Recent Comments
Prev 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 Next
Comments 1751 to 1800:
-
Doug Bostrom at 06:36 AM on 25 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
Further to ubrew12 and "adapt or die," it's helpful to remember that in nature adaptation is powered by what we humans call "excess mortality." But for us this means of adaptation is not axiomatic, no longer comprehensive.
As a product of nature we're a force of nature. Unlike other natural phenonena we have evolved a uniquely powerful adaptive feature called foresight. This means that we can control and change our own nature of adaptation, our chances for success— at least as pertains to our cultural practices.
By paying attention to and adapting our modes of living, we can certainly make ourselves more survivable as a natural threat to ourselves. With a lot less dying in the process.
So far, this seems to be a substantially latent competence. Perhaps we should more consciously exploit it.
-
nigelj at 04:55 AM on 25 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
Nick Palmer says "It's becoming increasingly clear that virtually all of the 'engine' behind 'denialim is the Machiavellian manoeuvring of highly motivated political ideologues who believe their cause is so overwhelmingly important that it justifies the use of mass deception and the naked propaganda that is in this film."
Love this statement. So accurate. It concisely sums up the whole thing.
At the level of the general public denialism is probably a bit more broadly based, including people with vested interests in the fossil fules industry, or just worried about costs, and others with a more ideological or political agenda. Or a combination. Just based on my anecdotal impression and reading studies by various people but the pattern is very clear.
As to Margaret Thatcher, not my favourite politician, but not totally bad either. She had a chemistry degree. She undestands science and accepted anthropogenic global warming. Probably also a bit opportunistic promoting nuclear power but at least she accepted the science. The idea it was all to impoverish poor people is in the realms of tin foil hat conspiracy theory.
Certainly I have read many comments by deniers where they cant help reveal their political ideologies, and its frequently small government, libertarian freedom loving (taken to an extreme), or very conservative, or sometimes hard left concern trolling (mitigation will hurt poor people). Sometimes the right use the same argument that mitigation will hurt poor people, but I would suggest they couldnt care less and just use any ammunition they can get.
According to psychological studies people who value security as a priority tend to vote left, those who value freedom (of action) as the main priority tend to vote right. However these tendencies exist on a spectrum and most people value both. The freedom loving libertarian ideologues are way out at the extreeme to the point its a bit pathological and where they resent all laws except very minimal and basic criminal and property law. You cannot run a society like that. It doesnt work. An example:
-
BaerbelW at 04:25 AM on 25 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
walschuler @9
Thanks for the heads-up! I switched the history graphic to a version where "Callendar" is spelled consistently with two "l". Having active links on these graphics isn't really feasible AFAIK. Your other suggestions will need jg's involvement for a possible future version (which may or may not be feasible, given that we also have a few translated versions of the image and I remember that it was quite an effort when we added Eunice Foote to this set of graphics a few years ago).
-
walschuler at 01:58 AM on 25 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
I meant to say changes in the graphical timeline...
-
walschuler at 01:57 AM on 25 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
This post is already useful and clear. A few suggested changes: choose which spelling of Callendar is correct (one "l" or two); add a temperature scale at the left margin for the green curve, in degrees C and F; make the web link to Weart's piece larger print and live, so one can jump directly to it.
You might also consider live links to the works of Fourier, Foote, Tyndall, Arrhenius, Keeling and successors; add an entry and link for the icework of Petit et al; define "enhanced greenhouse effect."
-
Bob Loblaw at 23:40 PM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
nico_macdonald @ 7:
You want a case against Climate The Movie using evidence and science? All you need to do is follow the links to the existing rebuttals of the old, tired, frequently-debunked myths it repeats. They are all linked in the table that lists them in this blog post. There is literally nothing new in this movie.
Or are you unwilling to do a bit of reading?
-
nico_macdonald at 23:19 PM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
A ‘mishmash of populist conspiratorial themes’; the BBC ‘only recently stopped giving deniers equal exposure’; ‘tired old cliches’; an ‘80-minute assault on reality’. Methinks you protest too much!
If you can make a case against Climate The Movie using evidence and science, why resort to such language?
As your comments policy notes, “using labels like 'alarmist' and 'denier' as derogatory terms are usually skating on thin ice’.
-
Nick Palmer at 21:06 PM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
Doug Bostrom's post #3 is very well thought out.
It's worth remembering that the producer of this Gish Gallop is Martin Durkin, who was also responsible for The Great Global Warming Swindle. Now, denialists will whine that the following is 'ad hominem' but it is highly relevant to assessing the motivation behind, and the (lack of) accuracy and credibility of Durkin's output. At the time he did TGGWS, he was a member of the Revolutionary Communist Party. It's clear that in that film he was trying to suggest that climate science was more or less invented by Maggie Thatcher to sabotage the mineworkers union, deny the poor people's of the world access to fossil fuel energy and also to encourage the nuclear industry.
He seems to have changed his politics somewhat nowadays and I believe he is now some form of libertarian but he now seems to be pushing the angle that climate science is an attack on industrial capitalism.
It's becoming increasingly clear that virtually all of the 'engine' behind 'denialim is the Machiavellian manoeuvring of highly motivated political ideologues who believe their cause is so overwhelmingly important that it justifies the use of mass deception and the naked propaganda that is in this film
-
Evan at 20:38 PM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
Nice piece John and Baerbel. Very informative!
-
BaerbelW at 19:42 PM on 24 March 2024It's El Niño
Please note: a new basic version of this rebuttal was published on March 24, 2024 and now includes an "at a glance“ section at the top. To learn more about these updates and how you can help with evaluating their effectiveness, please check out the accompanying blog post @ https://sks.to/at-a-glance
-
ubrew12 at 06:15 AM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
I'm sure everyone has heard this joke: Two guys are hiking and they run into a bear. The first takes off immediately, but the other stops to remove his boots and put on running shoes. The first says: "Are you crazy? That's a bear!" Says the second: "I don't have to outrun the bear. I just have to outrun you." It's funny, but this philosophy is no joke to people addicted to the concept that capitalism is a no-holds-barred cage match, in which the operating principle is 'Adapt or Die' (this is literally a response I've gotten from social media posts in which I complain about climate consequences). To push the analogy, 'some of us' prefer to use binoculars to check if we're wandering into bear territory before we are actually upon them. Unfortunately, to those regurgitating ad nauseum obvious lies about climate change, the act of 'seeing where you are going and adjusting your path on that basis' is, apparently, a form of communism. And communism must be fought above all else. And as Bostrom@#3 relates they are well-financed by the wealthiest industry in the history of commerce. Hence, we are now well into the part of this journey where people start running from bears, and 'Adapt or Die' becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy. The good thing is, even as 'The Devil takes the Hindmost', more and more people will be calling for binoculars, I believe, and Climate Science will finally get the respect it is due, after all this time.
-
Doug Bostrom at 04:04 AM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
"Climate vs. Freedom" is the main point of the movie, the mainspring of the climate denialist clockwork. Careful disassembly and reverse engineering of this particular brand of synthetic ignorance inevitably reveals solipsism expressed in ideology as the movement's power source; so-called "freedom" here means "I get to do whatever I want regardless of costs to others," and powers the entire affair.
The film's funders would like us to confuse the freedom to think that is central to enlightened governance with freedom to dump sewage at our property line. This brings us into the territory of irony. Enlightenment thinking delivered the facts governing the anxieties of the film's producers— and this film is essentially trying to wind back the clock on several hundred years of the results of freedom to think.
The producers of the film are not at all concerned with freedom of thought and its outcome of science and enlightened understanding of our world. Their fears are centered on application of scientific results to public policy dealing with climate effects of CO2 emissions, circumspect and informed decisions proscribing unaccounted external costs. This will threaten any ideology founded on "everything's all about me."
Is application of climate science to public policy decisions itself ideological, even socialist? In a way it's true that climate policy is "socialist" if we're thinking in terms of social vs. antisocial, if we're employing the word "social" in its basic meaning.
Climate policy is an outcome of "socialist ideology" in the same sense that traffic regulations are a social response to selfish automobile drivers. Individual irresponsible actions come at cost to bystanders. Society is generally concerned with fairness and rejects that one person may destroy another for no good reason.
Some small percentage of persons are so poorly socialized as to care nothing about others, so we must resort to various forms of coercion to force societally-compatible behaviors. Reckless driving is discouraged by force of policy and law, ranging from fines to imprisonment because we attach such high value to fairness.
So it's proving to be the case with the external costs of vending fossil fuels, and hence we end up with climate policy that ultimately will end up with sharp edges of coercion to deal with diehard antisocial elements, given that some very tiny fraction of our society is composed of people truly uncaring of anybody but themselves.
If vast amounts of money were to be made by driving over the speed limit, we'd find a vigorous public relations industry centered on denying that e=1/2mv2. The intent would be the same as with climate science and climate policy, to fool us into thinking we don't know established facts and by extension the outcomes of those facts.
We'll never see "Traffic Tickets: The Movie" because there's no group of people for whom a vast revenue stream is threatened by being forced to drive safely. In this case of climate science and (more importantly) climate policy there is indeed a postively astronomical vector of money that will change due to policy arranged around facts and fairness and informed by science. So here we are, dealing with a slickly produced film created entirely for the purpose of prolonging profoundly anti-social behavior and employing the tactic of propagating synthetic ignorance.
Freedumb isn't freedom. It's the opposite. Freedom to think well and to make informed choices isn't the same as freedumb, feeling free to make stupid decisions because we've been fooled into believing we're ignorant.
-
John Mason at 03:45 AM on 24 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
Re #1: if you object to anything we've posted here, just let us know and cite published information to back up your argument. Just waving your arms in the air and essentially saying, "I hate this", doesn't get you very far, I'm afraid.
-
textscape at 19:38 PM on 23 March 2024Climate - the Movie: a hot mess of (c)old myths!
what a load of nonsense.
You people have NO idea.
Not skeptical ... just stupid.
Moderator Response:[BL] As a new user, I assume that you took the time to read the Comments Policy?
Your first statement is correct - the "movie" in question is indeed a "load of nonsense".
Your second statement fails to explain who "you people" are, nor does it explain just what "ideas" those people are alleged to have missed.
Your third statement is also a very accurate description of "Climate - the Movie".
Thank you for taking the time to share with us. Skeptical Science is a user forum wherein the science of climate change can be discussed from the standpoint of the science itself. Ideology and politics get checked at the keyboard.
Please take the time to review the Comments Policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
Paul Pukite at 07:41 AM on 22 March 2024Skeptical Science New Research for Week #12 2024
NigelJ mentioned "extreme marine heatwaves"
Heatwave spikes in the each of the major ocean basin indices — Pacific (Nino 3.4), Atlantic (AMO), and Indian (IOD). These are additive in terms of a global anomaly.
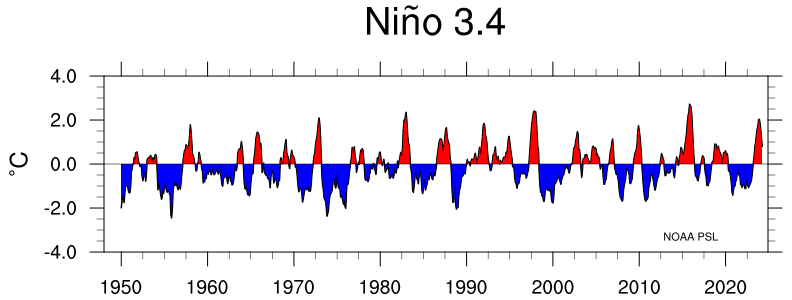
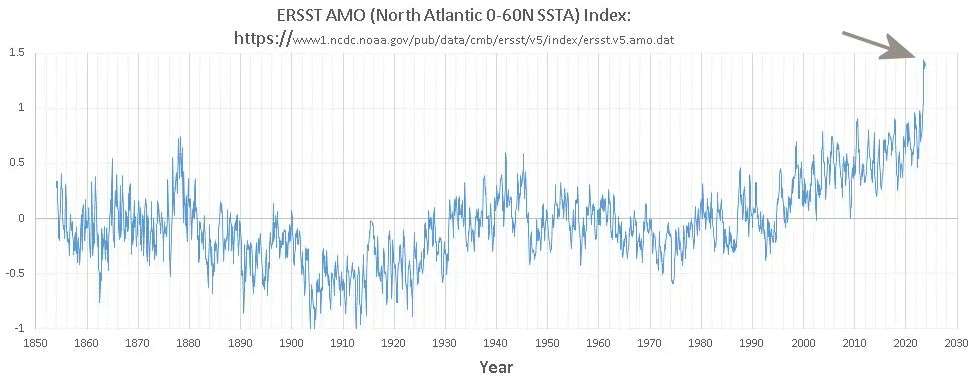
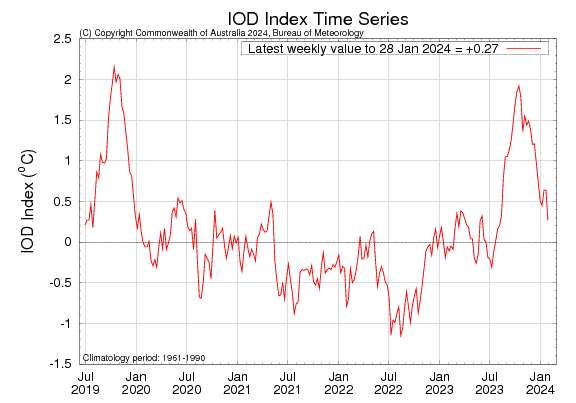
-
Paul Pukite at 06:55 AM on 22 March 2024It's a natural cycle
For the context of this thread, the important observation will be whether the anomalous global temperature rise of 2023 will recede back to "normal" levels. If that's the case, it will be categorized as a natural cycle.
So far it appears that there are simultaneous spikes in the temperature of 3 different ocean indices ENSO (Pacific), AMO (Atlantic), IOD (Indian). The last time that happened was in 1878, the year known for a super El Nino. Can see the 2 spikes in AMO for 1878 and 2023 in the following chart.

That holds interest to me in Minnesota in that this year's ice-out date for Lake Minnetonka almost broke the record for earliest date (in 1878 it occurred March 11, this year March 13)
https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2024/03/12/lake-minnetonka-ice-out/72941498007/
-
nigelj at 06:05 AM on 22 March 2024Skeptical Science New Research for Week #12 2024
Regarding "Climate models can’t explain 2023’s huge heat anomaly — we could be in uncharted territory, Schmidt, Nature [perspective]:"
This is very concerning and perceptive.
This following article by Copernicus has a great review of the effects of aerosols, and some interesting ideas of what may have contributed to last years unusually high temperatures in the nothern atlantic in partcular:
"Aerosols: are SO2 emissions reductions contributing to global warming?"
https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/aerosols-are-so2-emissions-reductions-contributing-global-warming
Excerpts:
In 2020, the International Maritime Organization adopted its ‘IMO 2020’ regulation to drastically reduce shipping-related sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions. Studies have concluded that the drop in emissions significantly reduced the formation of clouds over shipping lanes. An analysis by Carbon Brief estimated that that “the likely side-effect of the 2020 regulations to cut air pollution from shipping is to increase global temperatures by around 0.05C by 2050 (My note: Clearly this doesnt do much to explain the last 9 months unusual warming, and why would a change in 2020 shipping fuels that was implimented in that year, not slowly phased in, suddenly manifest 3 years later anyway? ). This is equivalent to approximately two additional years of emissions.” However, linking SO2 reductions directly to the recent extreme marine heatwaves omits part of the complexity of using models to calculate sulphate aerosol interactions in the atmosphere or estimating the effective application of the IMO 2020 regulation, and, more generally, the complexity of climate and atmospheric chemistry.
Reviewing the record North Atlantic Sea surface temperatures in June 2023, a preliminary analysis from CAMS scientists found a significant negative anomaly in Saharan dust aerosol transport over the tropical Atlantic Ocean, and an increased anomaly in biomass burning aerosol over the North Atlantic, coming from the massive Canadian wildfires. These aerosol anomalies are much bigger than the sulphate change from shipping emission reductions. This makes the estimation of the impact of reduced sulphate aerosol emissions on the sea surface temperatures very challenging.
June 2023 monthly mean aerosol optical depth (AOD) anomaly relative to June average AOD for the period 2003-2022 from the CAMS global reanalysis of atmospheric composition shows a negative anomaly related to reduced dust transport across the tropical North Atlantic (blue) and a positive anomaly related to smoke transport from Canadian wildfires over the extra-tropical North Atlantic (red). Base on non-validated data Credit: CAMS
The Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) also suggested that, among other factors, the reduced winds of a weakened Azores anticyclone - an extensive wind system that spirals out from a centre of high atmospheric pressure - could have reduced the ocean-atmosphere exchange and the vertical mixing of the ocean between colder and warmer waters, as well as reducing Saharan dust transport over the Atlantic, all of which has the potential to increase the ocean surface temperature.
“There will be, no doubt, long-term impacts from the reduced SO2 emissions, but it will demand dedicated research to understand the impact of sulphur changes. The changes in dust or black carbon have a more tangible effect in the short term”, says Richard Engelen CAMS Deputy Director.
My comments: Of course this doesn't easily explain the unusually high levels of warming in the pacific. Next year will be revealing. It should be relatively cooler year on past patterns but if it isnt IMO it would suggest a step change in anthropogenic global warming. We know the climate is non linear and abrupt changes are possible. Will be interesting to see what BS the denialists will come up with to counter another unusually warm year.
-
Bob Loblaw at 06:01 AM on 22 March 2024It's a natural cycle
Michael Sweet @ 38:
A ground-based aerosol monitoring network has existed for 25+ years. It uses optical instruments - a sort of "remote sensing looking up" approach. I don't know to what extent it has been analyzed for aerosol trends, but I'm sure someone has been using the data for that purpose.
-
John Mason at 02:11 AM on 22 March 2024It's a natural cycle
Re - #38: if you look at heat content graphs with uncertainty range included, it's possible that even more heat went into the oceans this past few years than we thought. For example:
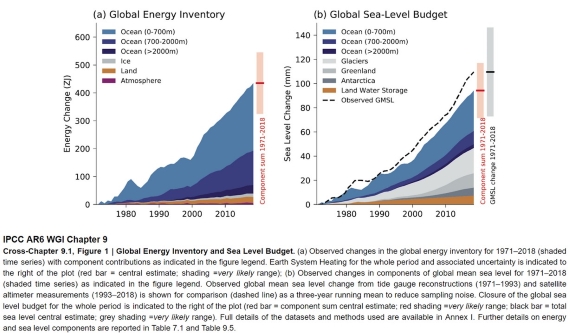
Could it be that being well on the high side of the central estimate is sufficient??
-
michael sweet at 23:39 PM on 21 March 2024It's a natural cycle
In Dr Schmidt's commentary, linked by Paul Pukite above, he reviews the possible causes of the high temperatures in 2023. He discusses the global warming trend, El Nino, aerosols and the volcano. He concludes that none offer enough to explain the temperature increase. This is the same conclusion that we reached in a discussion on a thread here at SkS. He suggests that the climate might have switched to a new, unmodeled regime. We will all have to wait for more data to see what the data indicates. If it was El Nino then (I think) we would expect a decrease in temperatures in a few months since that is switching to La Nina. It is interesting , in a macabre way, to see how this scientific question is answered.
NASA apparently finally launched a mission to measure aerosols in the atmosphere. Dr. Hansen has lobbied for such a mission for decades. How will scientists tell if aerosols changed significantly in the past 5 years?
It is very disturbing to me that Dr. Hansen predicted in advance that temperatures would substantially increase this decade due to the decrease in aerosols. It seems like more scientists think that aerosols do not explain the high temperatures in 2023. Dr Hansen has argued for years that the aerosol effect has been underestimated. I hope that Hansen is incorrect.
-
Paul Pukite at 10:18 AM on 21 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
Energy use is outside the deep expertise of climate followers. Most don't appreciate that even though USA is the largest extractor of crude oil in the world, they still need a large fraction of imported oil. The USA only extracts <13 million barrels/day of crude oil from it's territory, yet the USA consumes 20 million/day of finished product. Compare that to a USA wheat crop where we harvest much more than we consume.
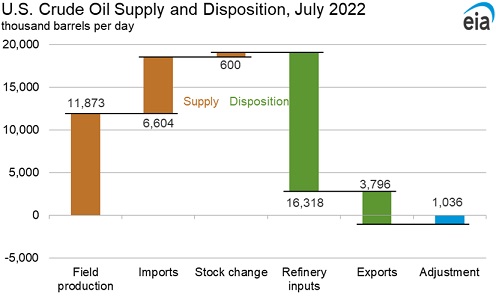
Note that the above is crude oil only, and other liquid fuels make up the amount to reach 20 million.
-
Paul Pukite at 08:51 AM on 21 March 2024It's a natural cycle
As per the latest observations, nothing is ruled out
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-00816-z
"Climate models can’t explain 2023’s huge heat anomaly — we could be in uncharted territory" :
- Taking into account all known factors, the planet warmed 0.2 °C more last year than climate scientists expected. More and better data are urgently needed.
By Gavin Schmidt
-
One Planet Only Forever at 12:04 PM on 20 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
I understand every part of the re-posted article. But it is not clear how this presentation helps increase awareness or improve understanding of the leadership (Business and Political) actions that need to become more popular to ‘produce’ the changes of attitude and action of the collective US population so that the US is clearly understood to be responsibly doing its part, and being a leader, in the undeniably essential global effort to, at least, meet the globally agreed Paris Agreement objectives.
That said,
I agree with wilddouglascounty #3. ‘Producing energy’ correctly applies to ‘making energy available for human consumption’.
And, along the lines of nigelj’s point that ‘producing energy’ is understood shorthand, I offer the following detailed description: Energy production = Human actions to convert natural energy sources into 'consumable/usable energy products'.
All that said,
I would add that an often ‘missed, or dismissed, understanding’ is the importance of pursuing ‘sustainable energy production and consumption’. The history of action, and a lack of corrective action is an action, by misleading leaders has ‘produced’ and ‘continues to grow’ tragic consequences for the future of humanity due to the production of ‘substantial amounts of unsustainable consumption (not just energy consumption)’.
Note that ‘consumer desires to benefit from fossil fuel use’ are the ultimate ‘product‘ pursued by fossil fuel profiteers. And recently leaders of Exxon and Saudi Aramco have blamed consumers for being ‘the problem’, not misleading leaders (undeserving wealthy, powerful and influential people).
-
nigelj at 05:44 AM on 20 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
IMHO terms like producing energy and sunrise are just convenient shorthand. To accurately describe whats really happening in a full sense would get very wordy: For example "The world produced xyz quantity of energy in 2023" would become " In 2023 the world converted xyz quantity of energy from a variety of sources to thermal energy to carry out various tasks " Do we really need to do that?
In the news hour on television "Sunrise" would become "Tomorrow the earth will rotate on its axis to expose the sun at 6.00 am". How ponderous. People know whats really meant. Nobody in todays world would take it literally and believe the sun really moves above the earth (except maybe the flat earth society, and a few indigenous tribes and they dont have television anyway).
-
Bob Loblaw at 04:55 AM on 20 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
It all hinges on the meanings of words, doesn't it?
Coal miners don't produce coal - they just dig it up and move it.
Newspapers don't produce news, they just report on it.
But remember: English is a language where people drive on parkways and park on driveways.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 02:20 AM on 20 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
[BL], I agree. That is why I focused my reponse on wavefunction's unjustified criticism "...can't handle critisism [sic]...". To be honest, I had a faint hope that opening with the suggestion that wavefunction's comment raised an important point would get them to read my full comment.
Eclectic, I agree. Also, a lack of a justified response by wavefunction would indicate that they "can't handle, learn from or deliver, justified criticism".
Moderator Response:[BL] Hope is a good thing....
-
wilddouglascounty at 23:28 PM on 19 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
Hey guys, BOTH are true in BOTH instances. Energy is not created in the universe, rather it follows the law of conservation of energy. But the miniscule part of that energy constant that is made available for human consumption is also produced.
As we know, the sun rising and setting on the local horizon is caused by the earth rotating in its trip around the sun. Nevertheless, the local rising and setting is a physically measurable reality that every plant and animal responds to.
So it depends on which frame of reference box you want to put onto reality: they both work and are not mutually exclusive!
-
Evan at 20:28 PM on 18 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
Well Doug, the sun doesn't rise or set, and yet every news channel reports the times for "sunrise" and "sunset". :-)
-
Doug Bostrom at 16:42 PM on 18 March 2024The U.S. has never produced more energy than it does today
Call me an old curmudgeon but I wish we wouldn't talk about "producing" energy. The best we can do is to convert it. :-)
-
Eclectic at 06:13 AM on 18 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
OnePlanet @661 : yes.
Now we await Wavefunction's first piece of "justified criticism".
Patience may be required ...
-
One Planet Only Forever at 04:03 AM on 18 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
Wavefunction @659 raises an important point.
As a professional engineer with an MBA I have pursued developing a well justified understanding, open to being improved by justified criticism, of what is required to develop sustainable improvements.
Everyone should welcome and engage in learning based on ‘justified’ criticism of developed beliefs and justified criticism of poorly justified or unjustified criticism. That is how ‘scientific understanding improves’, including how this site’s content has constantly improved. It is also how businesses and political groups can learn to be more sustainable (less harmful and more helpful actions have more of a future).
The persistence, and in some cases the tragic growth or regrowth, of unjustified confidence in harmful misunderstandings is an undeniable problem. An aspect of that problem is the unjustified angry responses to sensible efforts to increase awareness and improve understanding that help people learn to be less harmful and more helpful members of humanity.
Correction of tragically popular misunderstandings, especially misunderstandings regarding harmful profitable activity (including excusing or denying harm done because of perceived benefits), is essential to the development of sustainable improvements for the benefit of all children now and into the distant future.
Learning about required corrections of thoughts and beliefs is also necessary for the successful repair of the damaging results of the popularity and profitability of ‘lack of awareness and misunderstandings’. Popular and profitable lack of awareness and misunderstanding can be very resistant to ‘justified criticism that would improve and correct it’.
I welcome justified criticism to improve that understanding.
Moderator Response:[BL] I disagree that Wavefunction has raised any interesting points. He starts with an insult, continues with name-calling, and makes a wild claim that none of the "dozens of comments" he has read (on a topic that had 658 comments on it before he posted) "gives a straight answer" to some unspecified "question that's at the heart of the entire theory of human driven climate change".
- He's read a few % of the comments - seemingly only on this one thread, without looking at any of the other many sources of information on this web site.
- He can't be bothered to say which ones, or what they lack.
- He can't be bothered to tell us what he thinks the "question ...at the heart..." is.
- He thinks that moderators applying the Comments Policy are "telling people what they can and can't say". (The Comments Policy tells people how they are expected to behave - not the positions they are allowed to argue.)
The comment deserved to be deleted in its entirety, due to it's lack of anything specific, its tone, and its numerous violations of the policy - but it also deserves to be left up for anyone that reads it to see what Wavefunciton's behaviour is.
You have used Wavefunction's comment to make what are interesting and valid points. Reasonable discussion, justified criticism, avoiding angry unjustified response. All are worthwhile goals. The Comments Policy begins with:
The purpose of the discussion threads is to allow notification and correction of errors in the article, and to permit clarification of related points. Though we believe the only genuine debate on the science of global warming is that which occurs in the scientific literature, we welcome genuine discussion as both an aid to understanding and a means of correcting our inadvertent errors. To facilitate genuine discussion, we have a zero tolerance approach to trolling and sloganeering.
Genuine discussion requires a willingness to provide clear communications. Wavefunction hasn't even come close.
-
Eclectic at 21:27 PM on 17 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
Wavefunction @659 :
Hmm. Now that you have vented your emotions
. . . perhaps you would be so kind as to make an On-Topic comment that is interesting and relevant.
Or try posting at the WattsUpWithThat blogsite, where about 80% of comments are venting & echo-chambering of non-science.
-
wavefunction at 18:06 PM on 17 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
What an absolute joke of site this is. This isn't science, its a bunch of clowns that can't handle critisism and a hall monitor running around telling people what they can and can't say. Its no wonder that out of the dozens of comments I've read on this thresd, not ONE, gives a straight answer to the question that's at the heart of the entire theory of human driven climate change. You and those you parrot better be right.
Moderator Response:[BL] If your goal is to get banned, so you can go and tell your friends that Skeptical Science is unwilling to listen to your wisdom, then you are off to a good start. You'll save us all a lot of time if you just post a comment saying "please ban me".
If your goal is to actually discuss any of the science, then you actually have to be willing to make a specific, supported, scientific statement that is related to the discussion topic of the original post, then you'll need to read and follow the Comments Policy. There is a link to the policy above the box you used to post your comment.
The first two statements of the Comments Policy are:
- All comments must be on topic. Comments are on topic if they draw attention to possible errors of fact or interpretation in the main article, of if they discuss the immediate implications of the facts discussed in the main article. However, general discussions of Global Warming not explicitly related to the details of the main article are always off topic. Moderation complaints are always off topic and will be deleted
- Make comments in the most appropriate thread. Some comments, while strictly on topic, may relate to issues discussed in more detail in some other thread. Extended discussion of those points should be carried out in the more appropriate thread, with link backs to reference the discussion as needed. Moderator's directions to move discussion to a more appropriate thread should always be followed.
...but there are a couple more that you have violated in your brief rant. Surely someone of your great intellect will be able to read the policy and identify which rules you have broken.
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can be rescinded if the posting individual treats adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
BaerbelW at 05:11 AM on 17 March 2024It's a natural cycle
Please note: the new basic version of this rebuttal was published on March 16, 2024 and now includes an "at a glance“ section at the top. To learn more about these updates and how you can help with evaluating their effectiveness, please check out the accompanying blog post @ https://sks.to/at-a-glance
-
One Planet Only Forever at 03:24 AM on 17 March 2024Skeptical Science New Research for Week #11 2024
Note that in my comment at 1 the link to the report is the bolded title of the report Artificial Intelligence Threats to Climate Change.
I forgot that in these comments a bolded text string does not stand out as a link.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 03:20 AM on 17 March 2024Skeptical Science New Research for Week #11 2024
The link for the second item (description repeated below) highlighted from the Government/NGO section does not work for me:
The AI Threats to Climate Change, Climate Action Against Disinformation, Check My Adds, Friends of the Earth, Global Action Plan, Greenpeace, and Kairos:
The following links work for me:
Link to the Climate Action Against Disinformation webpage introduction and summary of the report (with a button linking to the report)
Link to the report from the CAAD introduction page: Artificial Intelligence Threats to Climate Change (a Friends of the Earth website location for the report)
Thank you OPOF. Fixed!
-
Charlie_Brown at 02:31 AM on 17 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
The mention of quantum mechanics warrants further discussion so one is not baffled or misled by a misrepresentation of it. Besides, the science is fascinating, and the concept is not that hard to understand. All molecules above absolute zero have internal energy. They vibrate, bend, and stretch in a limited number of ways that depend on their structure and ability to interact with electromagnetic radiation. Absorption and emittance of a photon changes the internal energy level by a discrete amount, which gives rise to discrete absorptance/emittance lines. CO2 is a linear, non-polar molecule that can stretch symmetrically and asymmetrically, but also polarizes temporarily when it bends. When molecules in the atmosphere have absorptance/emittance lines that fall within the wavelength range of IR at moderate temperatures by the Planck distribution, they become greenhouse gases. Discrete lines for CO2 and H2O are illustrated in Figure 3 in Introduction to an Atmospheric Radiation Model.
One more comment about the “quantum process” which is described incorrectly by RBurr @ 654. CO2 is “additive” and increasing. Thus, it is affecting the accumulation term in the global energy balance. -
Charlie_Brown at 09:26 AM on 16 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
RBurr @ 654
1) CO2 lags temperature rise at the end of an ice age because CO2 evolves from ocean waters as the temperature rises. This is Henry’s Law. In that case, temperature rises first due to the Milankovitch Cycles. Note that ice age temperatures cool slowly and warm rapidly. Modern CO2 emissions are different because they come from burning fossil fuels. Therefore, temperature rises as a result of CO2. Cause and effect in both cases is clear in both cases, and different in both cases.
2) The quantum mechanical mechanism on IR radiation that explains the greenhouse warming theory has been proven. It is based on fundamental principles of energy balance and radiant energy transfer and has been verified by massive amounts of data, cross-checks, and validation.
3) The Earth’s energy “balance” is fundamental:
Input = Output + Accumulation
Output is reduced as greenhouse gases increase. Thus, energy accumulates.
4) Your description of quantum mechanics does not make sense. Quantum mechanics is fundamental to the specific frequencies (i.e., wavelengths) that are absorbed and emitted by CO2, CH4, and H2O. There is a huge amount of energy carried by IR radiation. It is naturally emitted (not dissipated) and lost to outer space by IR. By the overall global energy balance at steady state:
Input solar = Reflected solar + Emitted IR
Accumulation is zero at steady state, as before CO2 emissions of the industrial revolution.
5) The hot object in this case is the sun at about 5800 Kelvin. That is more than hot enough to warm the earth. The temperature profile is 5800 K of the sun to 288 K (60F) of the Earth 217 K of the lower stratosphere to 2 K of outer space. Increasing CO2 reduces the energy loss to space at specific wavelengths (e.g., approx. 13-17 microns). The absorptance/emittance lines in that range increase, meaning that energy is emitted from a cold 217 K instead of a warm 288 K. This upsets the energy balance. The balance is restored by accumulating energy until the surface temperature increases enough to make up the reduction by CO2. Nothing about this violates either the 1st or 2nd law of thermodynamics. Some mistake the 2nd law by describing the energy balance being at steady state, but the steady state was upset by increasing GHG.
6) Neither the Milankovitch Cycles nor the Schwabe Cycles (sunspots) explain the cause of modern global warming. The long-term Milankovitch Cycles have not been in a period of significant change for the last 12,000 years after warming from the last ice age. Measured radiosity data from the sun show that short-term Schwabe Cycles have not changed significantly either and do not explain modern warming. -
Bob Loblaw at 01:16 AM on 16 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
Ah, RBurr's comment at 654 is indeed an odd duck. While demanding "proof", he is badly short on providing any "proof" for his wild assertions. He alludes to "new research" (Where? By who? What publication?), but then just asserts a bunch of old misconceptions.
RBurr's assertions on "quantum mechanics" can be roughly lumped into a denial of the conservation of energy, a gross misunderstanding of the concept of temperature (individual molecules don't have temperature, and temperature is not a property of radiation), with a mix of "violates the second law" bunk.
There are other threads here at SkS where such topics can be discussed (and have been, at length).
- The 2nd law myth. (number 62 on the list of most common myths).
- Has the Greenhosue Effect been falsified? (number 65 on the list)
- and an example of how a cooler object can indeed lead to additional heating of a warmer object. (The Dynamics of the Green Plate Effect.)
A little learning is a dangerous thing;
drink deep, or taste not the Pierian spring:
there shallow draughts intoxicate the brain,
and drinking largely sobers us again.Alexander Pope, An essay on Criticism
English poet & satirist (1688 - 1744) -
Eclectic at 20:26 PM on 15 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
RBurr @654 : Your ideas are interesting, to some extent.
But your ideas are based on semantics, not on physics. And sadly, the Greenhouse Effect cannot simply be talked away.
Education is the path forward for you. Good luck !
-
RBurr at 08:51 AM on 15 March 2024CO2 lags temperature
The analogy was cute, that the observation that CO2 rises lag temperature rises, means that the Temp rise causes the CO2 rise, is a bit like saying that chickens do not lay eggs because they have been observed to hatch from them. I would submit that, by the same token, opining that CO2 increases cause global warming is a bit like saying that chickens to not hatch from eggs, because they they’ve been observed to lay them.
This all suggests (as inferred) a co-dependent process.
However, this overlooks the same thing that MOST public blogs overlook, and that is the quantum mechanical mechanism on IR radiation (per greenhouse warming theory) has never been proven, and is actually false. New research indicates the fundamental error in the theory, presumes that Heat is ADDITIVE (eg. The Earth’s energy ‘budget’). The quantum process for Thermal transference is not additive. It is a function of frequency resonance. This is why microwave ovens work. Solar heating occurs because the spectrum of frequencies included in sunlight (which reaches the Earth’s surface) sets the maximum temperature which the recipient object may reach. An object in an oven set to 400 degrees will never reach 500 degrees no longer how long it is in the oven, because heat transference is not additive over time. The low energy IR waves received by CO2 molecules will naturally dissipate into the atmosphere with negligible net effect upon the atmosphere, but will never cause planetary ‘heating’ because, per thermodynamic law, no object can heat something beyond the temperature it possesses. Irradiated CO2 molecules can never heat the earth beyond the temperature frequency that already exists within the earth, which generated the IR light waves to begin with. IR Radiation does not raise the temperature of the Earth. The greenhouse warming theory is flawed. THAT is why the universally accepted historical record shows zero correlation between atmospheric CO2 levels and average temperature over the entirety of the past 4 Billion years. Zeroing in on the last 400k or 800k years, and pointing to an anomaly amounts to cherry picking, which disregards the other dynamics in play, such as Milankovitch Cycles. Note: Ozone depletion CAN increase surface temperatures because the range of UV frequencies that reach the surface is expanded. -
One Planet Only Forever at 05:14 AM on 12 March 20242024 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #10
Jim Eager.
I agree, with a slightly different perspective.
A better question is: How much of the harmful public misunderstanding and lack of care about the future is due to the deliberate development and dissemination of disinformation by the likes of Exxon anti-leadership and the political misleaders who chose to join the anti-leadership team effort?
I use the term anti-leadership because, from an ethical perspective, leadership obviously needs to responsibly pursue and promote improved awareness and understanding of what is harmful and unsustainable, learning and teaching how to be less harmful and more helpful. As justification for that perspective I would suggest that any organization that does not have that type of leadership may temporarily appear to be successful. But it will ultimately be unsustainable.
I learned that understanding in the marketing course of my MBA education in the 1980s. That course began with the professor stating we would learn about the science of marketing . We would learn about the powerful ability to fool many people some of the time by being misleading. But we would also learn that abusing that 'marketing science knowledge' should not be done because it would ultimately be unsustainable. (Also, the Ethics course started with the professor stating that there would be a lack of case study examples of 'ethical business behaviours'. Admittedly some case study examples of ethical leadership have developed since the 1980s).
Moderator Response:[PS] Slight edit to fix an unfortunate typo.
-
Jim Eager at 04:43 AM on 12 March 20242024 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #10
Sorry, but actually Exxon CEO Darren Woods may be right that consumers are too stupid to understand or want sustainable energy supplies, or at least too uninterested or too unself-aware.
If you want evidence you just need to get out more.
I wish I had a dollar for every small p**** in a big black tricked-out pickup truck that I've seen floor it to get around my hybrid EV just to beat me to the red light, and then floor it again when the light turns green, or push that 3 1/2 ton behemoth along at 80 on the highway.
You want consumers to understand or want sustainable energy supplies?
Double or even triple gasoline prices and maybe, just maybe it will get their attention.
Not that this absolves Exxon's Woods and his ilk one iota, mind you.
-
BaerbelW at 20:25 PM on 10 March 2024There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
Please note: the basic version of this rebuttal has been updated on March 10, 2024 and now includes an "at a glance“ section at the top. To learn more about these updates and how you can help with evaluating their effectiveness, please check out the accompanying blog post @ https://sks.to/at-a-glance
-
John Mason at 01:28 AM on 9 March 2024At a glance - What has global warming done since 1998?
While working on a vaguely-related project I updated this rebuttal AGAIN, despite it being less than 12 months old, because 2023 smashed temperature records. Depressing business this, sometimes! No need to do anything with this post as it's timestamped. Anyone wanting to read the updated version will find it here:
https://skepticalscience.com/global-warming-stopped-in-1998.htm -
Evan at 23:48 PM on 8 March 2024All this climate data is wild
There are even data loggers for tracking the migration of Monarch butterflies (read here).
-
Evan at 21:34 PM on 8 March 2024All this climate data is wild
wilddouglascounty@3 Good question. The pack was too small to contain continual broadcast. It needed to be small for a Purple Martin to carry it. It stored GPS data on a chip and could only be retreived were the bird found again, as it was in our case.
From what I've read, the current backpacks are able to transmit live so that the bird does not have to be caught.
-
wilddouglascounty at 03:23 AM on 8 March 2024All this climate data is wild
2/Evan,
You got me wondering: were they able to retrieve the data from the backpack? Or did they already gathering the data as the bird flew around?
-
Evan at 21:40 PM on 7 March 2024All this climate data is wild
While cleaning out our Purple Martin house one spring, I found a Purple Martin that had unfortunately died. I noticed it was tagged, and emailed the tag number to the US Department of Natural Resources. They politely thanked me for the information.
A day later I got a very excited email from them asking if there was an antenna protruding from its back. Sure enough, there was. A bird as small as a Purple Martin had been fitted with a small backpack to gather data on its migration, tracking its flight from Minnesota all the way down to Central America and back.
-
BaerbelW at 07:15 AM on 7 March 2024All this climate data is wild
This article brings back memories from almost 10 years ago, when I was lucky enough to get in touch via email with scientists doing just this kind of research, tagging elephant seals in Antarctica with sensors to gather data. Here is the link to the resulting blog post:
Seal of approval - How marine mammals provide important climate data































 Arguments
Arguments



























