Recent Comments
Prev 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 Next
Comments 22951 to 23000:
-
nigelj at 07:27 AM on 30 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
I would contend that until recently, society has mostly had faith in the honesty and fact based reporting of scientific bodies, government agencies, and the private sector. Even politicians and the media have been at least held in some degree of respect.
Of course we "all" know people lie sometimes or get things wrong, and we should all be sceptics to a point, but I would contend we have largely had basic faith in institutions being generally reliable. And institutions have mostly been reliable, with genuine problems exposed by the media.
But things have changed in recent years. I dont know if studies have quantified, this but the anecdotal evidence is so obvious and so strong it demands attention. Extreme levels of distrust have emerged regarding virtually all our institutions.This is very concerning because the functioning of society relies on trust and accurate information that can be relied on.
I think this discontent and cynicism has several origins. The precipitating factor could be the GW Bush invasion of Iraq and non existant weapons of mass destruction. I contend this more than anything has caused the distrust. It started with distrust of the CIA and politicians, and opportunists have used this to deflect distrust onto the climate science community and all agencies and institutions and also the globalisation agenda.
In fact globalisation (which seems basically good to me) has definitely had some problems along the way, and this has also eroded trust in the "authorities" or intellectual elite, unfortunately. Everyone has been smeared by this. Another problem has been the rampant paedophilia and sexual abuse exposed in a variety of institutions, further eroding tust in these institutions but also all institutions and the "elite" in general.
As a result the word of the authorities and objective truth has come into disrepute and something has to fill the gap. People now believe whatever they want to believe, or they believe "alternative" websites or writers.
Given the demise of facts and truth people have gone with nothing more than gut instincts, emotion, ideology, and beliefs. If something doesn't pass through their ideological filter it gets discarded. People talk about "truthiness" a concept so vague and emotive it surely doesn't make sense.
The more politicians or agencies of the state repeat mistakes like Iraq, make things up, or base decisions on emotion and assertion rather than hard evidence, the more the trend away from objective facts and truth will be reinforced, until society starts to seriously break down.
-
ramprasad at 06:51 AM on 30 December 2016Models are unreliable
There seems to be alot of confusion on setting up a model.... "fudging" "tweaking" "adjusting"....
Any good model is "Calibrated" and then "Verified". One dat aset--say climate data from 1900-1950--is used to calibrate the model. That is adjust coeficients and varibles, tweak if you will, to match existing data.
The model is then verified against a second data set--say 1951-2000— to "verify" if the "calibrated" model can predict actual data without any tweaking or fudging. Only then is a model ready to "predict" future conditions.
Though the question of whether the "calbration" dataset is similar enough to future conditions to ensure that predicted results are meaniful still remains.
-
william5331 at 04:56 AM on 30 December 2016Record-breaking Arctic warmth ‘extremely unlikely’ without climate change
To a large extent, statistical analysis and prediction of the likely frequency of various events depends on past records and that inputs are the same now, on average, as they have ever been. In this completely new scenario of Carbon dioxide above 400ppm and climbing, all bets are off. The now famous tipping points are likely to be sending the climate into new territory that past experience can not predict.
-
MA Rodger at 20:05 PM on 29 December 2016There's no empirical evidence
HB @324.
Addressing your comments in order:
☻ - 1- There is no problem with the numbers you present in themselves although using such rough figures are unnecesary. Your use of atm for bar is no great impediment although it is wrong. The problem with both your inexact numbers and inexact descriptions is purely one of clarity and becomes a problem only when combined with your incredibly bizarre assertions.
☻ - 2 - See Glenn Tamblyn @325. Note that the 1 bar altitude is set at some 50km on Venus and is roughly the altitude of the top of its troposphere. Above that altitude (65km) are SO2 cloud banks which are more important than any CO2 effect at this altitude. As for the rotation of Venus being slow, the planet's 'day' is some 2,800 hours but with the rotation of the optically thick atmosphere some 50 hours, this length of 'day' is not relevant. It is only relevant way up high in the upper atmosphere, for instance in the mesosphere above the cloud banks (1 μbar) where the day/night temperature range is 130K.
☻ - 3 - You say that you "would choose almost any other explanation than (GHGs being the reason for the high Venusian temeratures). All of them would include heat generation of some sort. Since that is what it takes to heat something up." This is you again arguing that the laws of thermodynamics are wrong. Trust me. Such argument has to be far far stronger than a pantomime.
I should add a correction to #324. The Venusian temperature at 1 bar (350K) is colder, not hotter, than a pro-rata 1 bar Earth temperature corrected for the elevated Venusian insolation (400K). However, the albedo of the Venusian atmosphere above 1 bar far exceeds that of the total Earthly albedo which makes the pro rata calculation a little unrepresentative.
-
chriskoz at 18:15 PM on 29 December 2016Record-breaking Arctic warmth ‘extremely unlikely’ without climate change
Some commenter here (sorry I forgot who & cannot find) suggested the years following extreme ElNino recorded very large summer ice extent minima (e.g. 2007, 2012) whereas the next years featured the"recovery" to the long-term trend. The commenter speculated if there is any mechanism responsible for such delayed influence of ElNino in the arctic so that the season of the relatively largest melt is likely tobe the following season, but no one came up with anything.
The topic is interesting and the speculation appears to be confirmed by this year's poor freezing season (past record 2015-16 ElNino) but it remains to be seen what the melting season of Northern autumn 2017 will bring.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 15:23 PM on 29 December 2016There's no empirical evidence
HB
You are missing one important point. Albedo. Venus is highly reflective with a Bond Albedo of between 0.75 to 0.9. So it only absorbs 10%-25% of the sunlight that strikes it. Incontrast the Earth absorbs around 70% of the sunligt that strikes it So, although it is much close to the sun, Venus actually absorbs less energy from the Sun than the Earth does.
Next, for the temperature at the surface to be high doesn't require heatgeneration. It only requires heat tranport from the upper atmosphere to the surface.
See my comment at 318. The atmospheric Lapse Rate determines th surface temperature, based on the upper atmosphere temperature which is set by radiative balance and GH gases - for Venus mainly CO2.
I suggest you do some reading to understand how vertical air movements, which can transport heat up or down, create the Lapse Rate. -
anticorncob6 at 15:12 PM on 29 December 2016It hasn't warmed since 1998
Here it says that 2015, 2014, 2010, and 2005 were hotter than 1998. But weren't 2013, 2009, and 2007 all hotter than 1998 as well?
That's what I determined after averaging these two data sets:
NASA land-ocean temperature data
NOAA land-ocean temperature data
(even though they use different bases for the abnormalities, we can still determine the relative ranks of years).
-
Andrew1776 at 14:42 PM on 29 December 2016So what did-in the dinosaurs? A murder mystery…
Why did you snip Q96? The quesiton of whether falling CO2 concentrations could cause mass extinction is a very legitimate scientific quesiton. The scientific literature shows CO2 dropping from 2000ppm to 180ppm betwee K and Pg (see phanerozoic carbon dioxide graph on wikipedia ). My question relates to how this drop in CO2 affected plant life on earth?
The most fundamental enzymatic reaction on earth for sustaining life is the fixation of carbon dioxide by the enzyme RuBisCO. (see wikipedia entry for RuBisCO). RuBisCO's activity is very slow and depends on the concentration of CO2. Indeed, RuBisCO is rate limiting for photosynethesis on earth. It has single digit turnover per second as compared to most enzymes which are in the 1000s/second (see wikipedia). It also makes up 50% of the soluble proteins in leaves (Id.). And despite it's slow activity, billions of years of evolution have failed to produce anthing better. Instead, plants have evolved mechanisms to deal with the low activity rate (e.g., C4 pathway). Since RuBisCO is rate limiting to life on earth and CO2 concentration determines the rate of RuBisCO, competition amongst plants for CO2 must be a driver of evolution, especially in a low CO2 environment.
My hypothesis is that flowering plants were more fit for low CO2 and outcompeted plants that relied on high CO2. The plants that thrived in high CO2 fixed carbon faster and could support large animals like the dinosaurs. The dinosaurs could not survive on the flowering plants and died off. A similar event occured in the ocean. Plankton that was more fit for lower CO2 (i.e., higher ocean pH and less availability of CO2) out competed existing plankton species.
Also note that the total caloric output of the earth's plants should be lower with lower CO2 since CO2 fixation is the rate limiting step. Lower CO2 concentrations therefore create a scarcity of food, which would increase competition amongst populations and should drive evolution (less food means more competition for the food and the fittest survive).
My hypothesis is not "gish-gallpingly time-wasting". Rather it is a hypothesis based on the scientific principle of evolution (e.g., flowering plants out competed their contemporaneous plants by being more fit to survive lower CO2 concentrations). What isn't science is the use of correlation to prove causation. The correlation of an impact event or massive volcanic activity is not proof that either of these things did or could cause mass extinction. These are just theories and the science supporting them are for the most part theories. In contrast, evolution by competition has been proven through scientific observation. The activity rates of RuBisCO are measured using repeatable biochemical assays. The rate limiting effects of low CO2 on RuBisCO are testable and repeatable. The ubiquety and utilization of RuBisCO by plants has been measured. In short, my hypothesis that low CO2 killed the dinosaurs, is a legit hypothesis because it is based on scientific data, not correlations.
If I were to speculate, I'd say low CO2 was probably the cause of the majority of mass extinctions on earth. CO2 is a gas and therefore equilabrates throughout the whole earth, including the oceans and the air on land. It sustains all life on earth. Its fixation is for the most part limited by a single enzyme, RuBisCO. And CO2's concentration has fluxuated by over an order of magnitude (4000-180ppm) during the earth's history (or at least we think it has).
A drop in CO2 from 4000 ppm to 180 ppm would be more catestrophic than a 6 degree change in temperature. Almost all ecosystems on earth experience temperature variations greater than 6 degrees every year (due to rotation of the earth about itself and the sun). Consequently, organisms adapted to relatively large temperature swings long ago. CO2 in contrast, does not vary much from year to year. Cycles of 1000's of ppm allegedly happen with a frequency on the order of millions of years. If so, it would take billions of years to evolve the mechanisms to deal with low CO2. Consequently, we would expect the drop in CO2 to be catestrophic because the plants would not be adapted to it. Note that rising CO2 levels would not be catastrophic because most plants would not need to adapt to it (because they evolved from plants that were adapted to it). Put another way, we expect a catastrophe when we starve a plant of CO2 when the plant has never experienced starving conditions, but giving a plant excess CO2 when it evolved from plants that lived in a high CO2 environment should not produce a catastrophic event, or at least not to the same degree.
I am not suggesting that today's rise in CO2 is a good thing. That's a different debate for a different day. Certainly some plants would do better and others wouldn't in a high CO2 environment. The purpose of this post is to propose the basis for mass extinction of the dinosaurs. The data suggests low CO2 may have been the culprit.
(snip)
I'm looking for a scientific based response. No need for ad-hominems.
Moderator Response:[RH] Andrew... Your erratic banter has more than run its course.
-
ubrew12 at 12:54 PM on 29 December 20162016 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #52
An excellent summary of the weeks highlights. Thank you. I would also alert your readers to another highlight, in HuffPo. The more information, the more ammunition, if you know what I mean.
Moderator Response:[JH] Thank you for the positive feedback and for the recommendation.
-
MA Rodger at 10:19 AM on 29 December 2016There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
HB @171.
Your difficulty seems to stem from an overly simplistic principle you apparently are wedded to - the idea that a cold object cannot warm a hot object. Given such a profound level of misunderstanding, it is best to to simplify the situation by ignoring the external source of heating for the system.
Imagine a hot body (heated magically) and radiating out into space. As space is close to absolute zero, the warm body will receive no energy flux from space, no downward radiation.
Now an atmosphere becomes formed around the hot body which is warmed by the hot body (this atmospheric warming you apparently have no problem with), the atmosphere reaching a chilly -18ºC = 255K at equilibrium. Being warmer than absolute zero, the atmosphere will radiate upward into space and downward back to the hot body. So will the extra energy flux back to the hot body not have a heating effect? Note - if it doesn't we will have to rewrite the laws of thermodynamics and we are not very keen on doing that.
HB @ 172.
If a hot body is flat in form, like an atmosphere surrounding a planet (if you ignore the curvature), it will have a top and a bottom, it will thus have to radiate up and down. Its surface, top and bottom, will be double the surface area of the planet it surrounds. Temperature and surface area dictate the total energy flux. Double the surface and you double the flux. The 400W/sq m was being presented in terms of sq m of the planet beneath, not in sq m of the atmospheric surface which has a top & bottom and thus double the radiation. As you imply in your rather confused final statements, air does not choose a particular direction to radiate to - it radiates in all directions but the sideways stuff has no net flux as that is just the atmosphere heating itself, leaving top and bottom radiation. (By the way, a cube has six sides - (1) top,(2) bottom, (3) left, (4) right, (5) front, (6) back. And the ratio 4:1 to convert discal area (πR2) to spherical area (4πR2) only applies to spheres.)
-
nigelj at 09:40 AM on 29 December 2016Record-breaking Arctic warmth ‘extremely unlikely’ without climate change
The arctic warmth in recent decades is being driven partly by a positive feedback from declining ice cover exposing more ocean, so this warmth would tend to stay near the surface for some time. Could this partly explain why the surface as measured by Giss is heating a little more rapidly than the middle of the atmosphere in the UAH data?
-
nigelj at 09:25 AM on 29 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
Nanuk @9
"There is no direct evidence of humans causing global warming."
Can you precisely specify what direct evidence you want, and what you mean by direct? Remember we cannot put the entire planet inside a laboratory.
We certainly have strong evidence fossil fuels are causing climate change due to basic greenhouse gas theory, basic correlations between CO2 and warming, CO2 signatures, sources of CO2, etc, as discussed in articles on this website and the IPCC reports.
"Well, the tub does have an insignificant effect on the overall temps but it is certainly NOT the main cause. "
What main cause do you propose? Why so shy about saying? Remember scientists have investigated and ruled out all alternative causes. Solar activity has been on a declining trend for decades, for example.
You are going over boring old ground, that has been dealt with by climate scientists 100 times over, so its hard not to conclude you are simply trolling and trying to cause doubts. Maybe you are the person paid to spread lies?
-
RedBaron at 08:26 AM on 29 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
Nanuk,
For evidence look here.
But since you mentioned "common folks" that might not even know the basics of science. Maybe this experiment by mythbusters will help you understand easier.
Mythbusters tests global warming theory - does CO2 warm air?
-
nanuk at 06:41 AM on 29 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
The fACTS are: there are NO facts! There is no direct evidence of humans causing global warming.
that the LIE is repeated is not going to make it suddenly come true! When are you folks going to realize you have been duped? You are being made fools of, but since you are getting paid for lying it is OK with you?!
Here is how your logic works:
you are baking bread. You get hot and sweaty so you decide to have a bath. As you fill your tub, you notice the kithen is still getting warmer! So you theorize the water in the bath is causin the warming trend.
Well, the tub does have an insignificant effect on the overall temps but it is certainly NOT the main cause. But your ideology/ religion is cemented and you refuse to accept it could be anything BUT the bath water! ;
THAT is what common sense folks see you saying!
Moderator Response:[JH] Inflamatory sloganeering snipped.
-
nigelj at 05:47 AM on 29 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
HB @6, good point. Very amusing.
Its fair to say the "warmists" sometimes make themselves easy targets, and this becomes an excuse for climate denialism by people like Trump. But I think people also blow minor mistakes by warmists out of all proportion like that glacier issue in one of the IPCC reports. Its like warmists are held to almost an impossible standard, yet sceptics are given a free pass to talk the most incredible nonsense without the slightest evidential foundation. Society is in effect crippling science, and will ultimately pay a price for this cynical approach.
Just changing the subject slightly, the climate issue has become very divisive indeed and it intrigues me to identify what is really driving this level of climate change denialism, division, and general tension. I have seen dozens of theories that are all quite convincing, and its tempting to say perhaps they just all add together, however there is usually a simple underlying principal explanation for most things in life. I dont think we have found this for climate denialism, although One Planet may be close.
I was briefly a climate change sceptic, ages ago, having watched a certain movie (I dont want to name it and give it any promotion). But I had lingering doubts about the sceptical claims, and when I looked more deeply I found the movie was full of factual errors and misleading claims, etc. I dont like being tricked like this, esspecially given I have a high level of education, and it has made me an advocate for the IPCC position and reducing emissions. If I can change my position, maybe Trump can.
However I do think Trump is likely to be more amenable to business arguments about advantages of renewable energy, etc.
-
william5331 at 04:49 AM on 29 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
No sense in pushing Trump into admitting that climate change is happening and likely to bring disaster. He will just get huffy puffy and sulk. Instead get the message to him how he could become the hero of the American people by stemming the flow of all that lovely wealth to other countries for oil and to use it for job creation in repairing American infrastructure. No need for subsidies. In fact since he is a true capitalist (cough cough), stop all subsidies including to fossil fuel and let renewables and fossil fuel battle it out on the economic playing field. More money saved from not having to pay subsidies. He is about to lower corporate taxes. Fine, but emphasize that he must then ensure that all companies actually pay their taxes. He wants to penalize American companies who manufacture overseas so he may be sympathetic to this message. We have to play the instrument we have been given. And emphasize that setting the economic playing field to favor electric cars and Wind and Solar will save even more money in foreign oil costa and better still, the people pay for the infrastructure.
-
Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
nigelj at 08:17 AM on 28 December, 2016
"However Trump is a proud person. If he could be shown that the denialist arguments are really just cheap tricks, he might take notice. He wouldnt like being taken for a sucker"
Which is the reason for him not listening to the people saying that we need a world government based on a hypothesis that has shown to be worthless for doing what it claims.I also think the stupidity of U.S. climatepoliticians when they decided to prosecute people that don´t think like them, might be a large cause for Trump ignoring the undemocratic forces behind the climate scam.
(In a whispering voice: I am starting to wonder if the nazis are behind the climate scam, they where the last ones that tried to take over the world;)
I am almost joking in the above sentence
-
There's no empirical evidence
323. MA Rodger at 01:25 AM on 29 December, 2016
HB @322.You presumably mean 1 bar when you say "1 atm pressure." On Venus 1 atm of pressure is about 90 bar and the surface temperature 462ºC. What your energy flux figures are meant to represent is not immediately clear to me. A simple S-B calculation suggests the Venusian surface emits some 17,000W/sq m as opposed to the Earth's 400W/sq m. I'm assuming the "~2500W/m^2" figure you quote is a stab at the Venusian insolation. But I could be wrong."
2500W/m^2 is insolation, that is correct. But I think it is a bit more. Why do I need to be exact? Do you have an argument based on the difference of 2000W between 15-17000W?
Did you really not understand that I used 1atm as it is on earth?
"I am no expert on the Venusian atmosphere but likely Robinson & Catling (2013) know a thing or two. Their figure 1 (below) uses data from Moroz and Zasova (1997) for its Venus Temperature-Pressure trace and shows Venus at 1 bar to be significantly warmer than Earth at 1 bar."
With more than 90% co2 in the atmosphere you would expect a bit more, wouldn´t you?
2500/4=625W/m^2
But for a slowroller like venus you should use the hemisphere:
2500/2=1250W/m^2
350K=850W/m^2
"This elevated temperature (350 K) exceeds a pro rata temperature wrt Earth due to the elevated Venusian insolation. Thus the GHG effect on Venus at 1 bar exceeds the full Earth atmosphere GHG effect. What contribution CO2 makes to this high-altitude Venusian GHG effect is a further issue. I assume your comment concerning this, that "there seems to be no effect of co2" has no evidential basis. But I could be wrong. So please surprise me if you can!"
So because people believing in greenhouseffect can´t understand the planetary temperature of Venus surface where co2 is so hot and dense that it is in a critical state, we can assume that a gas that is not a heat source, is the cause of high temperature?
I would choose almost any other explanation than that. All of them would include heat generation of some sort. Since that is what it takes to heat something up.
-
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
158. MA Rodger at 23:31 PM on 15 December, 2016
"Firstly, the atmosphere is insensitive to up or down. So in addition to radiating 200W/sq m upwards, it also radiates 200W/sq m downwards. It thus requires 400W/sq m to maintain a temperature of theoretically -40ºC (as Stefan-Boltzmann"
Do I understand you correctly?
Are you saying that air at a mean temperature of -18C contains enough energy to radiate 400W/m^2?
To radiate that amount of energy, ignoring the nonsense "photons in all directions", any radiating body has to have a temperature of 289.8K.
It doesn´t matter if it is an atmosphere, it has to have that temperature. Radiating bodys radiate according to their temperature, nothing else.
Where do you find these fairytales?
If your claim is "200W up and 200W down", the atmosphere would have to have a temperature of 243K. You cant add them to get 400W, since you only have one m^2. If your claim is that a cubic meter holds enough energy to radiate 200W in four directions, then you have to explain it much more carefully.
Why do you not divide by four like you do with solar radiation? the same rule applies for cold air as a planet when you treat it as a separate radiating body.
Do you really mean that air chooses to only radiate up and down? How does that work?
-
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
MA Rodger at 19:57 PM on 28 December, 2016
HB @165.
"You dispute the very idea that CO2 in the atmosphere results in an increase in surface temperatures. Yet your use a bowl-of-ice in a-warm-room as an analogy for atmospheric-CO2 above a-warm-surface suggests you are not really thinking through your position. And perhaps you are not entirely clear about what it is you are arguing against. You talk of an absence of “experimental data” to support what you call “the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of the heat source heating it,” this specific to the warming of a surface by the warmed CO2. "I dispute the claim that a cold gas sitting on top of a warm surface heated by a hot star can cause the temperature to rise beyond what the hot star can cause. I dispute the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of its own heat source, especially when it has a mean temperature of -18C in the atmosphere.
I dispute the claim that you can increase the temperature of anything by adding a cold gas, or fraction of a gas, without adding more energy.
I dispute the claim that in the atmosphere, the gasses and water vapor have the opposite effect to what we experience in our daily lives.
Have you ever increased the temperature of anything by adding water vapor that was not pre-heated, or by adding air flowing over it?
I dispute the claim that you have any science to back your claims, aside from hindcasting temperature graphs and showing a doubtful correlation with temperature.
-
MA Rodger at 01:25 AM on 29 December 2016There's no empirical evidence
HB @322.
You presumably mean 1 bar when you say "1 atm pressure." On Venus 1 atm of pressure is about 90 bar and the surface temperature 462ºC. What your energy flux figures are meant to represent is not immediately clear to me. A simple S-B calculation suggests the Venusian surface emits some 17,000W/sq m as opposed to the Earth's 400W/sq m. I'm assuming the "~2500W/m^2" figure you quote is a stab at the Venusian insolation. But I could be wrong.
I am no expert on the Venusian atmosphere but likely Robinson & Catling (2013) know a thing or two. Their figure 1 (below) uses data from Moroz and Zasova (1997) for its Venus Temperature-Pressure trace and shows Venus at 1 bar to be significantly warmer than Earth at 1 bar. This elevated temperature (350 K) exceeds a pro rata temperature wrt Earth due to the elevated Venusian insolation. Thus the GHG effect on Venus at 1 bar exceeds the full Earth atmosphere GHG effect. What contribution CO2 makes to this high-altitude Venusian GHG effect is a further issue. I assume your comment concerning this, that "there seems to be no effect of co2" has no evidential basis. But I could be wrong. So please surprise me if you can!
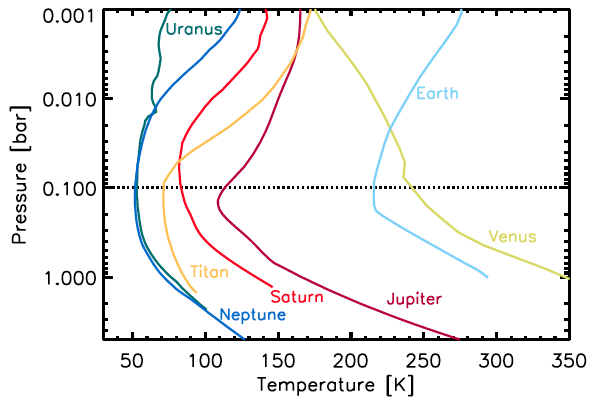
-
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
168. Tom Curtis
"In fact, the outgoing Short Wave radiation at the Top Of the Atmosphere is measured by the CERES instrument flown on the Terra and Aqua satellites. Together with Total Solar Irradiation (TSI) data from the TIM instrument, that allows the direct calculation of the energy balance and albedo as:
Energy balance = TSI/4 - (OLWR + OSWR)
Albedo = (TSI - 4 x OSWR)/TSI,
where OLWR is Outgoinging Long Wave Radiation, and OSWR is Outgoing Short Wave Radiation."
Then you can provide a reference where we can find an exact definition of albedo? With a description of the included parts and how much they each contribute to reflected radiation?
And how does it relate to the fact that more than 50% of TSI is IR that won´t be reflected?
"The upshot is that the adjustment to the albedo term in the energy budget amounts to approximately 3 W/m^2. HB instead describes it as a greater than 100 W/m^2 fudge."
TSI=1360W/m^2
After albedo=~960W/m^2
More like 400W.
I hope you are aware of that sunlight is much more intense than 340W/m^2?
Do you realise that there is a very large difference between reality where the sun heats the surface at an intensity between 700 and 1000+W/m^2, and your "budget" where you use 340W/m^2?
One is reality and one is your imagination. If the sun only would provide 340W, where is your heat pump connected to an indestructible heat source, that can add energy that isn´t there from the beginning?
I think it is you who need to provide references for your claims about how albedo is an exactly measured factor, with well known and well defined ingredients. While you are at it, provide a reference for the science showing how adding a cold gas to a hot surface can increase the surfacetemperature.
Otherwise you just have a correlation. There are lots of correlations to temperature rising the last century. I claim that increasing obesity in the states is the cause of global warming, it correlates nicely with the temperature. It is as valid as your co2-theory.
-
MA Rodger at 19:57 PM on 28 December 2016There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
HB @165.
You dispute the very idea that CO2 in the atmosphere results in an increase in surface temperatures. Yet your use a bowl-of-ice in a-warm-room as an analogy for atmospheric-CO2 above a-warm-surface suggests you are not really thinking through your position. And perhaps you are not entirely clear about what it is you are arguing against. You talk of an absence of “experimental data” to support what you call “the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of the heat source heating it,” this specific to the warming of a surface by the warmed CO2. Yet you go on to suggest that there is after all actually some data but which you consider inadequate, saying:-“Since the only thing you have is a weak and very short correlation of doubtful quality. That is the only argument you have, a correlation. That is hardly science.”
What is this "correlation" you mention?
(Note this discussion is not on-topic here and should move to somewhere more appropriate. Indeed, you may even find there your missing “experimental data.”) -
ecoid at 17:11 PM on 28 December 2016They changed the name from 'global warming' to 'climate change'
U.S. Koppen-Geiger climate classification (2000 - 2100)
http://www.vividmaps.com/2016/11/us-koppen-geiger-climate-classification.html
-
Tom Curtis at 14:29 PM on 28 December 2016There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
HB @167 claims:
"And yet you use a fudge factor called albedo. Trenberth himself makes no secret of how they adjust albedo to cover up for imbalance.
How can anyone make an argument of "540.1" when ~~~~30% is yanked from the input value without justification from real measurements?"
In fact, the outgoing Short Wave radiation at the Top Of the Atmosphere is measured by the CERES instrument flown on the Terra and Aqua satellites. Together with Total Solar Irradiation (TSI) data from the TIM instrument, that allows the direct calculation of the energy balance and albedo as:
Energy balance = TSI/4 - (OLWR + OSWR)
Albedo = (TSI - 4 x OSWR)/TSI,
where OLWR is Outgoinging Long Wave Radiation, and OSWR is Outgoing Short Wave Radiation.
TSI is divided 4 in the energy balance equation as it is measured relative to a flat plane perendicular to the incoming radiation, and needs to be averaged over the sphere to match the measured values of the other two products which are measured as averaged over the Earth's surface. Likewise, to convert the OSWR to the equivalent of the TSI, it needs to be multiplied by 4 in the Albedo equation.
For CERES best product (syn1deg), the values are:
OLWR: 237.2 +/- 10 W/m^2
OSWR: 97.7 +/- 3 W/m^2
Incoming Solar (=TSI/4): 341.3 +/- 0.2 W/m^2
That yields an energy imbalance of 6.4 W/m^2, which contradicts the far more accurately measured energy imbalance from ocean heat content measurements. Knowing the large errors in absolute magnitude of the values, they are therefore adjusted by 27%, 73% and 450% of the 2 sigma error values respectively (for the values shown in the figure shown @159 above). Note that graph is from a slightly different time period from the error values and absolute values I have shown, so that part of the discrepancy may be a difference in the observed values.
The upshot is that the adjustment to the albedo term in the energy budget amounts to approximately 3 W/m^2. HB instead describes it as a greater than 100 W/m^2 fudge. His fudge on the adjustment amounts to a factor of >33. At the same time he describes the OSWR as unobserved which is blatantly false, and neglects that the reason for the fudge is to bring the energy balance into line with observed changes in surface heat content, ie, a decision to use the more accurate determination of the total energy imbalance in preference to one whose inaccuracy due to instrument limitations was an order of magnitude greater. In HB's version of science, scientists should always place greatest weight on their least accurate observations.
I need only add that Trenberth describes the above sources of data, and the reasons for the adjustments at the same place as he mentions them. Given the standard etiquette of quotation and citation, if you are relying on somebody else's word as to what somebody said, you need to quote them rather than the original source. As HB mentions Trenberth directly, he should be assumed to be referencing Trenberth directly, and hence has demonstrated a complete inability to understand the cited source, or a breath taking dishonesty. Perhaps, however, he is as uninformed about the etiquette of citation as he is about climate science, and has merely demonstrated an abominable lack of desire to fact check any factoid he gleans which supports his bizarre theory of what science is.
-
sailingfree at 12:26 PM on 28 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
Thank you, Dana for the model-data updates!
We welcome a short article by you explaining the slides.
The deniers need to see them, with explainations.
-
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
HK at 06:01 AM on 14 December, 2016
"You have to include all the energy fluxes into and out of the atmosphere!
The energy input includes absorbed incoming solar radiation (77.1), absorbed radiation from the surface (358.2), thermals (18.4) and latent heat in water vapour (86.4), totalling 540.1.
The energy loss includes back radiation to the surface (340.3) and radiation to space (169.9 + 29.9), again totalling 540.1."And yet you use a fudge factor called albedo. Trenberth himself makes no secret of how they adjust albedo to cover up for imbalance.
How can anyone make an argument of "540.1" when ~~~~30% is yanked from the input value without justification from real measurements?
540W/m^2, that is a really low value for incident radiation. I want to see how the greenhousemodel calculate instantaneous radiation. In reality we have a real sun heating the surface at closer to 1000W/m^2 than 500.
-
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
Tom Curtis at 23:49 PM on 15 December, 2016
"The energy input into the atmosphere is 77.1 Solar absorbed by atmosphere + 358.2 Surface IR absorbed by atmosphere + 18.4 thermals + 86.4 latent heat, for a total of 540.1 W/m^2. Given that, it is very clear that the 199.8 W/m^2 of upward IR emission from the atmosphere is insufficient to maintain a constant energy content in the atmosphere, and consequently a stable temperature structure. Without the 340.3 W/m^2 IR radiation from the atmosphere to the surface, that energy balance cannot be maintained, and consequently neither can the stable temperature structure."
Seriously, have you heard of heat transfer?Don´t you know that the difference is found in the rate of transfer?
If you have 200W at tropopause and 400W at the surface, the difference of 200W is accounted for in the heat transfer. The surface uses 400W for it´s own temperature and on top of that it transfers 200W/m^2 to the atmosphere. That is basic heat transfer physics.
Where in the litterature do you find support for the claim that a decreasing flux from the atmosphere (a few watts) caused by co2, can affect the surface temperature? All I can find is that it is the other way around.
You know that increasing absorption, what you call an increase in radiative imbalance, always means that the absorber has gotten relatively colder? Also basic heat transfer physics.
Decreasing absorption and increasing flux from the atmosphere, that would be a sign of warming. You are making an argument about how co2 cools earth.
-
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
164. MA Rodger
"♣ - 3 - You do not have to prove anything but without proof we will consider your statements as worthless."
I guess that applies to all of us. So, can you provide the proof for the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of the heat source heating it?
Not proof of absorption, proof of temperature increasing from only co2. Experimental data. There is lots of data from experimental studys of co2, I have still not found anything in there supporting that claim.
Absorption is well documented.
Increasing temperature, nope.
Would you please provide the scientific proof of the foundation of your claims? Where are the experiments showing how co2 increase temperature?
If you don´t have any, I guess your statements is a bit weak as well. Since the only thing you have is a weak and very short correlation of doubtful quality. That is the only argument you have, a correlation. That is hardly science.
If I put a bowl of Ice in a warm room, it will absorb and emit energy. Do you mean that it also increase temperature? -
There's no empirical evidence
320. MA Rodger
"The climate of Venus is overwhelmingly CO2 and this does provide a strong greenhouse effect."
But at 1 atm pressure there seems to be no effect of co2. What the temperature is at higher pressure closer to the surface is not caused by the greenhouseeffect. Or do you have experimental data showing how co2 can increase the intensity from ~2500W/m^2 to ~15000W/m^2?
-
John Hartz at 09:33 AM on 28 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
Recommended supplemental reading:
Scientists just ran the numbers on how much Trump could damage the planet by Chris Mooney, Energy & Environment, Washington Post, Dec 27, 2016
-
nigelj at 08:17 AM on 28 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
Trump has indeed gone from acceptance to denial. In fact he signed an open letter supporting Obamas efforts to combat climate change as below.
However Trump has changed his position. Maybe some sceptic has got to Trump, or maybe its just he has given in to short term business interests, as opposed to thinking about future generations, or a combination of both seems likely.One problem capitalism has is it tends to favour the short term, and also is not good at dealing with environmenatal issues in a self regulating sort of way. Economists call this a market failure or negative externality and its well recognised in any course on economics.
It would be great if we could change this short term mindset, and also recognise that governments do sometimes have a philosophically justified role to ensure environments are protected, but yet we must also preserve the core strengths and features of capitalism in the process. Where there is a will there is a way. I actually dont think we have a choice, because physical reality will eventually force some ideological change anyway. Socialism is not the answer but a modified capitalism is at least possible in theory.
You have outlined a number of denialist arguments, that stem from people with associations with vested interests, or certain lobby or ideological groups. Vested interests are clearly significant. There is evidence that a small number of powerful and wealthy people are climate sceptics, like the Koch brothers.
They are clearly doing this while being quite agressive business people and hard line in various ideological views that emphasise individual rights to a very strong degree, and they have a view that future generations should look after themselves from what I read. Their wealth means they have a disproportionate influence on the debate. What is even more concerning is climate denialists in general often seem quite happy to make outrageous claims and game the system, when climate scientists are often held by their training and professional bodies to very high standards of integrity and properly so.
I think many things contribute to global warming science denialism. At the base simple dislike of cold weather could be a subconcious part, but vested interests and selfish interests have obviously been a big factor in spreading doubts about the science.
However Trump is a proud person. If he could be shown that the denialist arguments are really just cheap tricks, he might take notice. He wouldnt like being taken for a sucker.
-
nigelj at 05:52 AM on 28 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
And Michael Sweet, given you have just taliked about the importance of facts, dont jump to conclusions about what other teachers teach on climate change. I would be interesting to see some hard data. My guess (in the absence of such data) is it would follow general trends so at least the majority would teach something sensible.
Its frustrating if even one teacher teaches nonsense, man I can sympathise, but dont let it get you down. In the end we can only calmly but very firmly promote what we believe is solid science on the weight of evidence,and rational good sense. At least we can sleep well at nights if we do that.
-
nigelj at 05:32 AM on 28 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
Michael Sweet @26, your comment stung because normally I make a considerable effort to get facts right. I can tell you from memory unemployment under Obama dropped from approximately 12% to 5%. I just got trapped by the Clinton Sanders issue.
A very good website on economic data and trends is tradingeconomics.com which is basically a financial database for business, but covers a vast range of material including data and also graphical trends in data.
I know you want to forget the history. Maybe so, but I make this comment to anyone reading: the Democrat Party promoted a candidate with a criminal investigation hanging over her head, and I thought it was a dumb strategy from day one! I hope the Democrats take a lesson from this. There must have been other people besides Clinton or Sanders.
I have nothjing against Clinton. She had a fine set of sensible policies, and her heart and mind is mostly in the right place, but the email thing meant all this became buried, and most of what we saw in our media was about the email issue.
Everyone has to take some care to not become an easy target,me included, scientists included, everyone.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 03:42 AM on 28 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
An addition to, or development of, my previous comment (a seemingly never-ending work in progress with new related relevant material evidence being created almost daily) is that other terms that deserve to be used along with 'creating impressions' are creating illusions and creating delusions of grandeur - something that the likes of Trump clearly focus on.
-
Jeff18 at 03:37 AM on 28 December 2016There's no empirical evidence
I thank you all for your response. I didn't consider my comment to be off topic as I am concerned with the effect of CO2 on the atmosphere and was just using Venus as an example. Apparently not a very good example so scratch that one. From what Tom said, the increase in temperature from CO2 going from .04% to .05% would be less than what we have seen from the CO2 going from .03% to .04%. But what are the actual number? What is the temperature change due to CO2 alone and how do we know it's CO2 and not some other factor? I'm sure you are familiar with the show Mythbusters. In one episode they filled a tank with CO2, put in a block of ice, shined a light on it and compared that to a similar tank filled with air. The ice in the CO2 thank melted faster. No big surprise there. But no actual numbers either. I would like to have seen a tanks with 100% CO2, 10%, 1%, .1%, .01%, and zero and compared the melting rate in each. Then I would have a better idea of the effect of CO2. Anyone have some actual numbers?
-
One Planet Only Forever at 03:10 AM on 28 December 2016Facts matter, and on climate change, Trump's picks get them wrong
This is another part of the OP I owe SkS and am still trying to organize into a concise presentation of thoughts/perspective.
It appears that Trump is simply continuing his efforts to succeed through the creation of unjustified impressions.
A business mind-set can be a very dangerous thing. Many business leaders focus on striving to succeed by prolonging their ability to "win" through a lack of public awareness and better understanding of how their actions are contrary to the advancement of humanity to a lasting better future for all of humanity.
The act of impressing people - especially the development of perceptions of popularity, profitability, or prosperity - can be understood to be the unjustified deliberate creation of impressions in the minds of people, or “fooling them”. A key related action is the need to mask or hide or diminish the awareness and better understanding in the audience (the magicians tricks or diversion and misleading the attention awareness and understanding.
Creating unjustified impressions and hiding what is really being done is the antithesis of “Raising awareness and Better understanding of what is actually going on”. And those who succeed at it can clearly be very detrimental to the advancement of humanity until awareness and better understanding become so pervasive that their “Deliberately Deceptive Marketing Tricks” fail to impress enough for success”.
Trump's waffling on climate science could be a carefully developed ploy, performed to create the appearance of being thoughtful and considerate. However the best awareness and understanding is clearly that Trump and his likes give little thought, consideration, care or desire to advancing humanity to a lasting better future for all. They are focused on maximizing personal short term success any way they can get away with for as long as they can get away with.
That awareness and better understanding of the likes of Trump needs to grow rapidly in the USA, and many other places, or the future of humanity will suffer severely. It is undeniable that the current developed economies have been built, to different degrees, on unjustified perceptions of success and prosperity. And the more that that type of “Magic” is involved in creating the perceptions of wealth and prosperity the less of a future there is for it.
Trump is not the first 'Unjustified Celebrity Winner of undeserved wealth and power' in human history. And like the others who pursued celebrity success for reasons other than advancing humanity to a lasting better future, the amount of damage he will do depends on how rapidly 'raised awareness and better understanding and the desire to advance humanity to a lasting better future for all' grows in the USA (and around this amazing planet).
True development and advancement requires a deliberate nurturing of the development of responsible thoughtful considerate adults focused on advancing humanity to a lasting better future as a healthy helpful diversity of humans among the robust diversity of life on this amazing planet.
Current day 'so called advanced developed and developing societies/economies' clearly suffer to different degrees from a penchant for the unjustified belief that “Everyone free to believe as they wish and do as they please is the best way for things to be”. That is clearly fairy tale magical nonsense. And Trump is clearly creating a Group-Think Echo-Chamber Deceptive Marketing Machine to try to create and maintain believers of Fairy Tales and non-common sense. That group potentially hope to magically succeed at creating unjustified impressions to get away with personally beneficial but understandably damaging actions as much as possible for as long as possible, by impression creation to mask what they are actually trying to do and the likely results of their actions, and deliberately deceptive impression creation to try to manage what they cannot hide.
Hopefully there will be a rapid increased awareness and understanding of the truly unacceptable nature of the likes of Trump as a result of their attempts to create unjustified impressions regarding climate science and climate change (and all their other unjustified attempts to create impressions).
-
michael sweet at 23:12 PM on 27 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
Nigelj,
I am mostly letting this topic go by. I think it is not productive to cry over spilt milk. I did not mean to pick on you. Where do you live that the media was so uinformed? Hillary was ahead in the popular vote by a lot the entire election.
Acording to the Daily Kos, 43% of voters think unemployment increased under Obama and 32% think the stock market has gone down. The stock market is money!! How can we hope to get people behind climate action when the media are so biased and under the control of conservatives that these things are believed?
I teach High School science. If you are hoping that teachers will inform young people that AGW is a big problem you need to move out of the USA. I do what I can in my class but I hear that other teachers teach AGW is a scam.
-
Tom Curtis at 11:18 AM on 27 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
william @21:
1) On May 4th, when Trump became presumptive nominee of the Republican party to June 7th (the last major Democrat primary), Hilary Clinton's lead in the polls over Donald Trump dropped from 6.5% to 2%, a fact attributable to her being attacked from two sides: from a Donald Trump no longer needing to concentrate on Republican opponents, and from Bernie Sanders continuing to push for a nomination it was already clear he would loose. Arguably had Sanders withdrawn his candidacy when it was clear it was hopeless, Clinton would have started the election proper in a much better position, from which she would have won.
2) While Sander's poll results vs Trump were much better than Clinton's towards the end of the primary race, that is at least in part due to his not having been attacked by the Republicans. Certainly based on conventional wisdom, the US would never elect a President as left leaning as Sanders; and it is more than likely Sanders poll lead would have quickly evaporated. Of course, conventional wisdom was a poor guide in this election, and may also have been on this point - but that is just pure speculation.
3) As michael sweet notes, Sanders got less primary votes than Clinton, and always trailed her in the polls. That, however, is from results for Democrat voters, and not responsive to your actual point @21.
4) Your point about the DNC emails simply ignores the whole argument in the OP. In particular, the damaging emails are from a very few (<50) from >19,000 emails released and hence are not evidence of systematic bias. Further, they mostly come from after a period when it was clear Sanders was going to loose in any event. Several of the more damaging emails have a specific context which, if taken into account, show they are not evidence of bias. More importantly, no emails show the DNC taking any actions that disadvantaged the Sander's campaign, or were designed to do so. At least one suggestion that such action be taken was vetoed because "...the Chair has been advised not to engage".
-
nigelj at 08:50 AM on 27 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
Michael Sweet @23
"If you checked before you posted you would find out that Clinton had 3.8 million more votes than Saunders. Claims that Saunders got more votes are untrue. "
1. William is the person primarily claiming that Sanders had more votes, "in all polls". Why are you having a go at me, and not him as well?
2. The issue of how many votes they got is clearly beside the point of the comments I made.
3. I accept we should strive for accuracy, and provide sources of information, and your link appears authoritative, however Media in my country consistently stated that Sanders was getting more votes. I took them in good faith.
4. I generally back up what I say with links or stated sources, at least better than most people. Thats absolutely indisputable. Remember we are entitled to opinions, and should be able to explore issues with some freedom, and can't be expected to have a link beside every sentence like an entry in wikipedia! I think its a case of providing sources for critical aspects of things.
Nothing personal. We appear to agree on a lot of things!
-
michael sweet at 06:59 AM on 27 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
Nigelj,
At Skeptical Sciece we are expected to reference our claims. If you checked before you posted you would find out that Clinton had 3.8 million more votes than Saunders. Claims that Saunders got more votes are untrue. You need to start to support more of your claims. People can speculate now that Saunders would have done better against Trump because so many voters wanted change, which Saunders stood for, but that is just speculation. Republicans thought Trump woud do better against Saunders before the nomination.
-
nigelj at 06:10 AM on 27 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
William @21
I agree with your comments at least to the extent that the Democratic Congress obviously favoured Clinton over Sanders despite the fact he had a higher popular vote. But I wouldn't speculate too much about what was in Clintons emails. Like we have all said you could probably trawl through any organisations emails and find "issues" that are either genuinely problematic, or could be quoted out of context. There are therefore several reasons for deleting things. We just dont know and need to be careful before making accusations of serious wrong doing.
I think the preference for Clinton probably relates more to campaign donations. The democrats supporters include business interests who would almost certainly prefer Clinton to Sanders due to perceived policy positions. It's this campaign donation issue and lobbying in general that is the significant issue.I'm not making excuses for Clinton. I personally prefer Sanders, then Clinton, then Trump ( a distant third).
However the result of all this is the Democrats ended up with Clinton, who had this ongoing email problem. This was a huge gamble which didn't pay off and lost her the election, along with other things in her performance.
The real issue is more general, namely peoples private correspondence. Surely it should remain private? The only case I can see otherwise for publishing someones hacked emails is if there is absolutely clear evidence of illegal behaviour at a level that would have major public interest. However then surely the first course of action of hacker with the interests of the public genuinely at heart (and not just making money out of the issue) should be to go to the police. Only if the police ignore an obvious problem, or would have vested interests in ignoring it, would publication be justified. To be fair this does sometimes happen.
There was no public interest justification for either the Clinton hack or CRU hack because nothing of consequnce was found. The hackers could easily have established that the "hide the decline" issue was not what it seemed. The hackers went ahead and leaked material and its hard not to conclude they simply wanted to discredit the CRU climate scientists. -
william5331 at 03:24 AM on 27 December 2016The Perfect Tide: Sea Level and the Future of South Florida
More digging into why the insurance companies would insure such properties is needed. If they alone were carrying the risk, I bet they would completely stop issuing new policies and not renew old policies. Obviously they think this is a good investment. How does it work and who is really carrying the can.
-
william5331 at 03:11 AM on 27 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
The supposedly Russian hacked e-mails is one thing but the e-mails which were subpoenaed were first sanitized by the Clinton staff. They simply wiped out a large tranche of them. Do you think there might have been a reason for this??
As for the hacked e-mails, I understood (possibly mistakenly) that they showed a high level of corruption in the Democratic National Congress in spinning the ball toward Hillary and away from Bernie. This was supported later when Debbie Wasserman Shultz had to resign (to be hired almost immediately by Hillary). Since all polls showed that Bernie would have beaten Donald by a huge margin while the chances of Hillary were touch and go, the CF we find ourselves in at present is directly attributable to the DNC. If this isn't the crime of the century, I don't know what is. -
elreventon at 03:10 AM on 27 December 2016A Glimpse at Our Possible Future Climate, Best to Worst Case Scenarios
Excellent analysis. The thing that troubles me most about scientists' predictions is that there is ONE variable crucial to which scenario turns out to be the real one that the scientists always get wrong: the political one.... they assume that AT SOME POINT in the next 60 years, we WILL decide to go all out to stop global warming. Thus the scientists factor in a point at which emissions start to decline.
I believe that they make a big mistake in doing that. I think it's likely that the strangle hold the energy polluters have on the American government, and the minds of manhy of the superstitious American people mean that the USA will as a nation prevent any meaningful action being taken to stop global warming until AFTER the most catastrophic consequences of global warming have struck the USA. Around 2065, with Miami going under water, Texas turning into the new Sahara, carbon dioxide at 750 to 1000 ppm, and the future already irretrievably lost, THEN the American people and government will graciously consent to let the rest of humanity begin a futile effort to try to survive.
-
Tom Curtis at 22:34 PM on 26 December 20162016 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #52
Glenn Tamblyn @4, it may indicate that 97% aren't "skeptical", but it does not tell us how many accept the science of climate change. Many may be merely agnostic, and some may be "skeptical" but not have said so publicly. So we should not read too much into it. On the other hand, an AGW "skeptic" trying to find consolation from the fact that "many astronauts" support their position clearly needs to start looking at denominators.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 21:37 PM on 26 December 20162016 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #52
Thanks for that Tom. Rounded off that says that 97% of ex-Astronauts aren't skeptical. :-)
And an interesting observation. Those few were all from the generation of steely-eyed rocketmen.
Also maybe the experience of the space-station generation had an important difference. They spent a lot of time looking at the Earth, in detail. Whereas the lunar-race generation, for them it was the blue-marble, in the distance. Perhaps rather idealised. They didn't get to spend weeks on end looking at night lights, pollution hazes, fires in the Arctic etc. They may have only got a more superficial, rose-colored-glasses look at the Earth. -
Tom Curtis at 11:35 AM on 26 December 20162016 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #52
chriskoz @2, I think you may be giving astronauts a bad rap. Specifically, NASA lists 45 active and 294 former astronauts. Of those, eight signed the letter from 49 NASA employees, and Buzz Aldrin (who did not sign) has also expressed "skepticism" about AGW. That makes a total of just 9 out of 339, or 2.65% of current or former astronauts who are AGW "skeptics".
They do, however, all appear to come from Skylab missions, or earlier. That is, the most recent experience as an astronaut of a person I know to have signed or made a statement indicating "skepticism" about AGW was in 1979.
-
chriskoz at 10:55 AM on 26 December 20162016 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #52
Piers changed my mind about the astronauts. I think his legacy is representative of latest generation (1990s and 2000s) of astronauts: explorers and scientists who not only do not deny basic laws of physics but came to apreciate the beauty of said laws that came about to create such unique beautiful planet as Eartth.
That vision contrasts starkly with a legacy of an average astroanut of Apollo era (up to 1980s); mainly military pilots - "heroes" and "warriors" whose "gravity defying" acts entitled them in their mind to defy all laws of physics and science in general. Recall that many former astronauts have been the signatories of infamous Oregon petition, and some smaller similar anti-science petition singed by veteran NASA astronauts. Never mind that that science (starting from Konstantin Tsiolkovsky) was essential in constructing a survivable vessel on top of a firy missile, their role was objectively just of experimental rabbits, even if they like to view themselves as "heroes". Never mind their total disregard to the intergenerational ethics by boasting their "hero" statuses while degrading the planet for future generations. What a pitiful chapter of human history they are!
Piers, you've done a tremendous service to us scientists not only with your contribution to climate science but, with your personal example, you've reversed the negative image of astronauts. Let's hope the other astronauts (if there is a need for manned flights in future) do follow your ethics.
-
nigelj at 13:15 PM on 25 December 2016Russian email hackers keep playing us for fools
The terms trick and also hide the decline were a bit unfortunate in their wording and impression created, but of course had totally innocent meanings, as was established in at least 5 separate enquiries. Sadly this was probably not emphasised enough in the media.
Prev 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























