Recent Comments
Prev 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 Next
Comments 44051 to 44100:
-
Riduna at 10:39 AM on 13 August 2013Fox News found to be a major driving force behind global warming denial
Who owns Fox News? And the major newspapers in Australia?
-
Wcalvin@uw.edu at 09:23 AM on 13 August 2013No alternative to atmospheric CO2 draw-down
My proposal “Emergency 20-year Drawdown of Excess CO2 via Push-Pull Ocean Pumps” is a geoengineering finalist in the Climate CoLab competition at MIT.
-
Neven at 07:32 AM on 13 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming

-
kampmannpeine at 07:24 AM on 13 August 2013How much will sea levels rise in the 21st Century?
a bit OT:
When I look at the first curve above (http://www.skepticalscience.com//pics/CSIRO-92-13-sea-level-rise.JPG) then a perhaps interesting idea arises and I hope I am reasoning correctly:
You observe an increase in SL in the last years more than the "red" trend. Having said this and knowing about the "standstill" of global temperature during more than the last decade, this seems to be a good explanation that the heat of the sun went to the ocean more than before (which needs an oceanographic explanation - what I do not know). The only doubt which arises is that the timeperiod of this "steep" rise is only 3-4 years whereas the "standstill" of global temperature is about 10-15 years ... Maybe we find here somebody who has an explanation .... :)
Thus the typical argument of the denialists is kind of falsified by experimental evidence which I think is an important issue. -
Tom Curtis at 07:10 AM on 13 August 2013The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
dn @10 whatever ....
-
davidnewell at 07:03 AM on 13 August 2013The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
This is not a new "religion", it is an observable fact that we are not separate from our environment: and the principles of quantum physics support the premise. You may object to "Gaia"because of it's "in the poppys" overtone..
But don't think for a moment that "science" is a complete or sufficient matrix to describe phenomenae.
What you see is what you get: What you get is what you look for: What you look for is what you see.
If you want to look for something we are NOT "for",
examine the nature of activity hamans have conducted on this planet which threaten Life on it.
"Science", the "intellect" and "the ego", thinking that it is separate from "context", has led to this situation. Now, "science" , and "the intellect" have GOT to be employed to "get us out" of this situation. Only one change, Tom. "you" and "I" and "the planet" are NOT separate.
You can dispute this only in the face of incredibly overwhelming facts staring you in the face.
I'll call it Gaia, and have a sense of what I'm talking about, and it ain't "religion".
regards,
David
-
davidnewell at 06:42 AM on 13 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
KR: My apologies, I am new to this site, and have not explored all it's nooks and crannies.
this seeme to be "on subject", dealing essentially with "weathering of rock" , but I would be glad to start another thread, or do whatever I can to cooperate.
meanwhile, the following is in response to Michael's observations
In response to:
michael sweet
"David,
It strikes me that it is unrealistic to imagine that 100% of the CO2 that passes the waer jet would be absorbed. Find some data to support your claim, or withdraw it."
Michael:
I cannot withdraw an assertion I did not make.
No assertion that 100% would be captured was projected. If you COULD capture 100%, you most definitively would not want to, as downwind vegetation would be significantly affected.
My WAG as stated above, is here replicated for your reading convenience:
=
quote:
"i GUESS that between 8% and 15% can be 'caught": but this is a guess."
Unquote:
Further, the following tests are indicated:
from the paper:
"Attachment three" details these tests, (as well as a proposed field trial), but following is a summary of them.
1. Drift droplets of pure water, ocean water, and ocean water from over playa soils, through various sized nozzles, through an enclosed cylinder of air, while monitoring the reduction in the amount of CO2 in the air over a time interval.
This experiment will show the effectiveness of the proposed water source options, and the effects of changing the droplet size.
2. Perform the same tests through an extended archway with a specified rate of air flow through it, measuring the humidity and depletion % of CO2 in the air at the exit.
This experiment will generate a better profile of anticipated effectiveness of air droplets rising and falling in the proposed construct.
Proposed field trial:
3. An approximately 30 HP water pump should be provided to pump basic pH ~9.1) and saline Carson Sink water into the air in a breeze, utilizing the "tuneable spray nozzle" of "attachment one" (or similar), with upwind and downwind measurements of CO2.
This test will demonstrate the more expensive option, (which is likely to be the most effective), which relates to dumping water on the playa after it has been used to generate electricity, and using the power produced to drive a pump which sucks up the water again and produces the spray.
A "Request for Proposal" (RFP) is being drawn up in regard to these tests, and will generate actual quotes
==================
You (Michael) said:
"The volume transport of the overturning circulation at 24 N has been estimated from hydrographic section data ([4]) as 17 Sv (1 Sv = 106 m3/s),
The currents off of Chile also move a tremendous volume of water. How can you compare the amount of CO2 your scheme would remove to the CO2 those currents absorb?
Mr. Sweet, your source, http://www.pik-potsdam.de/\u126 ~stefan/thc_fact_sheet.html, doesn’t open.
Perhaps I’m missing something, but it appears you are speaking of the mass transport of the current, whereas the key point of the above proposal is a function of the surface area .
Would you like to see a calculation of surface area on the flow of water subdivided into various size droplets sprayed through the air?
(As stated by Glenn in post # 28:
The surface area of all those aerosols up there is huge. A sphere with a surface area of 1 m2 has a diameter a bit over 1/2 meter. Split that into micro spheres with a diameter of a micron and the total surface area increases by a factor of over 1/2 a million!)
michael,
Do you think that the principle mode of ocean CO2 absorption occurs directly across the surface of the ocean, or do you think it may significantly derive from rainfall and ocean spray?
What do you think happens to mists of neutral water collected in a tray after falling through 8 feet of fall?
The pH goes through interesting curves,, but winds up around pH 5.6 if I recall.
You asked (again, and I will answer again)
Where will all the salt go?
The 3% NaCl content of the water would be of no significant concern on the already saline playa under discussion.(Of which many others of similar saline character can be found) The volume of soils in which it would be mixed, over decades, would be be of no concern. On the other hand, if it is seen as a desireable commodity, the locus of the spray heads and their localized retention podns can be changed frequently, and the prior spray surface allowed to dry, at which time the NACl can be scraped up and utilized Other places. One way, or the other, it's not a problem.
Uou observed:
According to
the state of California, the total electricity generation in California is about 74,000 MW. Since you claim at post 24 that 835 MW is 1/3 of the power used in California I am inclined to think you need to check your math much more carefully. It is unreasonable to imagine that 1/3 of the power in California is used to pump that single water station. In general, the amount of water that would need to be pumped is far beyond any reasonable amount that could be pumped. Where would the gigantic amount of energy come from?
Thank you, Michael, I can’t find my source, and it appears to be in error anyway, I will retract that.
The salient point intended to be communicated, was that the "power source" for the enterprise can be compared to existing plant used for the same purpose: moving water.
Regards,
David
-
Tom Curtis at 05:56 AM on 13 August 2013The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
davidnewell @8, any mention of gaia that is not purely metaphorical is simply mysticism. Humans are not "for" anything within the purview of science; and if we are "for" something, that thing will be found within the texts of some traditional religion. Further, absent a direct causal link between the presence of highly alkaline soils and increased rainfall, claims that anticipated increased rainfall on one region with such soils have a teleological basis are (yet again) mysticism. Don't for a moment imagine that your new religion has any basis in science.
-
davidnewell at 05:27 AM on 13 August 2013The Albedo Effect and Global Warming
william at 06:43 AM on 1 August, 2013
releasing heat and water vapour to the atmosphere or thinner ice doing likewise. Gaia is trying to fight back.
Right on! Totally agree! We humanoids think we're "all that", and we HAVE evolved "intellects" which have gotten ALL of Gaia endangered...
but.."what we are for" ( as close as I can intuit/express it) is to see what the INNATE intelligence of the "larger system" is trying to "do", and help it along.
============
For instance, there is a focused change anticipated in weather patterns in the Northern Pacific, which is anticipated to drive precipitation into Northern Nevada. Why?? So that rain can fall on the pH 10 (or so) alkaliine soils found so abundantly in that locale, in the Great Basin.
Thus cometh (pat pending)
"Carbon Dioxide Direct Air Capture and Sequestration Utilizing Endorheic Basin Alkaline Deposits to Effect Mineral Carbonation"
all WE have to do, is quit being a "ME", and become open to ??whatever is apparent to do.."
We are all in this together.
-
DSL at 03:52 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
While concentration is not volume, it becomes an indicator of volume when looked at in the middle of September. I often use the following two images to stun people into awareness. I have them open up each in its own tab.
-
Geoff Hughes at 03:44 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
Thanks, everybody.
-
Chris G at 03:31 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
In case it isn't obvious, I'd just like to point out that the albedo flip feedback is not limited to sea ice. I've read that the extent and/or duration of snow cover on land is also decreasing, and that also creates an albedo flip.
-
Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
I would suggest that discussions of geoengineering methods (as per davidnewell above) be taken to an appropriate thread on geoengineering.
-
barry1487 at 02:29 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
Monthly averaged ice volume for September 2012 was 3,400 km3. This value is 72% lower than the mean over this period, 80% lower than the maximum in 1979, and 2.0 standard deviations below the 1979-2011 trend.
The figures quoted here and in the article represent the volume of ice loss for Septembers (when Arctic sea ice is at minimum extent/area/volume) since 1979.
-
barry1487 at 02:21 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
Geoff,
http://psc.apl.washington.edu/wordpress/research/projects/arctic-sea-ice-volume-anomaly/
-
jja at 01:45 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
Geoff Hughes
Wipneus PIOMASVolume data with various best-fit curves.
-
Geoff Hughes at 01:36 AM on 13 August 2013Global warming, Arctic ice loss, and armchair scientists
"the volume of ice has decreased approximately 75% over the past 3 decades."
Can this be true? The link shows the sea ice anamoly and trend, but I do not know how to calculate the percentage change in volume from the information on the graph. I was expecting to see some beginning and ending actual volumes, say, 100 units of ice declining to 25 units over the 30 years. Could you please explain the loss in volume more fully?
-
Leland Palmer at 15:38 PM on 12 August 2013Toward Improved Discussions of Methane & Climate
Here's an interesting paper, on the PETM and the series of smaller Eocene hyperthermal events with accompanying carbon isotope excurstions that followed it, called in this paper the ETM2 and ETM3 events:
Past extreme warming events linked to massive carbon release from thawing permafrost
The authors present seemingly convincing correlations between the ETM2 and ETM3 events and orbital variations in insolation. They suggest a negative correlation with CaCO3 content of sediments during a series of orbital variations surrounding and including these events.
They claim that high latitude melting of permafrost and associated positive feedbacks are the likely cause of these hyperthermal events.
Unfortunately, other authors claim that the PETM (called ETM1 in this paper) and the other Eocene events have similar C13 and O18 excursion correlations, which demonstrate that the carbon source is similar or identical.
And, the initial sharp phase of the PETM/ETM1 occurred very rapidly, in less than about 200 years- seeingly too rapidly for any other explanation except methane hydrate release.
So, if the PETM/ETM1 was a hydrate release event, and the other events have matching C13 and O18 isotope excursions, then ETM2, ETM3 were also likely mainly methane release events, I think.
So, we are arguably left with a series of orbital climate change driven methane releases.
-
dwr at 15:15 PM on 12 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
CBDunkerson: Thanks for the response.
I see that DMI states that its current 15% sea ice extent estimate "can differ slightly from other sea ice extent estimates".
Something of an understatement.
-
Glenn Tamblyn at 14:24 PM on 12 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
I have sometimnes wondered about an alternative approach to capturing and sequestering CO2, piggy-backing of the fact that we may well need to look at geo-engineering answers down the track.
The most technically viable geoengineering answer seems to be injecting large volumes of aerosols into the atmosphere to reflect sunlight and cause some cooling. Certainly it is a very far from ideal answer since you still get a lot of other climate impacts, even if aggregate warming were reversed, and it does nothing about ocean acidifcation. But we may need to go down that road anyway.
So, since we are possibly going to put 'something' up there any way, why not look at whether we can get that 'something' to do double duty and help with removing CO2 as well as reflecting sunlight. If we lofting large quantities of microscopic particles, the surface area of all that material is enormous - perfect for enhancing rates of chemical reactions.
What if we simply crushed the very terrestrial rocks that are involved in weathering into fine dust and lofted that into the atmosphere as an aerosol, massively accelerating the natural rate of weathering. Instead of Carbonic acid falling from the sky and weathering happening on the ground, we might instead have see things like calcium bicarbonate falling in the rain.
Would that sequester carbon? Or would it just mess up the chemistry of the oceans even further?
Failing that, could some smart chemist come up with another reaction that we could use that would achieve a similar result. Up there wwe have some wonderful resources; CO2, H2O, O2, N2 and energy in the form of sunlight. All the buidling blocks for most of the known chemicals found in Organic Chemistry. Surely someone can think of a chemical pathway that will work.
The surface area of all those aerosols up there is huge. A sphere with a surface area of 1 m2 has a diameter a bit over 1/2 meter. Split that into micro spheres with a diameter of a micron and the total surface area increases by a factor of over 1/2 a million!
A precious, precious resource.
And if we can get the chemistry right, a far far more efficient method of trying to draw down CO2 than any of the more mechanical approaches being considered down on the surface.
-
vrooomie at 12:51 PM on 12 August 20132013 SkS Weekly Digest #32
The cartoon reminds me of the hamster, in Joe Cartoon.....:)
-
scaddenp at 09:58 AM on 12 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Michael, not that it make a lot of difference but 74GW is capacity not generation. From the actual generation, it seems average generation is 22000MW.
-
michael sweet at 09:34 AM on 12 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
David,
It strikes me that it is unrealistic to imagine that 100% of the CO2 that passes the waer jet would be absorbed. Find some data to support your claim, or withdraw it. The volume of water you want to move seems to me to be much too small to absorb a significant amount of CO2. You realize that
The volume transport of the overturning circulation at 24 N has been estimated from hydrographic section data ([4]) as 17 Sv (1 Sv = 106 m3/s), source
The currents off of Chile also move a tremendous volume of water. How can you compare the amount of CO2 your scheme would remove to the CO2 those currents absorb?
Where will all the salt go?
According to the state of California, the total electricity generation in California is about 74,000 MW. Since you claim at post 24 that 835 MW is 1/3 of the power used in California I am inclined to think you need to check your math much more carefully. It is unreasonable to imagine that 1/3 of the power in California is used to pump that single water station. In general, the amount of water that would need to be pumped is far beyond any reasonable amount that could be pumped. Where would the gigantic amount of energy come from?
-
davidnewell at 02:39 AM on 12 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Oh yeah, and obviously the technique is imminently scaleable.
-
davidnewell at 02:37 AM on 12 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Michael:
Thank you for your question.
PHYSICAL PLANT PROPOSAL
Scale of the proposal, by comparison to an existing pumping structure
1/3 of the electricity used in California, year to year, is employed to power the Edmonston Pumping Station, which lifts fresh water across the Tehachapies, from Northern to Southern California
Edmonston Pumping Station profile:
Normal static head: 1,970 ft
Total flow at design head: 315 ft³/s (9 m³/s) (per unit)
Motor rating: 80,000 hp (60MW)
Flow at design head: 315 ft³/s (9 m³/s) (per uniit)
Total flow at design head: 4410 ft³/s (450,000 m³/h) (Combined)
Total Motor rating: 1,120,000 hp (835 MW)[2]
========================
Hypothesizing broadly, a 3/4 to 1 gigawatt power plant
could lift 1/3 the water, or ~1470 cu. feet of water second (150,000cu.M/ Hr.)
3 times as high, or ~ 6,000 feet.
This would enable a 2,000 foot "head" of pressure to effect delivery of the ocean water to wherever you may want to run the pipes: in Nevada, whose playas are at approximately 4,000 feet above sea level.
This comparison is made so that the project can be seen as imminently "doable" if the will to do so is established.
The envisioned structure would consist of pumps to convey Pacific Ocean water from (probably) the vicinity of Eureka, to lined retention basins located on the Eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada, and thence released and conveyed by piping as circumstances dictate through spray nozzles arranged on the upwind side of the playas to be so utilized. (Sketches are found in the attachment # 1)
In my sample, I used the Black Rock Desert Playa as the "example.": it is both relatively close, and better characterized than any of the many other playas which could be employed. (And is a "saline" playa, and thus not changed in this protocol..)
The spraying of ocean water through adjustable nozzles in fans of approximately 150 foot radius will generate "customizable " droplet sizes to effect varying degrees of CO2 absorption and water evaporation.
Presuming then a 150 foot radius spray fan, and an average wind speed of 10 MPH, the volume of CO2 which will pass through the plane of the fan half-circle, per year, is ~ 400,000 metric tonnes. This is for one "spray rig", and, ultimately, thousands are envisaged. (See note __)
============
It would be desirable to isolate portions of the Playa downwind of the sprayers to retain the water in shallow local ponds. The pH of the impounded waters would be monitored, and deeper levels of the playa soils would be accessed by the use of water jets to"drill down" through the consolidated clays, when necessary. As precipitated carbonates and salts build up in the impoundment, the location of the spray nozzle may be moved to a new area.
It remains the results of field tests to determine which method of spraying water will be the most satisfactory:
—The direct spraying of ocean water above the playa surface
—The vacuum induction of supernatant playa water into the nozzle stream, similar to an "aspirator" mechanism
or
— The regeneration of electricity at the spray head location so that supernatant playa water can be pumped through the nozzles.
In addition, imparting an electrostatic charge to the droplets through electrification of the spray nozzles may be contemplated, to both keep the droplets discrete from one another, and/or modify the residence time of the flight path of the droplets, as described in exhibit 2.
==============
The 3% NaCl content of the water would be of no significant concern on the already saline playa under discussion.(Of which many others of similar saline character can be found) The volume of soils in which it would be mixed, over decades, would be be of no concern. On the other hand, if it is seen as a desireable commodity, the locus of the spray heads and their localized retention podns can be changed frequently, and the prior spray surface allowed to dry, at which time the NACl can be scraped up and utilized Other places. One way, or the other, it's not a problem.
===============
Cost estimates, AKA Wild Guesses:
Estimated cost of the proposal implementation:
Edmonston Pumping Station was referred to earlier as an example of scale. It cost ~$6 billion dollars to build. It flows more water than the proposal, and therefore has larger pipes, but the distance of pumping is shorter than the proposal requires. These facts tend to offset one another.
Obviously, there are many variables beyond my best guesswork which will modify the actual cost.
Should the State of California redirect the energy for the Tehachapi pumps to this project, there would be no need for the construction of another power plant.
Since this seems unlikely, in would not be unrealistic to anticipate another $10 billion in the construction of another power plant.
It may be noted that if the power plant was co-located with the pumping plant, near the ocean, that the cooling water for the power plant could be part of the water pumped, thus alleviating the environmental problems related to hot-water discharge.
==============
The scale of the investment needed is (again a guess) about what farmers have put into central pivot irrigation systems over the past 40 years or so.
"my" proposal dwells with conditions extant in my "local endorheic basin", whose relatively recent collection of huge quantities of cations from the local fresh granite surface seem, to my eyes, to be a relatively rare occurrence:
however, there may be many other places in the world where it would be easier to provide ocean water to, and spray over alkaline clay-like soils: but I'm not familiar with them. It IS unlikely that the huge QUANTITIES of material are to be found elsewhere: (as is found in the Great Basin...) but if the source water is cheaper to obtain, then it's worth considering.
==================
If it works, it is of course worth the energy, despite the APA's summation of 18 months ago, which is that "Direct Air Capture" is a non-runner.
The differences in this are:
the huge area of sprayed liquid constitutes "the collector", and this offsets the fact that th pH is "moderate", not "highly" alkaline.
The "10 mph average breeze" consitutes the "air mover"
The "reactant" doesn't have to be "desorbed" from the collected CO2, at 600 degrees plus, and recycled.
There is no concern about taking "desorbed and liquified" CO2 to some other site and injecting it...
There is a certitude that the mineralization of CO2 will in fact provide "geologic interval" sequestration.
(gratuitous commentary alert..)
Also, on a personal level, I find this to be an exemplification of the (to me) apparent fact that "what we are for" on this planet, is to "help out" the planet "work", not drive towards individualized "wealth". ALL this is, is an elaboration and an "assist" to "how the planet works".
(end gratuitous comment.)
Please throw me another objection
I appreciate the opportunity to dialogue with people about this premise, who have an understanding of the perilous times we are in.
Sincerely,
David
-
John Hartz at 01:00 AM on 12 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #32B
Michael: Thanks for bringing the newly released California report, "Indicators of Climate Change in California," to everyone's attention. I'll highlight it in this week's Weekly Digest.
-
michael sweet at 21:30 PM on 11 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #32B
The state of California released a report that describes the measured effects of climate change in California. The linked page has a link to the press release, the report summary and the entire report. This is an update to a report originally written in 2009. The report summary includes a list of the effects that had been updated or were new. I found it interesting to see what the new effects were relative to what was known in 2009 (black carbon and ocean acidification were among the new sections).
-
chriskoz at 21:24 PM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
BC@13,
Thanks for the pointer to the excellent post by Tamino, of which I am aware. Note that Tamino (as well as Hudson 2011 in large part) estimate the forcing from just the sea ice extent data. They model the resulting albedo change between sea ice and open ocean as 0.2 and calculate the resulting extra amount of isolation penetrating water. They asume no changes in other parameters. In particular, the type of ice and the clouds stay the same.
Riihela et al., (2013) however went beyond that, and have derived the albedo from satelite observations and shown that the type of ice has also changed, quote from the abrstract:
...we present an analysis of observed changes in the mean albedo of the Arctic sea-ice zone using a data set consisting of 28 years of homogenized satellite data4. Along with the albedo reduction resulting from the well-known loss of late-summer sea-ice cover5, 6, we show that the mean albedo of the remaining Arctic sea-ice zone is decreasing.
I don't have access to the full text so I am not sure if my understanding is correct, but I think their sea-ice zone albedo of −0.029±0.011/decade is just the result of change in quality of the remaining ice: i.e. ice becoming darker. Therefore, the resulting climate forcing should be calculated and added on top of Hudson/Tamino forcing. Having reread the former, ignoring the math, I do not feel the extra forcing from Riihela et al., (2013) will increase the perceived .1-.13W/m2. In any case, without unknown methane feedbacks, it is not signifficant (yet) compared to the primary CO2 forcing.
I guess "dark snow" project by Jason Box may shed additional light on the decreasing albedo in Arctic. So I'm looking for its results... -
jja at 17:12 PM on 11 August 2013How much will sea levels rise in the 21st Century?
After crafting a lengthy response and then having it lost due to time out of login status I will summarize.
@davidnewell I am sorry, the 180 GTco2 was not 2100 it was 2050 here: figure 38 China LBL 2050 emission
MA Rogers @30
Thank you for showing me that, I do not exactly grasp the difference between the measured energy imbalance and the RF value, they should be the same in my mind. What am I missing?
The value I used was indeed RF values not energy imbalance. If I use your math and Hansen & Sotos value of .75 (they adjust for the solar minimum) I get a value of (7.5 * .75/.58) * 1.2 which is equal to 11.6 ZJ p.a. this will make a total earth cumulative energy imbalance of 1,000 ZJ by 2100 (86 years) If even a few of the non-linear feedbacks are taken into account and a higher (more realistic) emission scenario is used then the value of energy imbalance by 2100 could easily be 4-6X the current value. Therefore the total cumulative energy by 2100 will be closer to 3,000 +2,000/-1,000 ZJ . This will increase if I used the slightly higher values of Balmaseda, Trenberth & Kallen
In addition, if the ECS value is 4.3 then surface warming will be greater and the proportion of heat transferred by convection to land-based ice will increase.The AF is discussed in Terenzi & Khatiwala here:
We believe that the increase in AF can be explained simply by a decrease in the capacity of both the ocean and land-biosphere to absorb anthropogenic carbon, as evinced by decreases in both OF and LF (not shown). This is likely due to saturation effects such as changes in the oceanic Revelle buffer factor (e.g., Keeling, 2005). Indeed, when we linearize the chemistry, which in effect holds the buffer factor fixed, the upward trend disappears (not shown). Thus, even with a fixed emission growth rate, our model, with no carbon-climate feedbacks, predicts future increases in AF because of the nonlinearity of the carbon cycle.
Yes, with a more rapid loss of arctic sea ice, the increase in boreal emissions and the potential for collapse of natural carbon sinks will incrase the AF even greater, couple this with a more realistic emissions scenario and 5 or even 21 M of SLR by 2100 will be barely noticed by a loose group of remnant humanity living hand to mouth for basic survival.
-
Riduna at 17:01 PM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
Faster Warming Means Less Ice
-
Tom Curtis at 07:10 AM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
rockytom @15, whatever his other vices, Spencer cannot have lied simply by saying that Antarctic sea ice was increasing while Arctic sea ice was declining:
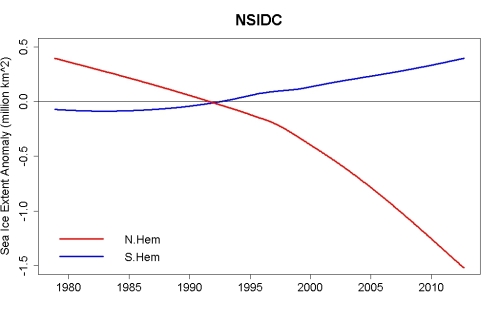
(Tamino)
Tamino had this to say in his most recent comment on Antarctic sea ice (of which I am aware):
"Both [Antarctic sea ice area and extent] have shown increase over time which is statistically significant. The smoothed values for extent have increased by about 0.57 million km^2, area by about 0.51 million km^2. The reason for its increase is uncertain, but two possibilities which have been suggested are: 1, increased precipitation (snowfall) due to warming near the tropics; 2, intensification of the “polar vortex” perhaps due to changes in stratospheric ozone concentration.
Despite the fact that the southern ice pack is larger overall than the northern, its increases are much smaller than the decreases noted for the northern hemisphere, 1.96 million km^2 in extent and 1.92 million km^2 of area. This puts the lie to claims (oft repeated) that southern gain even “almost” balances northern loss — the northern extent loss is 3.4 times as great as the southern extent gain while northern area loss is 3.8 times as great as southern area gain. When one is nearly 4 times as big as another, they are certainly not “balanced” and anyone who claims so is either a fool or an outright liar."
(Original emphasis)
I don't have much to add to that except to note that the extended satellite record from 1973 shows a declining trend in Antarctic sea ice due to an initial sharp decline from 1973 to 1978 (PDF). Further, while Manabe et al (1991) predicted a thickening of Antarctic sea ice, and some more recent models (3 of 12 assessed by Stroeve et al (2007) also show a declining trend - the models are not consistent enough on this point to say that either increasing or decreasing Antarctic sea ice in the short term are prediction of climate science. Sea ice dynamics are not captured well in climate models either in the Arctic (where the decline is massively under predicted) nor the Antarctic (where the predictions are inconsistent between models).
-
william5331 at 06:10 AM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
If the sea releases heat into the atmosphere, this cools, not warms, the ocean. It also releases more water vapour into the atmosphere which can cause low pressure weater systems with accompanying clouds. This increases Albedo. This is clearly seen this year (2013) and while it will only delay the ultimate melt, it is interesting to see Gaia fighting back.
-
CBDunkerson at 04:09 AM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
dwr, the DMI page states that it uses 15% sea ice extent. There is also a red note at the bottom which says they recently changed their methodology to adjust for coastal zones. A link in that red text goes to the version prior to the adjustment... which seems more in line with the other sources.
http://ocean.dmi.dk/arctic/icecover.uk.php
Thus, the higher ice extent DMI is showing compared to the other sources is apparently due to the fact that they are now measuring the ice extent over a larger total area.
-
rockytom at 03:28 AM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
I recently watched Roy Spencer lie to congress ( a U. S. Senate committee) by stating that although sea ice was declining in the Arctic, it was increasing in the Antarctic and concluding that other testimony to the same committee on Arctic sea ice was only part of the story. It was Spencer who told only part of the story as he did not mention that the polar ice in the Antarctic is land based while that in the Arctic is sea ice (adjacent to Greenland which is land ice) and that all areas are losing ice as the planet warms. There is solid evidence that ice shelves tied to land ice in Antarctica are losing ice by being undercut by warming seas, therefure speeding Antarctic glaciers movement to the sea. Spencer's testimony was astoundingly simplistic, but not unexpected from such an "expert."
-
keitho at 01:44 AM on 11 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
Thank you for posting this fascinating article. The effects of reduced albedo, even at very high latitudes and hence low angle of incidence of the sun's rays , are obviously very important.
The other effect of reduced sea ice must be the reduction in insulation of the Arctic ocean water. Presumably open sea water must be able to release heat to the cold atmosphere, without the inhibiting effect of a blanket of ice covering it, more readily. Does anyone have any thoughts on this?
-
StealthAircraftSoftwareModeler at 22:36 PM on 10 August 2013CO2 effect is saturated
Moderator [DB] post to my comment @266: I cover several things in my post, but they covered the three items in Tom Curtis’ post at @263. He was not called out for “being all over the map.”
He claims in 263:1 that I do not seem to understand what models are, and I show that I build software models for a living. I may not know a lot about LBL models, but I know a lot about software, physics based models, testing models, and so on.
Then Tom Curtis covers lots of excellent data in 263:2 and the Dessler 2008 paper. This shows that LBL models are accurate in computing reduced IR flux for CO2. This is directly related to whether not CO2 is fully saturated, is it not? I was questioning this because I was concerned about the accuracy of models because Myhre 1998 use models to arrive at the 5.35 coeffcient in the generally accepted CO2 forcing function (ΔF = 5.35*ln(C/C0) W/m2). TC showed support that models (including MODTRAN) are pretty accurate. I believe that now, for the most part.
In 263:3 he jumped on Lindzen with valid comments, so I with drew my usage of his comment about the effects of CO2.
Then my longest part is a lot of data about MODTRAN and the reduction of IR flux. MODTRAN has been shown to be accurate by Tom Curtis in 263:2 and Dessler 2008, so I am using its data. My ultimate point is that both Myhre and MODTRAN cannot be correct. The entire topic is about whether no CO2 is fully saturated. This is all about the CO2 forcing function (ΔF = 5.35*ln(C/C0) W/m2) from Myrhe 1998 and the coefficient of 5.35. I run MODTRAN and I get 4.58 in clear skies. In cloudy skies I get a value of 3.61. Most of the planet is cloudy, so the 3.61 value, if MODTRAN is correct, is probably more accurate. These values from MODTRAN disagree with Myrhe 1998. I am not claiming incorrectness on anyone’s part – only showing that they are inconsistent. You guys cannot claim that CO2 is not fully saturated and it has a large effect because of the 5.35 coefficient, then claim that MODTRAN is accurate.
Does this help clear up my point? And does it show that I am actually on topic?
-
Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
Chriskoz at 1. There was a post by Tamino 6 October analysing the forcing due to Arctic albedo changes
http://www.skepticalscience.com/arctic-antarctic-sea-ice-insolation.html
Here's an extract from the article -
In fact Hudson states that
"Results show that the globally and annually averaged radiative forcing caused by the observed loss of sea ice in the Arctic between 1979 and 2007 is approximately 0.1 W m-2"
-
dwr at 22:09 PM on 10 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
I've been pondering over the sea ice extent data recently. In particular I'm struck by the disparity between DMI's extent and that of JAXA, NSIDC, ROOS... in fact, *all* of the others.
As of 9th August, DMI indicates cover of 8.5 m/km^2; the others are around the 6.5 m/km^2.
I know that DMI use 30%, whereas most of the others use 15%; but then I'd have thought this would have made DMI extent smaller rather than larger than the others? Surely there are more cells with 15% ice than 30% ice?
And even accounting for the percentage difference, surely 2 m/km^2 is too large an extent difference to be explained by different counting methods?
Can anyone offer an explanation or tell me where I'm going wrong?
Thanks.
-
chriskoz at 18:38 PM on 10 August 2013Reflections on a changing Arctic: Less ice means faster warming
Russ@5,
I don't know what your "different picture of global ice" means because mod has snipped you (no doubt rightly so) but I agree the picture of antarctic ice is quite different. That's why this article about Arctic does not consider Antarctic, not because, as if, according to you, "the Earth had only one pole".
Other commenters already hinted the differences. I'd like to add, that the different response of antarctic ice is consistent with the global warming we are experiencing. Notably, the recent studies have linked the increased antarctic winter iceshelves with the decreased salinity of surface waters due to the melt of antarctic icesheet. So, that phenomenon should not be seen as a "sceptic"-proclaimed "recovery" but as another bad news, that we are loosing the antarctic icesheet - at increasing speed.
-
TonyW at 17:35 PM on 10 August 2013It's methane
Methane levels started to increase again, about 6 or 7 years ago, so this explanation needs updating.
-
scaddenp at 14:06 PM on 10 August 2013CO2 effect is saturated
Sorry looking further up, I see you have answered the question about the distinction in models.
-
scaddenp at 14:04 PM on 10 August 2013CO2 effect is saturated
Please can we make sure that you are not confusing models in the sense of GCM (which would have a complexity considerably larger than say CFD models for airplane simulation) and LBL models which would be at least an order of magnitude simpler, mathematically and computationally. I cant see why you think the accuracy of 5.35 is so important - how much difference does it make whether it is 5.1 or 5.8? To my mind, this part of the equation pales to insignificance compared to uncertainities in feedback.
It also puzzling how you can read and Dessler (read the more recent papers) and yet make a statements about effect of cloud uncertainties. The best we have would put the net effect of clouds about approximately zero. If you have a substantial criticism then perhaps follow up here or here. Note that clouds are both positive and negative.
It would also be interesting to know what your alternative hypothesis is. If the obviously change in net forcings is not cause of observed climate, what do you propose instead and what is your case for this making physical sense.
-
Klapper at 13:57 PM on 10 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #32A
@Klapper #3:"Moderator Response:[DB] Assertions lacking evidence get disregarded quickly."
Using data downloaded today from the NOAA/NCDC (ftp://ftp.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/anomalies/monthly.land_ocean.90S.90N.df_1901-2000mean.dat) show the following annual averages by global temperature anomaly rank for the calender year:
Rank Year Global SAT anomaly 1 2010 .658 2 2005 .651 3 1998 .633 4 2003 .623 5 2002 .612 6 2006 .597 7 2009 .595 8 2007 .589 9 2004 .578 10 2012 .575 As you can see the assertion that the rank range is 8 to 9 is incorrect. The RSS global TLT anomaly is 11th.
-
StealthAircraftSoftwareModeler at 13:23 PM on 10 August 2013CO2 effect is saturated
Tom Curtis @263:
It has been a little while for me. Sorry for responding slowly and appearing to drag out a topic, but I read what you guys send, I do some research, and I think about things a bit. I’m trying not to jump to conclusions and I am really trying to dig into things to get a better understanding.
1) I think I have a pretty good idea of what models are, why they are built, how they are used, and what many of their weakness are: I have a physics degree and computer science degree and have been software building models for 30 years for aircraft, threats, radars, missiles, various aircraft sensor and weapons, and earth components such as terrain and weather (not climate, but weather as it impacts these systems). I test my models for aircraft with other models, measurement data in labs and anechoic chambers (http://www.tdk.co.jp/tfl_e/chamber/chamber01/5.html), tests from poll models (http://www.thehowlandcompany.com/radar_stealth/Bluefire_Helendale.htm) and actual flight tests. I know from first hand experience that testing is critical and that models and lab tests do not always match very well to what happens in the real world.
My question @261 was more related to verification and validation of the various LBL models as they relate to the atmosphere. My concern was for the accuracy of the 5.35 coefficient in the CO2 forcing equation. If this value was derived from models without any real world measurements to back it up, then I would be highly suspicious of it.
I would not dispute Newtonian mechanics for orbital prediction since that is easy physics. The climate, however, is very complex and making accurate predictions is hard. Think more along the lines of trying to predict where a gold ball will land after being hit with a golf club. Let’s say we need 1% or 2% accuracy too. That is wicked hard even if you know the exact initial conditions of the ball when it leaves the club face. You will have to run a complex and iterative numerical-methods simulation that considers many things: winds, ball drag (which is a function of many things), spin on the ball, lift induced by rotating body, and so on -- hard stuff to be accurate. Think about why we have GPS and laser guided bombs (which I know a lot about) – we do not use dumb unguided bombs because they are very inaccurate -- we can model the physics with extreme precision but still cannot hit anything with a dumb bomb. There simply is too much uncertainty in the environment, even on a very small scale. Therefore, we install guidance and targeting systems to compensate for errors and drift as it develops during the bomb delivery. (I also think the iterative growth in errors within GCM is a huge problem, but I’ll get into that over on the models topic).
2) I dug into Dessler et al 2008 in JOGR, and that was an impressive study and test. That helps me gain confidence that the models are at least in the ball park in terms of accuracy with respect to the real world. Excellent charts, data, and a great study on Dessler’s part.
3) I was wondering if the Lindzen reference was the same guy at MIT. I wasn’t sure and I wasn’t claiming or supporting it at all. It was just a data point in a list of points about the effects of CO2 and how they varied a lot. Granted, Lindzen was an extreme outlier and I withdraw his data point from my previous point @261.
I spent a bit of time playing with MODTRAN running numbers on the reduced IR flux from CO2 and cloud effects. Since the chart you reference above shows that MODTRAN matches fairly close to IRIS Satellite data, I think my analysis below should be accurate.
I found that for no clouds and CO2 at 294.3 ppm the IR flux is 288.97 W/m2. At 800 ppm CO the IR flux is 284.39 W/m2. The ratio of 800 to 294.3 is approximately e, so the natural log of this is very close to1. Using this I compute that coefficient for the CO2 forcing function is 4.58. This is 15% less than Myhre 1998, and his value of 5.35 is 15% less than the previous IPCC value of 6.3. I am sure that Myhre is a good scientist, but it seems that MODTRAN has been shown to be accurate, yet its output disagrees with Myhre. I find the wide range of values from MODTRAN, Myhre, and IPCC over the last decade not very reassuring in that scientists have a solid grip on these values. I know and fully accept that it is a very noisy world, so I fully expect that this value is hard to determine.
Furthermore, when I run similar numbers using clouds in MODTRAN, I get an IR flux of 261.78 W/m2 for 294.3 ppm CO2, and 258.11 W/m2 at 800 ppm CO2. This yields a CO2 forcing function coefficient of 3.61, which is 21% less than MODTRAN with no clouds, and a full 33% less than Myhre. So while CO2 is not technically fully saturated, its effect is small relative to clouds. The reduced IR flux just from clouds alone is 27 W/m2 when compared to clear sly. Since 60% to 70% of the earth is covered with clouds, it seems logically correct to me that clouds are a major player in IR flux. If doubling CO2 reduces IR flux by 3.7 W/m2, but clouds reduce it by 27 W/m2, then clouds are over 7 times stronger than CO2. A small change in cloud coverage could easily overwhelm the effect of CO2, making the issue of whether or not CO2 is fully saturated really a moot point. Is this not correct?
Given the magnitude of the effect of clouds, how has climate science determined that most of the global warming since 1950 is most likely due to CO2? That seems like an impossible thing to determine. In 1950 CO2 was about 310 ppm and today it is 400 ppm. Even using Myhre’s CO2 forcing coefficient of 5.35, CO2 has only blocked 1.36 W/m2 in the clear sky portion of the atmosphere. Where there are clouds the effect is even less. Isolating CO2 when so many other moving parts of the earth’s energy balance are also changing seems impossible, especially given we do not have very good data on clouds since before satellites (about 1970). How can the IPCC claim that it is very confident that CO2 has caused most of the recent warming?
KR @265. The devil is always in the details. The horse is never dead. There is nothing that is *true*. Science can only falsify things and cannot prove something to be true. Some scientific theories are accepted as true only because they have withstood the test of time and have not been shown to be false. I seriously doubt that climate science is any where near achieving this status.
Moderator Response:[DB] You are all over the map here, with much of your comment off-topic for this thread. Please direct comments towards models to one of the model thread. Your question about attributions is discussed on a number of threads, summarized here.
Assuming scientists do not know what they are doing because it disagrees with your preconceptions is simply arguing from your personal ignorance. Much of what you claim is unknown is actually fairly well-understood by science.
It would be helpful to adopt a more streamlined approach to both your comment construction, the threads on which you place them and operate with less of a presumption that the science must be wrong.
-
DSL at 13:10 PM on 10 August 2013Fox News found to be a major driving force behind global warming denial
Change, the best recent piece I've seen on that observation is from Michael Fumento, a Reaganite, and it includes commentary on AGW.
-
A Change in the Weather at 12:24 PM on 10 August 2013Fox News found to be a major driving force behind global warming denial
I don't think "conservative" is the most accurate descriptor for Fox News. Limits, moderation, and restraint are conservative ideas. Respect for the truth is a conservative idea. The scientific method is the epitome of a conservative idea. Fox exhibits these rarely. More often, they loudly express radical, reactionary, antisocial ideas that deny science and disrespect the truth.
-
michael sweet at 12:00 PM on 10 August 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
David,
How much energy will it take to pump that much water from the Pacific up to the Great Basin? Where will that energy come from? Is that really the best use of that much energy? What will you do with the left over salt?
-
Klapper at 11:51 AM on 10 August 20132013 SkS Weekly News Roundup #32A
From the 2012 NOAA climate report:
"Four major independent datasets show 2012 was among the 10 warmest years on record, ranking either 8th or 9th, depending upon the dataset used."
That's not quite true according to my most recent analysis of RSS, UAH, GISS, NCDC and HADCRUT4 datasets. The range is from 9th to 11th (not 8th to 9th).
Moderator Response:[DB] Assertions lacking evidence get disregarded quickly.
-
Riduna at 09:23 AM on 10 August 2013How much will sea levels rise in the 21st Century?
MA Rodger – Thank you for your comment @ 28 in which you note that … “The paleoclimate evidence does show very convincingly that small increases in global temperature will result in very large SLR”.
It does indeed – but that very large SLR is likely to come from rapid loss of land based ice so it would seem that heat does get to polar ice causing mass loss, or the ice sheets are much more responsive to polar amplified temperature than hitherto thought is this a wrong assumption?
-
deweaver at 08:57 AM on 10 August 2013Ocean Acidification: Eating Away at Life in the Southern Ocean
Iana,
Considering that the discharges of Calcium from the rivers of the world are from weathering, where do you have any data showing volcanic emissions are a dominant source of Calcium for the oceans. The acid gas emissions from volcanic sources are real.http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/circ1133/chemsetting.html Notice the hardness (as CaCO3) is a fair fraction of seawater (50%) and often near saturation, whereas the concentrations of soluble salts (NaCl) is a small fraction of seawater.
Prev 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 Next































 Arguments
Arguments



























