all the CO2 from the air rather than this generation reducing emissions is blind optimism and very irresponsible.
-
SirCharles at 05:46 AM on 5 April 2019Asteroid to hit Earth in August 2046 - Emergency IPCC UN panel formed
Explained here, Wazoo:

=> Global warming will happen faster than we think
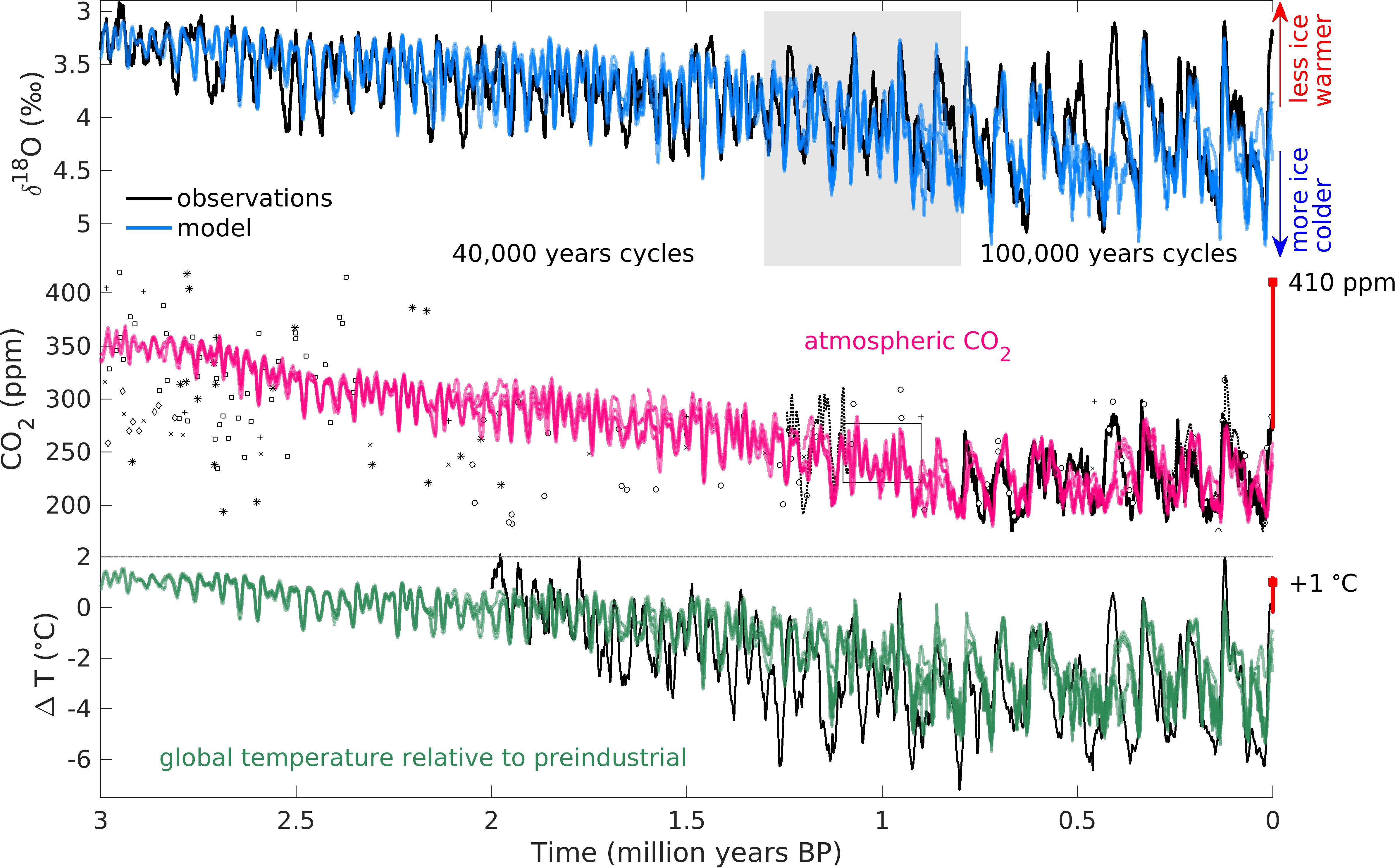
=> First successful model simulation of the past 3 million years of climate change
=> That’s how fast the carbon clock is ticking
-
One Planet Only Forever at 02:50 AM on 5 April 2019Why results from the next generation of climate models matter
Improved awareness and understanding like this is essential and always helpful.
And the parallel development of effective mitigation actions like CO2 removal (See BBC article here) is important and can also be helpful.
But their helpfulness can be challenged by morally corrupted leaders. Stephen Gardiner presented improved understanding of how and why such moral corruption occurs in his 2011 book "A Perfect Moral Storm: The ethical tragedy of climate change".
Such morally correpted leaders can be expected to continue to try to excuse doing less to reduce the use of fossil fuels. They may:
- claim that they like the new science, but, because of the diversity of model results, claim that more certainty needs to be established before they will penalize the current generation just because of 'hopes' that doing so will limit the 'potential harm done to future generatons'.
- claim that because of the technological potential to remove CO2 they can do less to reduce the use of fossil fuels, rather than adding the CO2 removal as an action to help do less harm to future generations.
- abuse the claim of the potential for future generations to develop more and 'better' technology for CO2 removal as justification for choosing to be more harmful now.
- continue to unjustiably claim that, based on past evidence and economic models (a history of development based on unsustainable and harmful pursuits and models that are far less reliable than even the older climate models), the economy only ever increases in value and the richer future generations will easily be able to enjoy their future while also brilliantly solving every problem (correcting every harm) created by the previous generations who chose not to correct how they lived.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 01:49 AM on 5 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
nigelj@12,
One of Gardiner's expressed concerns is that moral corruption can be subtle. An example would be diverting attention from the awareness and understanding of the main moral matter, like talking about particulate reduction benefits.
The governing moral issue is the need to rapidly curtail the use of fossil fuels. It is OK to make that point and add mention of the side-benefits like:
- reduced particulate
- reduced absolutely certain to occur environmental damage (the damage allowed to be done by the extraction, processing and use)
- reduced risk of harm due to 'accidents' (most of which are no accidents, and their likelihood was increased by the permission of cost-saving or time-saving approaches)
- reduced increased costs as the unsustainable harmful activity gets harder to do ethically (more sustainable economic activity, less future challenges for the less fortunate).
But it is morally corrupt to focus on the side-benefits without ensuring the main point about the need to rapidly curtail fossil fuel use is made Front and Center.
A diversion to the side-benefits can support claims about the acceptability of things like 'Clean Coal' as excuses to not more rapidly reduce the burning of coal.
In Alberta, where one of the least ethical fossil fuels is produced for sale (very high CO2 impact per unit of end usable energy), the current sales pitch is that the activity is being done very ethically because it is done to very high 'environmental standards'.
Even the potential to cost-effectively scrub CO2 from the air (As presented in BBC article here) could be abused for morally corrupt purposes to delay the curtailing of fossil fuel use. In addition to aggressive reduction of fossil fuel burning, the scrubbing of CO2 from the air could help limit the harm done to future generations.
A focus on the benefits of the 'magic bullet' of scrubbing CO2 from the air could be abused to excuse a diminished effort to reduce the use of fossil fuel. That would be a morally corrupt diversion of attention and action. Only as an addition to the required action is the 'magic bullet' helpful. It needs to be sold as the way the wealthiest of the current generations can be even more helpful to future generations.
In addition to leading by example towards the lowest impact ways of living, the wealthiest would pay to have the CO2 scrubbing done with no personal financial return benefit, done at their expense not-for-profit. All they get would be the recognition of moral character benefits. Anyone not interested in having status measured that way can be poorer and less influential, become the less fortunate and less powerful would be 'less expected' to be 'moral leaders by example'.
-
John Hartz at 23:54 PM on 4 April 2019Climate's changed before
TVC15:
Generally speaking, when a climate science denier is shoveling pseudo-science poppycock, always aggressively demand that they document the source(s). WUWT itself is not an acceptable source.
-
TVC15 at 10:15 AM on 4 April 2019Climate's changed before
@689 scaddenp
Much appreciated!
-
TVC15 at 07:39 AM on 4 April 2019Climate's changed before
@691 Daniel
Thanks!
-
nigelj at 06:33 AM on 4 April 2019Protecting oil companies instead of the climate-vulnerable is elitist
There are two types of change. Change with the promise of something better like the next model of smartphone and people mostly embrace this form of change. Then theres change forced by uncomfortable circumstances that requires paying a few costs and making a few lifestyle changes, like the need to stop using fossil fuels, and this is when people become much more conservative about change.
I've noticed that politicians who want to mitigate climate CO2 emissions and take moral positions on the climate issue are viciously insulted, labelled do gooders, or virtue signalling by the internent trolls.
Moralising about the climate only does so much. We are trying to draw a connection between a distant harm to future generations and present activity, and theres a lot of things that get in the way of making this connection. People claim future technologies will solve the problem, etc, and dont like being told they are doing the wrong thing.
Yet moral judgements form the basis of many of our laws so the morality of climate change seems very important. I just think its going to be a slow process educating people.
We could also additionally try to promote climate change mitigation by accentuating the positives, like less particulate emissions from burning coal. Shift the discussion more towards the first form of change of expecting something better because people embrace this.
Of course these things are not mutually exclusive. Raising awareness usually proceeds on several fronts simultaneously.
-
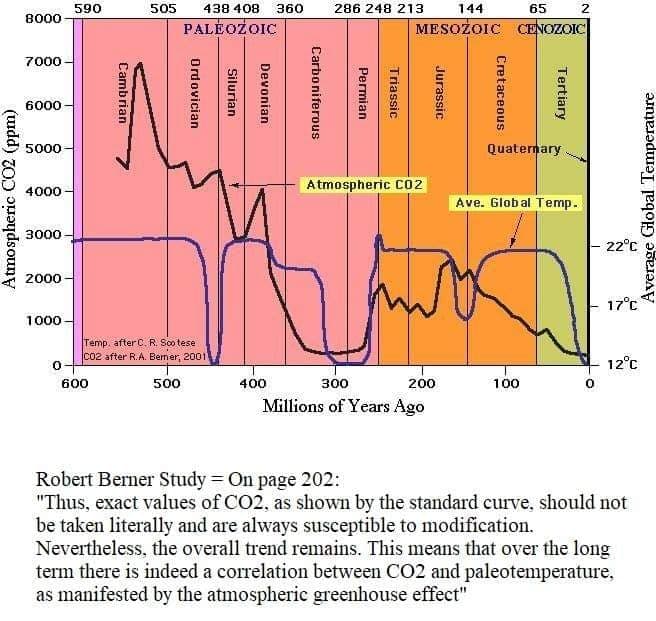
Daniel Bailey at 06:23 AM on 4 April 2019Climate's changed before
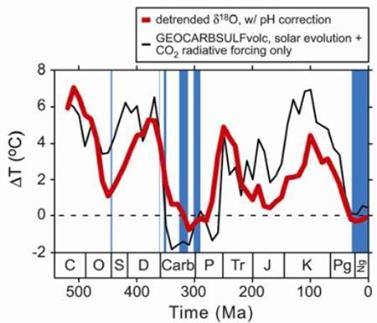
Berner authored those first graphics at the RC link. Here's the same image, with his comments about the overall correlation between atmospheric carbon dioxide and global temperatures over geologic time:
Of course, the Royer graphic also corrects for the Faint Young Sun and ocean pH changes over the same geologic timeframe, with the result of strengthening the correlation between those CO2 levels and global temperatures over geologic time:
-
scaddenp at 06:18 AM on 4 April 20193 clean energy myths that can lead to a productive climate conversation
Not to mention the advances in grid-scale storage that are coming on line. FF plants arent the only backup available.
-
TVC15 at 06:16 AM on 4 April 2019Climate's changed before
@ 688 John,
I found that this denier took it from wattsupwiththat blog site. (a blog site known for climate denialist propaganda)
I also found this in searching more about that graph.
Prev 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























