Global climate projections help civil engineers plan
Posted on 25 May 2017 by John Abraham
People who work on building infrastructure understand the risks of climate change. As the Earth warms, new stresses are applied to our buildings, bridges, roads, houses, and other structures. Some of the obvious threats to infrastructure are from extreme weather including heat waves, storms, and intense rainfalls. There are some other less obvious threats, and many of the threats vary by location.
Regardless, the planning for infrastructure relies upon a reasonable estimation of future climate changes. To help quantify such an estimate for the civil engineering community, a recent paper was published by the Institution of Civil Engineering Journal of Forensic Engineering (I was fortunate to be a coauthor). The article was prepared with the collaboration of Dr. Michael Mann from Penn State University and Dr. Lijing Cheng from the Chinese Institute of Atmospheric Physics.
The paper in question does not uncover new facts. We didn’t discover past warming that wasn’t known. We didn’t create new predictions that were previously uncreated. Rather, we assembled available information to provide a solid basis that can be used for future plans involving infrastructure.
The first thing we established was the long-term trend in the global temperature. While there are many groups around the world that collect global temperatures, two of the best known groups are NASA and NOAA. As shown in the data below, which I downloaded and graphed for the paper, temperatures have risen by about 1.4°C (approximately 2.5°F) from their low point circa 1900. Since scientists constantly argue against cherry picking; we used an average temperature over the 1880–1930 time period. Relative to that time, temperatures have risen about 1.2°C (1.8°F)
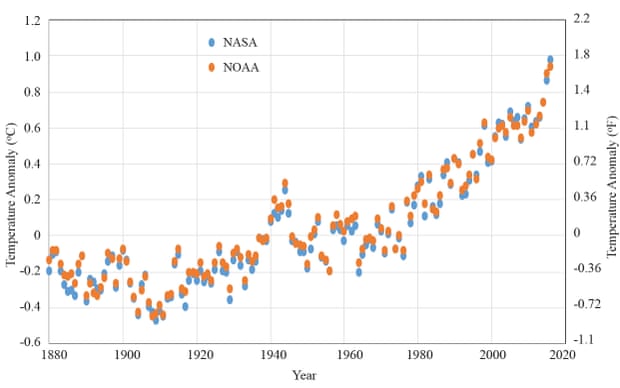
Global temperature anomalies since 1880. Illustration: Abraham et al., 2017, J. Forensics Engineering
I have long argued and certainly continue to believe, that the surface temperature trend is not the best way to quantify warming. If you really want to measure global warming, you have to look in the oceans where the vast majority of heat is being stored. As I have reported here before, the oceans are telling a similar story – climate change is certainly happening. However, since we are not building infrastructure deep in the oceans, its temperatures are not very relevant for the present discussion.
What all this proves is that the Earth is warming. But civil engineers want to know what the Earth will be like in a decade, or two decades, or even longer. To predict that, you need other tools. You could make predictions based on the past temperature record of the planet or you could use computer simulations of the climate. But if you are going to use a simulation, you want to have some reassurance that the results are valid. So, the next thing we did in the paper was compare computer simulations of Earth’s surface temperatures with measurements.
The results are shown below. The figure shows four different data measurement sets and a range of model predictions (grey-shaded region). I’ve highlighted the temperature of 2016 with a red star; it’s slightly above the middle dashed line, which means it’s slightly above the average prediction of the models but certainly within the grey range. As you all know, scientists don’t really care whether one year is hot or another is cold; what we look at is the long-term trend. Clearly, the long-term trends are going up, whether you look at the measurements or the predictions. While it is too early to put the 2017 temperature into the graph, so far, it is almost exactly equal to the 2016 value. If that trend holds for the rest of the year, it will be another case where the models are running slightly too cold.































 Arguments
Arguments






























"While people in the halls of Congress or in homes at holiday time may still argue about whether climate change is happening, scientists and engineers now have enough information to make informed decisions."
Yes exactly right. But one point, buildings and other civil works are mostly designed to building codes, which are ultimately political decisions! And many politicians are climate sceptics or are captive to lobby groups who are sceptics. In fact where I live politicians have not changed building codes, and have basically said it's up to the buyer and builders to do as they wish in terms of climate change. I think this is a totally inadequate political response.
It's possible of course to design above code, but this is just not always going to happen. This is human nature. As a result many people will go on building in vulnerable areas, and in silly ways, and this will ultimately become a burden on society as a whole.
You have to improve building codes and civil engineering codes, and make it mandatory. You may have to put some land off limits for development as well, if it's very vulnerable.
I would have thought that civil engineers are mostly interested in peak sstress values (rain, cold, warm, max wind) and seasonal averages in given locations rather than in global averages. Interesting that engineers are waking up to a new frontier.