The 97% consensus on global warming
What the science says...
| Select a level... |
 Basic
Basic
|
 Intermediate
Intermediate
|
 Advanced
Advanced
| ||||
|
97% of climate experts agree humans are causing global warming. |
|||||||
There is no consensus
"[...] And I'll mention that the stat on the 97% of - of scientists is based on one discredited study." (Ted Cruz)
At a glance
What is consensus? In science, it's when the vast majority of specialists agree about a basic principle. Thus, astronomers agree that the Earth orbits around the Sun. Biologists accept that tadpoles hatch out from frog-spawn and grow into adult frogs. Almost all geologists agree that plate tectonics is real and you'd be hard-placed to find a doctor who thinks smoking is harmless.
In each above case, something has been so thoroughly looked into that those who specialise in its study have stopped arguing about its basic explanation. Nevertheless, the above examples were all once argued about, often passionately. That's how progress works.
The reaching of scientific consensus is the product of an often lengthy time-line. It starts with something being observed and ends with it being fully explained. Let's look at a classic and highly relevant example.
In the late 1700s, the Earth-Sun distance was calculated. The value obtained was 149 million kilometres. That's incredibly close to modern measurements. It got French physicist Joseph Fourier thinking. He innocently asked, in the 1820s, something along these lines:
"Why is Planet Earth such a warm place? It should be an ice-ball at this distance from the Sun."
Such fundamental questions about our home planet are as attractive to inquisitive scientists as ripened fruit is to wasps. Fourier's initial query set in motion a process of research. Within a few decades, that research had experimentally shown that carbon dioxide has heat-trapping properties.
Through the twentieth century the effort intensified, particularly during the Cold War. At that time there was great interest in the behaviour of infra-red (IR) radiation in the atmosphere. Why? Because heat-seeking missiles home in on jet exhausts which are IR hotspots. Their invention involved understanding what makes IR tick.
That research led to the publication of a landmark 1956 paper by Gilbert Plass. The paper's title was, “The Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climatic Change”. It explained in detail how CO2 traps heat in our atmosphere. Note in passing that Plass used the term "Climatic Change" all the way back then. That's contrary to the deniers' frequent claim that it is used nowadays because of a recent and motivated change in terminology.
From observation to explanation, this is a classic illustration of the scientific method at work. Fourier gets people thinking, experiments are designed and performed. In time, a hypothesis emerges. That is a proposed explanation. It is made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
Once a hypothesis is proposed, it becomes subject to rigorous testing within the relevant specialist science groups. Testing ensures that incorrect hypotheses fall by the wayside, because they don't stand up to scrutiny. But some survive such interrogation. As their supporting evidence mounts up over time, they eventually graduate to become theories.
Theories are valid explanations for things that are supported by an expert consensus of specialists. Gravity, jet aviation, electronics, you name it, all are based on solid theories. They are known to work because they have stood the test of time and prolonged scientific inquiry.
In climate science today, there is overwhelming (greater than 97%) expert consensus that CO2 traps heat and adding it to the atmosphere warms the planet. Whatever claims are made to the contrary, that principle has been established for almost seventy years, since the publication of that 1956 landmark paper.
Expert consensus is a powerful thing. None of us have the time or ability to learn about everything/ That's why we frequently defer to experts, such as consulting doctors when we’re ill.
The public often underestimate the degree of expert consensus that our vast greenhouse gas emissions trap heat and warm the planet. That is because alongside information, we have misinformation. Certain sections of the mass-media are as happy to trot out the latter as the former. We saw a very similar problem during the COVID-19 pandemic and it cost many lives.
For those who want to learn more, a much longer detailed account of the history of climate science is available on this website.
Please use this form to provide feedback about this new "At a glance" section. Read a more technical version below or dig deeper via the tabs above!
Further details
We know full well that we don’t have the time or capacity to learn about everything, so we frequently defer to the conclusions of experts. Without experienced people using their expertise to perform many vital tasks – and without new people constantly entering such occupations – society would quickly disintegrate.
The same is true of climate change: we defer to the expert consensus of climate scientists. Indeed, public perception of the scientific consensus with regard to global warming has been found to be an important gateway into other enlightened climate-related attitudes - including policy support.
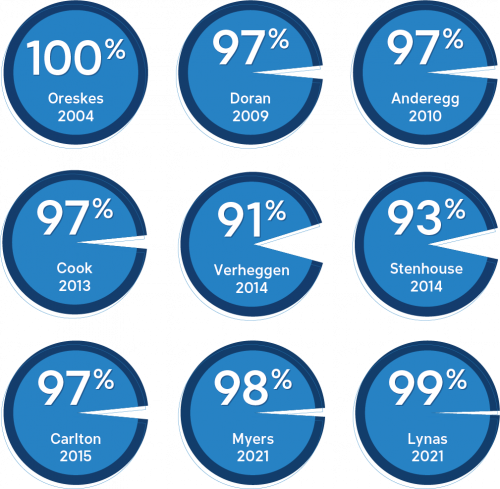
Let's take a look at summaries of the key studies, featured in the graphic above, into the degree of consensus. These have been based on analyses of large samples of peer-reviewed climate science literature or surveys of climate and Earth scientists. These studies are available online through e.g. Google Scholar. That slightly different methodologies reached very similar conclusions is a strong indicator that those conclusions are robust.
Oreskes 2004
In this pioneering paper, a survey was conducted into all peer-reviewed abstracts on the subject 'global climate change', published between 1993 and 2003. The work showed that not a single paper, out of the 928 examined, rejected the consensus position that global warming is man-made. 75% of the papers agreed with the consensus position while 25% made no comment either way.
Doran & Zimmerman 2009
A survey of 3,146 Earth scientists asked the question, "Do you think human activity is a significant contributing factor in changing mean global temperatures?" Overall, 82% of the scientists answered yes. However, what was most interesting was the type of response compared to the level of expertise in climate science. Of scientists who were non-climatologists and didn't publish research, 77% answered yes. In contrast, 97.5% of actively-publishing climatologists responded yes. As the level of active research and specialization in climate science increases, so does agreement that humans are significantly changing global temperatures. The paper concludes:
"It seems that the debate on the authenticity of global warming and the role played by human activity is largely non-existent among those who understand the nuances and scientific basis of long-term climate processes. The challenge, rather, appears to be how to effectively communicate this fact to policy makers and to a public that continues to mistakenly perceive debate among scientists."
Anderegg et al. 2010
This study of 1,372 climate science researchers found that (i) 97–98% of the researchers most actively publishing in the field support the tenets of anthropogenic climate change (ACC) as outlined by the IPCC and (ii) the relative climate expertise and scientific prominence of the researchers unconvinced of ACC are substantially below that of the convinced researchers.
Cook et al. 2013
A Skeptical Science-based analysis of over 12,000 peer-reviewed abstracts on the subject 'global climate change' and 'global warming', published between 1991 and 2011, found that over 97% of the papers taking a position on the subject agreed with the consensus position that humans are causing global warming. In a second phase of the project, the scientist authors were emailed and rated over 2,000 of their own papers. Once again, over 97% of the papers taking a position on the cause of global warming agreed that humans are causing it.
Verheggen et al. 2014
Results were presented from a survey held among 1868 scientists studying various aspects of climate change, including physical climate, climate impacts, and mitigation. The survey was at the time unique in its size, broadness and level of detail. Consistent with other research, it was found that as the level of expertise in climate science grew, so too did the level of agreement on anthropogenic causation. 90% of respondents with more than 10 climate-related peer-reviewed publications (about half of all respondents), explicitly agreed with anthropogenic greenhouse gases (GHGs) being the dominant driver of recent global warming. The respondents’ quantitative estimate of the GHG contribution appeared to strongly depend on their judgement or knowledge of the cooling effect of aerosols.
Stenhouse et al. 2014
In a survey of all 1,854 American Meteorological Society members with known e-mail addresses, achieving a 26.3% response rate, perceived scientific consensus was the strongest predictor of views on global warming, followed by political ideology, climate science expertise, and perceived organisational conflict.
Carlton et al 2015
Commenting that the extent to which non-climate scientists are skeptical of climate science had not so far been studied via direct survey, the authors did just that. They undertook a survey of biophysical scientists across disciplines at universities in the Big 10 Conference. Most respondents (93.6%) stated that mean temperatures have risen. Of the subset that agreed temperatures had risen, the following question was then asked of them: "do you think human activity is a significant contributing factor in changing mean global temperatures?" The affirmative response to that query was 96.66%.
Cook et al. 2016
In 2015, authors of the above studies joined forces to co-author a paper, “Consensus on consensus: a synthesis of consensus estimates on human-caused global warming”. Two key conclusions from the paper are as follows:
(i) Depending on exactly how you measure the expert consensus, somewhere between 90% and 100% of climate scientists agree humans are responsible for climate change, with most of our studies finding 97% consensus among publishing climate scientists. (ii) The greater the climate expertise among those surveyed, the higher the consensus on human-caused global warming.
Lynas et al. 2021
In this paper, from a dataset of 88,125 climate-related peer-reviewed papers published since 2012, these authors examined a randomly-selected subset of 3000 such publications. They also used a second sample-weighted approach that was specifically biased with keywords to help identify any sceptical papers in the whole dataset. Twenty-eight sceptical papers were identified within the original dataset using that approach, as evidenced by abstracts that were rated as implicitly or explicitly sceptical of human-caused global warming. It was concluded that the scientific consensus on human-caused climate change, expressed as a proportion of the total publications, exceeds 99% in the peer reviewed scientific literature.
Myers et al. 2021
This study revisited the 2009 consensus among geoscientists, while exploring different ways to define expertise and the level of agreement among them. The authors sent 10,929 invitations to participate in the survey, receiving 2,780 responses. In addition, the number of scientific publications by these self-identified experts in the field of climate change research was quantified and compared to their survey response on questions about climate change. Perhaps not surprisingly, the study found that agreement on anthropogenic global warming was high at 91% to 100% and generally increases with expertise. Out of a group of 153 independently confirmed climate experts, 98.7% of those scientists agreed that the Earth is warming mostly because of human activities such as burning fossil fuels. Among the subset with the highest level of expertise, these being independently-confirmed climate experts who each published 20+ peer-reviewed papers on climate change between 2015 and 2019, there was 100% agreement.
Public Polls and Consensus
Opinion polls are not absolute in the same way as uncontestable scientific evidence but they nevertheless usefully indicate in which way public thinking is heading. So let's look at a couple taken 13 years apart. A 15-nation World Public Opinion Poll in 2009 PDF), with 13,518 respondents, asked, among other questions, “Is it your impression that among scientists, most think the problem is urgent and enough is known to take action?” Out of all responses, just 51% agreed with that. Worse, in six countries only a minority agreed: United States (38%), Russia (23%), Indonesia (33%), Japan (43%), India (48%), and Mexico (48%). Conversely, the two highest “agree” scores were among Vietnamese (69%) and Bangladeshis (70%) - perhaps unsurprisingly.
The two other options people had to choose from were that “views are pretty evenly divided” (24% of total respondents), or “most think the problem is not urgent, and not enough is known to take action“ (15%). American and Japanese respondents scored most highly on “views are pretty evenly divided” (43 and 44% respectively).
How such a pervasive misperception arose, regarding the expert consensus on climate change, is no accident. Regular readers of this website's resources will know that instead, it was another product of deliberate misinformation campaigning by individuals and organizations in the United States and other nations around the world. These are people who campaign against action to reduce carbon emissions because it suits their paymasters if we continue to burn as much as possible.
Step forward to 2022 and the situation has perhaps improved, but there's still some way to go. A recent poll, Public Perceptions on Climate change (PDF), was conducted by the Policy Institute, based at King's College London, UK. It quizzed samples of just over 2,000 people from each of six countries (UK, Ireland, Norway, Poland, Italy and Germany). The survey asked the question: “To the best of your knowledge, what percentage of climate scientists have concluded that human-caused climate change is happening?” The following averages were returned: the UK sample thought 65%, the average of the whole survey was 68% and the highest was Ireland at 71%. Clearly, although public perception of expert consensus is growing, there's still plenty of room for strategies to communicate the reality and to shield people from the constant drip-feed of misinformation.
Expert and Public Consensus
Finally, let's consider the differences between expert and public consensus. Expert consensus is reached among those who have studied complex problems and know how to collect and work with data, to identify what constitutes evidence and evaluate it. This is demanding work requiring specific skill-sets and areas of expertise, preparation for which requires years of study and training.
Public consensus, in contrast, tends to occur only when something is blindingly obvious. For example, a serial misinformer would struggle if they tried running a campaign denying the existence of owls. Everyone already knows that of course there are owls. There is public consensus because we see and hear owls, for real or on the TV or radio. But complex issues are more prone to the antics of misinformers. We saw examples of misinformation during the COVID pandemic, in some cases with lethal outcomes when misinformed people failed to take the risks seriously. There's a strong parallel with climate change: it is imperative we accept the expert consensus and not kick the can down the road until the realisation it is real becomes universal – but utterly inescapable.
Update May 1, 2024: Corrected a typo in the publication year for Plass (1956) in the at-a-glance section.
Last updated on 26 May 2023 by John Mason. View Archives































 Arguments
Arguments







































Climate Myth...