Has the greenhouse effect been falsified?
What the science says...
| Select a level... |
 Basic
Basic
|
 Intermediate
Intermediate
| |||
|
The greenhouse effect is standard physics and confirmed by observations. |
|||||
Climate Myth...
Greenhouse effect has been falsified
"[T]he influence of so-called greenhouse gases on near-surface temperature - is not yet absolutely proven. In other words, there is as yet no incontrovertible proof either of the greenhouse effect, or its connection with alleged global warming.
This is no surprise, because in fact there is no such thing as the greenhouse effect: it is an impossibility. The statement that so-called greenhouse gases, especially CO2, contribute to near-surface atmospheric warming is in glaring contradiction to well-known physical laws relating to gas and vapour, as well as to general caloric theory.' (Heinz Thieme)
At a glance
Did you know that in the late 1700s, astronomers calculated the Earth-Sun distance to within 3% of the correct average value of 149.6 million kilometres? That was an incredible feat for the time, involving painstaking measurements and some pretty serious number crunching, with no help from computers.
Why is that mentioned here, you might ask. It's because not long afterwards, in the 1820s, French physicist Jean Joseph Baptiste Fourier made another crucial calculation. He worked out that at this distance from the Sun, Earth should have been an uninhabitable iceball.
Fourier suggested there must be some kind of insulating 'blanket' within the atmosphere. By the end of that century, Eunice Foote and John Tyndall had proved him quite correct through their experiments with various gases and Svante Arrhenius quantified matters in 1896, even calculating the effect of doubling the concentration of CO2. They had it largely figured out all that time ago.
If you are still sceptical about the existence of a greenhouse effect on Earth, there's something you can do in order to double-check. Go to the moon.
Well, you don't have to go personally, thanks to remote sensing and lunar landings by both unmanned and manned craft. Such intrepid expeditions mean we have a stack of data regarding lunar properties. The moon is pretty much the same distance from the Sun as Earth, but the lunar atmosphere is so thin it may as well not exist at all. There's virtually nothing to inhibit heat transfer, in or out.
In addition, the Moon turns but slowly on its axis compared to Earth. While a mean Solar day here lasts 24 hours, on the Moon it lasts just under a month. You get the best part of a fortnight of relentless Solar heating followed by a similar period of cooling in the long lunar night. So what's the temperature?
In the vicinity of the Lunar equator, daytime temperatures eventually reach a boiling hot 120oC. During the lunar night, that temperature drops away to -130° C. No atmosphere so no greenhouse effect. All that heat accumulated in the long lunar day just shoots straight back out into space. Nights on Earth may be much shorter, but nevertheless in the absence of a greenhouse effect they would be brutal.
Our approximately Earth-sized near neighbour, Venus, closer to the Sun, is different again. It has a massive dense atmosphere mostly consisting of CO2 with a side-helping of sulphur dioxide. Surface atmospheric pressure on Venus is so great that on Earth you would need to go a kilometre down in the ocean to find similar values. The planet rotates very slowly on its axis so days and nights are even longer than on the Moon. But unlike the Moon, Venus is always a hot place. Its surface temperature is over 450oC, day or night. An extreme greenhouse effect maintains that heat.
Remember: no atmosphere, no greenhouse effect and unimaginably cold lunar nights - but the example of Venus shows you can also have too much of a good thing. Earth really is a Goldilocks planet.
Please use this form to provide feedback about this new "At a glance" section. Read a more technical version below or dig deeper via the tabs above!
Further details
Some climate science deniers dispute the existence of the ‘greenhouse effect’. This is where their arguments lurch from silly - to beyond silly. The greenhouse effect keeps the surface temperature of Earth approximately 33oC warmer than it would be if there were no greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. In other words, without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be effectively uninhabitable.
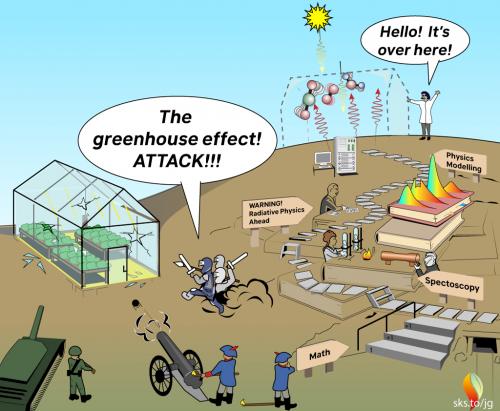
Fig 1: The greenhouse effect is an analogy not meant as a scientific model of effect; hence, detractors have attacked the wrong model. (source: jg)
How do we know for sure this effect is real? The principle is demonstrated through basic physics, because a bare rock orbiting the Sun at the Earth-Sun distance (mean = 149.6 million kilometres) should be far colder than the Earth actually is. This was realised by Jean Joseph Baptiste Fourier in the 1820s, but the explanation why it was the case was not forthcoming for a few more decades. Fourier considered it to have something to do with the atmosphere having the properties of a kind of insulating blanket.
The existence of Fourier's hypothetical 'blanket' was confirmed by the experimental studies done by Eunice Foote and John Tyndall, working independently on either side of the Atlantic in the 1850s. Foote's results were announced at the 1856 meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and published in the American Journal of Science and Arts in the same year. The paper was entitled, ‘Circumstances Affecting the Heat of the Sun’s Rays’, with an excellent recent review by Ortiz and Jackon (2020). A key passage is as follows:
“The highest effect of the sun’s rays I have found to be in carbonic acid gas. An atmosphere of that gas would give to our earth a high temperature; and if as some suppose, at one period of its history, the air had mixed with it a larger proportion than at present, an increased temperature from its own action, as well as from increased weight, must have necessarily resulted.”
In his 1861 paper, “On the absorption and radiation of heat by gases and vapours, and on the physical connexion of radiation, absorption, and conduction” (PDF here), Tyndall stated:
“Now if, as the above experiments indicate, the chief influence be exercised by the aqueous vapour, every variation of this constituent must produce a change of climate. Similar remarks would apply to the carbonic acid diffused through the air; while an almost inappreciable admixture of any of the hydrocarbon vapours would produce great effects on the terrestrial rays and produce corresponding changes of climate.”
Tyndall had in his own words identified methane as an even more potent greenhouse gas than CO2. Later that century, Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius put the numbers on the relationship between greenhouse gas concentrations and surface temperatures. He was able to calculate the effect of doubling the CO2 concentration in the air. The result was a globally-averaged figure of 5-6°C of warming, not that dissimilar to modern values.
Empirical Evidence for the Greenhouse Effect
We only have to look to our moon for evidence of what the Earth might be like, without an atmosphere and greenhouse effect. It's not as though we're short of data about our satellite. While the moon’s surface reaches 120oC (248oF) in direct sunlight at the equator during the long lunar day, when it gets dark the temperature drops down to a frigid -130oC (-202oF).
Since the moon is virtually the same distance from the sun as we are, it is reasonable to ask why at night the Earth doesn’t get as cold as the moon. The answer is that, unlike the Earth, the moon has no insulating blanket of greenhouse gases, because it has virtually no atmosphere at all. Without our protective atmosphere and its greenhouse effect, the Earth would be as barren as our lifeless moon. In the absence of the heat trapped overnight in the atmosphere (and in the ground and oceans) our nights would be so cold that few plants or animals could survive even a single one.
Conclusive evidence for the greenhouse effect – and the role CO2 plays – can also be seen in data from the surface and from satellites. By comparing the Sun’s heat reaching the Earth with the heat leaving it, both things we can measure with great accuracy, we can see that less long-wave radiation (heat) is leaving than arriving. Since the 1970s, less and less radiation is leaving the Earth, as the levels of CO2 and other greenhouse gases build up. Since all radiation is measured by its wavelength, we can see that the frequencies being trapped in the atmosphere are the same frequencies absorbed by greenhouse gases.
To conclude, disputing that the greenhouse effect is real is to attempt to discredit centuries of science, the laws of physics and indeed direct observation. Without the greenhouse effect, we would not even be here to argue about it.
Last updated on 26 November 2023 by John Mason. View Archives































 Arguments
Arguments

































A new variant of this has appeared on Goddard's blog. A guy, recently retired and so now "free to talk" (although he still writes under a pseudonym), who claims to be an infrared astronomer is saying that IR at the CO2 wavelength can't warm the Earth.
He says "In all the bands that are responsible for back radiation in the brightness temperatures (color temperatures) related to earth’s surface temperature (between 9 microns and 13 microns for temps of 220K to 320 K) there is no absorption of radiation by CO2 at all. In all the bands between 9 and 9.5 there is mild absorption by H2O, from 9.5 to 10 microns (300 K) the atmosphere is perfectly clear except around 9.6 is a big ozone band that the warmists never mention for some reason. From 10 to 13 microns there is more absorption by H2O. Starting at 13 we get CO2 absorption but that wavelength corresponds to temperatures below even that of the south pole. Nowhere from 9 to 13 microns do we see appreciable absorption bands of CO2."
So obviously I'm not buying into the overturning of years of well tested science by some anonimous conspiracy theorist on a blog and ask those who mention it to tell me when he's publishing his paper or for a scientific reference where I can check his claims. On the other hand I wouldn't appreciate if someone could give me a more scientific understanding of why he is wrong. Always looking to learn.
Sigh, it is pretty hard to take Steve "Co2 falls as snow in Antarctica" Goddard seriously. Now its conservation of energy is wrong? It pretty hard to make sense of what he is saying - I dont think he knows. However, there is excellent series taking you through the text book details at Science of Doom.
rugbyguy59, that argument demonstrates a fundamental lack of understanding of the greenhouse effect. The Earths energy budget is determined at the top of the atmosphere by the temperature of the atmosphere at the height at which outbound IR is no longer absorbed by CO2. The lapse rate means this is much colder than the surface. As we add more CO2 the height of this layer rises, which means that the radiating layer is colder and hence radiates less energy. The Earth as a whole then gains heat until the temperature of the radiating layer warms enough for the radiated energy to be high enough for the energy budget to be balanced.
Now, as the atmosphere as a whole warms, it will radiate heat at a range of frequencies, because it is due to the heat of the atmosphere as a whole, not just the IR radiated from CO2. So of course it isn't all at the absorption bands for CO2.
Gilbert Plass worked out the details of this back in the 1950s.
Direct evidence of CO2 causing warming is in the following news article and original paper.
http://newscenter.lbl.gov/2015/02/25/co2-greenhouse-effect-increase/
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v519/n7543/full/nature14240.html
The above describe direct measurement of the incoming and outgoing radiation of the Globe at various wavelengths over a decade, and show that warming is directly due to more CO2.
[PS] Fixed link. Please learn to do this yourself with the link button in the comments editor.
"the moon’s surface reaches 130 degrees C in direct sunlight at the equator"
So GH gasses and the GH effect reduce maximum temperature too.
ConcernedCitizen @112, no. Rather, the equalization of temperatures by the distribution of energy (by the atmosphere and ocean) reduces maximum temperatures and increases minimum temperatures - as anybody knows who compares maximums and minimums in a desert with those on the coast.
And in case you are wondering, the estimated 33 C increase in Global Mean Surface Temperature due to the Earth's greenhouse is relative to a situation with perfectly distributed energy on the surface (ie, all points are the same temperature, whether polar or equatorial, and whether day or night). That means it is an under estimate of the temperature impact of the greenhouse effect.
ConcernedCitizen @112.
Another take on answering your question.
Sort of yes, but only a little bit of that implied by the moon's maximum temperatures. The main reason the moon reaches 130ºC is because it has a 655 hour rotation so the equatorial moon surface is being heated by sunlight for 2 weeks at a stretch rather than the 12 hours here on Earth.
A quick look at some max/min temperatures for places on the Earth's equator shows a difference of about 10ºC night to day. This is an air temperature. I would imagine rock temperatures on Earth (which is the equivalent of what is being measured on the moon) would show a greater variation. Looking at a graph of moon surface temperatures, the moon temperature rises from 300K something like 40ºC in 12 hours.
Part of the reason for extra heating on the moon will be because our atmosphere reflects away sunlight as well as also absorbing sunlight before it reaches the ground (famously the UV component of sunlight). The atmosphere also cools the surface through evaporation and conduction/convection. I'm not sure that any of these mechanisms would be called a "GH effect" but rather the effect of having an atmosphere.
@111 Without reading the links I suspect that they are about spectral signs of absorption from co2?
The strange thing with co2-theory is that a massive decrease in spectral intensity is interpreted as increase in temperature. That is a direct opposite of how spectral intensity works. A decrease in intensity by co2 absorption is a decrease in temperature. There is no way around that. Any heating at any level must show up as an increase in intensity. Heat doesn't hide
@113
The 33 degrees you point at as a proof for the greenhouse effect is enirely a product of lacking understanding of the physics in radiation and heat. I will show you why.
If we use measured values from real observations of solar irradiation at the surface, we find that 1000W is a median value when we look at variations from pole to pole.
If we use that, the real value of irradiation, and an emissivity of 0.8 derived from measured surface flux OLR, we get:
1000W is 800W transformed into heat in the surface. Since only half of the surface is heated we must divide this in 2. So, 800W/m^2/2m^2 gives 400W OLR. Which fits very nicely with the average temperature of about 290K. Without even have entered the atmospher on it´s way to space.
So, when we calculate radiative flux from the surface with measured real values, we can see that the surface temperature has no room for any greenhouseeffect.
The reason is that you use an average flux density that is wrongly calculated by using TOA irradiation/m^2 and divide by four. That gives a surface flux equivalent to 4 small weak suns which heats a m^2 with an intensity of 259W, when the surface cools with a flux of 390W.
Do you see the difference? The problem comes from the fact that flux and temperature is not linear but logarithmic. Four suns with a flux that adds upp to the same wattage as one sun can not heat the surface as much as the one sun in reality does.
You use a deeply flawed approach to solar irradiation flux when you average to a value that we know is wrong according to measurements. It totally ignores that the connection between flux and temperature is non-linear.
You use values in a calculation that gives a temperature of 255K, which is wrong according to measurements that show 288K, and then you apply a greenhouseeffect to cover up the difference. No other explanation than the difference of 33 degrees is given to show how this rise in temperature from greenhousegasses occur. There are no calculations that show how icecold gas can heat a warm surface, other than your calculation of surface temp that give the wrong temperature compared to measured values.
I think that by using measured real values as I did, and arriving at pretty much exactly the right temperature without any fictive greenhouseeffect, before it even has entered the atmospheric gasvolume, I have proven that there is no greenhouseeffect.
Remember that you calculation uses values of flux that is not real, they don´t exist anywhere as a value of irrradiative flux density, and that I use a value that is measured in reality. In my calculation the numbers fit perfectly, in yours there is need for a fudgefactor.
There is a big difference in how you treat radiation when you calculate temperature. You must pay attention to the relationship between Watt and K, only if you do that you realize why the model you use get the wrong value of 255K.
If you think about it, 4 suns around the earth that radiates @255K in 4m^2, will only heat 1m^2 to 255K.
But one sun heating 1m^2 @ a median 1000W, which is a real measured value, will heat 2m^2 to 290K.
I´m pretty proud of this point I´m making. I think I have just proven that there is no greenhouse effect.
@114
That is not correct. The reason that surface temp of the moon under irradiation is 130C, is that it gets 1370W/m^2 of flux density. (1370/0.0000000567)^0.25=394K. That is 121C. Right?
You see that there is no need for any other explanations. I cannot understand why you include night temperature in a calculation of heating from solar irradiation? The night side is not irradiated, why should that be taken in to the calculation of the effect of irradiation?
Mean temperature is a useless value in radiative heating of a surface, it is a measure of cooling, not heating. And it is the result of adding colling to heating for a net value.
On earth we are lucky enough to have an atmosphere that evens out the mean temperature by cooling irradiated surface area with air that distributes the heat in every heated point to the whole volume of the atmosphere. Sure, we get a higher night temp but that is the result of cooling, not warming. The surface of the earth would be 394K without an atmosphere. No one kan argue the fact that irradiative flux density is lowered by the atmosphere. Solar irradiation is what heats the earth, if that is lowered by the atmosphere it means that the atmosphere cools the earth.
That is the No Bullshit Approach that is the beauty in using real measured values.
[JH] A word of advice: "Don't count your chickens before they are hatched."
Sloganeering is prohibited by the SkS Comments Policy.
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can be rescinded if the posting individual treats adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
@105
I don´t want to call you a liar so instead i say that your words does not tell the truth.
a) The surface receives about 1000W/m^2 of solar irradiation flux. It emits about 400W. There is no way around that other than using methods that gives values that is not real.
b) Flux at TOA is not 1370W/m^2 in average. Not 1000W or 400W either. So you are not telling the truth. Sure, it may add up to your fictive values, but those does not correlate with observations and can be disregarded as they must be wrong.
c) I can see no argument here. You are saying that a decrease in spectral intensity is a sign of rising temperature. That is as wrong as it can get. If the atmosphere shows an effect on flux that is decreasing intensity, that means that the atmosphere is cooling. You mus pay attention to the fact that absorption is not the same as emission. Only increased emission that gives increased temperatur/flux density, is a sign of heating. Only that. Heat doesn´t hide.
It is not a sign of warmer surface if the tropopause show that co2 decreasing intensity in spectral flux. Co2 shows that it effectively keep tropopause flux in peak wavelenghts down to a 220K balckbody curve. What you see is the bottom regulator of the temperature in the atmosphere. Co2 makes sure that tropopause keeps its temperature @ 220K, according to spectrum.
Since we all know that it radiates equally both up and down, we can be sure that 220K is the contribution downwards as well. Not very hot, don´t you think?
c´) If co2 was increasing temp we would see an increase in those wavelenghts that it absorbs. Are you aware of that heat can be absorbed and transformed into lower temperature?
That happens when it takes more heat for the absorbing body to reach the same temperature. And we know that co2 radiates at 220K, so it apparently will not heat up unless it gets a lot more energy. That could be an effect from the molecule colliding with other gasses and dissipating the energy. It doesn´t matter, the measured spectrum at TOA is proof of co2 cooling, not heating.
c´´´) In heat transfer the rate of transfer is the difference in T. The smaller the difference, the slower transfer we get. The hot body that transfer heat to the cold body is not affected by the rate of transfer. It keeps the same T all the way up to when the cold body reaches the same T, and then there is no measurable transfer.
I like photons as much as anyone, but we know from experimental evidence that they must not be included in heat transfer. Because a hot body does not change it´s temperature because a cold body absorbs heat from it´s radiation field.
That is, a hot body does not get warmer because a cold body is colder.
And you are right, it is necessary for the greenhouse effect to have cold IR-radiation adding to surface temp. But it is not necessary for reality.
[JH] Comments that include snarky and inflamatory insuations are not welcome on this website. Please cease and desist immediately. If you do not, you will relinquish your privilege of posting comments.
@113
As I have shown in my other posts, No.
The 33 degrees is entirely a product of you using 4 weak suns irradiating 4m^2 with the intensity of 290W/m^2. Since the surface is heated with an intensity of almost 400K/1000W transformed into heat equivalent to 400W/2m^2 with a surface emissivity of 0.8, the 33 degrees is a product of imagination. Or just flawed application of physics.
[JH] Comments that include snarky and inflamatory insuations are not welcome on this website. Please cease and desist immediately. If you do not, you will relinquish your privilege of posting comments.
Edit in 119:
That should of course be 400W*2m^2 of surface heat from irradiation of 1000W/m^2.
fake reality @115-120.
Hurrah! I thought the theory of a flat Earth was behind us but evidently not with you. @116 you tell us "Since only half of the surface is heated we must divide this in 2." This can only mean you subscribe to a flat Earth. It is truly fantastic to see such a wonderful theory maintained in the face of modern science. Well done you!!
@177 you address my comment @114 that concerns Lunar temperature. You declare that I am "not correct" (which is thankfully less strongly put than some of your other comments @115-120) and provide what you describe as "the No Bullshit Approach" which perhaps may be some terminology used by 'flat Earth' theory? I am also in the dark over your comment about the "using real measured values." Who is/is not using such values?
The 130ºC quoted @114 is a rough value and not the measured temperature which would likely be nearer 117ºC for the noon-time equatorial temperature. (I'm hoping the concept of 'equator' does not clash with your 'flat Earth' beliefs.)
However, you do rather queer you own pitch with your reference to Earthly temperatures. With a Lunar day lasting ~29 days, Lunar temperatures at noon are not far off that of steady-state. This is far from true on Earth. So when you state "we get a higher night temp but that is the result of cooling, not warming," this is of course correct. But critically you must account for the 'something' that is "cooling" which allows the night-time to be 'warmed'. That 'something' would be the day-time. (Thankfully, flat Earth theory does not refute the existance of night & day so that should make sense to you.) Warmer nights due to cooler days. Simples.
@110
There is no balance at the top. 1370W/m^2 going in and a tenth of that going out. If you want you can double OLR from 220K or whatever value you use, since it represents the amount absorbed in 1m^2 from solar irradiation when it is emitted from twice the surface area. That doesn´t help much though, it´s not possible to find any balance in those numbers. And of course we should not expect to, earth is not a lossles system, it leaks energy at every point of absorption and emission as it is a greybody and not a blackbody.
A greybody is defined by it´s lacking ability to convert irradiation into radiation. It is cooler than a blackbody.
You might be right in that more co2 would increase height of tropopause, but wrong in the assumption that it would affect surface temperature. Everything radiates according to it´s own temperature. That temperature might be the product of heat from a more intense source, but it never is a product of a less intense source.
You claim that earth surface radiates with an intensity that is influenced by a cold body absorbing heat in it´s radiation field. That is in direct opposition to what we know of heat transfer, that the rate is the difference in T and that the hot body never changes in temperature even when the absorber has reached an equally excited state.
In fact, when you want to increase heat transfer from the hot body, one method is to add another surface that absorbs energy and radiates more energy from a larger surface area. Then more energy will transfer to the surroundings, in this case that is the optimal heat sink in 3K space vacuum.
Ooops, I just said that according to heat transfer as heat and thermal radiation in theory and practice, the atmosphere increase heat transfer to space. Well, that is in line with science and we don´t need to violate it with horrific ideas about how much cold we need to get something warm.
Where did you get the idea that the surface is communicating with TOA about what balance needs to be attained. The surface radiates according to it´s own temperature, as everything does, and the surface temperature is the suns. It radiates as a greybody in relation to the sun, and the atmosphere radiates in longwave as a greybody in relation to earth, and through the earth it radiates as a greybody in relation to the sun.
The atmosphere radiates according to what it receives. And in heat transfer we learn that even if photons might be funny little things, they should never be included in calculations of heat transfer as heat or thermic radiation. That would give the wrong results.
Still, that is just what you do.
Another detail is that all radiation in earth system is thermic radiation, from visible at 500nm through the whole spectrum of IR. It is a product of temperature/heat. The hotter the brighter.
Why would an intensity of 250K/300W in the atmosphere add anything to the 1000W we get from the sun? It is not a question of the numbers adding up to more energy, it is about excitance of matter.
The maxwell-boltzmann distribution tells us that a temperature is a measure of the probability of different states of excitance=levels of energy in a particle/photon. The higher temperature having more probable states of higher energy in more photons/particles. So you can see why a 100 sources of radiation at 250K will not give a higher probability for higher states in particles/photons. Much less an icecold atmosphere in relation to a hot surface, it actually decrease overall probability of higher states. That is cooling.
Only something hotter can increase temperature of a body in an open system.
@121 MA rodger
Do you realize what you just did there? You were trying to discredit me by attaching a belief in unscientific theorys to my character. That is very bad behaviour, you should keep to the things discussed. That was bad rethoric.
You dont understand the simple concept that radiation absorbed at any surface area from solar irradiation, is emitted from twice that area?
Are you saying that the earth is not cooled by half and heated by half?
And about measured values, 1000W/m^2 is a common value in a pretty big area from the equator and outward towards the poles. It represents a mean value uf emitted intensity since it is absorbed as a ~maximum and will distribute through the earth evenly and emitted from twice that area.
That makes it the value defining the maximal averaged intensity possible=mean temperature emitted.
So I am using measured values, when I use 1000W/m^2.
About the 130degrees on the moon, 117 is even closer to my calculation. So you prove my point. And please stop attacking my character by attaching views to me that I don´t have.
I got a warning further up for being snarky, if the mod is not biased you will have one for this.
"you must account for the 'something' that is "cooling" which allows the night-time to be 'warmed'."
This is why I get snarky. I gave you numbers in calculations and instead of addressing that with scientific arguments, you talk about "something" "allowing" something else to be "warmed".
Do you realize how far from science such an argument is?
[JH] Moderation complaints are prohibited and will be summarily deleted per the SkS Comments Policy.
In order to be taken seriously on this website, you must document the sources of the information you present. You have not done so in either this comment or in previous comments. Without documentation, you are merely expressing your personal opinion which carries very little weight in a serious discussion about science.
Fake,
It is common knowledge that for a spherical object you have to devide the cross-sectional radiation by four, not two times. That means the incident radiation is about 240 w/m2, not 400 as you calculate. It follows that if you cannot calculate the incident radiation within a factor of two, your calculation of the temperature is grossly in error. Since you were so assertive that you are correct and the rest of the world is stupid, MA Rodgers probably thought it was a waste of time to engage you and discuss the actual calculations.
If you want to drop your attitude and ask how you came to have such absurd ideas there are people at this site who would help you to understand what the real data calculations are. If you continue to insist your incorrect calculations are correct I doubt many will engage with you. Ask quesitons about those ideas you do not understand. If you think you have discovered an error everyone else is making consider that you probably have made another basic math error.
@125
I know how and why you do it that way. But since flux density is not linear it is the wrong way to handle it. And most of all, if there is a way to calculate with measured values at the surface, and that gives you the right number immediately, then you know that it is right. The main point is real observed flux density at the surface.
Do you agree that dividing by four is equal to 4 weak suns @ 250-ish K?
Do you agree that maxwell-boltzmann is correct about energycontent in matter by describing the probability of diffrent states of excitance in matter, is correct?
If you do, then you should agree that it is the wrong approach to divide flux density en four equal smaller suns that each has the same probability for a certain exited state in matter, and that it is the same when they all is added as irradiative flux at their respective m^2.
And you would also agree that a single sun at the same fluxdensity as the sum of the 4 suns, will deliver a flux density to the total surface area in one irradiated m^2 that is emitted radiation from 2m^2 surface.
It´s not like I´m making numbers up here, they are real measured values at the surface. If I´m remembering right solar cells are calibrated to 1kW. There is of course a real reason for that.
Your number is not real, it may be measured in a cold place sometimes, but a uniform value of 240W is not more than sunlight worth of 255K from all directions at the surface. You must realize that 255K irradiating the earth from all directions heats the surface less than 1000W in one direction.
I think I wrote wrong value earlier, 1000W=364K nothing else. If I have written 390K somewhere that is the value of TSI-1370W.
Show me where the absurdity comes from in my calculation. Then show me what is not absurd in calculating the temperature with a value that is way off from observations in reality.
I get the right number at the surface. You get the wrong number. Isn´t the absurd residing in you saying that your number, that we know is not right from observations, is more valid than my calculation that use measured value from real observation that is documented?
We have measured 1000W/1m^2 at the surface, it is absolutely right to use that number emitted as /2m^2 when calculating OLR. And since we agree on OLR surface flux at about 400W, we can use real observed emissivity as well. All real values from reality, and it gives the right surface temp. You have 4 suns evenly heating 4 m^2 each with 255K=240W, and you say that it should be equal to 1000W/m^2 which comes from 1370W at TOA, same as you are using.
You are saying that 240W/m^2 is equal to 1000W/m^2 that is averaged as 400W/m^2 when emitted by double the size Area?
What is real about that?
I have this attitude as I have seen your collective attitude against the ones not agreeing with you. My comments is nothing compared to that I was attacked above when I was assigned the belief in a flat earth. That is really low rethoric.
I am very sure that I didn´t make an error since I use real measured values and get the correct results. And I am sure that the basic math error is made in your theorys calculation since it is not anything real about 4 weak suns heating the earth to 255K with 240W/m^2.
But OK,if you want questions I can ask: where did you get the idea that 240W/m^2 from 4 suns irradiating 4m^2 is equal to 1370W/m^2 in heat transfer, since temperature and Watt/m^2 is not linear?
Why do you use an absorbing body at a low temperature in earths radiation field for heat transfer to the surface, when we know that heat transfer from a warm to a cold body is something that only affects the cold body?