Recent Comments
Prev 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 Next
Comments 29551 to 29600:
-
John Hartz at 11:27 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@Tom Curtis #60:
You state:
Note that (contrary to John Hartz) coal was only a factor in this pollution when used for domestic heating. Industrial, and particularly power station use burns coal at very high temperatures, with almost complete combustion and with significant deployment of scrubbers so is not a primary contributor; although petrol engines in cars are.
Your statement does not squre with the following:
"The Chinese capital has for many years suffered from serious air pollution. Primary sources of pollutants include exhaust emission from Beijing's more than five million motor vehicles, coal burning in neighbouring regions, dust storms from the north and local construction dust. A particularly severe smog engulfed the city for weeks in early 2013, elevating public awareness to unprecedented levels and prompting the government to roll out emergency measures."
Source: Beijing air pollution, Topics, South China Morning Post
It is my understanding that many of the coal-fired power plants built in China during the early years of its economic expansion were not equipped with any pollution control devices including scrubbers.
-
Yail Bloor III at 11:21 AM on 8 July 2015Carbon cycle feedbacks and the worst-case greenhouse gas pathway
Tom, I would agree that Earth not being susceptible to a runaway greenhouse effect is good news. However, it would not be necessary for Earth to have temperatures hot enough to burn us to ashes or pressures that would crush us to jelly and yet be entirely unsatisfactory for the continued existence of our species. My personal level of optimism would have to be described as "cautiously hopeful." Humans are a stubborn lot...perhaps they can shift that mule-headedness toward a more constructive purpose.
-
Tom Curtis at 10:51 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Rob Honeycutt @62, I am only able to rely on my source:
"The reasons for haze-fog pollution formation are many, and the main reasons can be summarized as follows [26,27]:
(i)
The automobile exhaust is the main source of pollutants. In recent years, there are more and more cars in the cities in China and the components in automobile exhaust are the main components of the haze-fog;
(ii)
Secondary pollution from factories is also an important reason. There is much benzene and aldehydes in chemical pollution emissions, and they are important components of haze-fog;
(iii)
The relative humidity near the ground in the haze-fog areas is relatively high, and the ground has lots of dust, so particulate matter can easily form;
(iv)
Burning garbage and burning coal in winter for heating can also generate pollutants."(My emphasis)
China, however, is a big country with a lot of cultural divergence, so I differ to your more direct knowledge of customs in Chongquing without accepting that coal is not used for winter heating in other parts of China.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 09:57 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Just as an interesting aside... 10-15 years ago I used to see this scene everywhere around Chongqing (where my wife's family lives). These lovely little bricks of black death were used primarily for cooking in rural homes. You see them much less now as more and more people are moving into high rise apartments in the cities where all the cooking is done on gas cooktops.

And no, no one would use these for heating homes because no one there heats their homes, even in below freezing weather. They just put on more cloths and wonder why the silly American is shivering. And if said American tries to close a window to stave off frostbite, the next family-member entering the room says, "It's stuffy in here, we need some fresh air!" and opens the window again. :-)
-
Tom Curtis at 09:21 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
I should note, by the way, that ryland has only one drum to beat - that the third world (and in particular China and India) will not transition to a fully industrial economy except by the use of coal and other fossil fuels, and that therefore western attempts to curtail CO2 emissions are pointless. That point is only valid if he can categoricaly state exactly what policies with regard to greenhouse emissions both nations will pursue over the next two decades. Given the standard of evidence he has now indicated he considers appropriate; I suggest that he no longer be heard (on grounds of excessive repetition, and sloganeering) until he states categorically and exactly what the policies of those two nations will be, on an appropriate thread.
-
Tom Curtis at 09:06 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
If I can take us back to ryland's claim @46 in response to John Hartz @43:
"Yes, I rather think I am ["...stating that you cannot form an opinion about air quality in Inida and China without personally observing and experiencing it"]. China is a very large country as indeed is India and it seems highly unlikely that there is uniform air quality over the entirety of either country. So when you ask ""At what cost to their respective environments, especially clean air?" the question is somewhat loosely worded. Do you mean the environment and air in the cities or in rural areas or in the mountains or on the coast?"
Again note the ridiculous standard, ie, that China (or India) must have "...uniform air quality over the entirety of either country" in order for us to form an opinion about the air quality in China. Transparently we can form an opinion about the average air quality in China (which by definition is uniform over the entire country). More importantly, we can form an opinion about the air quality in specific locations:
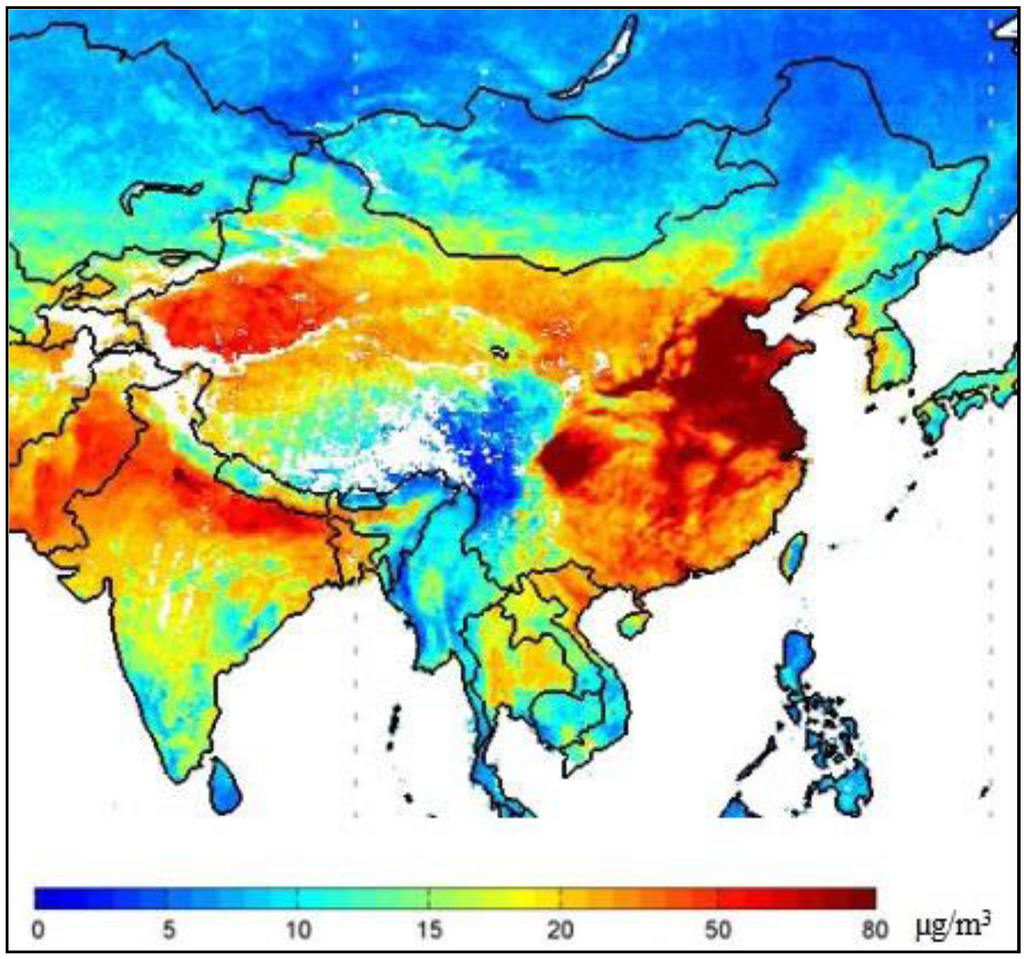
"There was continuous haze-fog weather in most parts of China, including Tibet and Xinjiang. The areas with serious haze-fog pollution included the Beijing and Tianjin areas, South Hebei Province, Northeast Henan Province, Western Shandong Province, Jiangsu Province, Anhui Province, Western Zhejiang Province, Northwest Fujian Province, Central Hunan Province, South Jiangxi Province, Central Hubei Province and the Northern Sichuan Basin Area. Southwest China became the only unpolluted land."
(Source)
Note that (contrary to John Hartz) coal was only a factor in this pollution when used for domestic heating. Industrial, and particularly power station use burns coal at very high temperatures, with almost complete combustion and with significant deployment of scrubbers so is not a primary contributor; although petrol engines in cars are.
We can also form a view as to the geographical extent of acid rain over China, to which coal is a major contributor:

ryland's response to John Hartz' statements on pollution in China consists entirely of empty rhetorical points, just as was his response in impacts (which was introduced to distract from the issue of pollution in China).
-
Tom Curtis at 08:27 AM on 8 July 2015Carbon cycle feedbacks and the worst-case greenhouse gas pathway
tmbtx @1, you do not consider the proof that the Earth cannot undergo a runaway greenhouse effect good news? Or the recent indications that climate sensitivity may not have a long tail? The later does not eliminate the risk of severe impacts from climate change, but it does largely eliminate the risk of extreme impacts, which is surely good news. If you are not finding any evidence of optimistic developments, you are relying to much on biased sources. There is good news out there, particularly in the technical development of low carbon technologies (renewable energy, electric transport).
-
Tom Curtis at 08:11 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
ryland @58, what is the exact cost to the Earth's climate system of a meteor strike? Or the cost in GDP, or the cost in lives? Even when there is absolute certainty that a meteor will strike the Earth, there remains no certainty about impacts.
Come to that, what is the exact emotional cost of an excessive dose of anaesthetics? Please elucidate.
Your examples of certitude are transparently of a different category to the examples of the costs you ask questions about. Worse, you ask costs of an undefined quantity (how much coal will be burnt exactly, by which nations, and what steps to reduce or increase emissions by other nations)? Therefore you are clearly expecting an unrealistic level of certitude with regard to the impacts of emissions.
Of course, that was transparent in your original statement, even without clarrification, which called for a certainty so absolute it risked no rebutal ("categorically state") and admitted of error bars so small as to be inconsequential ("exactly"). Indeed, you ask for a level of certainty that is not even found in tracking airpaths until after the event (think turbulence, pilot error); meteor strikes (which are often only predicted in terms or probabilities, and are never predicted precisely as to location on Earth); or the precise dose of anasthaetics (which varies between people).
-
ryland at 07:47 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
I have no idea where you got the idea I "insist that the computation of the costs of burning fossil fuels must be done with near absolute certainty". What I actually wrote was "As for the cost to the Earth's climate system of their burning coal again, I don't know and I'm not sure that anyone can categorically state exactly what that cost is."
You appear to have taken it that I mean financial cost. I don't. I mean exactly what I wrote namely cost to the Eath''s climate system. For example it is said that increasing the global temperature by >2C will lead to climate change evidenced by longer and more severe drought. more flooding, increased incidence of hurricanes, increased sea levels, glacier loss etc. This is what I mean by cost to the Earth'scliate system. As I said, "I don't know and I'm not sure that anyone can categorically state exactly what that cost is."
On reflection perhaps what that cost will be would have been better
-
tmbtx at 06:19 AM on 8 July 2015Carbon cycle feedbacks and the worst-case greenhouse gas pathway
This is what happens when there's little upside and large downside in the uncertainties - the more things are refined the greater chance that they're worse than previously thought. I can't recall any time there was a new discovery or refinement that made the situation look a bit more optimistic than pessimistic.
-
John Hartz at 05:49 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland:
I specifically chose the compution of GDP because it is used by governments, finacial institutions, investors, and others as input into making major policy decisions that have major fiscal impacts. Why then do you insist that the computation of the costs of burning fossil fuels must be done with near absolute certainty when the computation of GDP is not?
-
ryland at 04:48 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Thanks Michael Sweet. In future I will remember your advice and in future will put links in instead of just the URL.
John Hartz. First thanks for your very gracious comment at 55. I'm not surprised you did not consider my examples were appropriate. But let's take theadministration of anaesthetics. If you get it wrong your patient may die or become brain damaged. I guess that is only a personal tragedy confined to the patient and the immediate family but I would argue it is more significant than determining the GDP. Let us say you come in for, let us say, a heart bypass, and I give you too much anaesthetic so you are not revived. To you and your family that is of a lot more significance than calculating the GDP. I would also contend that tracking the course of a meteor that could destroy the earth is orders of magnitude more important than calculating the GDP especially as calculations of GDP are not always accurate. If the meteor is likely to hit the earth there are means to divert its course such as the use of explosives that destroy the meteor.
In fact I cannot see that determining the GDP is anyhwere near as significan t as any of the examples I gave. But then , I would say that wouldn't I?
-
John Hartz at 03:18 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland:
If I have misrepresented your modus operandi, I aplogize.
-
michael sweet at 03:10 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland,
Thank you for giving your links. To clean them up, go to the insert section of the comments box. Highlight the words you want to be linked and then click on the chain icon. A box will appear where you can copy the URL you want to link to. After you do it once it is easy.
The moderators start to complain you are sloganeering when you only give your opinions and do not link sources. In a scientific discussion you want to present data to be convincing, not go into your personal philosophy. You will get less moderator complaints when you cite links.
Once you have linked a source, it is not necessary to refer to that link again. If you continue to refer to the same source that is repetition and is also considered sloganeering. If everyone has cited their sources the conversation has run its course. Readers can then decide which argument they thought was stornger.
-
John Hartz at 03:09 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@ryland #51:
You state:
As for examples of high bar of certitude. How about diagnosis of a fatal disease that cannot be cured? How about determining the track of a meteor that may hit the earth? How about determining the correct amount of anaesthetic to give to a patient prior to and during major surgery? How about determining the flight paths of passenger aircraft converging on a busy airport. :
Thank you for the examples. Unfortunately, they are not in the same category as is computing the costs of fossil fuel emissions. More comparable might be the computation of national GDPs. Do you believe the compution of national GDPs should be done with a high bar of certitude?
-
ryland at 02:53 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
John Hartz @50 with regard to your comment "you pull the victim card and then depart the scene" please note my reply at 51. I clearly have not departed the scene. Your comment at 50 is rather puzzlig as I don't remember it being there when I wrote my comment (@51) in answer to your comment @49. If I had seen it I would have responded to it in my comment above. I really cannot understand how I missed it.
-
macoles at 02:12 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #27
Perhaps you are right CBDunkerson, but one of the things that makes this site unique from many other pro-science sites is it strives to explain the science while trying to keep the usual argy-bargy at arms length. When we provide links to articles here from conservative forums we know we won't convince the unconvincable, but we do hope others will follow and find their assumptions challenged. The toon of the week seemed to me to only reinforce conservative assumptions.
-
ryland at 01:59 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
If I address your points I may well be accused of sloganeering and excessive repetition. As much of the "repetition" was answering your questions that seems somewhat unusual.. My original post was to point out the editorial in the Australian FinanciaL Review which can hardly be called sloganeering. Can it? As for "general assertions" most were in answer to your questions and I provided supporting evidence for many of those "assertions". As for examples of high bar of certitude. How about diagnosis of a fatal disease that cannot be cured? How about determining the track of a meteor that may hit the earth? How about determining the correct amount of anaesthetic to give to a patient prior to and during major surgery? How about determining the flight paths of passenger aircraft converging on a busy airport.
-
John Hartz at 01:48 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland:
As do many of my colleagues in the all-volunteer SkS author team, I routinely moinitor what is posted on this site's comments threads. With respect to your postings, I have noticed a distinct modus operandi at play. You start out on a given comment thread by posting rather generalized comments. When you are challenged, you will readily engage in a dailogue with oither commenters up to a point. When you feel overwhelmed by the responses to your posts, you pull the "victim" card and depart the scene. After a short respite, you begin the pattern all over again on another comment thread.
-
CBDunkerson at 01:27 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #27
I somewhat disagree. Within the 'conservative' camp you've got people who will never break from tribalism, people who might (those you are concerned about alienating), and people who don't even realize what their side is really doing. (Ditto liberals/progressives, though the percentages are different).
The cartoon above is beneficial for educating that last group. Whether that outweighs the potential harm of alienating some portion of the middle group is hard to say, but I'd argue that both are fairly small in comparison to the bloc that won't change until their 'leaders' tell them that they believed differently all along.
Moderator Response:[JH] Thank you.
-
John Hartz at 01:15 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@ryland #38:
You state:
As for the cost to the Earth's climate system of their burning coal again, I don't know and I'm not sure that anyone can categorically state exactly what that cost is.
If I take your statement literally, you have set an extremely high bar of certitude for anyone determining the cost to the Earth's climate system of the burning of coal by India and China.
Please provide an example or two of where such a high bar of certitude is required in other determinations.
-
John Hartz at 01:05 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@ryland #46:
You state:
I have take endeavoured to answer your questions wit appropriate civility and as fully as I can. Clearly I have not succeeded as you continually express dissatisfaction with my answers and your replies seem, as I mentioned above, rather aggressive.
You make many general assertions that border on sloganeeing. They will be agressively challenged on this website and sooner or later will be deleted for violating the SkS Comments Policy re sloganeering and excessive repitition. Because I am engaging you in discussion, I have recused myself from moderating this thread.
-
RobH at 00:58 AM on 8 July 2015Announcing the Uncertainty Handbook
I find uncertainties in climate change are like the uncertainties in Darwinism. You can happily pick holes in any single area - it is the total and vast picture encompassing a range of disciplines that gives overwhelming certainty. Not many are willing to plough through Darwin's treatise and similarly not many can be bothered in this case to acquaint themselves with the facts.
-
John Hartz at 00:55 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@ryland #46:
You state:
"Are you stating that you cannot form an opinion about air quality in Inida and China without personally observing and experiencing it?" Yes, I rather think I am.
Are you telling us that you do not accept the validity of the analyses of air quality made repectively by appropriate agencies in China and India?
-
ryland at 00:46 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
"Are you stating that you cannot form an opinion about air quality in Inida and China without personally observing and experiencing it?" Yes, I rather think I am. China is a very large country as indeed is India and it seems highly unlikely that there is uniform air quality over the entirety of either country. So when you ask ""At what cost to their respective environments, especially clean air?" the question is somewhat loosely worded. Do you mean the environment and air in the cities or in rural areas or in the mountains or on the coast? However, from the usual, rather aggressive, thrust of your questions I assume the air quality is poor.
Nevertheless the decisions to burn coal and to continue to burn coal are decisions made by the governments of the two countries not by Western World do-gooders who believe they know what's best for China and India. Perhaps India and China should remonstrate with the US regarding fracking or with Canada regarding recovery of oil from tar sands or with Australia regarding the very high car ownership or the world'airlines regarding the fleets of aircraft continually criss-crsossing the globe carrying in the main, well heeled passengers from the Western World.
I have take endeavoured to answer your questions wit appropriate civility and as fully as I can. Clearly I have not succeeded as you continually express dissatisfaction with my answers and your replies seem, as I mentioned above, rather aggressive.
-
Ger at 00:36 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Reminder:
5980 million tons of steam coal (mainly power plants and large heat plants), 950 million tons of cokeing coal (steel) and 950 millions tons of lignite (like) for cement production. Steel and cement are hardly using the heat generated to turn this into electricity and cement production releases an extra amount of CO2. Efficiency of thermo powerplants can easily be moved up from 30% to a 50%, cement production can switch to bio-coal. Both cement & steel can recupperate the heat and turn this into electricity. Steel production can reduce coal use by using more efficient generated power and waste heat from powerplants.
No bussiness is hurt by implementing such, just the wallet of greedy plant owners not willing to spend a cent more than they have done yet for the sake of the holy grail of business: Money.
Mining can be done with remote controlled equipment, afterall this the 21th century. Mining does deliver GOB, gasses (methane) wich can be used to power all mining operations and much more.
Not that we shouldn't switch to truly renewable sources but during transistion a 5% saved by using better -available- reduces additional CO2 emissions far more.
-
John Hartz at 00:17 AM on 8 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland:
Your understanding of energy use in China and India seems to be very shallow. If you want to move beyond platitudes and talking points into serious a serious discussion of the issues at hand, you need to do your homework.
For starters, I recommend that you carefully read:
The case for Australian coal in India is weakening by Lynette Molyneaux*, The Conversation, June 24, 2015
Pertinent paragraphs from the article:
Looking more closely at energy use in India weakens the economic case even further. The Indian states with the lowest levels of domestic access to energy tend to be in the north east.
They are rural agrarian communities with, according to the Indian Planning Commission, an annual per capita gross domestic product of just US$500-1000. Low income levels provide little room for expenditure on electricity or electric goods. Consequently, the Planning Commission reports that state electricity utilities run at a loss due to high levels of unauthorised use and technical failure.
++++++++
China is the poster child for the coal industry’s message that coal can end energy poverty. But China’s success has come at a cost.
China’s Health Minister from 2007-2013, Chen Zhu, a professor of medicine and molecular biologist, stated in an article in the Lancet in 2013, that lung cancer is now the leading cause of death in China and that between 350,000 to 500,000 people die prematurely each year as a result of pollution. There is not a single Australian that would welcome the privilege of having to live with the air pollution that has come with China’s development.
___________
*Lynette Molyneaux is a member of the Energy Economics and Management Group in the University of Queensland’s School of Economics. She was involved with the University of Queensland’s energy research series of papers entitled Delivering a Competitive Australian Power System.
Lynette’s research interests include: the measurement of resilience in systems; and systems for carbon abatement with particular emphasis on incentives for investment abatement technologies. Prior to her involvement with the University of Queensland, Lynette has a career spanning 20 years in the Information Technology industry working for large corporations like IBM and British Telecom as well as small Internet and IT consultancies.
-
John Hartz at 23:59 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@ ryalnd #38:
You state:
You ask in reference to China and India burning coal "At what cost to their respective environments, especially clean air?" I don't know having not visited either country recently. Presumably India and China decided to burn coal in the best interests of the economic progress of their citizens. Again, presumably, the governments of both countries considered the environmental aspects of burning coal were of secondary importance to that economic progress.
Are you stating that you cannot form an opinion about air quality in Inida and China without personally observing and experiencing it?
-
One Planet Only Forever at 23:44 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland, The 'popularity of coal in China' was promoted by irresponsible wealthy people who realized they could get away with irresponsible dirty coal burning in China. And a lot of that development push was supported by already fortunate people who 'wanted things cheaper' and would buy the stuff made by the crappy cheaper way that could be gotten away with in China. And it was all defended because some of the people in China got richer in the process. Of course what is always ignored by claim-maker-uppers trying to excuse the inexcusable development because of the 'benefit to the poor' is the way that in spite of the massive growth of wealth in a place like China there remain massive numbers of incredibly poor people, with some of those poor people facing life circumstances that are worse than the life they had before the 'development'. I won't bother with links to any specific item for that. There is more than enough evidence available to anyone who is actually interested in better understanding what is going on. But one thing I will mention to assisty you in better understanding the unacceptability of things is that a person who was typically able to live a hard but decent basic life with fresh water and air, almost self-sufficiently living a decent life, is deemed to be zero-income. If that person is displaceds form their land and ends up in a desperate in a dirty city and earning $1 a day (which is nothing close to enough to live decently in the city), they are deemed to have improved from zero-income to $1 a day. And the people making the claims about the 'improvement' are either unaware of the reality of the evaluation they perfomr or are deliberately making up the evaluation to suit their interest.
And the unacceptable displacement of people from sustainable ways of living does not just happen in developing nations. When the Narita Airport was being built the nation's farmers protested violently to the point of military protection needing to be provided for the Airport. I flew out of Narita during those early years and experienced first hand the measures put in place to try to defend the unjustified 'cheaper way to get an airport' from the backlash of people aware of the unacceptability of that 'development'.
Moderator Response:[JH] The readability of your posts would be improved if you were to break-up your text into smaller paragraphs.
-
John Hartz at 23:41 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #27
Macoles:
You have a point. I will be more judicious when selecting future Toons of the Week.
-
John Hartz at 23:35 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #27
I accidentally deleted the following comment. My apologies to macoles.
macoles at 14:46 PM on 7 July 2015
Am I the only one here who thinks the toon of the week above is 0% climate science 100% unhelpfully divisive?
Yes conservatives can get some dreadful things through the supreme court (poster of the week above for example), but whether we like it or not getting them on board is a big part of the solution. Gay marriage only just passed 5-4 because one normally conservative judge was able to be convinced.
Lampooning conservative bad liberal good on a respectible site like this only plays into the hands of those who think climate change is some ideological hoax.
-
ryland at 23:24 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Thanks Michael Sweet it looks as if I didn't bungle linking although its not as crisp as links by others
-
ryland at 23:22 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Michael Sweet. Clearly I don't know enough about posting as I don't know what you mean bt "link yur quotes" As far as I know I gave the URL for each of the quotes made by others to which i refer. except for that in #3 which is paywalled to non-subscribers to the AFR.
In the hope that this is what you requiire but I don't think I've managed to link corectly
#9 The quote mentioned is from theURL gov en by John Hartz @7. I thought that was clear but apparently not so my apologies are necessary
#25 the URL is given and is (http://euanmearns.com/renewable-energy-growth-in-perspective/).
#28 the url is given and is (http://www.bbc.com/news/business-27142377). But I din’t give a URL for France generating 75% of is electricity from nuclear power it is
(http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Country-Profiles/Countries-A-F/France/)#38 URLs are given and are
(http://science.time.com/2013/01/29/the-scariest-environmental-fact-in-the-world/)
(http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2012/oct/29/coal-threatens-climate-change-targets).
(http://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2013/04/the-problem-with-predictions/) -
michael sweet at 21:49 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland,
Please link your quotes so that they can be read in context. Please provide links to raise your level of argument. A story is just your opinion. A link supports your argument and shows more substance.
-
ryland at 16:49 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
scaddenp I wasn't asked by John Hartz to comment on how to provide clean air so I didn't. In my original comment I said burning fossil fuels did not preclude having clean air. It doesn't. My "anecdote" was relevant to the point I had made
You comment "since you are keen for developing world to have cheap energy" I'm neither keen or not keen on the developing world having cheap energy but the developing world certainly is. This from Time seems pertinent:
"Of course, there’s a reason why coal is so popular in China and in much of the rest of the world: it’s very, very cheap. And that’s why, despite the danger coal poses to health and the environment, neither China nor many other rapidly growing developing nations are likely to turn away from it. (If you really want to get scared, see this report from the International Energy Agency — hat tip to Ed Crooks of the Financial Times — which notes that by 2017, India could be burning more importing as much coal as China.) That’s likely to remain the case in poor nations until clean energy can compete with coal on price — and that day hasn’t come yet.
The EIA’s chart also shows how limited President Obama’s ability to deal with climate change really is. The reality is that the vast majority of the carbon emissions to come will be emitted by developing nations like China — and much of that will be due to coal." (http://science.time.com/2013/01/29/the-scariest-environmental-fact-in-the-world/)
It seems that not only does the developing world like coal so does the developed world. A report from the Guardian in 2012 notes that "Coal is enjoying a renaissance, with the highest consumption of the fuel since the late 1960s. The unexpected development threatens to put climate change targets out of reach – and much of the reason is the rise of a supposedly "green" fuel, natural gas." (http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2012/oct/29/coal-threatens-climate-change-targets).
In answer to your question "are you then ready for developed world to ditch FF so they can?" Of course I am but is the rest of the developed world? Somehow I can't see the oil, gas and coal exporting economies gleefully embracing that course of action. Nor can I see the consumers of oil, particularly petroleum products, being overly keen. Ironically, the burning of fossil fuels is an essential pre-requisite for the air travel that enables attendance at the meetings held around the world to discuss the developed world ditching FF. And of course for participation in the many conferences held to discuss climate change. Curiously, that irony never seems to be mentioned by those attending these meetings and conferences.
John Hartz. You ask in reference to China and India burning coal "At what cost to their respective environments, especially clean air?" I don't know having not visited either country recently. Presumably India and China decided to burn coal in the best interests of the economic progress of their citizens. Again, presumably, the governments of both countries considered the environmental aspects of burning coal were of secondary importance to that economic progress.
As for the cost to the Earth's climate system of their burning coal again, I don't know and I'm not sure that anyone can categorically state exactly what that cost is. According to author and mathematician David Orrell
"predicting the future is difficult. And what’s more, the search for the “perfect model” of prediction often reveals as much about people’s sense of aesthetics as it does about the future" and more cogently to the discussions here he comments:
"Climate change prediction, for example, is no better now than it was 30 years ago," (http://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2013/04/the-problem-with-predictions/) Whether that is true or not I'm sure you know better than I
Moderator Response:[JH] Link activated.
-
villabolo at 16:09 PM on 7 July 2015Announcing the Uncertainty Handbook
Communicate through images and stories
I like to use manual gestures in explaining different aspects of global warming. It gives an advantage over mere verbalization.
When I explain how ice is shrinking in the Arctic Ocean I form a circle with the thumbs and forefingers of my hands representing the nearly circular ice cap. Then I "shrink” the circle to indicate its loss of extent. Like this, with the parenthesis representing my fingers on both hands and the zero representing my face: ( (0) ).
When indicating the loss of Arctic ice thickness I put my forefinger and thumb horizontally in parallel to each other and move them closer to each other to indicate shrinking thickness. I also use the Navy's CICE ice thickness map. I make it a point to emphasize that the US Navy puts those maps out. That projects an air of authority in the public's mind.
Then there is the issue of the colder than average winters in the United States. I like to state that during our last winter "97-99% of our earth was as warm, warmer and hotter than average while only 1-3% was colder”. The United States is only 1.8% of the world’s surface and only a third of it was colder.
As the old saying goes, one picture is worth a thousand words so if possible I would go to GISS temp and show or print out the anomaly maps. They can immediately see and intuitively understand the color coding with blue being colder and only covering a small part of the Earth. Then I point to Alaska and Siberia's red and dark red indicating that it was 7-15 degrees Fahrenheit warmer than average for February, 2015. Juxtaposing Alaska with the Eastern states is important because it gives your audience an example of how dramatic a difference there is within the continental United States.
I often time like to say “big picture, little picture”. Then I state that “skeptics” always look at the “little picture”. I put out my open palms, vertically and in front of me, spread a couple feet apart to show the “big picture” after which I put my palms closer together to indicate the “little picture” - how they view things out of context. Like this, spread apart in front of my face: |---0---|; then I shrink it down like this, |-0-|. I thus imitate the appearance of a horse with blinders.
-
scaddenp at 15:04 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #27
I think you have a point.
-
macoles at 15:04 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS Weekly Digest #27
Only just noticed the "Coal-Fired Mercury Polluton" on the industrialist, so I guess that makes it 20% envionmental 80% unhelpfully divisive (5 separate issues presented). My point stands though, if I as a progressive reader misunderstood the context, then what is a conservative reader to make of it?
Moderator Response:[JH] My apologies to you for accidentallly deleting your prior comment. I will repost the text.
-
John Hartz at 14:45 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
@ Ryland #25:
You state:
Both China and India concentrated on providing energy via coal fired power stations. They chose coal because it was the cheapest option. In both countries coal fired power stations still provide the bulk of the energy needs.
At what cost to their respective environments, especially clean air?
At what cost to the Earth's climate system?
-
scaddenp at 14:35 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
" As for anecdote I have no idea what you mean" - you responded with anecdote as to your own living position as opposed to data on how to have clean coal.
Anyway, since you are keen for developing world to have cheap energy, are you then ready for developed world to ditch FF so they can?
-
One Planet Only Forever at 14:04 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland,
I have been reviewing this discussion and have a different perspective about the benefit of burning fossil fuels.
I am an avid supporter of providing assistance to the least fortunate. But the assistance must rapidly develop their ability to independently live a decent lasting lifestyle. That means the assistance is totally charitable, with no expectation of a personal return benefit for the person providing the assistance. And the person providing the assistance needs to seriously strive to rapidly 'work themselves out of that job'.
Essentially my view is that the least fortunate must be helped to rapidly transition up to a decent life that can continue to be enjoyed by all in the future generations. And they need to be helped by 'all of the already more fortunate'. And I also believe that a robust diversity of the ways of living is very important. So how the poorest develop to live should be the lasting sustainable way that best fits the location they are in (or they are allowed to, and assisted to, freely move to whatever location they wish - no borders - no barriers).
From that perspective burning fossil fuels would need to be used for a very restricted rapid transition to lasting ways of living decently. The understood harm of burning fossil fuels and the fundamental unsustainability of burning up non-renewable resources clearly mean it must only be a transition technology with the shortest possible duration (in spite of potential profitability or popularity). As has already been mentioned by others, in many cases the best assistance for the least fortunate would not even involve passing through a stage of benefiting from fossil fuels.
You are correct, popularity for the cheap and profitable ways that the most fortunate got accustomed to getting away with will make the required change of attitude a daunting task. It isn't daunting because of the inability for it to happen. It is daunting because of the lack of interest among all of the most fortunate to do what they all understand needs to be done.
Any already reasonably well off person should by now not be obtaining any further benefit from burning any fossil fuels, not even natural gas. So the pressure needs to be on 'all of them' to start behaving responsibly as a duty of being wealthy.
25 years ago what was required to be done was clearly understood by every wealthy powerful person on the planet. The efforts to discredit the understanding and to plant seeds of doubt have been ramped up by the worst among the wealthy and powerful. Many people have written about the campaigns against better understanding what is going on and have provided extensive examples of the unaccpetable efforts of those people. And it is easy to understand why moderately fortunate people immersed in entertainment or some other distraction are easlily impressed by the efforts of those wanting to discredit the developing understanding of what is going on and the required changes (or develop a misguided belief that supporting the benefiting from burning of fossil fuels by already fortunate people will help the less fortunate).
The key required change is simply the leadership by 'all of the most fortunate' to live and profit in ways that are truly totally sustainable, ways that all others can develop to match if it interests them to strive to live that way. That means that none of the already fortunate should be making any profit or be obtaining any benefit from burning fossil fuels. They have all had 25 years to work towards that. Only a few have seriously tried, and they are fighting against the competetive advantage obtained by the deliberate laggards who knowingly have changed as little as possible. And the worst among that group have deliberately abused their wealth and power as much as they thought they could get away with.
The reluctance of some wealthy powerful people to embrace the obligation and responsibility that is clearly required of them is the real problem. And lines of questioning like yours and the claims about what should be allowed to continue because it supposedly would help the poor is a poor excuse for the unacceptable inexcusable attitude of some of the wealthy and powerful. The poor do need help, and many among the most fortunate are only interested in helping in ways that they can personally profit from. And the worst among the most fortunate are not even interested in profiting from helping the poorest the best way they can be helped if it would be more profitable for them to claim to be helping the poor while doing something less helpful, or worse yet while benfiting from doing something that is actually going to be harmful to the poorest.
That is my truthful comment that I understand will be difficult for some to accept.
-
ryland at 13:51 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
scaddenp Whatever I write adds nothing to the debate. As for anecdote I have no idea what you mean. To truly elaborate etc etc is to truly elaborate on something I did not say. I know the provison of clean air is influenced by the amount of fossil fuel in the vicinity but I specifically did not say that.
John Hartz You write "for one more time" then proceeed to ask a completely different question. Energy should be cheap so that industries can grow and in so doing provide wealth to the nation. Both China and India concentrated on providing energy via coal fired power stations. They chose coal because it was the cheapest option. In both countries coal fired power stations still provide the bulk of the energy needs.
Whether the other items should be cheap or not is a red herring. They should be available to all and they're not. Can you not see that what we in the developed world take for granted as the most basic necessities of life would be considered by those living in many developing countries as luxury beyond the dreams of avarice? If you cannot then there is nothing further I can say to you on this.
-
John Hartz at 13:51 PM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Here's an impressive example of an African agressively moving forward with sustainable energy...
Kenya’s New Wind Farm Will Provide Nearly One Fifth Of The Country’s Power by Ari Philips, Climate Progress, July 6, 2015
-
dvaytw at 11:58 AM on 7 July 2015In charts: how a revenue neutral carbon tax cuts emissions, creates jobs, grows the economy
Thank you, Tom. Unfortunately I think the same point can be made regarding the decline in gas consumption itself (see #2 above).
And #3 above is to me the kicker, in any case. If gas consumption is back up, it suggests that people have just shrugged their shoulders and adapted to the new price regime.
-
climatesight at 10:32 AM on 7 July 2015Cracking the mystery of the corrosive ocean
The definition of "corrosive" means that calcium carbonate (CaCO3) ions are undersaturated in the ocean, so sedimentary CaCO3 will keep dissolving until saturation is achieved. It doesn't necessarily have anything to do with pH.
-
John Hartz at 10:15 AM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland:
Let's go over this one more time. You stated:
Other luxuries are clean water, food, housing sanitation, medicines and cheap energy.
You obviously believe that the "luxury" item, energy should be "cheap."
Should the other "luxury" items you have listed also be "cheap?"
If not, why not?
-
PhilippeChantreau at 09:30 AM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Incidentally Ryland, I have lived on 3 different continents (including Africa) and an island. I have a very good notion of what constitutes luxury in this world, and an acute perception of the the reality of the every day living conditions in the majority of said world. It is rather outrageous that basic necessities are such a luxury in some parts, while in others luxury means delirious extravagance. Advocates of unabated FF use do not show how things are going to in fact get better that they have been until now with the status quo. Surely nobody would suggest we continue doing eactly the same and expect different results, right?
-
scaddenp at 09:29 AM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
Ryland - you replied with anecdote and frankly with a contribution that adds absolutely nothing to the debate. Would France still have its clean air and water (on the whole, as opposed to in selected places) if it generated its electricity from FF?
I did misread your comment (reading "developed" for "developing"). I do agree that developing world should be allowed to continue to burn FF (but that they should kill the subsidies since it promotes unsustainable development) and that to make that possible , the western world needs to reduce FF consumption by about 85% - and I think a carbon tax is probably the best way to get that happenings.
-
PhilippeChantreau at 08:44 AM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
"I hope that is sufficient elaboration."
Not really. France burns FF mainly for transportation or residential heating, as its electricity generation is mostly from Nuclear. In rural areas, the burning of FF for transportation and heating remains at low concentrations and has naturally a lower adverse effect on air quality. In urban areas, the use of FF for transportation is a problem, as shown by the dismal air quality seen in Paris. Even some rural areas experience terrible air quality if the traffic is concentrated enough, as is the case in the Vallee de L'Arve, which suffer awful air quality because of the traffic caused by the Tunnel du Mt Blanc.
To truly elaborate, one would have to say that burning fossil fuels does not preclude clean air, provided the burning is limited to small scale point sources that are separated by large enough distances. In the case of large industrial sources, air quality is negatively impacted in close proximity to the source over an area much larger than the direct vicinity of the source, and air quality down wind from the source can be negatively affected over hundreds of miles. Complete elaboration would lead to the conclusion that the burning of fossil is compatible with satisfying air quality in a narrow subset of circumstances far different from real conditions.
-
ryland at 07:44 AM on 7 July 20152015 SkS News Bulletin #6: Pope Francis & Climate Change
scaddenp Try reading what John Hartz asked me to do. I did as asked which was to explain a comment. You may not like what I wrote but it is correct as you yourself have acknowledged. Burning fossil fuels does not preclude having clean air and water. And France generates 75% of electricity by nuclear power while Australia has no nuclear capacity.
And as for my comment about the developing world I'm not saying anything about them being slow and stupid, those are your words not mine. What I was saying is what has been said by developing nations at various conferences on climate change. As you may or may not know subsidy for fossil fuels is high in the developing world (http://www.bbc.com/news/business-27142377)
Prev 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























