Recent Comments
Prev 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 Next
Comments 31201 to 31250:
-
Tom Curtis at 12:08 PM on 22 April 2015Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
Joel_Huberman @52, two other minor but relevant points. First, the temperature series shown in Fig 1 C are only for 82.5 North to 70 South and therefore exclude part of the most rapidly warming region of Earth. Second, the observational records shown are tropospheric rather than surface records. The troposphere responds far more strongly to volcanic and ENSO influences than do surface records. Any dampening of the trend due to the small volcanoes in the satellite record will be greater than that at the surface. Ergo, it is likely that had surface records been used, and particularly truly global surface records such as GISS, or BEST, there would still have been a positive trend including the effects of the small volcanic erruptions.
-
jja at 10:32 AM on 22 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Andy,
Predicated on the idea that early arctic ice loss is not modeled under the scenario, that the albedo effects are underrepresented when they are included (due to algae bloom) and microbial heating effects are also not included then these emission profiles will be severely underrepresented.
If summer arctic ice loss occurs within this decade as opposed to late 2040 as is currently being modeled, then this will allow microbial heat-driven decomposition to occur much more rapidly than modeled in Hollensen.
With a 3-meter depth decomposition profile establishing as early as 2060. -
Joel_Huberman at 07:12 AM on 22 April 2015Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
Thanks, KR. Your comments have helped me to distinguish between what Santer et al. were trying to say and what Homewood wanted to say by carelessly (or intentionally) mis-interpreting Figure 1. Your comments prompted me to more carefully examine the paper by Santer et al. Although much of their paper involves statistical tests that are beyond me, my re-examination of their paper, combined with your comments, lead me to the following revised interpretation of Figure 1:
In Figure 1A (raw data), there's only a poor fit between CMIP-5 model predictions and the TLT data (RSS and UAH). In Figure 1b (ENSO removed), there's an excellent fit between data and model predictions up to 2002. That's because the CMIP-5 models were already adjusted to account for the El Chichón and Pinatubo eruptions but not for subsequent 21st-century minor eruptions. In Figure 1B, the model-predicted and satellite-observed cooling effects of the two big eruptions are evident in the big dips in 1983 and 1992. Notice that, when the effects of El Chichón and Pinatubo are also removed (Figure 1C), those big dips are remove, and the adjusted TLT data continue to agree with the adjusted model data until about 2002, but now both sets of adjusted data have consistently higher values (than in Figure 1B) from 1982 until 2000. In other words, removing volcanic influences causes the observed temperature data, as well as the model predictions, to increase during the time period of volcanic influence. One of the points that Santer et al. are trying to make is that failure to take cumulative 21st-century minor volcanic activity into account is what gives rise to the divergence between model-predicted (the models didn't account for these volcanoes) and observed (affected by these volcanoes) TLT data after 2000.
I think it's unfortunate that Santer et al. couldn't include a Figure 1D in which the effects of minor 21st century eruptions were removed from the TLT observations and then compared with the model predictions. I suspect such a figure would have shown significantly better agreement between models and data than in Figure 1C. In addition, such a figure would have shown a rising trend in the TLT data. I suspect that Santer et al. didn't want to create such a figure because our understanding and measurements of the effects of these minor eruptions are still too primitive to allow accurate graphing. Their doubts are reflected in the last sentence of their summary: "To reduce these uncertainties, better observations of eruption-specific properties of volcanic aerosols are needed, as well as improved representation of these eruption-specific properties in climate model simulations."
Thanks to your help, I no longer feel mystified by Figure 1, and I certainly no longer feel susceptible to Homewood's siren interpretation.
-
Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
will - Temperatures are the result of all forcings (emissions including aerosols, land use, solar, volcanic) and internal cyclic and acyclic variations (ENSO, PDO, etc), modulated by thermal inertia and plain weather, so no, the shorter term temperature trend will not be exactly the emissions trend. Emissions are the dominant forcing change as per AGW, but far from the only one.
-
wili at 05:04 AM on 22 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Thanks again, Andy. My impression is that RCP 8.5 was indeed _intended_ to represent a worst case scenario. But at least up to recently it has seemed more to reflect BAU. I will feel happier about the 2014 energy emissions figures when the actual atmospheric data start reflecting it. Just now weekly averages are in the 403 to 404 range...higher than they should be even under 'normal' rates of increase/acceleration. (I know, I know--warming Pacific and even local weather may be playing a role, and weekly bumps are to be expected...still a bit worrying, imho.)
But I my basic question/confusion was whether a temperature trend is the same as an emissions trend. (Obviously, they will correspond over time, but it seems to me that over short periods, such as our current so-called 'hiatus,' they may diverge for a while.)
-
Tom Dayton at 04:51 AM on 22 April 2015Global warming stopped in
1998,1995,2002,2007,2010, ????
Potholer54 has a good new video, "Why Temperatures Never Go Up In Straight Lines."
-
Andy Skuce at 02:53 AM on 22 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
wili @10
It's true that years prior to 2014 showed an emissions trend slightly above RCP8.5, but I think that the 2014 emissions figures give some hope that this tendency may be ending.
My opinion is that it is wrong to characterize RCP8.5 as business-as-usual as some people have done. I think that more correctly it's an unlikely but still plausible worst-case scenario.
-
wili at 02:05 AM on 22 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Thanks for the thoughtful reply and the context, Andy.
The portion you quoted mentions "current warming trajectory" but you mention RCP. Are these really the same thing? Isn't the current warming trajectory (especially if they left out 2014) on the low end while we are actually on or above the ghg emissions trajectory laid out in RCP 8.5?
-
Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
Joel - Homewood has, not surprisingly, got his picture roughly backwards. From Santer et al 2014:
On the basis of the results presented here, we argue that the divergence of modelled and observed low-frequency TLT changes over the final 15 years of the satellite record is partly due to systematic errors in the post-Pinatubo volcanic forcing in the ALLC8.5 simulations. (emphasis added)
In short, that illustration shows ENSO and two large eruptions removed, but with remaining early 21st century volcanic forcings not included in the model forcings present. And that Homewood is quite wrong - there is an underlying warming trend over the last two decades, masked in part by volcanic variability that wasn't part of the model forcing sets.
In fact, you can see the error in Homewoods insistence on: "Ignore the misdirection about early twenty-first-century volcanic eruptions." In short, ignore the core of the paper so that he can mislead you. Nothing but denial.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 23:48 PM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Ranyl @ 8,
"A 50/50 chance at 450ppm of keeping warming to 2C by 2100, so that is akin to Russian Roulette with 3 bullets in the barrel, not sure why our policy makers are such brave gamblers considering the risks?"
The gamblers are gambling with consequences that otehrs will face. And they are able to round up popular support for getting away with damaging but cheaper ways of benefiting today because those unacceptable activities will only affect future generations, or people in other nations, or poeple who are not as fortunate.
Such leaders are not gamblers at all. They are more like criminals since they actually have the ability to better understand what is going on yet they deliberately do not push for the action they can understand is required.
Popularity and profitability fueled by successful deliberately misleading marketing is a fundamental problem that has been massively successful. I am hopeful that humanity can overcome the temptations. But it seems those temptations will not be overcome before massive irreparable damage occurs. The impacts of CO2 accummulation are going to be massive compared to the impacts of the accummulation of junk mortgages in the USA that led to the global economic catastrophe of 2008.
-
Joel_Huberman at 22:56 PM on 21 April 2015Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
Thanks very much, CBDunkerson. The graph you've posted is the one Homewood is talking about. Homewood is looking at panel c in the figure, the bottom panel, after removal of ENSO, El Chichón and Pinatubo effects. Note that Santer et al. removed those effects not only from the CMIP-5 calculations, but also from the RSS and UAH observations. After removal from the observations, the observations do, indeed, appear flat after 1993. Homewood interprets this to mean that all of the rise in RSS and UAH temperatures after 1993 (panel a) must be due to "natural variability" (ENSO and volcanoes). Santer et al. don't appear to comment on this in their paper (at least I couldn't find a comment), meaning that they're not surprised. I'm upset by it, because the denial crowd appears to be jumping on this as just another "proof" of the "hiatus". I want to be able to debunk denialist claims, and this one's (temporarily, I hope) got me stumped. Thanks for any additional help you can offer.
-
CBDunkerson at 21:22 PM on 21 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
Got it. A smaller 'global carbon sink' has resulted in greater atmospheric CO2 from fossil fuel emissions than would have existed otherwise.
However, wouldn't the slowly degrading carbon sink have resulted in atmospheric increases from the natural emissions cycle? That is, assuming natural emissions and sinks were roughly in balance (otherwise atmospheric levels would have been changing) wouldn't human degradation of the natural carbon sinks have resulted in rising atmospheric CO2 levels? The only way I can see to avoid this would be if natural emissions somehow declined at essentially the same rate as natural sinks. That's possible, but would need to be demonstrated.
Meanwhile, the problems with carbon isotope levels and vastly different estimates from other studies remain.
-
CBDunkerson at 21:06 PM on 21 April 2015Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
Joel, well the first thing which jumps out at me is that his starting principle is simply false;
"After taking out the effect of ENSO and eruptions, it is apparent that temperatures have been flat since the early 1990’s; indeed they have arguably been falling since."
Is he looking at a different graph? Because the one in the study, and copied on his page, clearly shows a rising trend from the early 90s to present;
 Moderator Response:
Moderator Response:[RH] Adjusted image size.
-
ranyl at 20:53 PM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Thanks Andy intersting but not sure we have a carbon budget really more of a debt and the permafrost melting is akin to interest on it.
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/03/150309155521.htm
Ground water methane releases.
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/03/150330095359.htm
More methanogensis bugs in the lakes as they warm and the lakes are full carbon for them to eat.
When do the models melt the Arctic summer ice away in the paper by?
Last CMIP5 RCP8.5run I’ve seen still had plenty of summer ice up to 2070, so presume that there might be a type 1 error model underestimation, given the way the arctic sea ice is melting already (can only get faster as we warm further and last 12 months have been the hottest in the temperature record, with an EL Nino just starting to brew), and most experts seem to suggest that an Arctic ice free summer by 2050 is inevitable at current rate of heating, and there is nothing we can do to slow the rate of heating by 2050, apart from geo-engineering and that is unlikely to be a safe bet.
And melting the sea ice has been shown to accelerate Arctic warming.
“We find that rapid sea ice loss forces a strong acceleration of Arctic land warming in CCSM3 (3.5-fold increase, peaking in autumn) which can trigger rapid degradation of currently warm permafrost and may increase the vulnerability of colder permafrost for subsequent degradation under continued warming.”
Keep in mind that stopping burning fossil fuels will also stop the emissions of SO2 and that is providing a very significant cooling effect at present and thus when go warming increase markedly, as the CO2 levels wouldn't drop enough to slow warming even if all emissions stopped today for millennia.
Atmospheric CO2 300ppm, sea levels 6-9m higher(LIG).
CO2 350-400ppm, sea levels 20-25m higher (Early Pliocene), Arctic 14-19C hotter.
CO2 400-450ppm, sea levels 30-40m higher (Miocene).
We've emitted 500GtCO2, does anyone really think that the same can be released again and civilization can be safe (Whatever that means)?
Not to mention ocean acidification and considering the changes already being witnessed.
BECCS also needs to take into account the CO2 emissions from the cultivation of the biomass which some incidences can be higher than fossil fuel emissions if done poorly, (like taking tree brash and roots out forcing the soil respiring bugs to feast on old soil carbon), so no negative carbon, and CCS reduces power output significantly therefore you have burn more biomass to get the same output than without CCS.
Scary that RCP2.6 is totally dependent on it!
And can't help feeling climatic changes might make growing food alone, never mind extra biomass, more challenging in many places, like California say?
Do we really have a carbon budget at all?
Don't we need to get CO2 to 350ppm at least and adapt massively at the same time to new climatic systems the earth is heading for?
Do we really have the luxury of being able to gamble anymore carbon emissions?
A 50/50 chance at 450ppm of keeping warming to 2C by 2100, so that is akin to Russian Roulette with 3 bullets in the barrel, not sure why our policy makers are such brave gamblers considering the risks?
Moderator Response:[JH] Links activated.
[AS] I hot-linked the Lawrence reference. The long URL was breaking the page
-
RedBaron at 20:17 PM on 21 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
@CBDunkerson,
Flat when it should be dropping is significant. I have tried to get at the flaw from both angles, the emissions and the mitigation. In simple abstract terms.... moving from -3 to +3 is not moving 3..it is moving 6. The emissions are not the whole story when discussing biome effects. Sure in discussing fossil fuel emissions you can simply measure the CO2 released because FF are so slowly formed that it approaches 0 in our timeframe. But when you talk about emissions from the soil due to ecosystem degradation, you must include both the emissions and the carbon that would have been sequestered if the ecosystem hadn't been degraded and add them together. Essentially what we have done by degrading the terrestrial biomes of the planet is to damage the capabilty for the ecosystems to moderate the excess carbon produced by fossil fuels. In no way am I denying the fossil fuel emissions. Instead I am pointing out the loss of the ecosystem service of carbon sequestration found naturally in healthy ecosystems.
So please don't confuse what I am saying with climate deniers arguments. I am actually saying that AGW is roughly twice as bad as the arguments presented on this forum. Fortunately though that is potentially a good thing because it also means that restoring the ecosystem function will likely have a much greater effect than projected here as well.
Please go back to post #258 and look at reference #5 soil degradation map. That whole area with degraded soils is either currently + emissions sources or has been +emissions sources since distubance by Man. Yet most of that area should have been a carbon sequestration sink over that same period. In the case of grasslands a very large sequestration sink. In the case of forests a smaller sequestration sink, but in both cases a sink not a source. So you must add the two together.
That is my explanation as to why in the Ruddiman (citation on post #251) graphs figure 1 and figure 2 the curve deviates from its downward trend and flattens. Next comes fossil fuels, and lacking the ecosystems ability to sequester carbon, the atmosphere instead begins to become saturated with excess CO2. Thus in reality the hockey stick is actually a result of ecosystem services loss rather than fossil fuel emissions alone, my original premise.
-
scaddenp at 18:36 PM on 21 April 2015Human CO2 is a tiny % of CO2 emissions
One other little gotcha is that turning desert/grassland to forest say reduces the albedo of the planet - it doesnt reflect as much radiation to space but I think that would be a minor concern.
-
scaddenp at 18:34 PM on 21 April 2015Human CO2 is a tiny % of CO2 emissions
Well mushrumps, I have made a mess of this sort of calculation in past but lets see how I go. The difference between emissions and absorption of land/vege is 11Gt. Land area of earth is 150,000,000 km2. 1/3 is desert, so non-desert is 100,000,000 or .1Gkm2. So land/vege currently is moping up 110 tonne/km2. To mop up an extra 17Gt at current rate, then need 17G/110 = 150,000,000km. That's current area of planet. Cant plant that much forest. Looks like a challenging problem to me.
-
mushrumps at 16:51 PM on 21 April 2015Human CO2 is a tiny % of CO2 emissions
The chart at the top tells me that vegetation and land, plus the oceans absorb 17 more gigatons than they emit. Assuming we can't do much about the oceans, all we need to do is increase veg&land absorption by 12 gigatons to balance human production of CO2!
-
Andy Skuce at 13:53 PM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
jja:
The Hollesen paper was not cited by Schuur et al.
I would imagine that the models cited in this paper do take albedo changes into account since that's a rather basic effect, but I don't know for sure.
Can you provide a reference or more reasoning for the 300% amplification?
-
jja at 13:23 PM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Do these models incorporate the microbial heating of Hollesen et. al. (2015)? paper here: http://www.nature.com/nclimate/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nclimate2590.html
Also, are these models including regional forcing feedbacks associated with ice-loss dynamics or do they simply look at radiative forcing parameters from the RCP runs? If they do not include ice-loss albedo functions (as well as a 20% increase in regional temperature due to arctic surface algae growth) (carbon brief today: http://www.carbonbrief.org/blog/2015/04/tiny-marine-plants-could-amplify-arctic-warming-by-20-percent-new-study-finds/ ) Then these models could be underrepresenting frozen soil feedbacks by over 300%
We really need to get a handle on these regional feedback parameters under a potential arctic summer ice free condition within the next 10 years to be safe. -
Joel_Huberman at 13:06 PM on 21 April 2015Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
I want to change the topic, back to the content of the original posting. One of the paragraphs in the original posting is:
"Volcanic eruptions generally cool the planet's surface. A study in the journal Nature Geoscience found that some climate models did not properly account for the higher levels of volcanic activity in the early 20th century. This meant that some models had overestimated the amount of atmospheric warming during the so-called slow-down."
A friend of mine alerted me to a contrarian web site (https://notalotofpeopleknowthat.wordpress.com/2015/04/18/no-underlying-global-temperature-increase-for-20-years/) where a blogger, Paul Homewood, has posted Figure 1 from the above paper in Nature Geoscience (the first author of the paper is Benjamin Santer). Homewood points out that Figure 1 appears to show that, after ENSO effects and volcanic effects have been removed from satellite data on lower tropospheric temperatures, there has been no significant change in those temperatures since 1993. Homewood concludes: "What Santer’s study shows is that there has been no underlying upward trend in global temperatures for more than 20 years."
I'm sure that Santer's conclusion must be incorrect, even for the lower troposphere (which, as I understand it, hasn't warmed as much as surface temperatures). But I can't see what's wrong with Homewood's reasoning. Can someone help me? Thanks!
-
DMarshall at 12:14 PM on 21 April 2015Global warming hiatus explained and it's not good news
@Peter Carson
A certain well-known, heavily-trafficked "contrarian" site had a lively discussion about 3 years ago regarding undersea volcanos and ENSO.
The overwhelming "consensus" was that it ha zero-to-minimal impact.
When you find yourself putting forward an idea that NEITHER side of a polarized debate finds plausible, you're either about to overturn an entire field of study or - more likely - are treading on razor-thin basalt. -
ubrew12 at 06:32 AM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
"Just because the emissions are uncertain does not mean that they should be excluded, after all, projections of fossil-fuel emissions are probably even more uncertain." Another good reason to include these emissions: as a matter of policy they are largely beyond human control. Based on new information (or, more likely, a long-delayed epiphany), the U.S. can always say "Oops, my bad" and cut its emissions dramatically. But the 'permafrost U.S.' is doing no such thing.
-
Andy Skuce at 05:38 AM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
wili. thank you.
Here's what the paper says, verbatim:
Our expert judgement is that estimates made by independent approaches, including laboratory incubations, dynamic models, and expert assessment, seem to be converging on ~5%–15% of the terrestrial permafrost carbon pool being vulnerable to release in the form of greenhouse gases during this century under the current warming trajectory, with CO2-carbon comprising the majority of the release. There is uncertainty, but the vulnerable fraction does not appear to be twice as high or half as much as 5%–15%, based on this analysis.
I should have added the word "carbon" after "permafrost (which I will now do). From their second sentence, I would expect that, while there is admitted uncertainty, the GHG release is very likely to be bigger than 2.5% in their judgement and likely bigger than 5%. The "current warming trajectory" that this is based on is something close to RCP8.5, so mitigation efforts could defer or cancel some of this, as well.
-
wili at 05:07 AM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
Thanks for this great update, and especially for the very apropos final 'rant.' One point for now that I would love further clarification on:
The second bullet-point under "The bottom line" section says:
"During this century, 5-15% of the land permafrost is vulnerable to release in the form of carbon dioxide or methane."
That seem rather low to me, given how rapidly the Arctic is warming. Are there uncertainty bars on the upper end that we're not seeing here? Does this assume a particular (perhaps optimistic?) emissions pathway?
There is now a very wide range of possible increases in global temperature by the end of the century. How can the range of potential melt of permafrost be so relatively narrow?
Also, is the low end of 5% pretty solid--that is, have we pretty well by now guaranteed that at least that much will thaw by the end of the century no matter what we do?
Thanks ahead of time for any light you can throw on my (typical state of) bewilderment.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 02:51 AM on 21 April 2015Andy Lacis responds to Steve Koonin
Ger @21... You should read this article on the relationship between gravity and glacial melt.
-
Ger at 02:40 AM on 21 April 2015Andy Lacis responds to Steve Koonin
@20. Gravity has nothing to do with it. Gravity is an expression of potential energy (water above sea level) No mass is going away by melting ice, nothing will change in the gravity. Water will get some kinetic energy when going down, converted into some heat and extra flow of seawater when it smacks into the fast inertia of the sea.
Moderator Response:[TD] Actually, gravitational attraction from ice does pull water toward it. Amazing but true. For example, see this post about Jerry Mitrovica's work.
-
Andy Skuce at 01:58 AM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
"Reserves" definitions always imply commerciality. At today's commodity prices many undeveloped bitumen deposits may not be economically viable. Indeed, some oil sands development projects are currently being shelved.
Here is the Society of Petroleum Engineers definition:
RESERVES are those quantities of petroleum anticipated to be commercially recoverable by application of development projects to known accumulations from a given date forward under defined conditions. Reserves must further satisfy four criteria: they must be discovered, recoverable, commercial, and remaining (as of the evaluation date) based on the development project(s) applied.
Many commentators including Alberta's ERCB do refer to the established number as "reserves" (my emphasis)
Established reserves—those reserves recoverable under current technology and present and anticipated economic conditions, specifically proved by drilling, testing, or production, plus that judgment portion of contiguous recoverable reserves that are interpreted to exist, from geological, geophysical or similar information, with reasonable certainty.
That was written a few years ago, before the oil price crash took many forecasters (especially the Alberta government) by surprise. It will be interesting to see if they downgrade their established reserves numbers in the face of the new reality.
Until then, I will keep using "resource" for any undeveloped deposit that may or may not be commercial.
It's worth noting also that in a recent paper by McGlade and Ekins in Nature, they used much lower numbers for Canada's reserves, although it is not completely clear to me what assumptions they used.

[Comment updated]
-
bouke at 01:21 AM on 21 April 2015Permafrost feedback update 2015: is it good or bad news?
The established bitumen resource in the Athabasca oil sands is approximately 169 billion barrels
Small terminology nitpick: 'resource' should be 'reserve'. 'Resource' refers to the total amount of stuff present, 'reserve' is the portion that can potentially be mined. Wikipedia uses the terminology correctly.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 00:29 AM on 21 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
Leto @1,
There is more reason to oppose the support of Lomborg than the fact that he is a discredited denier of the constantly improving understanding of climate science.Bjorn Lomborg is also one of the many 'financial analysts' whose evaluations are based on the belief that it is OK for part of a current generation of humanity to benefit in a way that cannot be continued into the distant future and that creates consequences for others, especially future generations, as long as the benefit the current generation get can be shown to exceed the costs inflicted on others, even if only a few in the current generation benefit.
That is essentially the belief behind a comparison of the 'lost opportunity or cost to some in a current generation' to the 'added costs expected to be dealt with by others, particularly future generations'.
And many of those type of analysts go further than that fundamentally absurd belief. They overstate the 'lost opportunity or cost of the few in the current generation' and understate the 'consequences others will suffer'.
-
CBDunkerson at 00:02 AM on 21 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
The Cryosat article above links to a new site where they are now providing recent arctic sea ice data on an ongoing basis. In the past, Cryosat results were only released a few times per year.
-
CBDunkerson at 22:01 PM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
RedBaron, setting aside the (equally valid) arguments based on carbon isotope levels and lower land use estimates from other sources... I'm having a temporal causality problem with your position that AGW is largely driven by "~300 GtC emissions pior to 1850".
If that were the case, wouldn't atmospheric CO2 levels have risen significantly from those emissions prior to 1850? Yet the "CO2 emissions vs Atmospheric CO2 levels" graph in the main article above shows that atmospheric levels were nearly flat through 1850... increasing significantly only after fossil fuel emissions rose greatly.
Basically, it seems like you are looking at various estimates of total CO2 emissions from different sources and saying, 'Aha, this estimate over here puts a large total on ancient land use emissions... that is the cause!' without considering the timing. How could all of the CO2 emissions from land use prior to 1850 'hide out' and avoid raising atmospheric CO2 levels until after large scale burning of fossil fuels began?
-
Leto at 19:28 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
To clarify what I have said above... I am certainly not accusing scientists of cherry-picking. I haven't even read their paper. I am just saying the break into two trends looks odd, and the article should provide more information about what motivated the selection of that particular break point. (The paper should also provide this information, but for all we know it does this already.)
I would be (pleasantly) surprised if the statistical tests used to break one trend into two produced that particular break point, but I know it is hazardous to pit visual intuition against maths. Until we read the original paper, this is all guesswork.
-
Tom Curtis at 18:10 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
bozza, there are statistical methods that can be used to determine whether or not it is appropriate to use a single linear trend for the whole data, two seperate trends, a sinusoid, etc. One such is the akaike information criterion. There are others. If the the authors of the paper used such a criterion to establish the appropriateness of using two linear trends, then it is not cherry picking. If they did not, there case for using two linear trends has not been made (at best) and it may be cherry picking. If such methods do not show the two trends to be appropriate and they did not perform the test, then it is cherry picking. Unfortunately I do not have the paper so I cannot comment on whether or not they justified their choice of two trends or not, nor whether the choice is justified independently of whether they attempted to do so.
I will note that in the well known cases of denier cherry picking, it has been shown quite frequently by Tamino that the AIC does not justifiy their choice, and that they are definitely cherry picking.
-
bozzza at 15:31 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
ah, yes: I was going to raise the very same question about this last graph being cherry picked for its ripe data... the plot doth thicken methinks!
(..and I'm not altogether sure I'm too happy about it mind you!!)
-
bozzza at 15:23 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B

This shows the possibility of continuing normal sinusoidality: or does it?
This is the graph I am currently interested in btw but please: all questions about cherry picking of data for deception need to be considered and discussed- I will always agree with that!!
Graphical Information is well known to prove deceptive and must be carefully interpreted, like any data- it's just graphical information can be quite powerful in the mind.
-
bozzza at 15:11 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
Cherry picking accusations could be made but it is part of the process of trying to find a trend and then establishing why... life is sinusoidal and any departure from that begs for an explanation. This could be part of normal sinusoidal behaviour (hence the legitimate complaint of unfair cherry picking of data/starting points) but given that the context of previous data is there how can it be cherry picking for the sake of deception... this is cherry picking for the sake of tying to establish realationship!!
This is the process of science...
-
Tom Curtis at 15:01 PM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
Red Baron @262:
"The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730±40 years. Any SOM older than 5,730±40 years to the end of the last glaciation period would have a C-14 at 50%-75% similar to Fossil fuels"
In other words, where fossil fuels are 100% depleted in C14, soils are around 75% or less depleted in C14. Put another way, to deplete tropospheric C14 by the same amount, you need 33% more soil carbon than you would fossil fuel carbon. That, however, means you are also depleting C13 in the troposphere 33% faster. That means that if you assume significantly more soil carbon emissions over the last 150 years, you rapidly get a measurable mismatch in the isotope ratios.
That does not mean there is not room for some more soil carbon in the mix. The carbon model predictions are very close to observations, but not perfect, and they have error margins. Therefore it is open for you to show for some potential increase soil emissions, they better match the observations, or match them as well as current estimates. Until you actually do that, however, we have no reason to accept your theory. Just waving your hands is not a scientific argument.
Indeed, given the current accuracy of the models, we can already preclude the possibility that the majority of the emissions hockey stick is from soil carbon rather than from fossil fuels and cement.
-
bozzza at 15:01 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
I'm certainly interested in the Greenland albedo stuff and welcome any debate about cherry picking of data as it should always be a legitimate line of enquiry. Are there any links to the contentious data being discussed?
-
Tom Curtis at 14:31 PM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
Red Baron @262:
"His arguments are generally sound and I accept his sources. Excepting his measurements include highly degraded ecosystems found now and not even close to what they were before human impact."
First, it is not at all clear that the "extirpation and extinction" of megafauna would result in significant carbon emissions. In particular, while it may result in reduced bioturbation at depth, that would merely result in existing carbon being left at depth, rather than it being brought to the surface. It is only where that is coupled with significant erosion and/or desertification that it would potentially lead to emissions, and that is not typically the case.
The most noted desertification, ie, the Sahara, was brought about by changes in rainfall, not by the extinction of megafauna (which were not, in general, driven extinct in Africa) and hence does not fit your model. Come to that, neither does North America (where the survival of bison maintained the lush grasslands you consider so important), nor Australia, which has always lacked hoofed grazers until Europeans brought cattle.
Second, and most importantly, any emissions from soil due to the "extirpation and extinction" of megafauna is already included in Ruddiman's estimations due to the associated C13 signal. Ergo it was taken into account by my tabulation.
Third, whatever the effect of the "extirpation and extinction" of megafauna (or whatever other combination of factors caused the early holocene carbon emissions, ie, Ruddiman's fatal flaw), they occured before the nineteenth century agricultural revolution. Ergo the emissions consequent of that revolution come from the (according to you) already depleted reservoir. Therefore there did not exist the potential in the nineteenth century for the agricultural revolution to cause a hockey stick in emissions. Put another way, if we accept your argument about depletion, it gives us no reason to question Houghton's figures Houghton's estimates are for LUC emissions from (according to you) already depleted soils.
Finally, my critique of Teague's argument about sequestration used the sum of Houghton and Ruddiman's figures, thereby accounting for all LUC over the entire Hollocene. It, therefore, represents the only basis against which to check Teague's claims. You may certainly speculate that Ruddiman got his figures wrong because Teague is (somehow) infallible, but you are then no longer basing your estimates on data, only wishful thinking.
-
Leto at 14:22 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
Edit... I mean the points are above the continuation of the first trend line
-
Leto at 13:30 PM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
Chiskoz @2,
I agree that the step looks odd, and I'd be interested in knowing if the timing of that step point was data-driven or chosen arbitrarily. The majority of the initial data points after the step are above the second trend line, so it is odd to suggest, as the graph does, that the first part of the second trend line accurately reflects the beginning of a downward trend.
If nothing else, the division of the data into two groups needs better justification in the figure legend.
Does anyone have a link to the original paper?
-
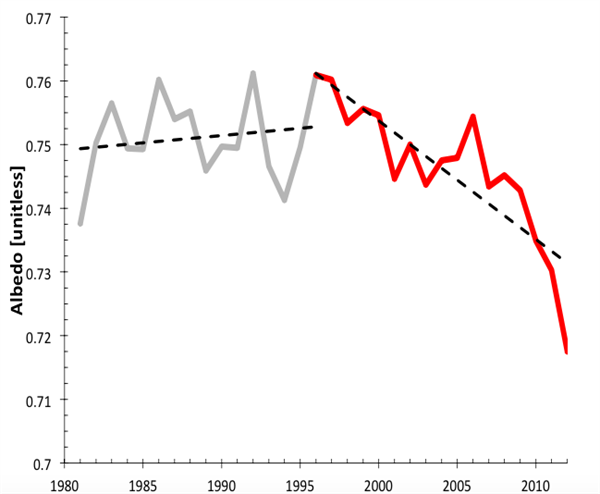
bozzza at 12:55 PM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence

Do the Albedo Changes in Greenland constitute evidence?
Moderator Response:[JH] Image reduced to conform with SkS guidelines.
-
RedBaron at 11:53 AM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
@scaddenp
The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730±40 years. Any SOM older than 5,730±40 years to the end of the last glaciation period would have a C-14 at 50%-75% similar to Fossil fuels. But that's not the whole story, carbon-14 occurs in trace amounts, i.e., making up about 1 part per trillion (0.0000000001%) of the carbon in the atmosphere. Certainly measurable locked in a biological source, but very difficult to distinguish the difference between a stable humus source 50-70% similar to a fossil fuel source having been released into the atmosphere and mixed together. Both will dillute atmospheric C-14 levels, and both have dilluted atmospheric C-14 levels. But that deep SOM largely wasn't released in huge amounts before the industrial age and the spread of the John Deer Plow pulled by tractors and haber process nitrogen fertilizers, disturbing far more acreage far deeper than any previous agricultural practices. That's the key to the puzzle too. The signature is largely hidden in the fossil fuel signature. Very easy to overlook by anyone studying the atmosphere. Mostly the knowledge of this release has been discovered by soil scientists and agricultural scientists (and the quite rare paleosoil scientist like Retallack). Previous to the industrial age the released C-14 isotope ratio from agriculture would have blended in far closer to the O-horizon short term carbon cycle. So it follows the same hockey stick, as they are closely related.
The important thing to note when discussing the Ruddiman hypothesis is his admitted "fatal flaw". He fully admits that the so called "tortoise carbon release" measured is actually larger than his projected effects from human agriculture. Instead of following the concave curve of population growth (and thus the extent of agriculture in populations using agriculture), the release is far larger, earlier and more convex shaped. Ruddiman's "fatal flaw" though is resolved by by factoring in the evidence from Retallack and Sandom. ie the effect the extirpation and extinction of the megafauna by man and the effect that had on the grasslands ecosystems, all of which preceeded agriculture.
In addressing Tom as you requested: In general I have no problems with his rebuttal actually. His arguments are generally sound and I accept his sources. Excepting his measurements include highly degraded ecosystems found now and not even close to what they were before human impact. Not allowing for that change is where his rebuttal fails to actually disprove soil source for AGW hypothesis. In discussing Ruddiman, Tom fails to acknowledge the "fatal flaw" in Ruddiman's hypothesis, unlike Ruddiman himself. Tom actually uses the "fatal flaw" to argue against Teague! Instead of using them to counter each other, it is far better to combine their separate lines of inquiry, each explaining the flaws still present in the other when viewed alone. The evidence and context of all the sources combined into a new systems science synthesis paints a much clearer picture. That is the synthesis I am trying to get at here.
-
sauerj at 11:03 AM on 20 April 2015Shell: internal carbon pricing and the limits of big oil company action on climate
Good Article! ... If I understand right, the $40/tonne-CO2 shadow tax only applies to the CO2 emitted by Shell in the extraction process, not for the CO2 emitted by combusting the product itself.
If true, then the $40/tonne only amounts to $1.69/barrel of crude [math: $40/tonne CO2 x 0.317tonne CO2/barrel_crude(per internet) x 80mmtCO2/600mmtCO2 = $1.69/barrel ... where the (80extraction CO2/600total CO2) ratio comes from data in this article]. If this is all true, the $1.69/barrel is not nearly enough to sway a project's evaluation.
I believe this is point of this article: That, if instead, the shadow tax ALSO included the combustion CO2, then the $/barrel would be 600/80X higher, or $12.7/barrel. Still a bit low. I'm guessing that the real pay-forward/cultural change impacting cost would probably be above $20/barrel.
However, I suppose, even this higher $12.7/barrel "adder" would still fail to influence potential projects (at least for projects involving only FF's), as the $12.7/barrel "adder" would be an equal "adder" on all FF projects, since, in general, all FF's have the near same CO2 combustion/kJ ratio. Now, if non-FF projects were thrown in the project evaluation mix (thus adding to Shell's energy portfolio diversity), then this $12.7/barrel "adder" would then have a lot of sway. ... Again, this is probably what the article is ultimately saying. Thanks! ... GHU!
-
scaddenp at 09:50 AM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
It may have C13 profile that is closer to FF, but I fail to see how even soils from several millenia can have same C14 profile (ie zero) as FF. Are you implying that mass numbers quoted by you so far are only for for deep SOC? (I dont think so) and what evidence you have that there is a substantial contribution of deep soil carbon (the hardest to lose). I would also be interested in your response to points made by Tom.
-
RedBaron at 09:07 AM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
Scaddenp,
Please keep in mind that I am making a clear distinction between "recalcitrant" SOM and "labile" SOM. The SOM isotope profile in the O-horizon is not much different than that found in living vegetation, having a turnover in the carbon cycle measured usually in decades or less and never much more than a couple hundred years unless locked in permafrost. The SOM deep in the A-horizon is very different, often lasting for millenia in a very stable form (unless disturbed), and has a very similar isotope profile as fossil fuels.
-
Tristan at 08:13 AM on 20 April 2015The Scientific Guide to Global Warming Skepticism
Skeptical Science is a strong brand - has there been any discussion related to using the framework and name for other areas in need of science communication (I'm thinking vaccines and GMOs for starters)?
-
scaddenp at 08:08 AM on 20 April 2015There's no empirical evidence
RedBaron, any theory that tries to explain the net increase in CO2 from soil degradation also needs to explain the carbon isotope D13 and D14 ratios in the atmosphere which fit accurately with fossil fuel source (eg see here and here which also accounts for spatial distribution).
-
wili at 06:24 AM on 20 April 20152015 SkS Weekly News Roundup #16B
Thanks for another great roundup.
Minor point--the second title "'3D Cryosat' tracks Arctic winter sea ic" is missing the final 'e.'
Something to consider for inclusion in the next roundup:
Russian Ecologists Warn Summer Could See Repeat of Devastating 2010 Wildfires – or Worse
Moderator Response:[JH] The missing "e" has been inserted. Thank you for pointing this out and for the positive feedback.
Prev 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























