Recent Comments
Prev 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 Next
Comments 45101 to 45150:
-
KK Tung at 02:06 AM on 5 July 2013The anthropogenic global warming rate: Is it steady for the last 100 years? Part 2.
Our exchanges on analysis procedures of a technical nature probably have left most of our readers confused. So let me summarize the major points under debate. Both Dumb Scientist (DS) and Dikran Marsupial have focused on the technical aspects of the Multiple Linear Regression analysis (MLR). This was one of the three data analysis methods that were used on the problem with the aim of deducing the secular trend after removing the oscillatory influence of Atlantic Multi-decadal Oscillation (AMO). Our PNAS paper used two methods, the MLR and the wavelet analysis, and obtained approximately the same result. Previously, Wu et al (2011, Climate Dynamics) used the method of Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and obtained similar results. The EMD method was relatively new, and there were questions on whether other, more commonly used methods could yield the same result. Our PNAS paper was in part (though a small part) trying to reproduce their results using two other methods. The larger aim of our PNAS paper was to argue that the AMO is mostly natural.
Two technical aspects of the MLR have been debated here. Dikran chose to focus on our use of a linear regressor as a placeholder in an intermediate step of the MLR process. This issue was discussed in part 1 of my post, and shown that when the residual is added back as in the published papers (Foster and Rahmstorf (2011), Zhou and Tung (2013), Tung and Zhou (2013)), the sensitivity to the particular intermediate step is greatly reduced. While Dikran may disagree with my summary, I think he has failed to come up with an example where our procedure fails to yield the right answer within the 95% confidence interval (CI) most of the time. Please see my posts 171 and 172 for a summary.
Although I had originally thought that Dumb Scientist also focused on our use of linear regressor as the reason for his assertion that our argument was circular, he later clarified that his focus was on how the definition of the AMO index from the North Atlantic temperature affects the deduced anthropogenic trend. This is a more worthwhile challenge. My collaborator Dr. Zhou and I were interested to follow this debate to find out under what condition the MLR procedure would fail. After all, no empirical method is expected to work under all conditions. So we thank DS for his efforts.
His sequence of examples has evolved into the following: Consider a hypothetical example where we know what the true answer is, and make such an example as realistic as possible (with respect to the correlation between the global mean data and the N. Atlantic data, and the variances in each) so that if the MLR procedure fails in this hypothetical case it is likely to fail in the real case also. The observed temperature (HadCRUT4) warms at the rate of 0.17 C per decade after 1979. This was proposed previously by Foster and Rahmstorf (2011) as the “true anthropogenic trend”. Tung and Zhou (2013), on the other hand, argued that this observed rate of warming includes the rising half cycle of the AMO, which when removed, would yield an anthropogenic trend that is approximately half as large. So the question is, what if the true anthropogenic warming trend is actually 0.17 C per decade in a hypothetical example, will the MLR procedure erroneously say that it is smaller? While I have always maintained that such a theoretical possibility exists, it has been surprisingly difficult to actually come up with an example where MLR fails, and we collectively have gone through examples where the hypothesized anthropogenic warming goes from quadratic to a fifth order polynomial. The example that DS finally came up with consists of a 7th order polynomial for the anthropogenic trend (called human). It has the property that it is warming at 0.17 C per decade post 1979, but no warming before that. The latter fact is unrealistic but necessarily follows from the high order polynomial form assumed for this anthropogenic warming if one uses only analytic forms. There is in addition a 70-year oscillation, which is the AMO (called nature by DS). The global mean temperature is assumed to consist of human + nature + random noise. The N. Atlantic temperature that is used to define an AMO index also consists of these three components but in different proportions. The AMO Index is obtained by linearly detrending the N. Atlantic temperature. The idea is that because the anthopogenic trend is highly nonlinear, linearly detrending the N. Atlantic temperature yields an AMO contaminated by the nonlinear part of the anthropogenic trend. Therefore, if this “AMO” is removed by the MLR procedure, what remains is a more linear trend that is an underestimate of the true nonlinear anthropogenic trend. At least that is the aim of DS, as I understand it.
MLR can fail if the two components that we try to separate (in this case, the AMO and the nonlinear anthropogenic trend) have approximately the same scale, about 35 years, as is the case with DS’s latest example with the high order polynomial. Although the MLR method still can yield the right answer within the 95% CI most of the time (see my posts 178 and 179), it is nevertheless showing symptoms of non-robustness, e.g. sensitivity to the choice of regressors (smoothed vs non smoothed), which neither DS nor we understand at the moment, and we don't have the time to investigate it deeper. In the real case considered in our papers, such sensitivity does not exist and we got approximately the same answer. However, this example is not relevant, despite efforts by DS to make it realistic in other aspects, because we know, based on our current understanding of greenhouse warming, that there has been a warming since 1900. So the time scale for the anthropogenic warming is not 35 years but over 100 years.
The following example remedies this one deficiency in the example by DS that makes his case study less relevant. That is, we still use the hypothesis, as DS did, that the true post-1979 warming is entirely anthropogenic, and so the true human warming rate is 0.17 C per decade. Before that time there is a gentler warming, which is equal to the smoothed secular trend in the observed warming from 1850 to 1979. Everything else remains the same as in DS’s example. We perform 10,000 Monte-Carlo simulations using his method for the MLR. (We think 10,000 is sufficient; there is no need for 100,000 Monte-Carlo simulations.) The MLR procedure obtains the correct answer, defined as within the 95% CI of 0.17 C per decade for the post 1979 trend, most of the time. Specifically, we obtain the correct answer 80% of the time if we use the linear regressor in the intermediate step, 95% of the time correct if we use the QCO2 as the regressor in the intermediate step, and 91% of the time correct if we use human as the regressor, as DS did. Therefore, regardless of the intermediate steps, the MLR is able to successfully separate the components to obtain the “true” answer. The reason that this time the MLR is able to separate the two components is because the anthropogenic warming and the AMO have different time scales, as they should in the real case.
Some details of how we came up with the hypothetical anthropogenic warming follow. As did DS, we tried to be consistent with observation. We start with the HadCRUT4 surface temperature data. We fit it with a 6th order polynomial over the entire period of 1850-2011, instead of just over the period 1979-2011 as DS did. This produces the observed 0.17 C per decade of warming after 1979, the same as in DS. But in contrast, the warming here exists over the entire period, not just after 1979. The polynomial is smoothed by a cubic spline so that the trend is monotonic before 1979. This anthropogenic component will be called human. It is denoted by the red curve in Figure a. To create the AMO the-above-obtained human is subtracted from HadRUT4 data. The difference is smoothed with a 50-90 year wavelet band pass filter. This is the AMO (note: not the AMO Index). This is called nature (denoted by the purple curve in Figure b) and is the counterpart to DS’s 70-year sinusoid.

The global data consists of these two components plus a random noise of standard deviation of 0.1. The AMO Index is created using the N. Atlantic temperature, linearly detrended. For the N. Atlantic temperature, we assume it is composed of an anthropogenic warming given by 0.8*human (since the observed long-term trend in the N. Atlantic is smaller than that in the global mean) and the natural component is 1.4*nature (since the AMO in the N. Atlantic is known to be larger than that in the global mean). The correlation coefficient between the global data and the N. Atlantic data in this synthetic example is 0.74+/-0.06, very close to the observed correlation of 0.79. There is in addition a random noise in the N. Atlantic with standard deviation of 0.15. The synthetic global variance is 0.071+/-0.008 and the synthetic N. Atlantic variance is 0.066+/-0.011, very close to the real variances of 0.07 and 0.05, respectively.
In conclusion, it has been surprisingly difficult to come up with a synthetic data where the MLR method fails to yield the right answer most of the time. The latest example by DS comes closest, but has an unrealistic deficiency. In all the cases considered, none has failed both of our methods, the MLR and the wavelet method. These debates have served the purpose of strengthening our confidence in using these methods, and in the technical correctness of the results that we obtained in our PNAS paper using the two methods, although we should always be on guard for the possible failures of any method we use. It should be pointed out however that none of these technical discussions concerns the larger picture: whether the AMO is forced or natural.
I hope with this summary we can conclude the technical discussion on the MLR procedure, and can now move on to the other threads, such as the “thermodynamic argument”, which supposedly sets an upper limit on how large natural internal variability can be.
Moderator Response:[RH] Fixed image width.
-
PluviAL at 01:15 AM on 5 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
Wonderful observation. I am not use to the term "Energy" yet but it seems to gets at something that needs to be made clear at each step of any discussion. Greater "energy" will affect every weather event. It seems too much emphasis it put on saying any event is not the direct result of climate change. That is incorrect, I don't really know what people mean when they say that. It seems to mean that climate change is supposed to create different weather phenomenon, as in "bad" things. What must be the case is that energy always effects every weather event. I wish there was a way for teachers of weather reporters and reporters in general could make this understanding clear, so that they can disseminate it accordingly. Excellent perception, thanks.
As to preventing determined miss-information industry from misusing the term: maybe, but a liar can always figure a way to twist the mind in perverse ways.
-
johncl at 00:42 AM on 5 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
What I often feel is missing from the terms is the effect beside climate change. There is no doubt the chance of a major "biosphere change" - not not only climate. I believe many people dont consider a bit more wind in their hair now and then a problem - but if the heat and acidification of the seas kill of a lot of oxygen producing phythoplankton then that might grab the attention. The focus on weather incidents is of course natural, but I do believe the general biological effect a warmer planet has on life in all forms is one of more concern.
I like to think if it like, there is a different between a major storm on a lifeless planet, and one on earth - we still have life here, but shouldnt take that for granted if the planet gets excessively hot in the coming centuries. Life is fragile, and climate change is just one of the things that will affect a global warming planet. I think AGW coins the term better than any as its warming (and all of its consequences, weather and biological), AND its caused by the burning of fossil fuels.
-
DSL at 00:35 AM on 5 July 2013There is no consensus
participley, I've just gone through all of them. I can't find one that has issued a statement of disagreement. Did I miss one?
-
participley at 00:05 AM on 5 July 2013There is no consensus
[-snip-]
Moderator Response:[RH] Your question has been responded to. Reposts of the same question have been deleted.
-
Tom Curtis at 23:43 PM on 4 July 2013Nils-Axel Mörner is Wrong About Sea Level Rise
DSL @65, the photo shown @62 is certainly not the "original" version of any part of the photoshoped photo. The rocks in the foreground are different, and the boats in the background are different, not to mention the missing house and tree in the middle distance on the right of the new photo that is absent from the photoshopped photo. It is possible, but not likely that it is a photo of the original tree whose folliage is shown in the photoshopped picture.
Klaus Flemlose @62 on rereading your post I note that you still believe that the tree whose foliage is shown in the photoshopped picture was "cut down". Axel-Morner's claim was that it was uprooted ("torn down") rather than that it was cut down. It is essential to his story that it was uprooted, for if it had been cut down, it would not have been possible to replant it.
The fact that his story requires that the tree be uprooted shows what a work of fiction that story is. Only if erosion has removed almost all soil from around the roots of a tree can it be uprooted without strenuous digging and (preferably) a tractor.
Further, Axel-Morner's account is as follows:
"You know what happened? There came an Australian sealevel team, which was for the IPCC and against me. Then the students pulled down the tree by hand! They destroyed the evidence. What kind of people are those? And we came to launch this film "Doomsday Called Off,” right after that, and the tree was still green. And I heard from the locals that they had seen the people who had pulled it down. So I put it up again, by hand, and made my TV program...."
So not only did these herculean and malicous Australians uproot the tree, but Axel-Morner replanted the tree and then, purportedly, to the photo (explicitly identified as the photoshopped photo in the caption). That being the case, the roots would still be loose in the photo and (given the freshness of the foliage) the marks of the Australians efforts in digging out the tree would still be evident. Neither is the case.
I believe the entire basis of the story of the uprooted tree is to be found in Axel-Morner's imagination. Not only does he find it useful to embellish the envidence via photoshopping, he finds it usefull to slander scientists with complete fictions.
-
Non-Scientist at 23:29 PM on 4 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
For the denialists, you'll need to explain
how nearly all geologic records were created by one global flood
and
how all of this occurred within 6124 years.
-
DSL at 22:58 PM on 4 July 2013Nils-Axel Mörner is Wrong About Sea Level Rise
Klaus, you say Nils sent you the original, and then you say the one he posted was a double exposure. Double exposure does not occur after the photo has been developed. A double exposure is an original. You should have said, "He sent me a different shot of the same tree, a shot that was not a double exposure." If you know enough to understand what a double exposure is--to the point of believing that it absolves Morner--then you should know that saying "Prof Nil-Axel Mörner has been so kind to e-mail me the original photo" doesn't make sense. You're either trying to play games, or you're incredibly naive, naive enough to trust Morner's "double exposure" explanation without knowing what a double exposure is.
Morner also did not send you the original. He sent you a scan of the developed original, unless he's lying about the double exposure. I seriously doubt that Morner, if he actually took the picture in question, used a film camera, the only type of camera able to create a double exposure (unless the digital camera has an extremely rare firmware error that just happens to occur intermittantly and just happened to occur with this particular, highly-controversial exposure). He's wealthy enough to be able to afford a digital camera capable of performing as well as a film camera.
-
michael sweet at 22:15 PM on 4 July 2013Nils-Axel Mörner is Wrong About Sea Level Rise
Klaus,
A heads up to you. People who support obviously false explainations damage their own reputations. Why should I believe anything from someone who supported obviously false proposals? Consider the sourse of the information you present to others as accurate. Why do you believe such claptrap? Why have you been taken twice by the same fraudster? Why would you continue to believe the material on those websites that support this fraud?
-
Cornelius Breadbasket at 20:22 PM on 4 July 20132001-2010, A Decade of Climate Extremes
The BBC have a nice little online article on this. However, it did not feature very highly in news broadcasts. I wonder if society is going through the five stages of greif? We've had denial, anger and bargaining and perhaps we are entering depression? After all, who wants to hear bad news? I'd like the zeitgeist to move onto acceptance. There may be ways we can help this.
-
Tom Curtis at 20:16 PM on 4 July 2013Nils-Axel Mörner is Wrong About Sea Level Rise
Klaus Flemlose @62:
1) Regardless of the tale told by Nils Axel-Morner, the photo I discuss @55 above was not an double exposure. Double exposure is a technique of exposing the same frame of film twice (or more), thereby creating multiple overlaping images. Unless great care it taken, it will result in ghosting as in the photo below. It will not result in sharp demarcation lines as discussed above. Therefore, there remains no doubt that Nils Axel-Morner edited a photo of a tree by deleting portions of it and grafting sections of other photos to replace those portions that were deleted.

2) It is not possible to positively identify the tree in the new photo as that in either of the photos discussed in my 55 above. There are some similarities, but also some distinct differences. The differences may be because they are different trees, or because the pictures were taken from different angles, or at different times.
Based on the similarity of the background, the new photo probably does show the tree shown here in connection to Axel-Morner's claims. I was previously aware of the photo at the link, but did not previously discuss it as it was not directly claimed to be an identical tree, and was not attributed to Axel-Morner. Given the new claim by Axel-Morner, however, I will point out that the root base of this tree and that in the photoshopped picture are definitely distinct. This can be seen because:
a) The size of the rocks in the foreground are very disimilar;
b) The large flat rock on the left of frame and near the tree in both pictures is dissimilar in shape; and
c) The root base of the tree in the new photo is much thicker than that in the photoshopped picture.
3) It is easy to see why Axel-Morner has been using the photoshopped picture rather than the one he has just sent you. The picture he has sent you clearly shows an erosional face in the current tidal zone. It also shows the nearest tree to the one in the center of the photo to also have erosion undercutting its roots. Finally, it shows a slab of concrete lying partially within the tidal zone, and clearly undercut by wave action. All three are indications of rising sea levels at that location.
Until Nils Axel-Morner gives a clear account of how he photoshopped the picture @55, shows us all three pictures he used in doing so, and gives a clear account of why he did so, the only sensible thing to do is to treat this as an example of fraud, and to disregard any "evidence" on which we are reliant on Axel-Morner as our informant. Brushing of the incident with patently absurd claims (ie, that the photo resulted from double exposure) only calls into further question his trustworthiness.
-
Klaus Flemløse at 15:20 PM on 4 July 2013Nils-Axel Mörner is Wrong About Sea Level Rise
Prof Nil-Axel Mörner has been so kind to e-mail me the original photo. The photo shown in post #55 was a double exposure, not a photo shop picture.
It is very unfortunate, that prof Nils-Axel Mörner published a double-exposed image, thereby creating a myth about fraud and deception.
The only way to remove any doubt is to publish as much as possible of the documentation before and after the tree have been cut down.
Moderator Response:[DB] Adjusted image width
-
DSL at 12:20 PM on 4 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
I often explain it thusly:
"'Global warming' refers to temperature increase, but climate is much more than temperature. It's also wind, rain, snow, ocean currents, etc. Climate change is change in all of those elements as a result of increased temperature. It's not that everything stays the same but gets hotter. Everything changes--it gets hotter, winds change, the jet stream changes, precipitation changes, ocean currents change: climate changes."
-
villabolo at 10:52 AM on 4 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
Some short answers and talking points that could be understood at a High School level:
In order to explain the difference between Global Warming and Climate Change we can say:
"Global Warming is the cause, Climate Change is the result."
In order to give the shortest answer possible to the issue of our erratic weather we can say:
"The Earth is 1.4 degrees Fahrenheit higher than before while the Arctic is 3-5F and up to 10-18F above normal at certain times and places. This creates a chain reaction of events that give us cold winters and hot summers. However the heat records exceed the cold records."
In order to grab people's attention to the results of Global Warming we can say:
"When the Arctic Ocean loses its ice we start to lose our crops due to severe weather."
In order to explain the leveling off of temperatures we can say:
"Temperatures rose in 1978 and then leveled off followed by another rise in 1998 which also leveled off even though the sun started cooling off in 2002 and went low in 2010. Now that the sun is getting back up to normal we're going to get even higher temperatures."
-
Chris G at 09:26 AM on 4 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
Using the word 'energy' instead of 'heat': Yes, the tradeoff between energy not being as salient as heat (to the layman) and heat not really capturing the meaning correctly is most often worth it.
I also agree that a fair percentage of the contrarian arguments I see are a result of the person believing that the simple explanation implies something it does not. Possibly they are motivated to find flaws with the explanation and so interpret an ambiguous, simple explanation in the least favorable way.
-
Rob Honeycutt at 08:00 AM on 4 July 2013There is no consensus
participley... The wiki page on the scientific opinion on climate change they have this statement regarding dissenting opinions:
"As of 2007, when the American Association of Petroleum Geologists released a revised statement,[11] no scientific body of national or international standing rejected the findings of human-induced effects on climate change.[10][12]"
If anyone can find a legitimately recognised scientific body that rejects climate change, I think everyone here would be interested to know about it.
-
DSL at 07:23 AM on 4 July 2013There is no consensus
I should also point out that it's unlikely that any organization of professional scientists would actually issue a statement rejecting the theory. Such a move would require evidence, and no such evidence exists.
-
DSL at 07:19 AM on 4 July 2013There is no consensus
Participley, as far as I know, no one has published a complete list of scientific organizations' positions on AGW. However, the professional denial industry hasn't located any organizations that disagree, and they'd be the ones most anxious to find such an organization. Perhaps you can locate one?
-
william5331 at 06:29 AM on 4 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Our decendants a few thousand years from now will be grateful for the geological carbon sink but we need to encourage and preserve carbon sinks that act a tad quicker if we are to live to leave such decendants. Fabulous article.
http://mtkass.blogspot.co.nz/2012/02/carbon-sinks.html
-
Rob Painting at 06:10 AM on 4 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
arncliffe - the thin cool-skin layer of the ocean already is an insulating barrier. Warming the atmosphere, through additonal greenhouse gas emissions, simply increases the efficiency of that insulating barrier.
Reduced equatorial cloud cover during La Nina (due to the cooler sea surface temperature), combined with the strong upwelling (Ekman suction) in the eastern equatorial Pacific, does indeed lead to greater warming of the ocean - because it's bringing cool subsurface water to the surface, where it can be heated by the sun. I briefly touched on that in this post: Search For 'Missing Heat' Confirms More Global Warming 'In The Pipeline'.
Once the posts explaining the wind-driven ocean circulation and deep ocean warming are completed, it will be definitely worthwhile explaining how all the pieces of the puzzle fit together. Many readers overlook the obvious implications.
-
participley at 05:47 AM on 4 July 2013There is no consensus
"There are no national or major scientific institutions anywhere in the world that dispute the theory of anthropogenic climate change. Not one."
Is there a reference for this statement ?
-
rockytom at 05:32 AM on 4 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Absolutely a fine article, John. A great deal of the information will aid me in updating the Ph.D. I received in 1968, although I did use Turner and Verhoogan as a textbook in "Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology." I look forward to your next post. BTW, in the next version of the excellent illustration beginningthe article could you show a more obviously continuous and recently uplifted mountain range and label it as such? This would possibly have more significance to incipient geologists and emphasize the importance of exposing newly elevated rock to the weathing (re: rock) cycle.
-
David Kirtley at 04:29 AM on 4 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
Contrarian cries that us alarmists are trying to change "global warming" to a new name in 1, 2, 3...
-
BillEverett at 03:34 AM on 4 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
"To the public it can appear that there is less warming, because the rate of temperature increase at the Earth’s surface has slowed down in the last decade."
According to the World Meteorolgical Organization, "The decadal rate of increase in the global temperature accelerated between 1971 and 2010. The global temperature increased at an average estimated rate of 0.17°C per decade during that period, compared with 0.062°C per decade for the entire 1880-2010 period. The average 2001-2010 decadal temperature was 0.21°C warmer than 1991–2000, which in turn was +0.14°C warmer than 1981-1990."
Moderator Response:Sure, but sceptics look at short term data, preferably picking a really hot outlier like 1998 as the baseline. The Escalator shows the how the trick works...but anyway:
"The planet has continued to accumulate heat since 1998 - global warming is still happening. Nevertheless, surface temperatures show much internal variability due to heat exchange between the ocean and atmosphere. 1998 was an unusually hot year due to a strong El Nino."
-
arncliffe at 02:35 AM on 4 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Bob Painting:
Sorry-first para: your paper of OCTOBER 2011
-
arncliffe at 02:04 AM on 4 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Rob Painting @
In my reply to Glenn Tamblyn I was referring to your recent article on climate shift that only referenced the Tangaroa experiments. I have subsequently found your article of June 2011 with the references that you mention. In simple terms it seems that the effect of downwelling LR radiation is not to heat the ocean directly, but to turn the thin cool skin layer into a thermal insulating barrier and thus increase OHC by reducing heat transmission to the atmosphere. Is this a reasonable summary?
You mention Bob Tynsdale: whilst I do not subscribe to his view that that global warming has nothing to do with CO2 but is caused by ENSO, his position on the ability of ENSO neutral and La Nina modes to increase OHC seems similar to yours.
-
ajki at 01:28 AM on 4 July 2013Climate change science: what’s in a name?
I've said it before and I say it again: that one phrase I'd like to see above all other nice&true facts and figures is "AGW".
Global: it's NOT about weather, it's not about your hometown or the hometowns of your beloved ones, it's not about your country or continent - it's about the whole blue Marble. Go see a nice picture of it - there are legions out there.
Warming: it's NOT about models that you can endlessly quibble about, it's not about plant food, it's not about more greening in the north or deep south. It's about measuring of temperatures just everywhere and finding one clear trend: upwards - hence warming.Anthropogenic caused: it's not about your or mine moral guiltyness, it's not about your nice car and house, it's not about your really perfect energy consuming footprint. It's about keeping warm little fires burning by 7 Billion of you and me.
And the one figure I'd like to see is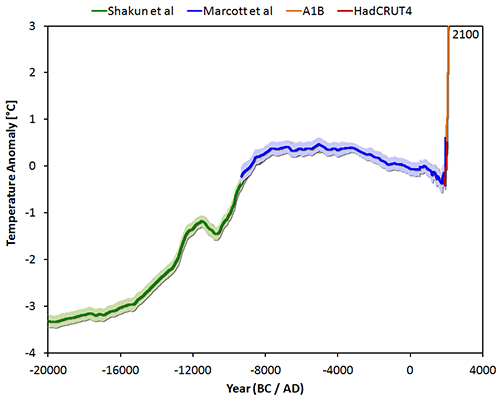
but without any model projection.
The title should be: Rise of ManThere should be two points in it with a legend: one before the rise named "1 Billion of you and me" and the second at the momentary end of the measured data points named "You and me and the other 7 Billion are here!"
-
philipm at 19:32 PM on 3 July 2013Agnotology, Climastrology, and Replicability Examined in a New Study
Where do these guys learn their stuff? In my first year applied maths course, a lecturer told us that interpolation can give useful results, but extrapolation should be treated with extreme caution -- if it purely amounted to curve fitting.
I also recall the mantra "correlation is not causation" from the denial camp when the theory of climate change was a bit less complete than it is now. Funny how the argument they used then against the theory almost entirely applies now to them.
A deep fundamental problem in public perception of science is the desire of the media to portray the big breakthrough. This very rarely happens and may only be recognised in retrospect after a lot of retries of an apparently failed experiment.
-
John Mason at 18:55 PM on 3 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
@Slioch - absolutely - the key minerals are the plagioclase feldspars (the calcic ones), mg-rich members of the olivine group and Ca/Mg rich pyroxenes and amphiboles. Granite - the coarse-grained, intrusive equivalent of rhyolite - likewise tends to have Ca and Mg contents in a similar range, present in plagioclase feldspar. However, it could be argued that the weathering of granite is still significant simply because granite is such an abundant rock-type, both in its primary state and as detritus making up sedimentary rocks. Incidentally, the propensity of rok-forming minerals to weathering is roughly as follows, starting at most susceptible and ending with least susceptible (note that there is a continuous compositional series between the sodi and calcic end-members of the plagioclase feldspar group):
Olivine, Plagioclase (calcic)
Pyroxene
Amphibole
Biotite (black mica), Plagioclase (sodic)
Orthoclase
Muscovite (white mica)
Quartz
If you visit the famous china clay-pits of Cornwall, which exploit altered and weathered granite, you will find that it is the feldspar that has decomposed: the waste-heaps left after the kaolinite (one of the weathering-products) has been extracted are the residual, relatively unscathed quartz and mica.
-
Kevin C at 18:33 PM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
While I have enormouse respect for Robert Rhode's work at BEST, the rest of that paper wouldn't have passed review in a climate journal.
"We are not aware of any global climate models that predicted the reversal of slope that we observe."
That's weasel wording for "The diurnal temperature literature looked difficult, so we didn't read it".
There is an extensive literature on diurnal temperature range and it is far more complicated than the BEST paper makes out. DTR does decrease with greenhouse forcing, but is much more strongly influenced by aerosols, clouds, soil moisture and so on, as even two minutes with google scholar will reveal.
To be fair SkS's material on DTR is similarly lacking in nuance - it's on my list of things to fix if we ever get a breathing space between debunking new nonsense. Glenn is correct that in the absence of other factors solar warming would cause an increase in DTR, however the other influences are sufficiently large that we would have to eliminate them to draw a strong conclusion from this effect alone. Drost et al use multiple fingerprints in combination to obtain a much more robust result.
More compelling still is the fact that we can see the increase in greenhouse warming in both the outgoing infrared radiation spectrum, and in the infrared glow looking up at greenhouse gases from the surface. -
Slioch at 17:33 PM on 3 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Silicate rocks are a complex mix of (mostly) silicate minerals. These minerals do not have a fixed composition: in feldspars, for example, sodium, potassium and calcium (and other) atoms can substitute for one another, and the exact composition of the feldspar crystal depends upon both the composition of the melt from which it crystallised and the temperature and pressure at which it did so. Thus, the composition of silicate rocks is more easily and accurately recorded as a list of oxides of various amounts, rather than of minerals per se. For example, a typical basalt lava has the following composition:
SiO2 49.06%
TiO2 1.36%
Al2O3 15.70%
Fe2O3 5.38%
FeO 6.37%
MnO 0.31%
MgO 6.17%
CaO 8.95%
Na2O 3.11%
K2O 1.52%
H2O 1.62%
P2O5 0.45% (from Turner and Verhoogan, "Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology").
Giving the composition of silicate rocks in this way enables one to immediately appreciate their potential for carbon sequestration via weathering, in this case, from the 8.95% of CaO and 6.17% MgO. Another (less common) extrusive igneous rock called rhyolite has only 1.22% CaO and 0.38% MgO and has thus much less potential for carbon sequestration.
-
JasonB at 15:45 PM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
I had a quick look and found the claim in the BEST paper here: http://www.scitechnol.com/GIGS/GIGS-1-101.php
Specifically, Figure 4 on page 4 shows a decline in diurnal range from 1900 to 1987, followed by an increase in diurnal range:

The paragraphs above the figure note that "The rise takes place during a period when, according to the IPCC report, the anthropogenic effect of global warming is evident above the background variations from natural causes" and "We are not aware of any global climate models that predicted the reversal of slope that we observe".
Personally, I wouldn't be rushing to point to this as evidence that the current understanding of AGW is wrong.
Firstly, the recent figures don't like look like they stand out with respect to the long-term trend extrapolated forward from about 1970; the steep decline from the late 60s to the mid 80s followed by the rebound back up to the long-term trend is perhaps the portion that needs explaining. Indeed, the steep incline seems to have levelled off again.
Secondly, even with that dip and recovery, there is still an overall decline on longer time scales, exactly as expected. Although BEST are fairly confident in their results as shown by their uncertainty estimates, I think they are talking about the uncertainty in the true value, not the uncertainty introduced by short-term fluctuations about the trend. The highly "certain" dip and recovery could well be a highly certain natural variation that is in no way unusual (the uncertainty in the earlier figures makes that hard to determine) and it could be that, in fact, there was no change in the long term trend underlying that natural variability. (In other words, even if the monthly anomalies reported for GISTEMP, for example, were accurate to 0.00001 degrees, it wouldn't change the fact that we'd need well over a decade of readings to ascertain the long-term trend, because the variability is real feature of the system and not simply a measurement error.) Since temperature readings are affected by more than just CO2, it's possible that the diurnal temperature range is, too.
Thirdly, this is just one study by one group. As it notes, four previous studies reported significant decreases in the diurnal temperature range.
-
JasonB at 10:13 AM on 3 July 2013Media Overlooking 90% of Global Warming
netprophet,
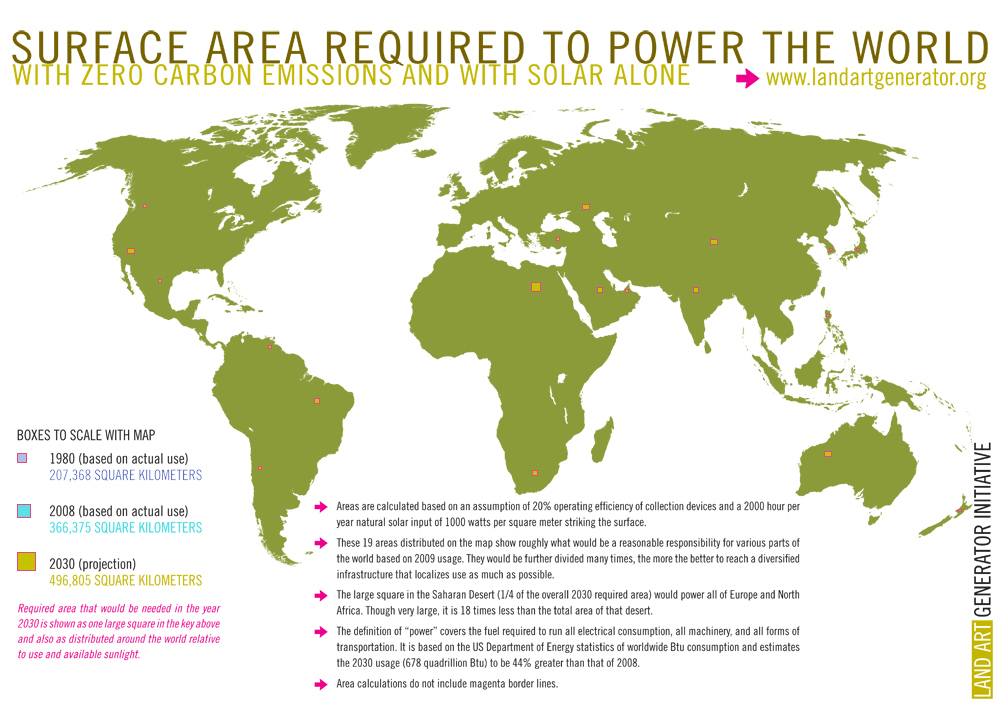
As KR mentioned, space for solar isn't a problem. Using an existing parabolic trough system like Nevada Solar One as a benchmark (134 GWh/year, 1.6km2) you could generate the entire planet’s current annual energy consumption (not just electricity) using just 17% of the Sahara desert.
Consider also the fact that we have already disturbed, by coal mining, an area (~8.4 million acres in the US alone) equal to that required to provide all power using solar thermal, and that coal mining has a much bigger impact on the area affected than simply putting it in the shade, and that coal also usually happens to be located in much higher-value areas than solar thermal plants would be.
Solar PV is even less of an issue, because it can sit on existing rooftops, and it has the advantage that it's competing with the end-user retail price of electricity.
If you're worried about cost, however, then you should be comparing to wind, rather than solar. Wind is now cheaper than new coal, which is why it's had such a dominant position in terms of new installed capacity for a while now. (Going forward, you can see the EIA's current estimates for 2018 here. Note that those figures are excluding "targeted tax credits such as the production or investment tax credit available for some technologies".) Wind can also co-exist with other uses of the land (most wind farms I've seen have been on working farms running sheep and cattle).
-
KR at 09:32 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
arncliffe - "...a paper published last year by the team at BEST showed that the gap between night and day temperatures has actually been increasing for some twenty five years."
That's not what the data shows - Vose et al 2005; "Minimum temperature increased about twice as fast as maximum temperature over global land areas since 1950, resulting in a broad decline in the diurnal temperature range...", and Zhou et al 2009; "Observations show that the surface diurnal temperature range (DTR) has decreased since 1950s over most global land areas..." would disagree.
If you have a reference, it would be interesting to look at - but your assertion is contrary to the data I know of.
-
Manwichstick at 07:10 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
@arncliffe
I would be very skeptical of the claim:
the team at BEST showed that the gap between night and day temperatures has actually been increasing for some twenty five years.
Not in my country, Canada. Winters are warming faster than summers and daytime minimums are increasing faster than daytime maximums. Just as predicted.
And BTW, if someone provides you with data, or explictly argues, that the sun is magically, or increasing some sort of output that is the cause of the earth's additional heat accumulation... they are instantly not a trustworthy source.
-
KR at 06:13 AM on 3 July 2013Media Overlooking 90% of Global Warming
netprophet - I don't believe either cost or area is a serious concern. I would suggest looking at one of the Renewable Baseload Energy threads, where this has been discussed in detail.
Space is simply not a problem - here are some maps indicating required generation area for solar or for wind:
[Source]
As to cost, Apple hasn't released figures, but it's estimated to be similar to the cost of its other data centers - all of which are powered from renewable energy sources, and none of which has bankrupted the quite profitable company.
-
Dumb Scientist at 05:14 AM on 3 July 2013The anthropogenic global warming rate: Is it steady for the last 100 years? Part 2.
I set "custom" parameters equal to mine (with my 7th order human influence, etc.) but with Dr. Tung's noise parameters, and 10,000 runs seemed to show that the sensitivity to smoothing was similar to simulations using Dr. Tung's overall parameters. This would have suggested that my simulation's sensitivity to smoothing the AMO index was related to the relative noise levels. However, running 100,000 simulations of the custom parameters reveals sensitivity similar to my overall parameters, so my hypothesis was wrong.
I still don't know why my simulation is more sensitive to smoothing, but I think the important point is still that my parameters produce more realistic timeseries, correlations, variances, and error bars. (Also, attribution is still really a thermodynamics problem.)
-
Rob Painting at 05:03 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Arncliffe - 1.My post on the cool-skin layer of the ocean hyper-links to 3 different papers on the topic, and those three papers cites numerous others in support of the physics, math, and observations involved. Climate science contrarians on the other hand cite none. Why do you think that is?
2. The simple experiment carried out by Professor Minnett whilst aboard the New Zealand research vessel Tangaroa (Maori for the god of the sea) is rather compelling. Why else would the surface waters warm under cloudy conditions? The typical contrarian response of furious handwaving is not an explanation.
3. The amount of sunlight reaching Earth has declined over the last 3 decades due to a decline in the sun's radiation output. Instead of a decline in ocean heat content, we have seen a dramatic increase - as the greenhouse gas-forcing of the ocean's cool-skin layer predicts.
4. Attempts to blame current ocean warming on natural factors are generally by people who have little understanding of oceanography - such as the contrarian Bob Tisdale, and whose ideas are contradicted by the observations.
5. For example, mainstream science not only correctly predicted the current ocean warming, but accounts all previous Earth warming episodes that involved increased atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases - due to the fact that over 90% of heat goes into the oceans. The clearest illustration of this is the correlation between global temperature and atmospheric carbon dioxide (the main greenhouse gas) as shown in the ice core records dating back 800,000 years. The last 400,000 years of which is shown below:

How does Bob Tisdale's idea fare when you run it backward in time?
-
arncliffe at 04:49 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Glenn Tamblyn
Sorry, another error: para 5 - Four Hiroshima bombs PER SECOND
-
netprophet at 04:42 AM on 3 July 2013Media Overlooking 90% of Global Warming
Okay, let's assume we must act now as the President expects all Americans to do. Apple announced today it is putting a 43,500 kwhr (~20 MW unit) generating solar plant in Reno, NV. It is equivalent to the carbon generation of some 17,000+ homes. The capital cost will be ~ $75M based on costs of similar sized plants. In order to replace coal, which generates 1,517,000,000,000 kwhr, with solar, we would need some 35,000 such Apple size plants if the entire US had the sunlight of NV which it doesn't. Adjusting for many cloudy regions, we would need more like 70,000 such plants. The total investement would be over $5.0 trillion and in many regions there simply isn't enough space to put solar panels. How would we fund this?
-
shoyemore at 02:52 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Taking Tom Curtis' point about etnropy, the energy accumulating in the atmosphere was once of high entropy, when it began in the sun's thermonuclear furnace. So the proviso around the "4 Hiroshima bombs" can be posed as "If we express this energy in units appropriate to where it began .... ", relateable to the sun's arriving energy on earth.
It still carries the image of a lorra, lorra energy, which is why I like it. And people can express it in more than one way .... "Here are different ways you can express this energy .. 4 Hiroshima bombs per second, or illuminating 71 billion Wembley sized areas with thirty five 100 Watt bulbs .... "
Obviously, no one should use the unit if they feel uncomfortable with its accompanying imagery, but a concrete example that you can explain is very usful.
Stephen Schneider: Each of us has to decide what the right balance is between being effective and being honest. I hope that means being both.
-
arncliffe at 02:50 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Glenn Tamblyn
Whoops Typo: 4th para - winds that move this mass of upwelling waterWESTWARD
-
arncliffe at 02:45 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Glenn Tamblyn @22
Thank you for the time and trouble taken in your three responses. They were both informative and thought provoking.
I have two points that I think are worth making on your very clear 'walk through' of the likely role of CO2 in increased OHC.
Firstly, a paper published last year by the team at BEST showed that the gap between night and day temperatures has actually been increasing for some twenty five years. I don't have the reference to give you, nor the skills to provide a link if I did, but no doubt it is easily traceable.
The second point is the possibilty of solar radiation contributing to increased OHC. There seems to be general agreement across the Climate Science Blogosphere that when ENSO is in a 'La Nina', or 'neutral' phase the eastern equatorial pacific ocean and land regions cool due to easterly winds driving surface water westwards and generating an upwelling of cold water in the east. I understamd that the winds that move this mass of upwelling water eastward also create minimal cloud cover, thus exposing the water to high levels of solation on its long journey across the Pacific - over a third of the way around the globe. When this heated water reaches the western extremity of the Pacific, some moves through to the Indian Ocean, some diverts towards the poles, some remains in a pool to fuel the next El Nino and some goes down. As 'neutral' or 'La Nina phases have been dominant this century it seems credible to assume that this process has been a net contributor to OHC.
If I understand 'Shoyemore' @4 above correctly, the earth receives 1,900 Hiroshima bombs worth of solation per second (Elsewhere I have seen a figure of 1,000). As the process described above is occurring at the equator, a gain in OHC of 4 hiroshima bombs from solation alone doesn't seen too far fetched? - but I'm sure somone cleverer than me can do some sums to see just what the figure could be.
Turning to the question of the thin, cool- skin hypothesis: I agree that if it is flawed it may well be a question of swings and roundabouts as far as OHC is concerned. However, as the mechanisms by which CO2 affects OHC are so completely different in each case, I find it surprising that this issue can even be questioned at this stage (When so much effort and money has been expended on climate science over the last twenty or so years) and in re-reading Rob's article on the layer he references only one paper on the subject.
And so finally to the Roy Spencer paper that I mentioned. I am amazed to read that trends generated by the three bodies processing the same satellite temperature data vary by a factor of three. Someone ought to get them round a table!
Apologies for such a long winded post, but I felt that I owed you the best response that a layman can provide.
-
Richard Lawson at 02:16 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Some of the heat goes into the melting of Arctic Ice. If we apply gentle heat to a beaker of water containing a lump of ice, the water temperature will not increase until the ice has finished melting.
So how much ice has melted?
The figure here:
http://psc.apl.washington.edu/wordpress/research/projects/arctic-sea-ice-volume-anomaly/
shows that the September mean volume for 1979-2012 stands at 12,000 cubic km of ice.
The September value for 2012 stands at 3,000 cubic km of ice.
Therefore we have lost 8,000 cubic km of ice, since about 1997.1 cubic kilometer of ice = 10^15 grammes of ice
80 calories of heat are required to melt 1 gramme of ice.
Therefore to melt 1 cubic km of ice we need 8 * 10^16 calories
To melt 8000 cubic km ice we need 6.4 * 10 ^ 20 caloriesThat is 2.7 * 10^21 Joules which have gone into melting the Arctic ice since 1997.
This is clearly a lot of heat, but I have no idea how significant it is compared to the earth's energy budget.
It is 2*10^8 Hiroshima bombs, but how much surface warming would it represent, if, instead of going into melting ice, it went directly into heating the surface air?
-
danielbacon at 02:16 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Very eloquent!
IMHO: The rate should be more important. You should say that by 1998. We were at a rate of ~2 Hiroshima bomb detonations per second and since that so called pause we have move to 4 Hiroshima bomb detonations per second. Or put it in step with time. Like in 198x we were at 1 by 199x at 2... and today at 4. How much many more Hiroshima bomb detonations does it need to increase before we start taking this seriously.
-
johncl at 01:44 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
I do believe that many of us convinced in the seriousness of AGW really is trying to figure out how we can explain this to people so they are able to act upon it. Its really one of humanities biggest challenges, one that could have consequences on a planetary scale if not handled in time. Many believe we are really running of out of time. Talking about CO2 emission cuts of a certain % by 2050 isnt going to cut it. What is needed is for people to wake up and understand that our CO2 emissions through our addiction to fossil fuel burning is really turning up the thermostat of the planet causing a shift that the planet likely only have experienced in rather more cataclysmic events like the big siberian traps vulcanism or asteroide impact. The data shows a dramatic concentration of CO2 in both the air and seas at rates 10x past extinction events. I think its really cause for concern even though we dont really see the big consequences right this second. A tipping point can be passed (and most likely several have been passed now with the Arctic melting fast) where the changes happen so fast that global average temperatures could rise rapidly.
I do believe there is enough evidence now that the planet is absorbing more of the suns energy than it has in the past, and that this amount is significant even on a planetary scale (some are trying to make the 4 abombs per second sound like a small number, just like CO2 is only a small part of the atmosphere - this is a dangerous way of thinking - it only takes 0.25g of arsenic to kill a person). Looking at the broad picture, its really fantastic that life even exists on the planet, and while humans might feel like small gods wielding the power of fossil fuels, we really are quite insignificant and vulnurable, like all living things on this planet. I do believe we should treat our lucky position in this galaxy with some respect and at least acknowledge what we have discovered about simple physics. Sometimes one does not need proof in order to know something is right, if I fall out of a 10 story building, I will likely die - but I dont really need to watch someone fall to their death to understand this is a physical fact. The same way we do know CO2 is a greenhouse gas and that it traps heat. Glenn Tamblyn's line of reasoning perfectly explains a valid reason for the extra heat stored and I my opinion it shouldnt be hard for people to grasp this if they are willing to listen.
Cheers
-
Eclectikus at 01:10 AM on 3 July 20134 Hiroshima bombs worth of heat per second
Hi all
I do not understand this obsession here with "science communicating". Science is not communicated (not as political propaganda), is disseminated and/or popularized, and as far as possible, when it has already passed the rigors of scientific method (empirical validation at least).
Glenn Tamblyn #24 says "It is a couple of decades too soon to claim that the models are wrong." Yep, However it is not too early to say that the models are correct... I think this is a version of scientific validation quite asymmetric, being naive.
Last but not less important. Using Hiroshima bomb (more than one hundred thousand dead), gives people an idea of the ethical level, and of the balance between popularize (or explaining) on the one hand, and convince (terrify rather), on this side of debate. From my point of view is a wrong strategy, to the point that it can only work with the more illiterate society. But hey, I'm aware that my opinion is worthless here. It's your choice.
Sincerely.
-
John Mason at 00:33 AM on 3 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
LOL I missed that one when I corrected the others. It was around 0600 this morning when I did the other ones and I hadn't had enough coffee at the time! Sorted now :)
-
Slioch at 00:06 AM on 3 July 2013Understanding the long-term carbon-cycle: weathering of rocks - a vitally important carbon-sink
Another minor typo:
CaSiO3- (ie showing an overall -1 charge) in equation in top illustration should be simply CaSiO3 (ie with no charge).
-
DSL at 23:33 PM on 2 July 2013It's El Niño
Li et al. 2013 might be a good basis for an intermediate article here:
"Predicting how the El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) will change with global warming is of enormous importance to society. ENSO exhibits considerable natural variability at interdecadal–centennial timescales5. Instrumental records are too short to determine whether ENSO has changed6 and existing reconstructions are often developed without adequate tropical records. Here we present a seven-century-long ENSO reconstruction based on 2,222 tree-ring chronologies from both the tropics and mid-latitudes in both hemispheres. The inclusion of tropical records enables us to achieve unprecedented accuracy, as attested by high correlations with equatorial Pacific coral and coherent modulation of global teleconnections that are consistent with an independent Northern Hemisphere temperature reconstruction. Our data indicate that ENSO activity in the late twentieth century was anomalously high over the past seven centuries, suggestive of a response to continuing global warming. Climate models disagree on the ENSO response to global warming, suggesting that many models underestimate the sensitivity to radiative perturbations. Illustrating the radiative effect, our reconstruction reveals a robust ENSO response to large tropical eruptions, with anomalous cooling in the east-central tropical Pacific in the year of eruption, followed by anomalous warming one year after. Our observations provide crucial constraints for improving climate models and their future projections."
Prev 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 Next































 Arguments
Arguments