What is the net feedback from clouds?
What the science says...
| Select a level... |
 Basic
Basic
|
 Intermediate
Intermediate
| |||
|
Evidence is building that net cloud feedback is likely positive and unlikely to be strongly negative. |
|||||
Climate Myth...
Clouds provide negative feedback
"Climate models used by the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assume that clouds provide a large positive feedback, greatly amplifying the small warming effect of increasing CO2 content in air. Clouds have made fools of climate modelers. A detailed analysis of cloud behavior from satellite data by Dr. Roy Spencer of the University of Alabama in Huntsville shows that clouds actually provide a strong negative feedback, the opposite of that assumed by the climate modelers. The modelers confused cause and effect, thereby getting the feedback in the wrong direction." (Ken Gregory)
At a glance
What part do clouds play in your life? You might not think about that consciously, but without clouds, Earth's land masses would all be lifeless deserts. Fortunately, the laws of physics prevent such things from being the case. Clouds play that vital role of transporting water from the oceans to land. And there's plenty of them: NASA estimates that around two-thirds of the planet has cloud cover.
Clouds form when water vapour condenses and coalesces around tiny particles called aerosols. Aerosols come in many forms: common examples include dust, smoke and sulphuric acid. At low altitudes, clouds consist of minute water droplets, but high clouds form from ice crystals. Low and high clouds have different roles in regulating Earth's climate. How?
If you've ever been in the position to look down upon low cloud-tops, perhaps from a plane or a mountain-top, you'll have noticed they are a brilliant white. That whiteness is sunlight being reflected off them. In being reflected, that sunlight cannot reach Earth's surface - which is why the temperature falls when clouds roll in to replace blue skies. Under a continuous low cloud-deck, only around 30-60% of the sunlight is getting through. Low clouds literally provide a sunshade.
Not all clouds are such good sunshades. Wispy high clouds are poor reflectors of sunlight but they are very effective traps for heat coming up from below, so their net effect is to aid and abet global warming.
Cloud formation processes often take place on a localised scale. That means their detailed study involves much higher-resolution modelling than the larger-scale global climate models. Fourteen years on, since Ken Gregory of the dubiously-named Big Oil part-funded Canadian group, 'Friends of Science', opined on the matter (see myth box), big advances have been made in such modelling. Today, we far better understand the net effects of clouds in Earth's changing climate system. Confidence is now growing that changes to clouds are likely to amplify, rather than offset, human-caused global warming in the future.
Two important processes have been detected through observation and simulation of cloud behaviour in a warming world. Firstly, just like wildlife, low clouds are migrating polewards as the planet heats up. Why is that bad news? Because the subtropical and tropical regions receive the lion's share of sunshine on Earth. So less cloud in these areas means a lot more energy getting through to the surface. Secondly, we are detecting an increase in the height of the highest cloud-tops at all latitudes. That maintains their efficiency at trapping the heat coming up from below.
There's another effect we need to consider too. Our aerosol emissions have gone up massively since pre-Industrial times. This has caused cloud droplets to become both smaller and more numerous, making them even better reflectors of sunlight. Aerosols released by human activities have therefore had a cooling effect, acting as a counter-balance to a significant portion of the warming caused by greenhouse gas emissions.
But industrial aerosols are also pollutants that adversely affect human health. Having realised this, we are reducing such emissions. That in turn is lowering the reflectivity of low cloud-tops, reducing their cooling effect and therefore amplifying global warming due to rising levels of greenhouse gases.
It sometimes feels as if we are between a rock and a hard place. We'd have been better off not treating our atmosphere as a dustbin to begin with. But there's still a way to fix this and that is by reducing all emissions.
Please use this form to provide feedback about this new "At a glance" section. Read a more technical version below or dig deeper via the tabs above!
Further details
The IPCC's Sixth Assessment Report eloquently sums up where we are in our understanding of how clouds will affect us in a changing climate:
"One of the biggest challenges in climate science has been to predict how clouds will change in a warming world and whether those changes will amplify or partially offset the warming caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human activities. Scientists have made significant progress over the past decade and are now more confident that changes in clouds will amplify, rather than offset, global warming in the future."
The mistake made by our myth-provider, writing in 2009, was to leap to a conclusion without the information needed in order to do so. He is suggesting that clouds are inadequately represented in climate models, so they must have a negative effect on temperatures. Instead of making such leaps of faith, however, the specialists in cloud behaviour have recognised the challenges and met them square-on. We now know a lot more about clouds as a result.
In the at-a-glance section, we explain the important difference between high clouds and low clouds, agents of warming and cooling respectively. Careful examination of older satellite records has detected large-scale patterns of cloud change between the 1980s and 2000s (Norris et al. 2016). Observed and simulated cloud change patterns are consistent with the poleward retreat of midlatitude storm tracks, the expansion of subtropical dry zones and increasing height of the highest cloud tops at all latitudes. The main drivers of these cloud changes appear to be twofold: increasing greenhouse gas concentrations and recovery from volcanic radiative cooling. As a result, the cloud changes most consistently predicted by global climate models have indeed been occurring in nature.
With respect to the cooling low clouds, one particularly important area of study has involved marine stratocumulus cloud-decks. These are extensive, low-lying clouds with tops mostly below 2 km (7,000 ft) altitude and they are the most common cloud type on Earth. Over the oceans, stratocumulus often forms nearly unbroken decks, extending over thousands of square kilometres. Such clouds cover about 20% of the tropical oceans between 30°S and 30°N and they are especially common off the western coasts of North and South America and Africa (fig.1). That's because the surface waters of the oceans are pushed away from the western margins of continents due to the eastwards direction of Earth's spin on its axis. Taking the place of these displaced surface waters are upwelling, relatively cool waters from the ocean depths. The cool waters serve to chill the moist air above, making its water vapour content condense out into cloud-forming droplets.

Fig. 1: visible satellite image of part of an extensive marine stratocumulus deck off the western seaboard of North America, with Baja California easily recognisable on the right. Image: NASA.
With their highly reflective tops that block a lot of the incoming sunlight, the marine stratocumulus clouds have a very important role as climate regulators. It has long been known that increasing the area of the oceans covered by such clouds, even by just a few percent, can lead to substantial global cooling. Conversely, decreasing the area they cover can lead to substantial global warming.
Although many cloud-types are produced by convection, driven by the heated land or ocean surface, marine stratocumulus clouds are different. They are formed and maintained by turbulent overturning circulations, driven by radiative cooling at the cloud tops. It works as follows: cold air sinks, so that radiatively-cooled air makes its way down to the sea surface, picks up moisture and then brings that moisture back up, nourishing and sustaining the clouds.
Stratocumulus decks can and do break up, though. This happens when that radiative cooling at the cloud tops becomes too weak to send colder air sinking down to the surface. It can also occur when the turbulence that can entrain dry and warm air, from above the clouds into the cloud layer, becomes too strong.
The importance of such processes has been further investigated recently, using an ultra-high resolution model with a 50-metre grid size. (Schneider et al. 2019). Global climate models typically have grid sizes of tens of kilometres. At that resolution, they cannot detail such fine-scale processes. This model, by contrast, is able to resolve the individual stratocumulus updraughts and downdraughts.
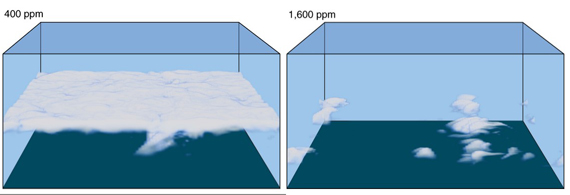
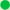
Fig. 2: results of modelling of marine stratocumulus behaviour in a high-CO2 world. This one compares conditions at 400 ppm (present) and 1600 ppm (hopefully never, but relevant to the Palaeocene and Eocene when a super-Hothouse climate prevailed). Redrawn from Schneider et al. 2019.
The modelling shows how oceanic stratocumulus decks become unstable and break up into scattered cumulus clouds. That occurs at greenhouse gas levels of around 1,200 ppm (fig. 2). When that happens, the ocean surface below the clouds warms abruptly because the cloud shading is so diminished. In the model, the extra solar energy absorbed as stratocumulus decks break up, over an area estimated to cover about 6.5% of the globe, is enough to cause a further ~8oC of global warming. After the stratocumulus decks have broken up, they only re-form once CO2 levels have dropped substantially below the level at which the instability first occurred.
These results point to the possibility that there is a previously undiscovered, potentially strong and nonlinear feedback, lurking within the climate system. These findings may well help to solve certain palaeoclimatic problems, such as the super-Hothouse climate of the Palaeocene-Eocene, some 50 million years ago. It's been hard to fully explain that event, given that estimates of CO2 levels at the time do not exceed 2,000 ppm. Present climate models do not reach that level of warmth with that amount of CO2. But the fossil record presents hard evidence for near-tropical conditions in which crocodilians thrived - in the Arctic. Something brought about that climate shift!
The quantitative aspects of stratocumulus cloud-deck instability remain under investigation. However the phenomenon appears to be robust for the physical reasons described by Schneider and co-authors. Closer to the present, the recent acceleration of global warming may be partly due to a decrease in aerosols. Aerosols produce smaller and more numerous cloud droplets. These have the effect of increasing the reflectivity and hence albedo of low cloud-tops (fig. 3). It follows that if aerosol levels decrease, the reverse will be the case. Of considerable relevance here are the limits on the sulphur content of ship fuels, imposed by the International Maritime Organization in early 2015. These regulations were further tightened in 2020. An ongoing fall in aerosol pollution, right under the marine stratocumulus decks, would be expected to occur. As a consequence, the size and amount of cloud droplets would change, cloud top albedo would decrease and there would be increased absorption of solar energy by Earth. That would be on top of the existing greenhouse gas-caused global warming. James Hansen discussed this in a recent communication (PDF) here.
Fig. 3: NASA graphic depicting the relationship between clouds, incoming Solar radiation and long-wave Infrared (IR) radiation. High clouds composed of ice crystals reflect little sunlight but absorb and emit a significant amount of IR. Conversely low clouds, composed of water droplets, reflect a great deal of sunlight and also absorb and emit IR. Any mechanism that reduces low cloud-top albedo will therefore increase the sunlight reaching the surface, causing additional warming.
In their Sixth Assessment Report, the IPCC also points out that the concentration of aerosols in the atmosphere has markedly increased since the pre-industrial era. As a consequence, clouds now reflect more incoming Solar energy than before industrial times. In other words, aerosols released by human activities have had a cooling effect. That cooling effect has countered a lot of the warming caused by increases in greenhouse gas emissions over the last century. Nevertheless, they also state that this counter-effect is expected to diminish in the future. As air pollution controls are adopted worldwide, there will be a reduction in the amount of aerosols released into the atmosphere. Therefore, cloud-top albedo is expected to diminish. Hansen merely suggests this albedo-reduction may already be underway.
Last updated on 15 October 2023 by John Mason. View Archives































 Arguments
Arguments































- Solar insolation (barely changes)
- Orbital forcings (changes predictably on huge time scales)
- CO2 (changes on any of 3 time scales, geologic=very slow, natural feedback=medium, anthropogenic=very fast
- H2O (changes relatively quickly in direct proportion to temperature, and so it is the primary amplifier in power, but not a controller since it exerts no independent control of its own)
- Albedo (can change relatively quickly, or slowly, but almost always as a response to other factors)
- Clouds (change almost instantaneously, and positive/negative effects are arguable, but relatively inconsequential compared to the bigger factors).
- Land mass dispositions (which greatly affect albedo and the results of orbital forcings, but which only themselves vary on massively long timescales)
Which is primary? At the onset and termination of glacial periods, the orbital forcings, but only through an albedo feedback, and in conjunction with a strong CO2 feedback, which in turn operates in conjunction with the strong H2O feedback. Outside of those periods of orbital forcings, under natural conditions, CO2 is the main long term driver, amplified by albedo, cloud and H2O feedbacks. During anthropogenic pollution, CO2 is the only control mechanism that operates on the time scales that we are witnessing, again amplified by all of the usual feedbacks.